你被请来给一个要举办高尔夫比赛的树林砍树。树林由一个 m x n 的矩阵表示, 在这个矩阵中:
0 表示障碍,无法触碰1 表示地面,可以行走比 1 大的数 表示有树的单元格,可以行走,数值表示树的高度
每一步,你都可以向上、下、左、右四个方向之一移动一个单位,如果你站的地方有一棵树,那么你可以决定是否要砍倒它。
你需要按照树的高度从低向高砍掉所有的树,每砍过一颗树,该单元格的值变为 1(即变为地面)。
你将从 (0, 0) 点开始工作,返回你砍完所有树需要走的最小步数。 如果你无法砍完所有的树,返回 -1 。
可以保证的是,没有两棵树的高度是相同的,并且你至少需要砍倒一棵树。
示例 1:
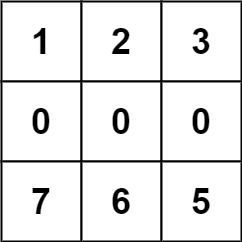
**输入:** forest = [[1,2,3],[0,0,4],[7,6,5]]
**输出:** 6
**解释:** 沿着上面的路径,你可以用 6 步,按从最矮到最高的顺序砍掉这些树。
示例 2:
**输入:** forest = [[1,2,3],[0,0,0],[7,6,5]]
**输出:** -1
**解释:** 由于中间一行被障碍阻塞,无法访问最下面一行中的树。
示例 3:
**输入:** forest = [[2,3,4],[0,0,5],[8,7,6]]
**输出:** 6
**解释:** 可以按与示例 1 相同的路径来砍掉所有的树。
(0,0) 位置的树,可以直接砍去,不用算步数。
提示:
m == forest.lengthn == forest[i].length1 <= m, n <= 500 <= forest[i][j] <= 109
前言 题目要求从 (0, 0) 开始并按照树的高度大小进行砍树并求出最小步数,假设所有树按照从高度从小到大的排序顺序为 t_1, t_2, t_3, t_4, \cdots, t_n,设 d(x, y) 表示从 x 到 y 之间的步数,设 t_0 = (0, 0) ,则可推出砍树的总的步数为 total} = \sum_{i=0}^{n-1} d(t_i, t_i+1),若使得 total 最小,只需满足所有的 d(i, i+1) 都为最小,即可使得 total 最小,该题即转为求相邻树的两点之间的最短距离。
方法一:广度优先搜索 思路与算法
首先对矩阵中的树按照树的高度进行排序,我们依次求出相邻的树之间的最短距离。利用广度优先搜索,按照层次遍历,处理队列中的节点(网格位置)。visited 记录在某个时间点已经添加到队列中的节点,这些节点已被处理或在等待处理的队列中。对于下一个要处理的每个节点,查看他们的四个方向上相邻的点,如果相邻的点没有被遍历过且不是障碍,将其加入到队列中,直到找到终点为止,返回当前的步数即可。最终返回所有的步数之和即为最终结果。
代码
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 class Solution : def cutOffTree (self, forest: List [List [int ]] ) -> int : def bfs (sx: int , sy: int , tx: int , ty: int ) -> int : m, n = len (forest), len (forest[0 ]) q = deque([(0 , sx, sy)]) vis = {(sx, sy)} while q: d, x, y = q.popleft() if x == tx and y == ty: return d for nx, ny in ((x - 1 , y), (x + 1 , y), (x, y - 1 ), (x, y + 1 )): if 0 <= nx < m and 0 <= ny < n and forest[nx][ny] and (nx, ny) not in vis: vis.add((nx, ny)) q.append((d + 1 , nx, ny)) return -1 trees = sorted ((h, i, j) for i, row in enumerate (forest) for j, h in enumerate (row) if h > 1 ) ans = preI = preJ = 0 for _, i, j in trees: d = bfs(preI, preJ, i, j) if d < 0 : return -1 ans += d preI, preJ = i, j return ans
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 class Solution {public : int dirs[4 ][2 ] = {{-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {0 , 1 }}; int bfs (vector<vector<int >>& forest, int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) if (sx == tx && sy == ty) { return 0 ; } int row = forest.size (); int col = forest[0 ].size (); int step = 0 ; queue<pair<int , int >> qu; vector<vector<bool >> visited (row, vector <bool >(col, false )); qu.emplace (sx, sy); visited[sx][sy] = true ; while (!qu.empty ()) { step++; int sz = qu.size (); for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; ++i) { auto [cx, cy] = qu.front (); qu.pop (); for (int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; ++j) { int nx = cx + dirs[j][0 ]; int ny = cy + dirs[j][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col) { if (!visited[nx][ny] && forest[nx][ny] > 0 ) { if (nx == tx && ny == ty) { return step; } qu.emplace (nx, ny); visited[nx][ny] = true ; } } } } } return -1 ; } int cutOffTree (vector<vector<int >>& forest) vector<pair<int , int >> trees; int row = forest.size (); int col = forest[0 ].size (); for (int i = 0 ; i < row; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < col; ++j) { if (forest[i][j] > 1 ) { trees.emplace_back (i, j); } } } sort (trees.begin (), trees.end (), [&](const pair<int , int > & a, const pair<int , int > & b) { return forest[a.first][a.second] < forest[b.first][b.second]; }); int cx = 0 ; int cy = 0 ; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < trees.size (); ++i) { int steps = bfs (forest, cx, cy, trees[i].first, trees[i].second); if (steps == -1 ) { return -1 ; } ans += steps; cx = trees[i].first; cy = trees[i].second; } return ans; } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 class Solution { int [][] dirs = {{-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {0 , 1 }}; public int cutOffTree (List<List<Integer>> forest) { List<int []> trees = new ArrayList <int []>(); int row = forest.size(); int col = forest.get(0 ).size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < row; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < col; ++j) { if (forest.get(i).get(j) > 1 ) { trees.add(new int []{i, j}); } } } Collections.sort(trees, (a, b) -> forest.get(a[0 ]).get(a[1 ]) - forest.get(b[0 ]).get(b[1 ])); int cx = 0 ; int cy = 0 ; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < trees.size(); ++i) { int steps = bfs(forest, cx, cy, trees.get(i)[0 ], trees.get(i)[1 ]); if (steps == -1 ) { return -1 ; } ans += steps; cx = trees.get(i)[0 ]; cy = trees.get(i)[1 ]; } return ans; } public int bfs (List<List<Integer>> forest, int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) { if (sx == tx && sy == ty) { return 0 ; } int row = forest.size(); int col = forest.get(0 ).size(); int step = 0 ; Queue<int []> queue = new ArrayDeque <int []>(); boolean [][] visited = new boolean [row][col]; queue.offer(new int []{sx, sy}); visited[sx][sy] = true ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { step++; int sz = queue.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; ++i) { int [] cell = queue.poll(); int cx = cell[0 ], cy = cell[1 ]; for (int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; ++j) { int nx = cx + dirs[j][0 ]; int ny = cy + dirs[j][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col) { if (!visited[nx][ny] && forest.get(nx).get(ny) > 0 ) { if (nx == tx && ny == ty) { return step; } queue.offer(new int []{nx, ny}); visited[nx][ny] = true ; } } } } } return -1 ; } }
[sol1-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 public class Solution { int [][] dirs = {new int []{-1 , 0 }, new int []{1 , 0 }, new int []{0 , -1 }, new int []{0 , 1 }}; public int CutOffTree (IList<IList<int >> forest ) List<Tuple<int , int >> trees = new List<Tuple<int , int >>(); int row = forest.Count; int col = forest[0 ].Count; for (int i = 0 ; i < row; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < col; ++j) { if (forest[i][j] > 1 ) { trees.Add(new Tuple<int , int >(i, j)); } } } trees.Sort((a, b) => forest[a.Item1][a.Item2] - forest[b.Item1][b.Item2]); int cx = 0 ; int cy = 0 ; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < trees.Count; ++i) { int steps = BFS(forest, cx, cy, trees[i].Item1, trees[i].Item2); if (steps == -1 ) { return -1 ; } ans += steps; cx = trees[i].Item1; cy = trees[i].Item2; } return ans; } public int BFS (IList<IList<int >> forest, int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty ) if (sx == tx && sy == ty) { return 0 ; } int row = forest.Count; int col = forest[0 ].Count; int step = 0 ; Queue<Tuple<int , int >> queue = new Queue<Tuple<int , int >>(); bool [,] visited = new bool [row, col]; queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<int , int >(sx, sy)); visited[sx, sy] = true ; while (queue.Count > 0 ) { step++; int sz = queue.Count; for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; ++i) { Tuple<int , int > cell = queue.Dequeue(); int cx = cell.Item1, cy = cell.Item2; for (int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; ++j) { int nx = cx + dirs[j][0 ]; int ny = cy + dirs[j][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col) { if (!visited[nx, ny] && forest[nx][ny] > 0 ) { if (nx == tx && ny == ty) { return step; } queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<int , int >(nx, ny)); visited[nx, ny] = true ; } } } } } return -1 ; } }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 typedef struct { int x; int y; int height; } Tree; static int cmp (const void *pa, const void *pb) { return ((Tree *)pa)->height - ((Tree *)pb)->height; } static int dirs[4 ][2 ] = {{-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {0 , 1 }};int bfs (const int **forest, int row, int col, int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) { if (sx == tx && sy == ty) { return 0 ; } int step = 0 ; int *queue = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) * row * col); int *visited = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) * row * col); int head = 0 , tail = 0 ; memset (visited, 0 , sizeof (int ) * row * col); queue [tail++] = sx * col + sy; visited[sx * col + sy] = true ; while (head != tail) { step++; int sz = tail - head; for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; ++i) { int cx = queue [head] / col; int cy = queue [head] % col; head++; for (int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; ++j) { int nx = cx + dirs[j][0 ]; int ny = cy + dirs[j][1 ]; if ( nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col) { if (!visited[nx * col + ny] && forest[nx][ny] > 0 ) { if (nx == tx && ny == ty) { free (queue ); free (visited); return step; } queue [tail++] = nx * col + ny; visited[nx * col + ny] = true ; } } } } } free (queue ); free (visited); return -1 ; } int cutOffTree (int ** forest, int forestSize, int * forestColSize) { int row = forestSize; int col = forestColSize[0 ]; int treeSize = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < row; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < col; ++j) { if (forest[i][j] > 1 ) { treeSize++; } } } Tree * trees = (Tree *)malloc (sizeof (Tree) * treeSize); int pos = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < row; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < col; ++j) { if (forest[i][j] > 1 ) { trees[pos].x = i; trees[pos].y = j; trees[pos].height = forest[i][j]; pos++; } } } qsort(trees, treeSize, sizeof (Tree), cmp); int cx = 0 ; int cy = 0 ; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < treeSize; ++i) { int steps = bfs(forest, row, col, cx, cy, trees[i].x, trees[i].y); if (steps == -1 ) { return -1 ; } ans += steps; cx = trees[i].x; cy = trees[i].y; } return ans; }
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 const dirs = [[-1 , 0 ], [1 , 0 ], [0 , -1 ], [0 , 1 ]];var cutOffTree = function (forest ) { const trees = []; const row = forest.length ; const col = forest[0 ].length ; for (let i = 0 ; i < row; ++i) { for (let j = 0 ; j < col; ++j) { if (forest[i][j] > 1 ) { trees.push ([i, j]); } } } trees.sort ((a, b ) => forest[a[0 ]][a[1 ]] - forest[b[0 ]][b[1 ]]); let cx = 0 ; let cy = 0 ; let ans = 0 ; for (let i = 0 ; i < trees.length ; ++i) { let steps = bfs (forest, cx, cy, trees[i][0 ], trees[i][1 ]); if (steps === -1 ) { return -1 ; } ans += steps; cx = trees[i][0 ]; cy = trees[i][1 ]; } return ans; }; const bfs = (forest, sx, sy, tx, ty ) => { if (sx === tx && sy === ty) { return 0 ; } const row = forest.length ; const col = forest[0 ].length ; let step = 0 ; const queue = []; const visited = new Array (row).fill (0 ).map (() => new Array (col).fill (0 )); queue.push ([sx, sy]); visited[sx][sy] = true ; while (queue.length ) { step++; const sz = queue.length ; for (let i = 0 ; i < sz; ++i) { const cell = queue.shift (); const cx = cell[0 ], cy = cell[1 ]; for (let j = 0 ; j < 4 ; ++j) { const nx = cx + dirs[j][0 ]; const ny = cy + dirs[j][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col) { if (!visited[nx][ny] && forest[nx][ny] > 0 ) { if (nx === tx && ny === ty) { return step; } queue.push ([nx, ny]); visited[nx][ny] = true ; } } } } } return -1 ; }
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 var dir4 = []struct { x, y int }{{-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {0 , 1 }}func cutOffTree (forest [][]int ) int ) { type pair struct { dis, x, y int } trees := []pair{} for i, row := range forest { for j, h := range row { if h > 1 { trees = append (trees, pair{h, i, j}) } } } sort.Slice(trees, func (i, j int ) bool { return trees[i].dis < trees[j].dis }) bfs := func (sx, sy, tx, ty int ) int { m, n := len (forest), len (forest[0 ]) vis := make ([][]bool , m) for i := range vis { vis[i] = make ([]bool , n) } vis[sx][sy] = true q := []pair{{0 , sx, sy}} for len (q) > 0 { p := q[0 ] q = q[1 :] if p.x == tx && p.y == ty { return p.dis } for _, d := range dir4 { if x, y := p.x+d.x, p.y+d.y; 0 <= x && x < m && 0 <= y && y < n && !vis[x][y] && forest[x][y] > 0 { vis[x][y] = true q = append (q, pair{p.dis + 1 , x, y}) } } } return -1 } preX, preY := 0 , 0 for _, t := range trees { d := bfs(preX, preY, t.x, t.y) if d < 0 { return -1 } ans += d preX, preY = t.x, t.y } return }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m^2 \times n^2),其中 m 为矩阵的行数,n 为矩阵的列数。矩阵中最多有 m \times n 颗树,对树的高度进行排序,时间复杂度为 O(m \times n \times \log (m \times n)),利用广度优先搜索两颗树之间的最短距离需要的时间为 O(m \times n),因此总的时间复杂为 O(m \times n \times \log (m \times n) + m^2 \times n^2) = O(m^2 \times n^2) 。
空间复杂度:O(m \times n),其中 m 为矩阵的行数,n 为矩阵的列数。矩阵中最多有 m \times n 颗树,对树的高度进行排序,所需要的栈空间为 O(\log (m \times n)),利用广度优先搜索队列中最多有 O(m \times n) 个元素,标记已遍历过的元素需要的空间为 O(m \times n),因此总的空间复杂度为 O(m \times n)。
方法二:Dijkstra 算法 思路与算法
我们还可以利用 Dijkstra 算法求矩阵中两点的最短距离,Dijkstra 算法也是利用的广度优先搜索,不同的是,每次对队列中优先选择最短路径的元素。visited 记录在某个时间点已经添加到队列中的节点,这些节点已被处理或在等待处理的队列中。每次从队列中取出当前从起点开始的最少步数的点,对于下一个要处理的每个节点,查看他们的四个方向上相邻的点,如果相邻的点没有被遍历过且不是障碍,将其加入到队列中,直到找到终点为止,返回当前的步数即可。最终返回所有的步数之和即为最终结果。
代码
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 class Solution {public : int dirs[4 ][2 ] = {{-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {0 , 1 }}; int bfs (vector<vector<int >>& forest, int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) if (sx == tx && sy == ty) { return 0 ; } int row = forest.size (); int col = forest[0 ].size (); priority_queue<pair<int , int >, vector<pair<int , int >>, greater<pair<int , int >>> pq; vector<vector<bool >> visited (row, vector <bool >(col, false )); pq.emplace (0 , sx * col + sy); visited[sx][sy] = true ; while (!pq.empty ()) { auto [dist, loc] = pq.top (); pq.pop (); for (int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; ++j) { int nx = loc / col + dirs[j][0 ]; int ny = loc % col + dirs[j][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col) { if (!visited[nx][ny] && forest[nx][ny] > 0 ) { if (nx == tx && ny == ty) { return dist + 1 ; } pq.emplace (dist + 1 , nx * col + ny); visited[nx][ny] = true ; } } } } return -1 ; } int cutOffTree (vector<vector<int >>& forest) vector<pair<int , int >> trees; int row = forest.size (); int col = forest[0 ].size (); for (int i = 0 ; i < row; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < col; ++j) { if (forest[i][j] > 1 ) { trees.emplace_back (i, j); } } } sort (trees.begin (), trees.end (), [&](const pair<int , int > & a, const pair<int , int > & b) { return forest[a.first][a.second] < forest[b.first][b.second]; }); int cx = 0 ; int cy = 0 ; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < trees.size (); ++i) { int steps = bfs (forest, cx, cy, trees[i].first, trees[i].second); if (steps == -1 ) { return -1 ; } ans += steps; cx = trees[i].first; cy = trees[i].second; } return ans; } };
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 class Solution { int [][] dirs = {{-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {0 , 1 }}; public int cutOffTree (List<List<Integer>> forest) { List<int []> trees = new ArrayList <int []>(); int row = forest.size(); int col = forest.get(0 ).size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < row; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < col; ++j) { if (forest.get(i).get(j) > 1 ) { trees.add(new int []{i, j}); } } } Collections.sort(trees, (a, b) -> forest.get(a[0 ]).get(a[1 ]) - forest.get(b[0 ]).get(b[1 ])); int cx = 0 ; int cy = 0 ; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < trees.size(); ++i) { int steps = bfs(forest, cx, cy, trees.get(i)[0 ], trees.get(i)[1 ]); if (steps == -1 ) { return -1 ; } ans += steps; cx = trees.get(i)[0 ]; cy = trees.get(i)[1 ]; } return ans; } public int bfs (List<List<Integer>> forest, int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) { if (sx == tx && sy == ty) { return 0 ; } int row = forest.size(); int col = forest.get(0 ).size(); PriorityQueue<int []> pq = new PriorityQueue <int []>((a, b) -> a[0 ] - b[0 ]); boolean [][] visited = new boolean [row][col]; pq.offer(new int []{0 , sx * col + sy}); visited[sx][sy] = true ; while (!pq.isEmpty()) { int [] arr = pq.poll(); int dist = arr[0 ], loc = arr[1 ]; for (int j = 0 ; j < 4 ; ++j) { int nx = loc / col + dirs[j][0 ]; int ny = loc % col + dirs[j][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col) { if (!visited[nx][ny] && forest.get(nx).get(ny) > 0 ) { if (nx == tx && ny == ty) { return dist + 1 ; } pq.offer(new int []{dist + 1 , nx * col + ny}); visited[nx][ny] = true ; } } } } return -1 ; } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m^2 \times n^2 \times \log (m \times n)),其中 m 为矩阵的行数,n 为矩阵的列数。矩阵中最多有 m \times n 颗树,对树的高度进行排序,时间复杂度为 O(m \times n \times \log (m \times n)),利用 Dijkstra 求最短距离需要的时间为 O(m \times n \times \log (m \times n)),因此总的时间复杂为 O(m \times n \times \log (m \times n) + m^2 \times n^2 \times \log (m \times n)) = O(m^2 \times n^2 \times \log (m \times n)) 。
空间复杂度:O(m \times n),其中 m 为矩阵的行数,n 为矩阵的列数。矩阵中最多有 m \times n 颗树,对树的高度进行排序,所需要的栈空间为 O(\log (m \times n)),利用 Dijkstra 算法队列中最多有 O(m \times n) 个元素,标记已遍历过的元素需要的空间为 O(m \times n),因此总的空间复杂度为 O(m \times n)。
方法三:A* 启发式搜索算法 思路与算法
「A* 算法 」算法是另一种路径查找算法。设当前搜索的起点为 (\textit{sx}, \textit{sy}),终点为 (\textit{tx}, \textit{ty}), 对于位置 (x, y) 的每个节点,设 A* 的估算函数为 f(x, y) = g(x, y) + h(x, y),其中 g(x, y) 表示从起点 (\textit{sx}, \textit{sy}) 到 (x, y) 的实际距离,评估函数 h(x, y) 在此选择 (x, y) 到 (\textit{tx}, \textit{ty}) 的曼哈顿距离。
我们利用优先队列优先选择估算函数值最小的节点,实际上 A* 搜索是 Dijkstra 的一个特例,当评估函数的 h(x, y) = 0 时,此时该算法即为 Dijkstra 搜索。
代码
[sol3-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 class Solution {public : int dirs[4 ][2 ] = {{-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {0 , 1 }}; int bfs (vector<vector<int >>& forest, int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) if (sx == tx && sy == ty) { return 0 ; } int row = forest.size (); int col = forest[0 ].size (); vector<vector<int >> costed (row, vector <int >(col, INT_MAX)); priority_queue<tuple<int , int , int >, vector<tuple<int , int , int >>, greater<tuple<int , int , int >>> pq; costed[sx][sy] = abs (sx - tx) + abs (sy - ty); pq.emplace (costed[sx][sy], 0 , sx * col + sy); while (!pq.empty ()) { auto [cost, dist, loc] = pq.top (); pq.pop (); int cx = loc / col; int cy = loc % col; if (cx == tx && cy == ty) { return dist; } for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; ++i) { int nx = cx + dirs[i][0 ]; int ny = cy + dirs[i][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col && forest[nx][ny] > 0 ) { int ncost = dist + 1 + abs (nx - tx) + abs (ny - ty); if (ncost < costed[nx][ny]) { pq.emplace (ncost, dist + 1 , nx * col + ny); costed[nx][ny] = ncost; } } } } return -1 ; } int cutOffTree (vector<vector<int >>& forest) vector<pair<int , int >> trees; int row = forest.size (); int col = forest[0 ].size (); for (int i = 0 ; i < row; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < col; ++j) { if (forest[i][j] > 1 ) { trees.emplace_back (i, j); } } } sort (trees.begin (), trees.end (), [&](const pair<int , int > & a, const pair<int , int > & b) { return forest[a.first][a.second] < forest[b.first][b.second]; }); int cx = 0 ; int cy = 0 ; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < trees.size (); ++i) { int steps = bfs (forest, cx, cy, trees[i].first, trees[i].second); if (steps == -1 ) { return -1 ; } ans += steps; cx = trees[i].first; cy = trees[i].second; } return ans; } };
[sol3-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 class Solution { int [][] dirs = {{-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {0 , 1 }}; public int cutOffTree (List<List<Integer>> forest) { List<int []> trees = new ArrayList <int []>(); int row = forest.size(); int col = forest.get(0 ).size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < row; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < col; ++j) { if (forest.get(i).get(j) > 1 ) { trees.add(new int []{i, j}); } } } Collections.sort(trees, (a, b) -> forest.get(a[0 ]).get(a[1 ]) - forest.get(b[0 ]).get(b[1 ])); int cx = 0 ; int cy = 0 ; int ans = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < trees.size(); ++i) { int steps = bfs(forest, cx, cy, trees.get(i)[0 ], trees.get(i)[1 ]); if (steps == -1 ) { return -1 ; } ans += steps; cx = trees.get(i)[0 ]; cy = trees.get(i)[1 ]; } return ans; } public int bfs (List<List<Integer>> forest, int sx, int sy, int tx, int ty) { if (sx == tx && sy == ty) { return 0 ; } int row = forest.size(); int col = forest.get(0 ).size(); int [][] costed = new int [row][col]; for (int i = 0 ; i < row; ++i) { Arrays.fill(costed[i], Integer.MAX_VALUE); } PriorityQueue<int []> pq = new PriorityQueue <int []>((a, b) -> a[0 ] - b[0 ]); costed[sx][sy] = Math.abs(sx - tx) + Math.abs(sy - ty); pq.offer(new int []{costed[sx][sy], 0 , sx * col + sy}); while (!pq.isEmpty()) { int [] arr = pq.poll(); int cost = arr[0 ], dist = arr[1 ], loc = arr[2 ]; int cx = loc / col; int cy = loc % col; if (cx == tx && cy == ty) { return dist; } for (int i = 0 ; i < 4 ; ++i) { int nx = cx + dirs[i][0 ]; int ny = cy + dirs[i][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < row && ny >= 0 && ny < col && forest.get(nx).get(ny) > 0 ) { int ncost = dist + 1 + Math.abs(nx - tx) + Math.abs(ny - ty); if (ncost < costed[nx][ny]) { pq.offer(new int []{ncost, dist + 1 , nx * col + ny}); costed[nx][ny] = ncost; } } } } return -1 ; } }
复杂度分析
启发式搜索不讨论时空复杂度。