1029-两地调度
公司计划面试 2n 人。给你一个数组 costs ,其中 costs[i] = [aCosti, bCosti] 。第 i 人飞往 a
市的费用为 aCosti ,飞往 b 市的费用为 bCosti 。
返回将每个人都飞到 a 、b 中某座城市的最低费用,要求每个城市都有 n 人抵达 。
示例 1:
**输入:** costs = [[10,20],[30,200],[400,50],[30,20]]
**输出:** 110
**解释:**
第一个人去 a 市,费用为 10。
第二个人去 a 市,费用为 30。
第三个人去 b 市,费用为 50。
第四个人去 b 市,费用为 20。
最低总费用为 10 + 30 + 50 + 20 = 110,每个城市都有一半的人在面试。
示例 2:
**输入:** costs = [[259,770],[448,54],[926,667],[184,139],[840,118],[577,469]]
**输出:** 1859
示例 3:
**输入:** costs = [[515,563],[451,713],[537,709],[343,819],[855,779],[457,60],[650,359],[631,42]]
**输出:** 3086
提示:
2 * n == costs.length2 <= costs.length <= 100costs.length为偶数1 <= aCosti, bCosti <= 1000
方法一:贪心
分析
我们这样来看这个问题,公司首先将这 2N 个人全都安排飞往 B 市,再选出 N 个人改变它们的行程,让他们飞往 A 市。如果选择改变一个人的行程,那么公司将会额外付出 price_A - price_B 的费用,这个费用可正可负。
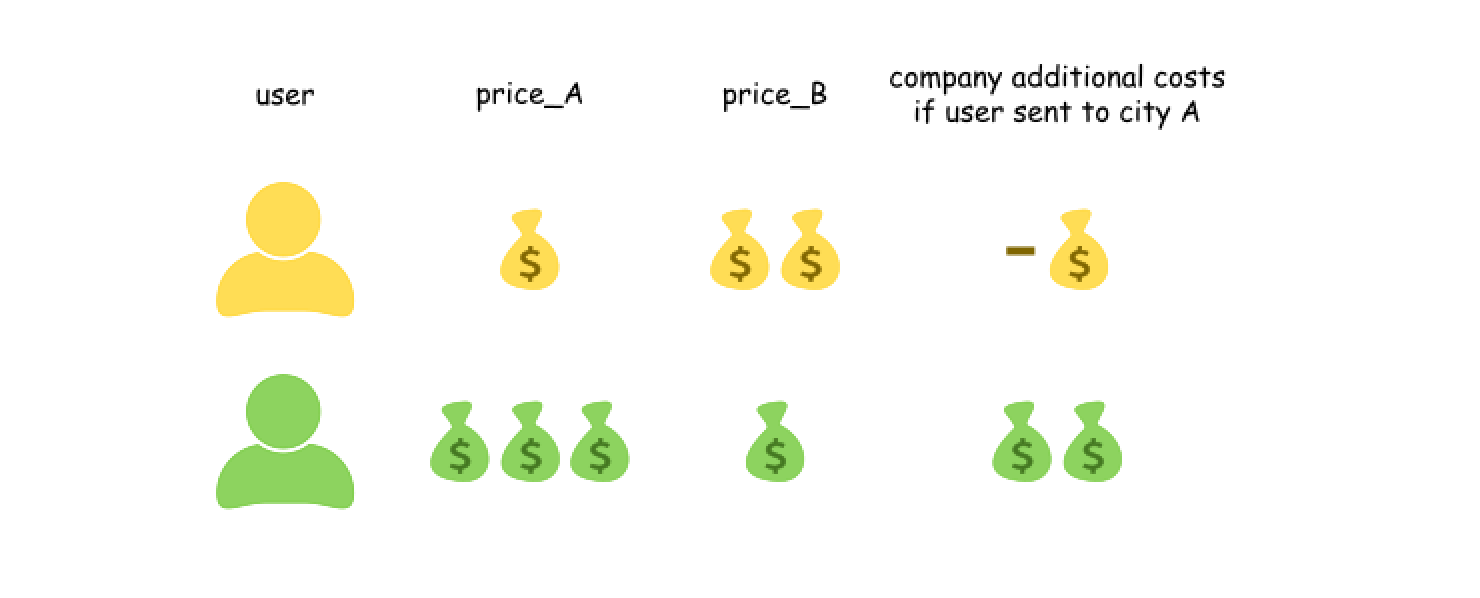 {:width=600}
{:width=600}
{:align=center}
因此最优的方案是,选出 price_A - price_B 最小的 N 个人,让他们飞往 A 市,其余人飞往 B 市。
算法
按照
price_A - price_B从小到大排序;将前 N 个人飞往
A市,其余人飞往B市,并计算出总费用。
1 | class Solution: |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N \log N),需要对
price_A - price_B进行排序。空间复杂度:O(1)。
Comments