给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回false 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
示例 1:
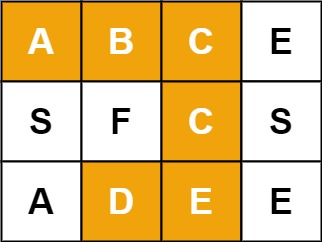
**输入:** board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED"
**输出:** true
示例 2:
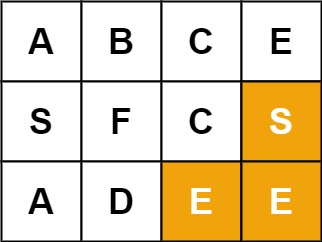
**输入:** board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE"
**输出:** true
示例 3:
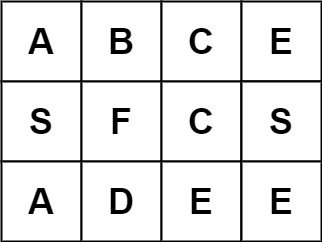
**输入:** board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB"
**输出:** false
提示:
m == board.lengthn = board[i].length1 <= m, n <= 61 <= word.length <= 15board 和 word 仅由大小写英文字母组成
进阶: 你可以使用搜索剪枝的技术来优化解决方案,使其在 board 更大的情况下可以更快解决问题?
方法一:回溯 思路与算法
设函数 $\text{check}(i, j, k)$ 表示判断以网格的 $(i, j)$ 位置出发,能否搜索到单词 $\textit{word}[k..]$,其中 $\textit{word}[k..]$ 表示字符串 $\textit{word}$ 从第 $k$ 个字符开始的后缀子串。如果能搜索到,则返回 $\texttt{true}$,反之返回 $\texttt{false}$。函数 $\text{check}(i, j, k)$ 的执行步骤如下:
如果 $\textit{board}[i][j] \neq s[k]$,当前字符不匹配,直接返回 $\texttt{false}$。
如果当前已经访问到字符串的末尾,且对应字符依然匹配,此时直接返回 $\texttt{true}$。
否则,遍历当前位置的所有相邻位置。如果从某个相邻位置出发,能够搜索到子串 $\textit{word}[k+1..]$,则返回 $\texttt{true}$,否则返回 $\texttt{false}$。
这样,我们对每一个位置 $(i,j)$ 都调用函数 $\text{check}(i, j, 0)$ 进行检查:只要有一处返回 $\texttt{true}$,就说明网格中能够找到相应的单词,否则说明不能找到。
为了防止重复遍历相同的位置,需要额外维护一个与 $\textit{board}$ 等大的 $\textit{visited}$ 数组,用于标识每个位置是否被访问过。每次遍历相邻位置时,需要跳过已经被访问的位置。
代码
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 class Solution { public boolean exist (char [][] board, String word) { int h = board.length, w = board[0 ].length; boolean [][] visited = new boolean [h][w]; for (int i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { boolean flag = check(board, visited, i, j, word, 0 ); if (flag) { return true ; } } } return false ; } public boolean check (char [][] board, boolean [][] visited, int i, int j, String s, int k) { if (board[i][j] != s.charAt(k)) { return false ; } else if (k == s.length() - 1 ) { return true ; } visited[i][j] = true ; int [][] directions = {{0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 }}; boolean result = false ; for (int [] dir : directions) { int newi = i + dir[0 ], newj = j + dir[1 ]; if (newi >= 0 && newi < board.length && newj >= 0 && newj < board[0 ].length) { if (!visited[newi][newj]) { boolean flag = check(board, visited, newi, newj, s, k + 1 ); if (flag) { result = true ; break ; } } } } visited[i][j] = false ; return result; } }
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution : def exist (self, board: List [List [str ]], word: str ) -> bool : directions = [(0 , 1 ), (0 , -1 ), (1 , 0 ), (-1 , 0 )] def check (i: int , j: int , k: int ) -> bool : if board[i][j] != word[k]: return False if k == len (word) - 1 : return True visited.add((i, j)) result = False for di, dj in directions: newi, newj = i + di, j + dj if 0 <= newi < len (board) and 0 <= newj < len (board[0 ]): if (newi, newj) not in visited: if check(newi, newj, k + 1 ): result = True break visited.remove((i, j)) return result h, w = len (board), len (board[0 ]) visited = set () for i in range (h): for j in range (w): if check(i, j, 0 ): return True return False
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 var exist = function (board, word ) { const h = board.length , w = board[0 ].length ; const directions = [[0 , 1 ], [0 , -1 ], [1 , 0 ], [-1 , 0 ]]; const visited = new Array (h); for (let i = 0 ; i < visited.length ; ++i) { visited[i] = new Array (w).fill (false ); } const check = (i, j, s, k ) => { if (board[i][j] != s.charAt (k)) { return false ; } else if (k == s.length - 1 ) { return true ; } visited[i][j] = true ; let result = false ; for (const [dx, dy] of directions) { let newi = i + dx, newj = j + dy; if (newi >= 0 && newi < h && newj >= 0 && newj < w) { if (!visited[newi][newj]) { const flag = check (newi, newj, s, k + 1 ); if (flag) { result = true ; break ; } } } } visited[i][j] = false ; return result; } for (let i = 0 ; i < h; i++) { for (let j = 0 ; j < w; j++) { const flag = check (i, j, word, 0 ); if (flag) { return true ; } } } return false ; };
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 type pair struct { x, y int }var directions = []pair{{-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {0 , 1 }} func exist (board [][]byte , word string ) bool { h, w := len (board), len (board[0 ]) vis := make ([][]bool , h) for i := range vis { vis[i] = make ([]bool , w) } var check func (i, j, k int ) bool check = func (i, j, k int ) bool { if board[i][j] != word[k] { return false } if k == len (word)-1 { return true } vis[i][j] = true defer func () false }() for _, dir := range directions { if newI, newJ := i+dir.x, j+dir.y; 0 <= newI && newI < h && 0 <= newJ && newJ < w && !vis[newI][newJ] { if check(newI, newJ, k+1 ) { return true } } } return false } for i, row := range board { for j := range row { if check(i, j, 0 ) { return true } } } return false }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 int directions[4 ][2 ] = {{0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 }};bool check (char ** board, int boardSize, int boardColSize, int ** visited, int i, int j, char * s, int sSize, int k) { if (board[i][j] != s[k]) { return false ; } else if (k == sSize - 1 ) { return true ; } visited[i][j] = true ; bool result = false ; for (int sel = 0 ; sel < 4 ; sel++) { int newi = i + directions[sel][0 ], newj = j + directions[sel][1 ]; if (newi >= 0 && newi < boardSize && newj >= 0 && newj < boardColSize) { if (!visited[newi][newj]) { bool flag = check(board, boardSize, boardColSize, visited, newi, newj, s, sSize, k + 1 ); if (flag) { result = true ; break ; } } } } visited[i][j] = false ; return result; } bool exist (char ** board, int boardSize, int * boardColSize, char * word) { int ** visited = malloc (sizeof (int *) * boardSize); for (int i = 0 ; i < boardSize; i++) { visited[i] = malloc (sizeof (int ) * boardColSize[0 ]); memset (visited[i], 0 , sizeof (int ) * boardColSize[0 ]); } int wordSize = strlen (word); for (int i = 0 ; i < boardSize; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < boardColSize[0 ]; j++) { bool flag = check(board, boardSize, boardColSize[0 ], visited, i, j, word, wordSize, 0 ); if (flag) { return true ; } } } return false ; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:一个非常宽松的上界为 $O(MN \cdot 3^L)$,其中 $M, N$ 为网格的长度与宽度,$L$ 为字符串 $\textit{word}$ 的长度。在每次调用函数 $\text{check}$ 时,除了第一次可以进入 $4$ 个分支以外,其余时间我们最多会进入 $3$ 个分支(因为每个位置只能使用一次,所以走过来的分支没法走回去)。由于单词长为 $L$,故 $\text{check}(i, j, 0)$ 的时间复杂度为 $O(3^L)$,而我们要执行 $O(MN)$ 次检查。然而,由于剪枝的存在,我们在遇到不匹配或已访问的字符时会提前退出,终止递归流程。因此,实际的时间复杂度会远远小于 $\Theta(MN \cdot 3^L)$。
空间复杂度:$O(MN)$。我们额外开辟了 $O(MN)$ 的 $\textit{visited}$ 数组,同时栈的深度最大为 $O(\min(L, MN))$。