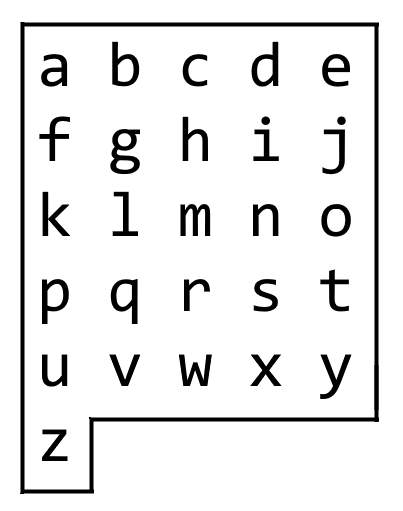
我们从一块字母板上的位置 (0, 0) 出发,该坐标对应的字符为 board[0][0]。
在本题里,字母板为board = ["abcde", "fghij", "klmno", "pqrst", "uvwxy", "z"],如下所示。

我们可以按下面的指令规则行动:
- 如果方格存在,
'U' 意味着将我们的位置上移一行;
- 如果方格存在,
'D' 意味着将我们的位置下移一行;
- 如果方格存在,
'L' 意味着将我们的位置左移一列;
- 如果方格存在,
'R' 意味着将我们的位置右移一列;
'!' 会把在我们当前位置 (r, c) 的字符 board[r][c] 添加到答案中。
(注意,字母板上只存在有字母的位置。)
返回指令序列,用最小的行动次数让答案和目标 target 相同。你可以返回任何达成目标的路径。
示例 1:
**输入:** target = "leet"
**输出:** "DDR!UURRR!!DDD!"
示例 2:
**输入:** target = "code"
**输出:** "RR!DDRR!UUL!R!"
提示:
1 <= target.length <= 100target 仅含有小写英文字母。
方法一:直接模拟
思路与算法
由于所有的字符在字母板上的位置是固定的,因此从任意字符 a 到字符 b 的路径也是固定的,我们从中选出一条最短路径即可。两个字符之间的最短距离即等于二者在画板中坐标的曼哈顿距离,可以直接按照“折线”的方式走即可。假设两个字符 a,b 在画板中的位置分别为 (x_a,y_a),(x_b,y_b),其中 x_a,x_b 表示字符 a,b 的行坐标,y_a,y_b 表示字符 a,b 的列坐标。假设当前处在字符 a 处,需要移动到字符 b,此时只需先上下移动 |x_a - x_b| 个位置,再左右移动 |y_a - y_b| 个位置,再执行一次添加操作即可完成字符 b 的添加。
当前字母板中的字符分布如下:

需要注意的是字符 `z’ 所在的行只有一列,此时有以下两种特殊情况需要考虑:
- 从字符
z' 开始移动到其他字符时,第一步只能上移到字符 u’。因此`z’ 移动到其他字符时,需要先往上移动到目标字符所在的行,再向右移动到目标字符所在的列;
- 由于字符
z' 所在的行只有一列,从其他字符移动到字符 z’ 时,必须先移动到字符 u',再向下移动到 z’,最后一步操作一定是下移。因此从其他字符移动到字符 z' 时,需要先往左移动到第 0 列,再向下移动到字符 z’ 即可;
- 对于其他字符的移动指令,可以先上下移动再左右移动或者先左右移动再上下移动均可。
综上所述,为了保证含有字符 `z’ 时能够正常移动,每次移动时优先保证选择上移和左移即可。
代码
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| class Solution:
def alphabetBoardPath(self, target: str) -> str:
cx = cy = 0
res = []
for c in target:
c = ord(c) - ord('a')
nx = c // 5
ny = c % 5
if nx < cx:
res.append('U' * (cx - nx))
if ny < cy:
res.append('L' * (cy - ny))
if nx > cx:
res.append('D' * (nx - cx))
if ny > cy:
res.append('R' * (ny - cy))
res.append('!')
cx = nx
cy = ny
return ''.join(res)
|
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| class Solution {
public:
string alphabetBoardPath(string target) {
int cx = 0, cy = 0;
string res;
for (char c : target) {
int nx = (c - 'a') / 5;
int ny = (c - 'a') % 5;
if (nx < cx) {
res.append(cx - nx, 'U');
}
if (ny < cy) {
res.append(cy - ny, 'L');
}
if (nx > cx) {
res.append(nx - cx, 'D');
}
if (ny > cy) {
res.append(ny - cy, 'R');
}
res.push_back('!');
cx = nx;
cy = ny;
}
return res;
}
};
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| class Solution {
public String alphabetBoardPath(String target) {
int cx = 0, cy = 0;
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < target.length(); i++) {
char c = target.charAt(i);
int nx = (c - 'a') / 5;
int ny = (c - 'a') % 5;
if (nx < cx) {
for (int j = 0; j < cx - nx; j++) {
res.append('U');
}
}
if (ny < cy) {
for (int j = 0; j < cy - ny; j++) {
res.append('L');
}
}
if (nx > cx) {
for (int j = 0; j < nx - cx; j++) {
res.append('D');
}
}
if (ny > cy) {
for (int j = 0; j < ny - cy; j++) {
res.append('R');
}
}
res.append('!');
cx = nx;
cy = ny;
}
return res.toString();
}
}
|
[sol1-C#]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| public class Solution {
public string AlphabetBoardPath(string target) {
int cx = 0, cy = 0;
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
foreach (char c in target) {
int nx = (c - 'a') / 5;
int ny = (c - 'a') % 5;
if (nx < cx) {
for (int j = 0; j < cx - nx; j++) {
res.Append('U');
}
}
if (ny < cy) {
for (int j = 0; j < cy - ny; j++) {
res.Append('L');
}
}
if (nx > cx) {
for (int j = 0; j < nx - cx; j++) {
res.Append('D');
}
}
if (ny > cy) {
for (int j = 0; j < ny - cy; j++) {
res.Append('R');
}
}
res.Append('!');
cx = nx;
cy = ny;
}
return res.ToString();
}
}
|
[sol1-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| char * alphabetBoardPath(char * target) {
int len = strlen(target);
char *res = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * 10 * len + 1);
int pos = 0, cx = 0, cy = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = target[i];
int nx = (c - 'a') / 5;
int ny = (c - 'a') % 5;
if (nx < cx) {
for (int j = 0; j < cx - nx; j++) {
res[pos++] = 'U';
}
}
if (ny < cy) {
for (int j = 0; j < cy - ny; j++) {
res[pos++] = 'L';
}
}
if (nx > cx) {
for (int j = 0; j < nx - cx; j++) {
res[pos++] = 'D';
}
}
if (ny > cy) {
for (int j = 0; j < ny - cy; j++) {
res[pos++] = 'R';
}
}
res[pos++] = '!';
cx = nx;
cy = ny;
}
res[pos] = '\0';
return res;
}
|
[sol1-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| var alphabetBoardPath = function(target) {
let cx = 0, cy = 0;
let res = '';
for (let i = 0; i < target.length; i++) {
const c = target[i];
const nx = Math.floor((c.charCodeAt() - 'a'.charCodeAt()) / 5);
const ny = Math.floor((c.charCodeAt() - 'a'.charCodeAt()) % 5);
if (nx < cx) {
for (let j = 0; j < cx - nx; j++) {
res += 'U';
}
}
if (ny < cy) {
for (let j = 0; j < cy - ny; j++) {
res += 'L';
}
}
if (nx > cx) {
for (let j = 0; j < nx - cx; j++) {
res += 'D';
}
}
if (ny > cy) {
for (let j = 0; j < ny - cy; j++) {
res += 'R';
}
}
res += '!';
cx = nx;
cy = ny;
}
return res;
};
|
[sol1-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| func alphabetBoardPath(target string) string {
cx, cy := 0, 0
res := []byte{}
for _, c := range target {
nx := int(c-'a') / 5
ny := int(c-'a') % 5
if nx < cx {
for j := 0; j < cx-nx; j++ {
res = append(res, 'U')
}
}
if ny < cy {
for j := 0; j < cy-ny; j++ {
res = append(res, 'L')
}
}
if nx > cx {
for j := 0; j < nx-cx; j++ {
res = append(res, 'D')
}
}
if ny > cy {
for j := 0; j < ny-cy; j++ {
res = append(res, 'R')
}
}
res = append(res, '!')
cx = nx
cy = ny
}
return string(res)
}
|
复杂度分析