城市的 天际线 是从远处观看该城市中所有建筑物形成的轮廓的外部轮廓。给你所有建筑物的位置和高度,请返回 由这些建筑物形成的 天际线 。
每个建筑物的几何信息由数组 buildings 表示,其中三元组 buildings[i] = [lefti, righti, heighti]
lefti 是第 i 座建筑物左边缘的 x 坐标。righti 是第 i 座建筑物右边缘的 x 坐标。heighti 是第 i 座建筑物的高度。
你可以假设所有的建筑都是完美的长方形,在高度为 0 的绝对平坦的表面上。
天际线 应该表示为由 “关键点” 组成的列表,格式 [[x1,y1],[x2,y2],...] ,并按 x 坐标 进行 排序 。关键点是水平线段的左端点 。列表中最后一个点是最右侧建筑物的终点,y 坐标始终为 0
注意: 输出天际线中不得有连续的相同高度的水平线。例如 [...[2 3], [4 5], [7 5], [11 5], [12 7]...][...[2 3], [4 5], [12 7], ...]
示例 1:
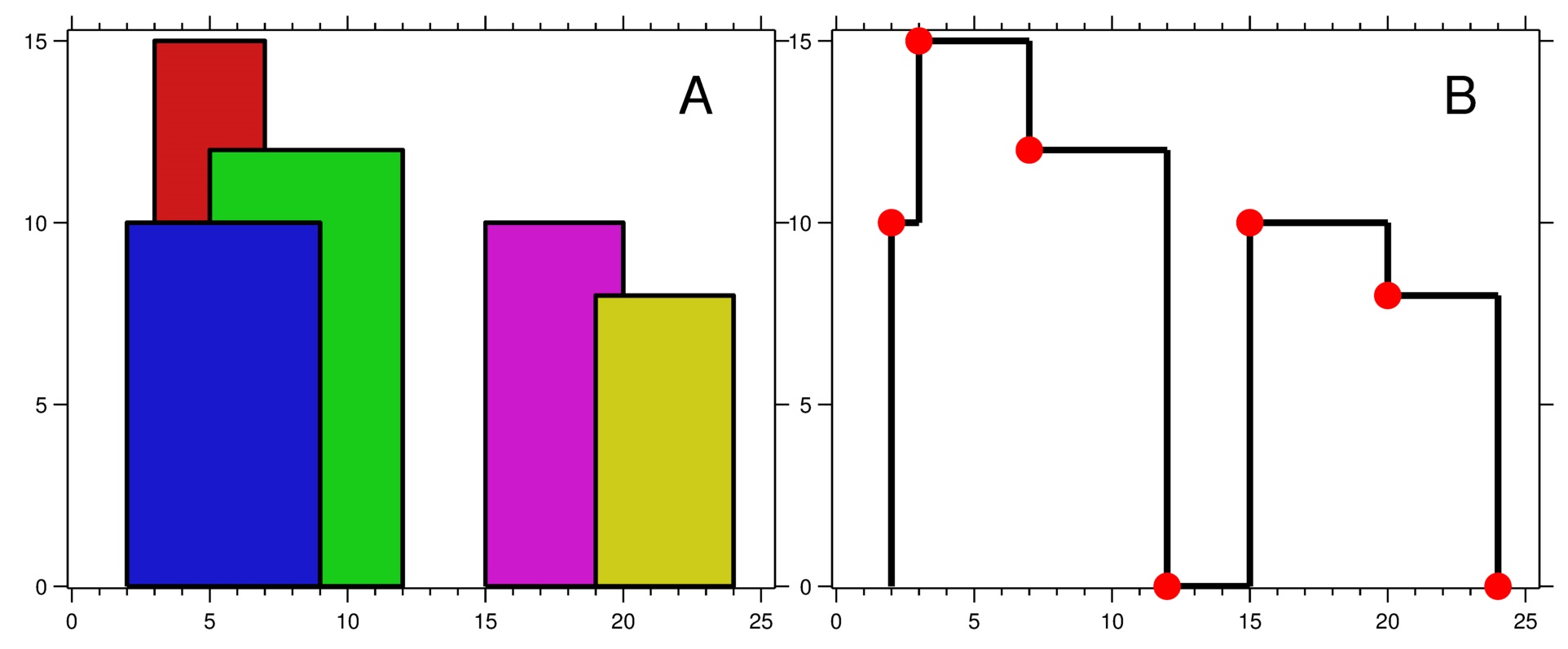
**输入:** buildings = [[2,9,10],[3,7,15],[5,12,12],[15,20,10],[19,24,8]]
**输出:** [[2,10],[3,15],[7,12],[12,0],[15,10],[20,8],[24,0]]
**解释:**
图 A **** 显示输入的所有建筑物的位置和高度,
图 B 显示由这些建筑物形成的天际线。图 B 中的红点表示输出列表中的关键点。
示例 2:
**输入:** buildings = [[0,2,3],[2,5,3]]
**输出:** [[0,3],[5,0]]
提示:
1 <= buildings.length <= 1040 <= lefti < righti <= 231 - 11 <= heighti <= 231 - 1buildings 按 lefti 非递减排序
方法一:扫描线 + 优先队列 思路及算法
观察题目我们可以发现,关键点的横坐标总是落在建筑的左右边缘上。这样我们可以只考虑每一座建筑的边缘作为横坐标,这样其对应的纵坐标为「包含该横坐标」的所有建筑的最大高度。
观察示例一可以发现,当关键点为某建筑的右边缘时,该建筑的高度对关键点的纵坐标是没有贡献的。例如图中横坐标为 $7$ 的关键点,虽然它落在红色建筑的右边缘,但红色建筑对其并纵坐标并没有贡献。因此我们给出「包含该横坐标」的定义:建筑的左边缘小于等于该横坐标,右边缘大于该横坐标(也就是我们不考虑建筑的右边缘)。即对于包含横坐标 $x$ 的建筑 $i$,有 $x \in [\textit{left}_i , \textit{right}_i)$。
特别地,在部分情况下,「包含该横坐标」的建筑并不存在。例如当图中只有一座建筑时,该建筑的左右边缘均对应一个关键点,当横坐标为其右边缘时,这唯一的建筑对其纵坐标没有贡献。因此该横坐标对应的纵坐标的大小为 $0$。
这样我们可以想到一个暴力的算法:$O(n)$ 地枚举建筑的每一个边缘作为关键点的横坐标,过程中我们 $O(n)$ 地检查每一座建筑是否「包含该横坐标」,找到最大高度,即为该关键点的纵坐标。该算法的时间复杂度是 $O(n^2)$,我们需要进行优化。
我们可以用优先队列来优化寻找最大高度的时间,在我们从左到右枚举横坐标的过程中,实时地更新该优先队列即可。这样无论何时,优先队列的队首元素即为最大高度。为了维护优先队列,我们需要使用「延迟删除」的技巧,即我们无需每次横坐标改变就立刻将优先队列中所有不符合条件的元素都删除,而只需要保证优先队列的队首元素「包含该横坐标」即可。
具体地,为了按顺序枚举横坐标,我们用数组 $\textit{boundaries}$ 保存所有的边缘,排序后遍历该数组即可。过程中,我们首先将「包含该横坐标」的建筑加入到优先队列中,然后不断检查优先队列的队首元素是否「包含该横坐标」,如果不「包含该横坐标」,我们就将该队首元素弹出队列,直到队空或队首元素「包含该横坐标」即可。最后我们用变量 $\textit{maxn}$ 记录最大高度(即纵坐标的值),当优先队列为空时,$\textit{maxn}=0$,否则 $\textit{maxn}$ 即为队首元素。最后我们还需要再做一步检查:如果当前关键点的纵坐标大小与前一个关键点的纵坐标大小相同,则说明当前关键点无效,我们跳过该关键点即可。
在实际代码中,我们可以进行一个优化。因为每一座建筑的左边缘信息只被用作加入优先队列时的依据,当其加入优先队列后,我们只需要用到其高度信息(对最大高度有贡献)以及其右边缘信息(弹出优先队列的依据),因此只需要在优先队列中保存这两个元素即可。
代码
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution {public : vector<vector<int >> getSkyline (vector<vector<int >>& buildings) { auto cmp = [](const pair<int , int >& a, const pair<int , int >& b) -> bool { return a.second < b.second; }; priority_queue<pair<int , int >, vector<pair<int , int >>, decltype (cmp)> que (cmp); vector<int > boundaries; for (auto & building : buildings) { boundaries.emplace_back (building[0 ]); boundaries.emplace_back (building[1 ]); } sort (boundaries.begin (), boundaries.end ()); vector<vector<int >> ret; int n = buildings.size (), idx = 0 ; for (auto & boundary : boundaries) { while (idx < n && buildings[idx][0 ] <= boundary) { que.emplace (buildings[idx][1 ], buildings[idx][2 ]); idx++; } while (!que.empty () && que.top ().first <= boundary) { que.pop (); } int maxn = que.empty () ? 0 : que.top ().second; if (ret.size () == 0 || maxn != ret.back ()[1 ]) { ret.push_back ({boundary, maxn}); } } return ret; } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> getSkyline (int [][] buildings) { PriorityQueue<int []> pq = new PriorityQueue <int []>((a, b) -> b[1 ] - a[1 ]); List<Integer> boundaries = new ArrayList <Integer>(); for (int [] building : buildings) { boundaries.add(building[0 ]); boundaries.add(building[1 ]); } Collections.sort(boundaries); List<List<Integer>> ret = new ArrayList <List<Integer>>(); int n = buildings.length, idx = 0 ; for (int boundary : boundaries) { while (idx < n && buildings[idx][0 ] <= boundary) { pq.offer(new int []{buildings[idx][1 ], buildings[idx][2 ]}); idx++; } while (!pq.isEmpty() && pq.peek()[0 ] <= boundary) { pq.poll(); } int maxn = pq.isEmpty() ? 0 : pq.peek()[1 ]; if (ret.size() == 0 || maxn != ret.get(ret.size() - 1 ).get(1 )) { ret.add(Arrays.asList(boundary, maxn)); } } return ret; } }
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 type pair struct { right, height int }type hp []pairfunc (h hp) int { return len (h) }func (h hp) int ) bool { return h[i].height > h[j].height }func (h hp) int ) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }func (h *hp) interface {}) { *h = append (*h, v.(pair)) }func (h *hp) interface {} { a := *h; v := a[len (a)-1 ]; *h = a[:len (a)-1 ]; return v }func getSkyline (buildings [][]int ) int ) { n := len (buildings) boundaries := make ([]int , 0 , n*2 ) for _, building := range buildings { boundaries = append (boundaries, building[0 ], building[1 ]) } sort.Ints(boundaries) idx := 0 h := hp{} for _, boundary := range boundaries { for idx < n && buildings[idx][0 ] <= boundary { heap.Push(&h, pair{buildings[idx][1 ], buildings[idx][2 ]}) idx++ } for len (h) > 0 && h[0 ].right <= boundary { heap.Pop(&h) } maxn := 0 if len (h) > 0 { maxn = h[0 ].height } if len (ans) == 0 || maxn != ans[len (ans)-1 ][1 ] { ans = append (ans, []int {boundary, maxn}) } } return }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 struct pair { int first, second; }; struct Heap { struct pair * heap ; int heapSize; bool (*cmp)(struct pair *, struct pair *); }; void init (struct Heap* obj, int n, bool (*cmp)(struct pair *, struct pair *)) { obj->heap = malloc (sizeof (struct pair ) * (n + 1 )); obj->heapSize = 0 ; obj->cmp = cmp; } bool cmp1 (struct pair * a, struct pair * b) { return a->second < b->second; } void swap (struct pair * a, struct pair * b) { struct pair tmp = *a = *b, *b = tmp; } void push (struct Heap* obj, int x, int y) { int p = ++(obj->heapSize), q = p >> 1 ; obj->heap[p] = (struct pair ){x, y}; while (q) { if (!obj->cmp(&(obj->heap[q]), &(obj->heap[p]))) { break ; } swap(&(obj->heap[q]), &(obj->heap[p])); p = q, q = p >> 1 ; } } void pop (struct Heap* obj) { swap(&(obj->heap[1 ]), &(obj->heap[(obj->heapSize)--])); int p = 1 , q = p << 1 ; while (q <= obj->heapSize) { if (q + 1 <= obj->heapSize) { if (obj->cmp(&(obj->heap[q]), &(obj->heap[q + 1 ]))) { q++; } } if (!obj->cmp(&(obj->heap[p]), &(obj->heap[q]))) { break ; } swap(&(obj->heap[q]), &(obj->heap[p])); p = q, q = p << 1 ; } } struct pair top (struct Heap* obj) { return obj->heap[1 ]; } bool empty (struct Heap* obj) { return obj->heapSize == 0 ; } int cmp (int * a, int * b) { return *a - *b; } int ** getSkyline (int ** buildings, int buildingsSize, int * buildingsColSize, int * returnSize, int ** returnColumnSizes) { int n = buildingsSize; struct Heap * heap =malloc (sizeof (struct Heap)); init(heap, n << 1 , cmp1); int boundaries[n << 1 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { boundaries[i << 1 ] = buildings[i][0 ]; boundaries[i << 1 | 1 ] = buildings[i][1 ]; } qsort(boundaries, n << 1 , sizeof (int ), cmp); int ** ret = malloc (sizeof (int *) * (n << 1 )); *returnColumnSizes = malloc (sizeof (int ) * (n << 1 )); *returnSize = 0 ; int idx = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < (n << 1 ); i++) { int boundary = boundaries[i]; while (idx < n && buildings[idx][0 ] <= boundary) { push(heap, buildings[idx][1 ], buildings[idx][2 ]); idx++; } while (!empty(heap) && top(heap).first <= boundary) { pop(heap); } int maxn = empty(heap) ? 0 : top(heap).second; if ((*returnSize) == 0 || maxn != ret[(*returnSize) - 1 ][1 ]) { int * tmp = malloc (sizeof (int ) * 2 ); tmp[0 ] = boundary, tmp[1 ] = maxn; (*returnColumnSizes)[*returnSize] = 2 ; ret[(*returnSize)++] = tmp; } } return ret; }
复杂度分析