给你一棵根为 root 的二叉树,请你返回二叉树中好节点的数目。
「好节点」X 定义为:从根到该节点 X 所经过的节点中,没有任何节点的值大于 X 的值。
示例 1:
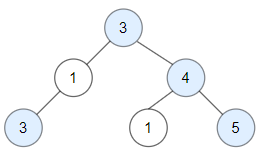
**输入:** root = [3,1,4,3,null,1,5]
**输出:** 4
**解释:** 图中蓝色节点为好节点。
根节点 (3) 永远是个好节点。
节点 4 -> (3,4) 是路径中的最大值。
节点 5 -> (3,4,5) 是路径中的最大值。
节点 3 -> (3,1,3) 是路径中的最大值。
示例 2:
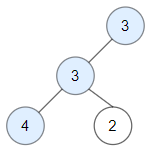
**输入:** root = [3,3,null,4,2]
**输出:** 3
**解释:** 节点 2 -> (3, 3, 2) 不是好节点,因为 "3" 比它大。
示例 3:
**输入:** root = [1]
**输出:** 1
**解释:** 根节点是好节点。
提示:
- 二叉树中节点数目范围是
[1, 10^5] 。
- 每个节点权值的范围是
[-10^4, 10^4] 。
方法一:深度优先遍历
思路与算法
在题目的定义中,从根到好节点所经过的节点中,没有任何节点的值大于好节点的值,等同于根节点到好节点的路径上所有节点(不包括好节点本身)的最大值小于等于好节点的值。
因此我们可以在深度优先遍历的过程中,记录从根节点到当前节点的路径上所有节点的最大值,若当前节点的值大于等于该最大值,则认为当前节点是好节点。
具体来说,定义递归函数求解以某个节点为根的子树中,好节点的个数。递归函数的参数为根节点以及路径上的最大值,若当前节点的值大于等于该最大值,则将答案加一,并更新路径最大值为当前节点的值。紧接着递归遍历左右子树时,将最大值以参数的形式传递下去。递归返回的结果需要累加到答案中。
最终,我们以根节点为入口,无穷小为路径最大值去调用递归函数,所得到的返回值即为答案。
代码
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class Solution {
public:
int dfs(TreeNode* root, int path_max) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
int res = 0;
if (root->val >= path_max) {
res++;
path_max = root->val;
}
res += dfs(root->left, path_max) + dfs(root->right, path_max);
return res;
}
int goodNodes(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root, INT_MIN);
}
};
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class Solution {
public int goodNodes(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
public int dfs(TreeNode root, int pathMax) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int res = 0;
if (root.val >= pathMax) {
res++;
pathMax = root.val;
}
res += dfs(root.left, pathMax) + dfs(root.right, pathMax);
return res;
}
}
|
[sol1-C#]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| public class Solution {
public int GoodNodes(TreeNode root) {
return DFS(root, int.MinValue);
}
public int DFS(TreeNode root, int pathMax) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int res = 0;
if (root.val >= pathMax) {
res++;
pathMax = root.val;
}
res += DFS(root.left, pathMax) + DFS(root.right, pathMax);
return res;
}
}
|
[sol1-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| int dfs(struct TreeNode* root, int path_max) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
int res = 0;
if (root->val >= path_max) {
res++;
path_max = root->val;
}
res += dfs(root->left, path_max) + dfs(root->right, path_max);
return res;
}
int goodNodes(struct TreeNode* root){
return dfs(root, INT_MIN);
}
|
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| class Solution:
def goodNodes(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
def dfs(root, path_max):
if root is None:
return 0
res = 0
if root.val >= path_max:
res += 1
path_max = root.val
res += dfs(root.left, path_max) + dfs(root.right, path_max)
return res
return dfs(root, -10**9)
|
[sol1-Go]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| func goodNodes(root *TreeNode) int {
return dfs(root, math.MinInt)
}
func dfs(root *TreeNode, path_max int) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
res := 0
if root.Val >= path_max {
res++
path_max = root.Val
}
res += dfs(root.Left, path_max) + dfs(root.Right, path_max)
return res
}
|
[sol1-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| var goodNodes = function(root) {
const dfs = (root, path_max) => {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
let res = 0;
if (root.val >= path_max) {
res++;
path_max = root.val;
}
res += dfs(root.left, path_max) + dfs(root.right, path_max);
return res;
}
return dfs(root, -Infinity);
};
|
复杂度分析