0999-可以被一步捕获的棋子数
在一个 8 x 8 的棋盘上,有一个白色的车(Rook),用字符 'R'
表示。棋盘上还可能存在空方块,白色的象(Bishop)以及黑色的卒(pawn),分别用字符 '.','B' 和 'p'
表示。不难看出,大写字符表示的是白棋,小写字符表示的是黑棋。
车按国际象棋中的规则移动。东,西,南,北四个基本方向任选其一,然后一直向选定的方向移动,直到满足下列四个条件之一:
- 棋手选择主动停下来。
- 棋子因到达棋盘的边缘而停下。
- 棋子移动到某一方格来捕获位于该方格上敌方(黑色)的卒,停在该方格内。
- 车不能进入/越过已经放有其他友方棋子(白色的象)的方格,停在友方棋子前。
你现在可以控制车移动一次,请你统计有多少敌方的卒处于你的捕获范围内(即,可以被一步捕获的棋子数)。
示例 1:
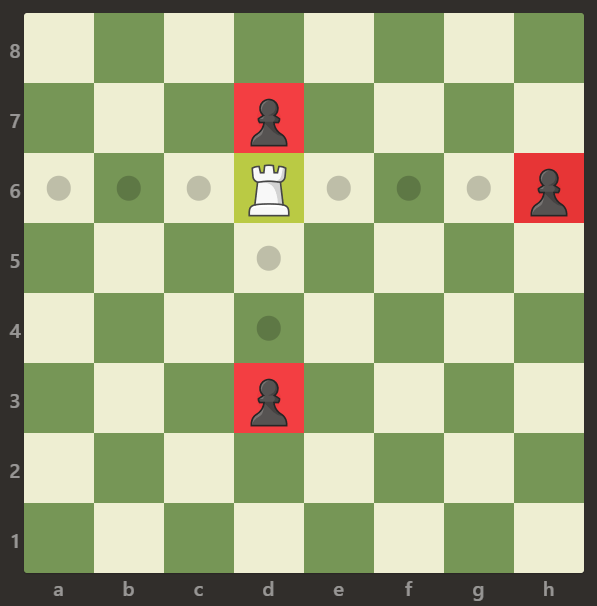
**输入:** [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","R",".",".",".","p"],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
**输出:** 3
**解释:** 在本例中,车能够捕获所有的卒。
示例 2:

**输入:** [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".","p","p","p","p","p",".","."],[".","p","p","B","p","p",".","."],[".","p","B","R","B","p",".","."],[".","p","p","B","p","p",".","."],[".","p","p","p","p","p",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
**输出:** 0
**解释:** 象阻止了车捕获任何卒。
示例 3:
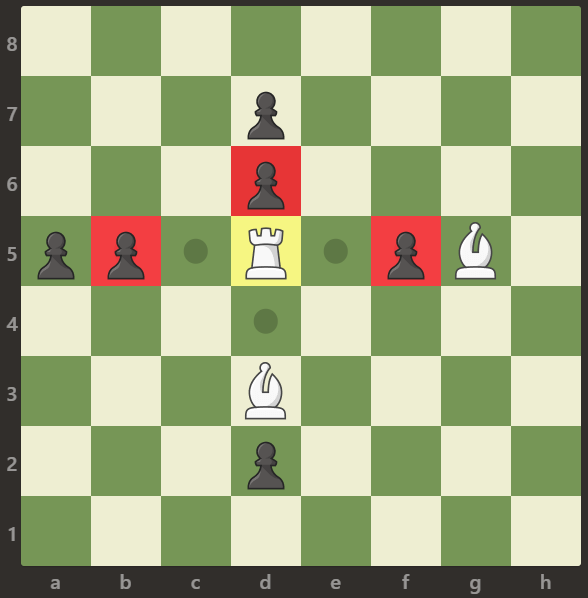
**输入:** [[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],["p","p",".","R",".","p","B","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","B",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".","p",".",".",".","."],[".",".",".",".",".",".",".","."]]
**输出:** 3
**解释:**
车可以捕获位置 b5,d6 和 f5 的卒。
提示:
board.length == board[i].length == 8board[i][j]可以是'R','.','B'或'p'- 只有一个格子上存在
board[i][j] == 'R'
方法一:模拟
思路和算法
根据题意模拟即可:
遍历棋盘确定白色车的下标,用 (st,ed) 表示。
模拟车移动的规则,朝四个基本方向移动,直到碰到卒或者白色象或者碰到棋盘边缘时停止,用 cnt 记录捕获到的卒的数量。
那么如何模拟车移动的规则呢?我们可以建立方向数组表示在这个方向上移动一步的增量,比如向北移动一步的时候,白色车的 x 轴坐标减 1,而 y 轴坐标不会变化,所以我们可以用 (-1, 0) 表示白色车向北移动一步的增量,其它三个方向同理。建立了方向数组,则白色车在某个方向移动 step 步的坐标增量就可以直接计算得到,比如向北移动 step 步的坐标增量即为 (-step, 0)。
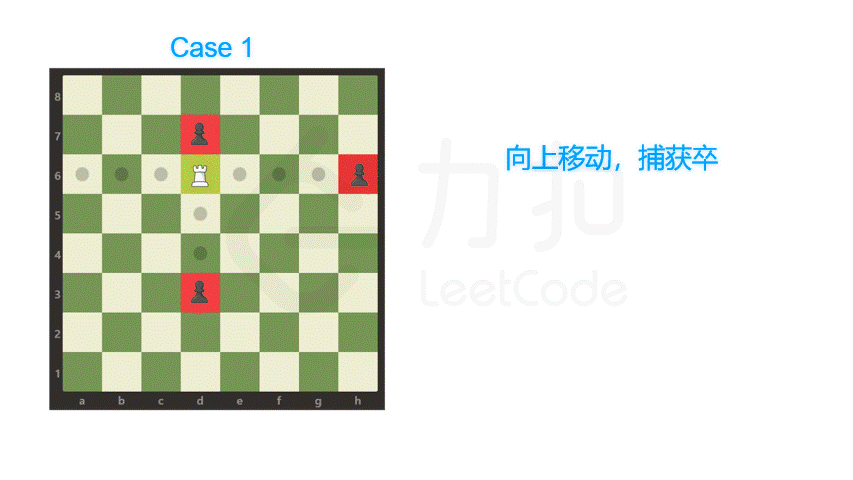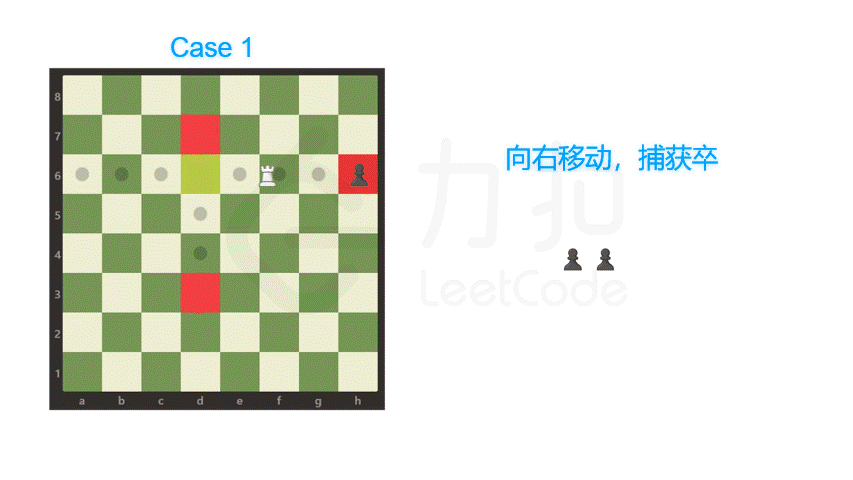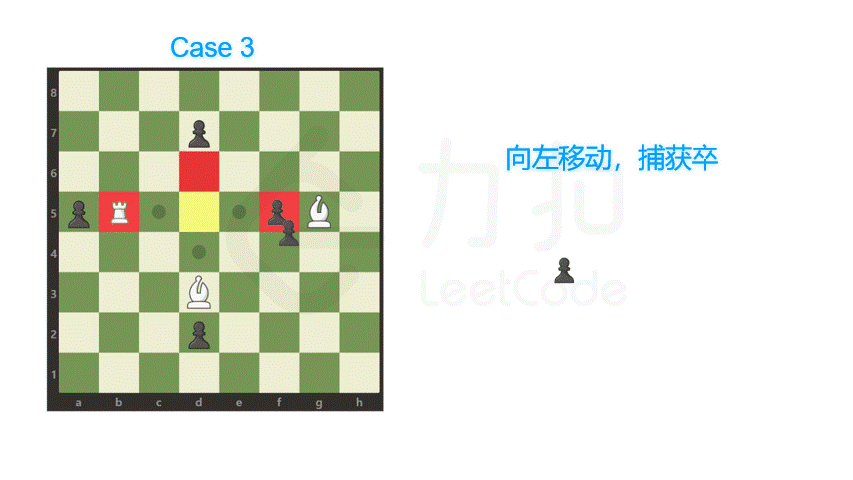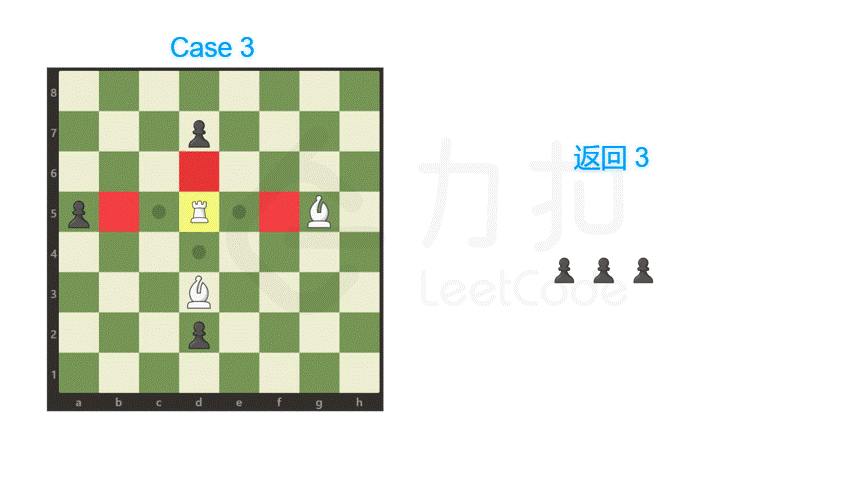
方向数组也可以根据相应的题意自行扩展,比如模拟象棋中马跳的坐标增量。
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | var numRookCaptures = function(board) { |
1 | class Solution: |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n^2),其中 n 是棋盘的边长。找白色车在棋盘中的位置需要 O(n^2) 的时间复杂度,模拟车在四个方向上捕获颜色相反的卒需要 O(n) 的时间复杂度,所以一共需要 O(n^2+n) = O(n^2) 的时间复杂度。
空间复杂度:O(1),只需要常数空间存放若干变量。