给你一个有 n 个结点的二叉树的根结点 root ,其中树中每个结点 node 都对应有 node.val 枚硬币。整棵树上一共有 n
枚硬币。
在一次移动中,我们可以选择两个相邻的结点,然后将一枚硬币从其中一个结点移动到另一个结点。移动可以是从父结点到子结点,或者从子结点移动到父结点。
返回使每个结点上 只有 一枚硬币所需的 最少 移动次数。
示例 1:

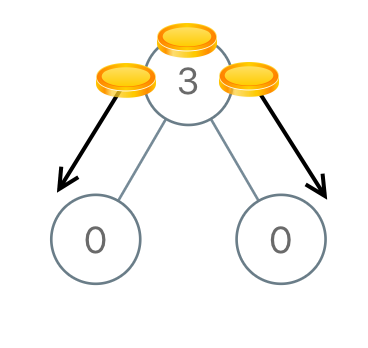
**输入:** root = [3,0,0]
**输出:** 2
**解释:** 一枚硬币从根结点移动到左子结点,一枚硬币从根结点移动到右子结点。
示例 2:

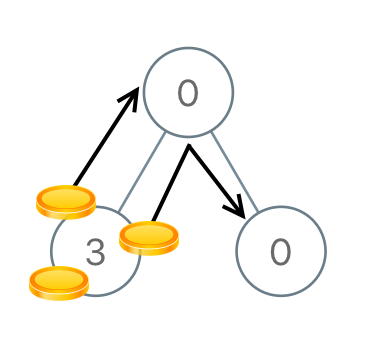
**输入:** root = [0,3,0]
**输出:** 3
**解释:** 将两枚硬币从根结点的左子结点移动到根结点(两次移动)。然后,将一枚硬币从根结点移动到右子结点。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目为
n
1 <= n <= 1000 <= Node.val <= n- 所有
Node.val 的值之和是 n
方法一:深度优先搜索
思路与算法
题目中要求求出移动步数,设 dfs}(a) 表示若使得以 a 为根节点的子树满足每个节点均只有一个金币时,节点 a 的父节点需要从节点 a 「拿走」的金币数目,我们可以定义如下:
- 如果 dfs}(a) > 0,则表示节点 a 需要向 a 的父节点移动 dfs}(a) 个金币;
- 如果 dfs}(a) = 0,则表示节点 a 与 a 的父节点之间不需要移动;
- 如果 dfs}(a) < 0,则表示节点 a 的父节点需要向 a 移动 |\textit{dfs}(a)| 个金币;
- 综上可知道无论哪个方向移动,节点 a 与其父节点之间的金币移动此时一定为 |\textit{dfs}(a)|;
设 count}(a) 表示当以节点 a 为根节点的子树中含有的二叉树节点数目,设 sum}(a) 表示以节点 a 为根节点的子树中含有的二叉树节点的值之和,此时可以知道 dfs}(a) = \textit{sum}(a) - \textit{count}(a),则可以按照以下几种情形分析:
- 假设 sum}(a) > \textit{count}(a),即此时子树中金币总数量大于节点的总数量,此时需要向 a 的父节点移动 sum}(a) - \textit{count}(a) 个金币;
- 假设 sum}(\textit{a}) < \textit{count}(a),即此时子树中金币总数量小于节点的总数量,此时需要从 a 的父节点需要移动 count}(a) - \textit{sum}(a) 个金币;
- 假设 sum}(a) = \textit{count}(a),即此时子树中金币总数量等于节点的总数量,此时 a 的父节点与 a 之间不需要移动即可,最优策略一定是 a 的左子树与右子树之间的金币互相移动即可,此处不再证明;
假设当前节点为 node,设 val}(\textit{node}) 表示节点 node 初始时的金币数目,它的左孩子为 left,它的右孩子为 right,则此时可以知道如下:
- 若要使得左子树每个节点的数目均为 1,此时 node 需要从 left「拿走」的为金币数目 dfs}(\textit{left}),此时 left 与 node 之间需要移动 |\textit{dfs}(\textit{left})| 次金币;
- 若要使得右子树每个节点的数目均为 1,此时 node 需要从 right「拿走」的金币数目 dfs}(\textit{right}),此时 right 与 node 之间需要移动 |\textit{dfs}(\textit{right})| 次金币;
- 此时根节点的金币总数目即为 move}(\textit{left}) + \textit{move}(\textit{right}) + \textit{val}(\textit{node}),由于 node 本身需要保留一个金币,此时 node 的根节点需要向它「拿走」的金币数目即为 move}(\textit{left}) + \textit{move}(\textit{right}) + \textit{val}(\textit{node}) - 1;
综上我们采用递归,每次递归遍历节点 node 时,返回其父节点需要从 node 「拿走」的金币数目,并统计当前节点与其子节点之间的移动金币的次数,我们通过递归遍历即可求得所有节点与其父节点之间的移动金币的次数统计之和即为总的金币移动次数。
- 由于本题中树中金币的数目与树中节点的数目相等,根据上述推论可以知道根节点 root 一定不需要再向其父节点移动金币。
代码
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Solution {
public:
int distributeCoins(TreeNode* root) {
int move = 0;
function<int(const TreeNode *)> dfs = [&](const TreeNode *root) -> int {
int moveleft = 0;
int moveright = 0;
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
if (root->left) {
moveleft = dfs(root->left);
}
if (root->right) {
moveright = dfs(root->right);
}
move += abs(moveleft) + abs(moveright);
return moveleft + moveright + root->val - 1;
};
dfs(root);
return move;
}
};
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| class Solution {
int move = 0;
public int distributeCoins(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return move;
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root) {
int moveleft = 0;
int moveright = 0;
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (root.left != null) {
moveleft = dfs(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
moveright = dfs(root.right);
}
move += Math.abs(moveleft) + Math.abs(moveright);
return moveleft + moveright + root.val - 1;
}
}
|
[sol1-C#]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| public class Solution {
int move = 0;
public int DistributeCoins(TreeNode root) {
DFS(root);
return move;
}
public int DFS(TreeNode root) {
int moveleft = 0;
int moveright = 0;
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (root.left != null) {
moveleft = DFS(root.left);
}
if (root.right != null) {
moveright = DFS(root.right);
}
move += Math.Abs(moveleft) + Math.Abs(moveright);
return moveleft + moveright + root.val - 1;
}
}
|
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class Solution:
move = 0
def distributeCoins(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
def dfs(root):
moveleft = 0
moveright = 0
if root is None:
return 0
if root.left is not None:
moveleft = dfs(root.left)
if root.right is not None:
moveright = dfs(root.right)
self.move += abs(moveleft) + abs(moveright)
return moveleft + moveright + root.val - 1
dfs(root)
return self.move
|
[sol1-Go]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| var move int
func distributeCoins(root *TreeNode) int {
move = 0
dfs(root)
return move
}
func dfs(root *TreeNode) int {
moveleft := 0
moveright := 0
if root == nil {
return 0
}
if root.Left != nil {
moveleft = dfs(root.Left)
}
if root.Right != nil {
moveright = dfs(root.Right)
}
move += abs(moveleft) + abs(moveright)
return moveleft + moveright + root.Val - 1
}
func abs(a int) int {
if a < 0 {
a = -a
}
return a
}
|
[sol1-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| let move;
var distributeCoins = function(root) {
move = 0;
dfs(root);
return move;
};
function dfs(root) {
let moveleft = 0;
let moveright = 0;
if (root === null) {
return 0;
}
if (root.left !== null) {
moveleft = dfs(root.left);
}
if (root.right !== null) {
moveright = dfs(root.right);
}
move += Math.abs(moveleft) + Math.abs(moveright);
return moveleft + moveright + root.val - 1;
}
|
[sol1-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| int dfs(const struct TreeNode* root, int *move) {
int moveleft = 0;
int moveright = 0;
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
if (root->left) {
moveleft = dfs(root->left, move);
}
if (root->right) {
moveright = dfs(root->right, move);
}
(*move) += abs(moveleft) + abs(moveright);
return moveleft + moveright + root->val - 1;
}
int distributeCoins(struct TreeNode* root) {
int move = 0;
dfs(root, &move);
return move;
}
|
复杂度分析