1007-行相等的最少多米诺旋转
在一排多米诺骨牌中,tops[i] 和 bottoms[i] 分别代表第 i 个多米诺骨牌的上半部分和下半部分。(一个多米诺是两个从 1 到 6
的数字同列平铺形成的 —— 该平铺的每一半上都有一个数字。)
我们可以旋转第 i 张多米诺,使得 tops[i] 和 bottoms[i] 的值交换。
返回能使 tops 中所有值或者 bottoms 中所有值都相同的最小旋转次数。
如果无法做到,返回 -1.
示例 1:
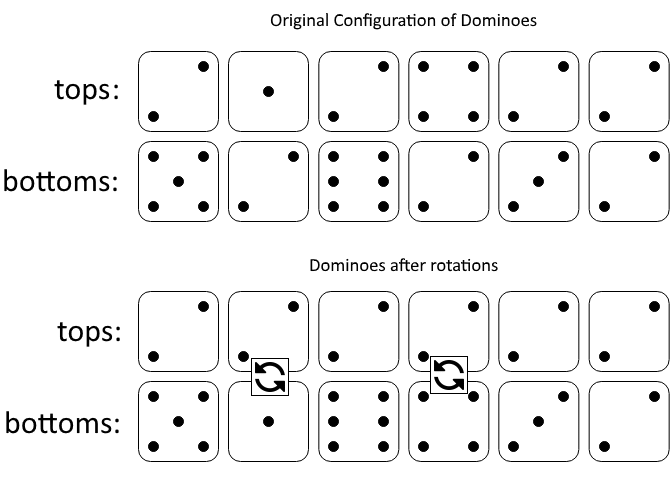
**输入:** tops = [2,1,2,4,2,2], bottoms = [5,2,6,2,3,2]
**输出:** 2
**解释:**
图一表示:在我们旋转之前, tops 和 bottoms 给出的多米诺牌。
如果我们旋转第二个和第四个多米诺骨牌,我们可以使上面一行中的每个值都等于 2,如图二所示。
示例 2:
**输入:** tops = [3,5,1,2,3], bottoms = [3,6,3,3,4]
**输出:** -1
**解释:** 在这种情况下,不可能旋转多米诺牌使一行的值相等。
提示:
2 <= tops.length <= 2 * 104bottoms.length == tops.length1 <= tops[i], bottoms[i] <= 6
方法一:贪心
分析
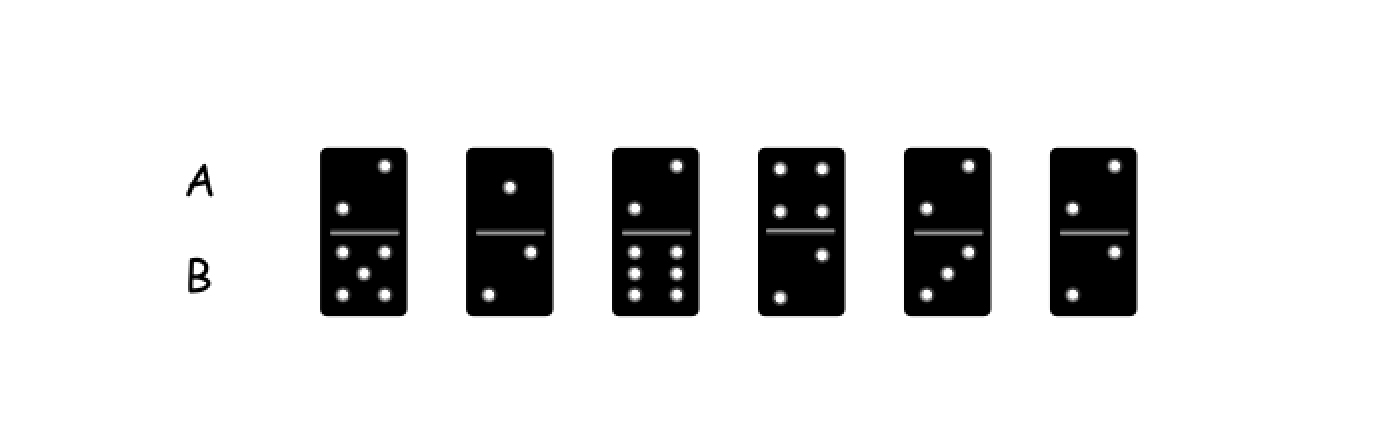
我们随便选其中的一个多米诺骨牌,它的标号为 i,上半部分的数字为 A[i],下半部分的数字为 B[i]。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
{:align=center}
此时可能会有三种情况:
- 以数字
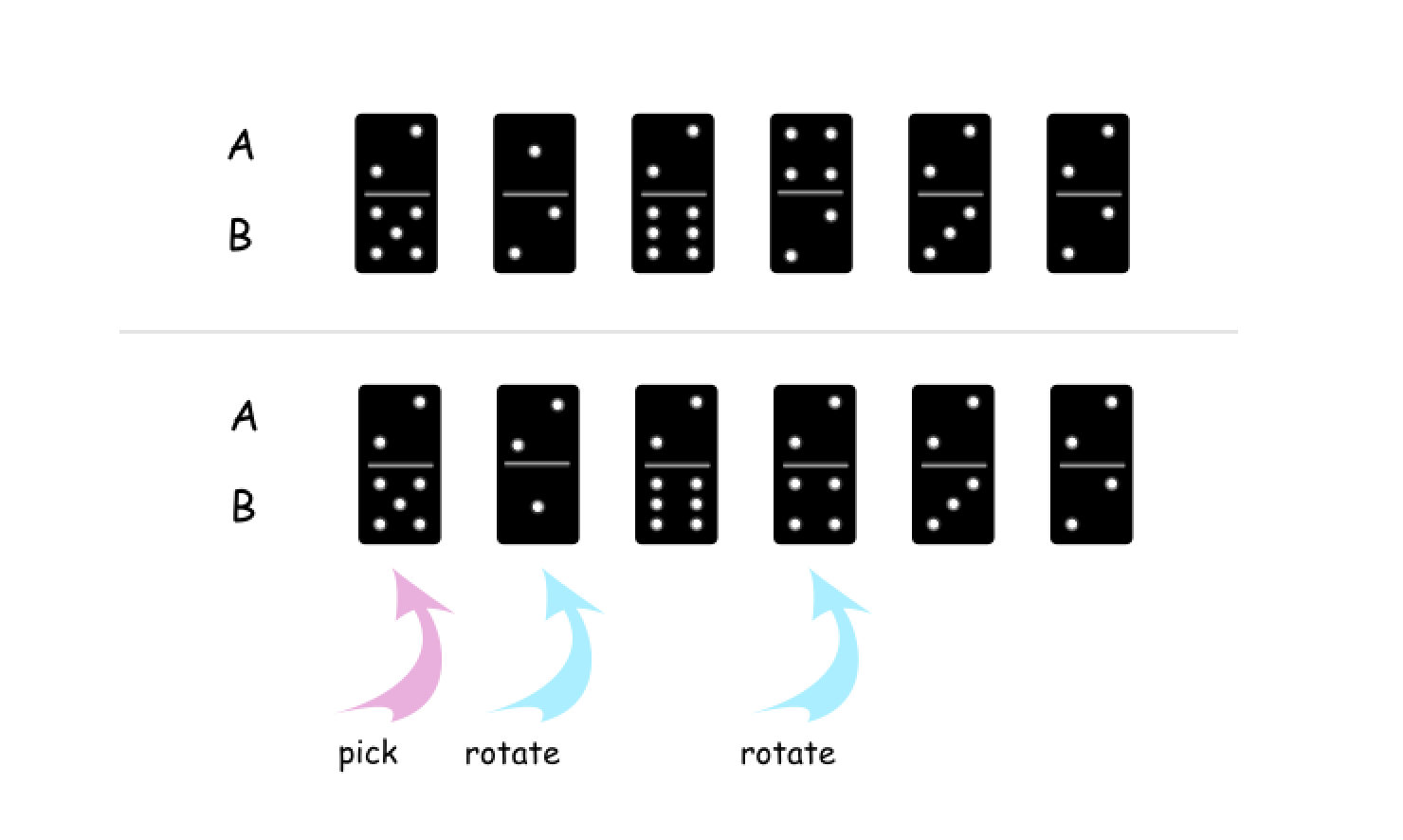
A[i]作为基准,将A或B中的所有值都变为A[i]。例如,下图中,我们选择了第 0 个多米诺骨牌,这样可以将A中的所有值都变为 2。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
{:align=center}
- 以数字
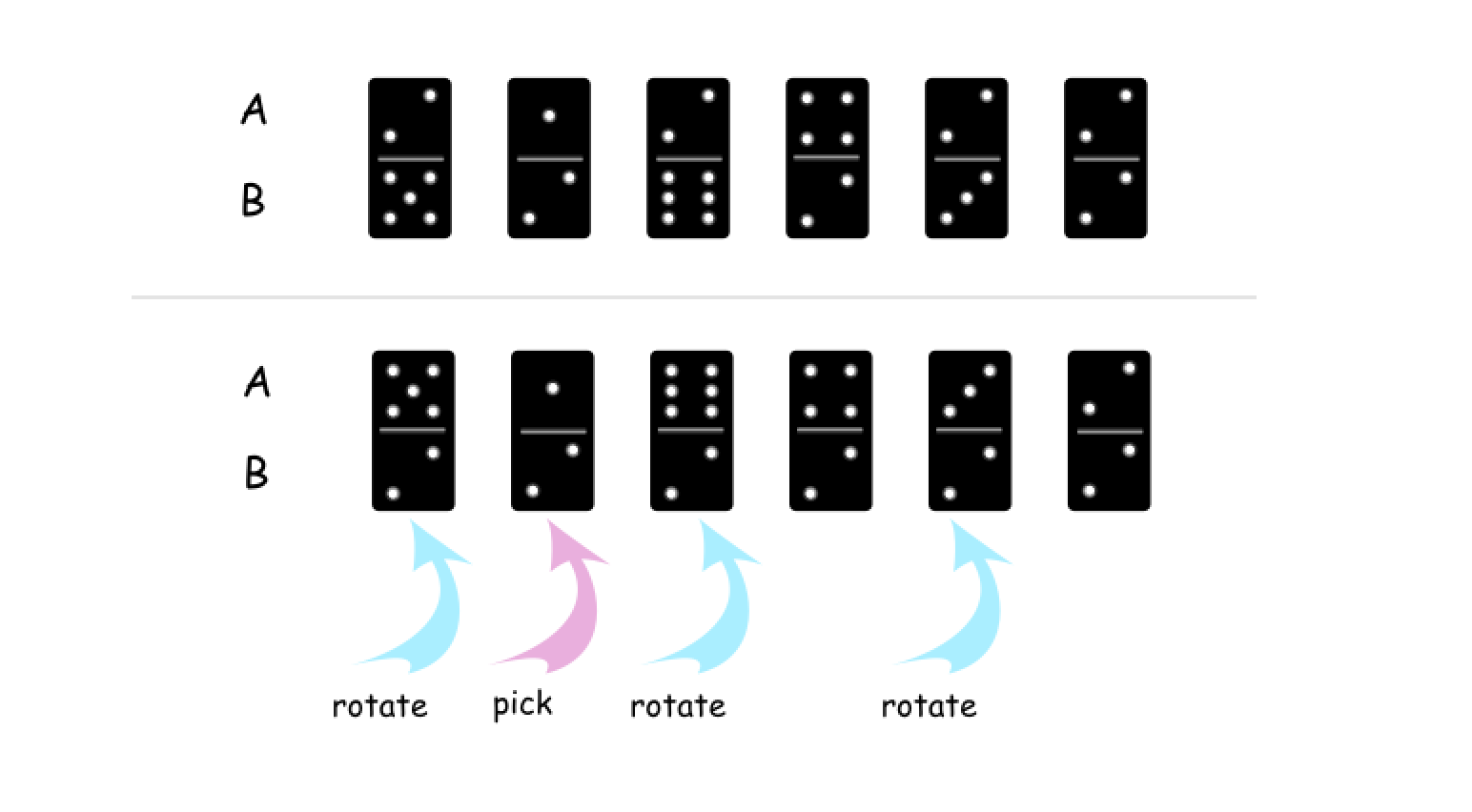
B[i]作为基准,将A或B中的所有值都变为B[i]。例如,下图中,我们选择了第 1 个多米诺骨牌,这样可以将B中的所有值都变为 2。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
{:align=center}
- 无论选择
A[i]还是B[i]都没有办法将A或B中的所有值变为都相同。例如,下图中,我们选择了最后一个多米诺骨牌,无论是它的上半部分 5 还是下半部分 4,都无法满足条件。
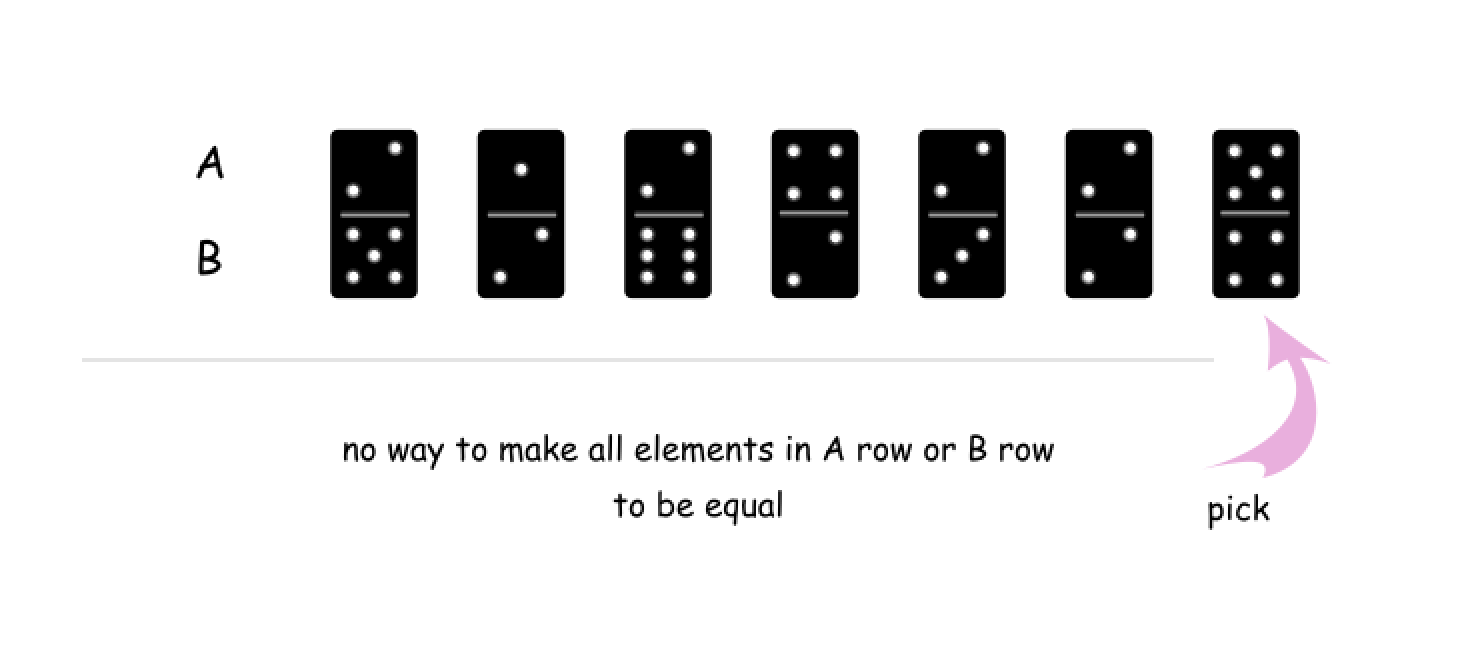 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
{:align=center}
如果要满足第 1 种或是第 2 种情况,就必须存在一块多米诺骨牌,它的上半部分或者下半部分的数字 x 在所有其它的多米诺骨牌中都出现过。若该条件满足,则说明所有多米诺骨牌中都出现了数字 x。因此,我们只要选择任意一块多米诺骨牌,判断它的上半部分或下半部分的数字是否可以作为 x 即可。
算法
选择第一块多米诺骨牌,它包含两个数字
A[0]和B[0];检查其余的多米诺骨牌中是否出现过
A[0]。如果都出现过,则求出最少的翻转次数,其为将A[0]全部翻到A和全部翻到B中的较少的次数。检查其余的多米诺骨牌中是否出现过
B[0]。如果都出现过,则求出最少的翻转次数,其为将B[0]全部翻到A和全部翻到B中的较少的次数。如果上述两次检查都失败,则返回
-1。
1 | class Solution: |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N)。我们只会遍历所有的数组最多两次。
空间复杂度:O(1)。