给你一个字符串 s,「k 倍重复项删除操作」将会从 s 中选择 k 个相邻且相等的字母,并删除它们,使被删去的字符串的左侧和右侧连在一起。
你需要对 s 重复进行无限次这样的删除操作,直到无法继续为止。
在执行完所有删除操作后,返回最终得到的字符串。
本题答案保证唯一。
示例 1:
**输入:** s = "abcd", k = 2
**输出:** "abcd"
**解释:** 没有要删除的内容。
示例 2:
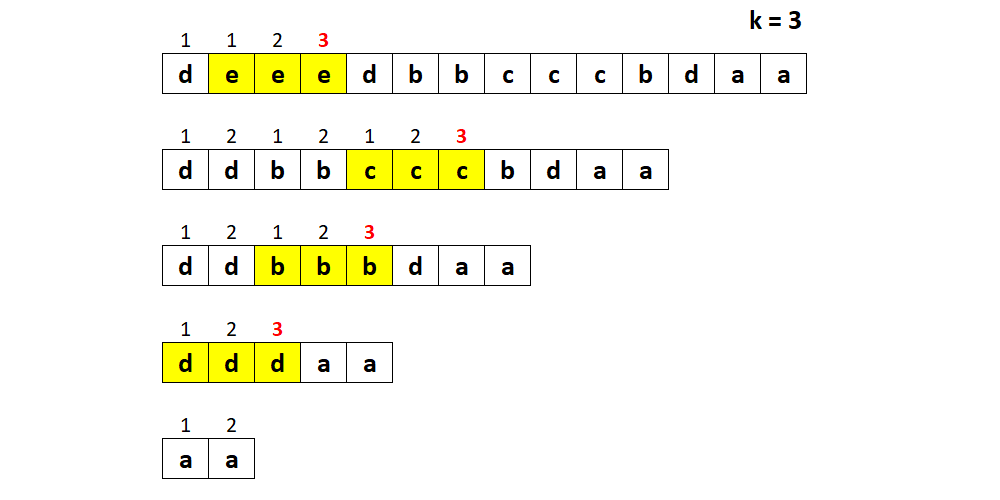
**输入:** s = "deeedbbcccbdaa", k = 3
**输出:** "aa"
**解释:** 先删除 "eee" 和 "ccc",得到 "ddbbbdaa"
再删除 "bbb",得到 "dddaa"
最后删除 "ddd",得到 "aa"
示例 3:
**输入:** s = "pbbcggttciiippooaais", k = 2
**输出:** "ps"
提示:
1 <= s.length <= 10^52 <= k <= 10^4s 中只含有小写英文字母。
方法一:暴力解法
按照问题要求操作:对重复的相邻字母计数,当计数达到 k 时将其删除。重复此操作,直到没有删除的字符为止。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
算法
记录字符串的长度。
遍历字符串:
如果当前字符与前一个相同,计数器加 1。
如果计数器等于 k,删除这 k 个字符。
如果字符串的长度被改变,从头开始重新遍历字符串。
[solution1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public String removeDuplicates(String s, int k) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s);
int length = -1;
while (length != sb.length()) {
length = sb.length();
for (int i = 0, count = 1; i < sb.length(); ++i) {
if (i == 0 || sb.charAt(i) != sb.charAt(i - 1)) {
count = 1;
} else if (++count == k) {
sb.delete(i - k + 1, i + 1);
break;
}
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
|
[solution1-Cpp]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| string removeDuplicates(string s, int k) {
int length = -1;
while (length != s.size()) {
length = s.size();
for (int i = 0, count = 1; i < s.size(); ++i) {
if (i == 0 || s[i] != s[i - 1]) {
count = 1;
} else if (++count == k) {
s.erase(i - k + 1, k);
break;
}
}
}
return s;
}
|
复杂度分析
方法二:记忆计数
从方法一中可以看出,如果为每个字符设置计数器,就不必每次删除完字符后从头开始。这种方法具有线性复杂度,但需要额外空间存储字符的计数器。
算法
初始长度为 n 的数组 counts。
遍历字符串:
[solution2-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public String removeDuplicates(String s, int k) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s);
int count[] = new int[sb.length()];
for (int i = 0; i < sb.length(); ++i) {
if (i == 0 || sb.charAt(i) != sb.charAt(i - 1)) {
count[i] = 1;
} else {
count[i] = count[i - 1] + 1;
if (count[i] == k) {
sb.delete(i - k + 1, i + 1);
i = i - k;
}
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
|
[solution2-Cpp]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| string removeDuplicates(string s, int k) {
vector<int> count(s.size());
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
if (i == 0 || s[i] != s[i - 1]) {
count[i] = 1;
} else {
count[i] = count[i - 1] + 1;
if (count[i] == k) {
s.erase(i - k + 1, k);
i = i - k;
}
};
}
return s;
}
|
复杂度分析
方法三:栈
当前字符与前一个不同时,往栈中压入 1。否则栈顶元素加 1。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
算法
迭代字符串:
注意:因为在 Java 中 Integer 是不可变的,需要先弹出栈顶元素,然后加 1,再压入栈顶。
[solution3-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public String removeDuplicates(String s, int k) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(s);
Stack<Integer> counts = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < sb.length(); ++i) {
if (i == 0 || sb.charAt(i) != sb.charAt(i - 1)) {
counts.push(1);
} else {
int incremented = counts.pop() + 1;
if (incremented == k) {
sb.delete(i - k + 1, i + 1);
i = i - k;
} else {
counts.push(incremented);
}
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
|
[solution3-Cpp]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| string removeDuplicates(string s, int k) {
stack<int> counts;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
if (i == 0 || s[i] != s[i - 1]) {
counts.push(1);
} else if (++counts.top() == k) {
counts.pop();
s.erase(i - k + 1, k);
i = i - k;
}
}
return s;
}
|
复杂度分析
方法四:栈重建
如果将计数器和字符都存储在栈中,则不需要修改字符串,只需要根据栈中结果重建字符串即可。
算法
迭代字符串:
使用栈中元素和计数器构建结果字符串。
[solution4-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class Pair {
int cnt;
char ch;
public Pair(int cnt, char ch) {
this.ch = ch;
this.cnt = cnt;
}
}
public String removeDuplicates(String s, int k) {
Stack<Pair> counts = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
if (counts.empty() || s.charAt(i) != counts.peek().ch) {
counts.push(new Pair(1, s.charAt(i)));
} else {
if (++counts.peek().cnt == k) {
counts.pop();
}
}
}
StringBuilder b = new StringBuilder();
while (!counts.empty()) {
Pair p = counts.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < p.cnt; i++) {
b.append(p.ch);
}
}
return b.reverse().toString();
}
|
[solution4-Cpp]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| string removeDuplicates(string s, int k) {
vector<pair<int, char>> counts;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i) {
if (counts.empty() || s[i] != counts.back().second) {
counts.push_back({ 1, s[i] });
} else if (++counts.back().first == k) {
counts.pop_back();
}
}
s = "";
for (auto &p : counts) {
s += string(p.first, p.second);
}
return s;
}
|
复杂度分析
方法五:双指针
该方法由lee215 提出,使用双指针可以优化方法二和三中的字符串操作。这里,使用快慢指针复制字符。每次需要删除 k 个元素时,只需要将慢指针回退 k 个位置。
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}
算法
初始慢指针 j 等于 0。
使用快指针 i 遍历字符串:
返回字符串的前 j 个字符。
[solution5-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public String removeDuplicates(String s, int k) {
Stack<Integer> counts = new Stack<>();
char[] sa = s.toCharArray();
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i, ++j) {
sa[j] = sa[i];
if (j == 0 || sa[j] != sa[j - 1]) {
counts.push(1);
} else {
int incremented = counts.pop() + 1;
if (incremented == k) {
j = j - k;
} else {
counts.push(incremented);
}
}
}
return new String(sa, 0, j);
}
|
[solution5-Cpp]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| string removeDuplicates(string s, int k) {
auto j = 0;
stack<int> counts;
for (auto i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i, ++j) {
s[j] = s[i];
if (j == 0 || s[j] != s[j - 1]) {
counts.push(1);
} else if (++counts.top() == k) {
counts.pop();
j -= k;
}
}
return s.substr(0, j);
}
|
复杂度分析
 {:width=500}
{:width=500}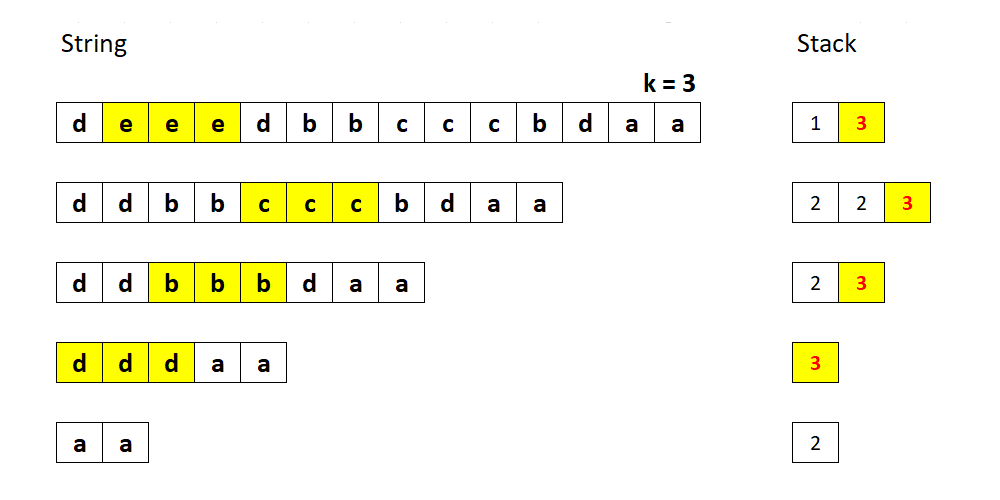 {:width=500}
{:width=500}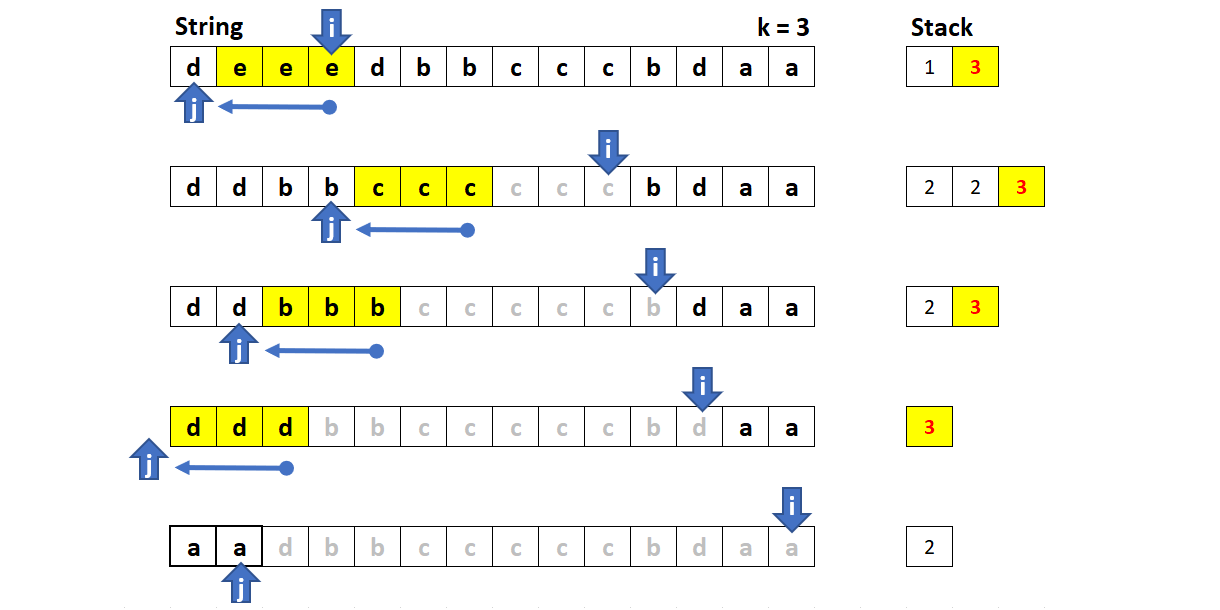 {:width=500}
{:width=500}