给定方法 rand7 可生成 [1,7] 范围内的均匀随机整数,试写一个方法 rand10 生成 [1,10] 范围内的均匀随机整数。
你只能调用 rand7() 且不能调用其他方法。请不要使用系统的 Math.random() 方法。
每个测试用例将有一个内部参数 n,即你实现的函数 rand10() 在测试时将被调用的次数。请注意,这不是传递给 rand10() 的参数。
示例 1:
**输入:** 1
**输出:** [2]
示例 2:
**输入:** 2
**输出:** [2,8]
示例 3:
**输入:** 3
**输出:** [3,8,10]
提示:
进阶:
rand7()调用次数的 期望值 是多少 ?- 你能否尽量少调用
rand7() ?
方法一:拒绝采样
思路与算法
我们可以用拒绝采样的方法实现 Rand10()。在拒绝采样中,如果生成的随机数满足要求,那么就返回该随机数,否则会不断生成,直到生成一个满足要求的随机数为止。
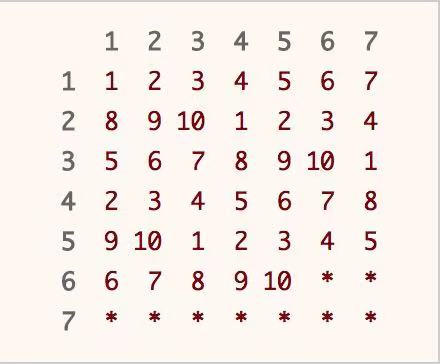
我们只需要能够满足等概率的生成 10 个不同的数即可,具体的生成方法可以有很多种,比如我们可以利用两个 Rand7() 相乘,我们只取其中等概率的 10 个不同的数的组合即可,当然还有许多其他不同的解法,可以利用各种运算和函数的组合等方式来实现。
- 比如我们可以利用两个Rand7()相乘,分别可以得到结果如下:
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
| 1 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
| 2 |
2 |
4 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
12 |
14 |
| 3 |
3 |
6 |
9 |
12 |
15 |
18 |
21 |
| 4 |
4 |
8 |
12 |
16 |
20 |
24 |
28 |
| 5 |
5 |
10 |
15 |
20 |
25 |
30 |
35 |
| 6 |
6 |
12 |
18 |
24 |
30 |
36 |
42 |
| 7 |
7 |
14 |
21 |
28 |
35 |
42 |
49 |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
| P |
1/49 |
2/49 |
2/49 |
3/49 |
2/49 |
4/49 |
2/49 |
2/49 |
4/49 |
|
10 |
12 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
18 |
20 |
21 |
24 |
| P |
2/49 |
1/49 |
2/49 |
2/49 |
2/49 |
1/49 |
2/49 |
2/49 |
2/49 |
|
25 |
28 |
30 |
35 |
36 |
42 |
49 |
|
|
| P |
1/49 |
2/49 |
2/49 |
2/49 |
1/49 |
2/49 |
1/49 |
|
|
题目中要求尽可能的减少 Rand7() 的调用次数,则我们应该尽量保证生成的每个不同的数的生成概率尽可能的大,即调用 Rand7() 期望次数尽可能的小。
我们可以调用两次 Rand7(),那么可以生成 [1, 49] 之间的随机整数,我们只用到其中的前 40 个用来实现 Rand10(),而拒绝剩下的 9 个数,如下图所示。

- 我们可以看到表中的 [1,49] 每个数生成的概率为 1}{49。我们实际上只取 [1,40] 这前 40 个数,转化为 [1,10] 时,这 10 个数中每个数的生成概率则为 4}{49。
代码
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| class Solution {
public:
int rand10() {
int row, col, idx;
do {
row = rand7();
col = rand7();
idx = col + (row - 1) * 7;
} while (idx > 40);
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
};
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| class Solution extends SolBase {
public int rand10() {
int row, col, idx;
do {
row = rand7();
col = rand7();
idx = col + (row - 1) * 7;
} while (idx > 40);
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
}
|
[sol1-C#]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| public class Solution : SolBase {
public int Rand10() {
int row, col, idx;
do {
row = Rand7();
col = Rand7();
idx = col + (row - 1) * 7;
} while (idx > 40);
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
}
|
[sol1-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| var rand10 = function() {
var row, col, idx;
do {
row = rand7();
col = rand7();
idx = col + (row - 1) * 7;
} while (idx > 40);
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
};
|
[sol1-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| func rand10() int {
for {
row := rand7()
col := rand7()
idx := (row-1)*7 + col
if idx <= 40 {
return 1 + (idx-1)%10
}
}
}
|
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| class Solution:
def rand10(self) -> int:
while True:
row = rand7()
col = rand7()
idx = (row - 1) * 7 + col
if idx <= 40:
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10
|
复杂度分析
进阶问题
函数调用次数的期望:我们来分析这种方法在平均情况下需要调用 Rand7() 的次数。我们称连续调用两次 Rand7() 为一轮,在第一轮中,有 40/49 的概率被接受,而有 9}{49 的概率被拒绝,进入第二轮随机;第二轮有 (9}{49})^{2 被拒绝,由此推理我们可以知道第n轮被拒绝的概率为 (9}{49})^{n 。因此调用 Rand7() 的期望次数为:
减少 Rand7() 的调用次数: 我们减小随机被拒绝的概率,从而减小 Rand7() 的调用次数的期望,即可减少 Rand7() 的平均调用次数。
- 我们可以通过合理地使用被拒绝的采样,从而对方法一进行优化。在方法一中,我们生成 [1, 49] 的随机数,若生成的随机数 x 在 [41, 49] 中,我们则拒绝 x。然而在 x 被拒绝的情况下,我们得到了一个 [1, 9] 的随机数,如果再调用一次 Rand7(),那么就可以生成 [1, 63] 的随机数。我们保留 [1, 60] 并拒绝 [61, 63]:这是 [1, 3] 的随机数。我们继续调用 Rand7(),生成 [1, 21] 的随机数,保留 [1, 20] 并拒绝 [1]。此时 [1] 已经没有任何用处,若出现了拒绝 1 的情况,我们就重新开始生成 [1, 49] 的随机数。我们可以算它的期望如下:
参考代码
[sol2-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class Solution {
public:
int rand10() {
int a, b, idx;
while (true) {
a = rand7();
b = rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 40) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
a = idx - 40;
b = rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 60) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
a = idx - 60;
b = rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 20) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
}
}
};
|
[sol2-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class Solution extends SolBase {
public int rand10() {
int a, b, idx;
while (true) {
a = rand7();
b = rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 40) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
a = idx - 40;
b = rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 60) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
a = idx - 60;
b = rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 20) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
}
}
}
|
[sol2-C#]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public class Solution : SolBase {
public int Rand10() {
int a, b, idx;
while (true) {
a = Rand7();
b = Rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 40) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
a = idx - 40;
b = Rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 60) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
a = idx - 60;
b = Rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 20) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
}
}
}
|
[sol2-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| var rand10 = function() {
var a, b, idx;
while (true) {
a = rand7();
b = rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 40) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
a = idx - 40;
b = rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 60) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
a = idx - 60;
b = rand7();
idx = b + (a - 1) * 7;
if (idx <= 20) {
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10;
}
}
};
|
[sol2-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| func rand10() int {
for {
a := rand7()
b := rand7()
idx := (a-1)*7 + b
if idx <= 40 {
return 1 + (idx-1)%10
}
a = idx - 40
b = rand7()
idx = (a-1)*7 + b
if idx <= 60 {
return 1 + (idx-1)%10
}
a = idx - 60
b = rand7()
idx = (a-1)*7 + b
if idx <= 20 {
return 1 + (idx-1)%10
}
}
}
|
[sol2-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| class Solution:
def rand10(self) -> int:
while True:
a = rand7()
b = rand7()
idx = (a - 1) * 7 + b
if idx <= 40:
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10
a = idx - 40
b = rand7()
idx = (a - 1) * 7 + b
if idx <= 60:
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10
a = idx - 60
b = rand7()
idx = (a - 1) * 7 + b
if idx <= 20:
return 1 + (idx - 1) % 10
|