给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数 distance 。
如果二叉树中两个 叶 节点之间的 最短路径长度 小于或者等于 distance ,那它们就可以构成一组 好叶子节点对 。
返回树中 好叶子节点对的数量 。
示例 1:
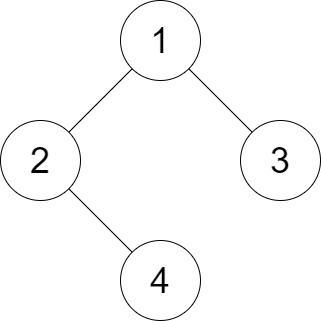
**输入:** root = [1,2,3,null,4], distance = 3
**输出:** 1
**解释:** 树的叶节点是 3 和 4 ,它们之间的最短路径的长度是 3 。这是唯一的好叶子节点对。
示例 2:
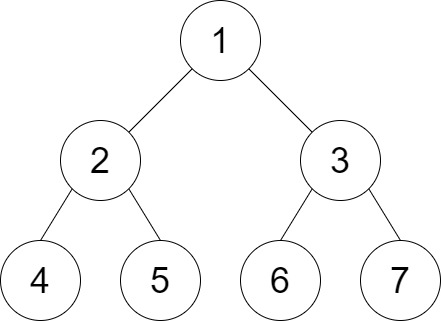
**输入:** root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7], distance = 3
**输出:** 2
**解释:** 好叶子节点对为 [4,5] 和 [6,7] ,最短路径长度都是 2 。但是叶子节点对 [4,6] 不满足要求,因为它们之间的最短路径长度为 4 。
示例 3:
**输入:** root = [7,1,4,6,null,5,3,null,null,null,null,null,2], distance = 3
**输出:** 1
**解释:** 唯一的好叶子节点对是 [2,5] 。
示例 4:
**输入:** root = [100], distance = 1
**输出:** 0
示例 5:
**输入:** root = [1,1,1], distance = 2
**输出:** 1
提示:
tree 的节点数在 [1, 2^10] 范围内。每个节点的值都在 [1, 100] 之间。
1 <= distance <= 10
方法一:递归 思路与算法
对于二叉树的任意两个不同的叶子节点 A、B,一个重要的性质是:它们之间有且仅有一条最短路径。设两个叶子节点的最近公共祖先为 P,则最短路径的长度,等于 A 到 P 的距离,加上 B 到 P 的距离。
于是,我们遍历所有非叶子节点 P,找到以 P 为最近公共祖先的所有叶子节点对,并根据上面的等式,计算每一对之间的距离,并统计距离不超过 distance 的节点对数目,就能够得到最终的答案。
那么怎么计算每个叶子节点对之间的距离呢?关键是要知道:以 P 为根节点的子树中的所有叶子节点,它们与 P 之间的距离。于是,对于任意的节点 P,我们先通过递归的方式,统计叶子节点与 P 的左孩子 left、右孩子 right 之间的距离;这样,两个以 P 为最近公共祖先的叶子节点 A、B,其中一个(例如 A)在以 left 为根的子树中,另一个(例如 B)在以 right 为根的子树中。A 与 B 之间的距离,就等于 A 与 left 之间的距离,加上 B 与 right 之间的距离,再加上 2。
由于本题中约束 distance} \le 10,因此对于每个非叶子节点 P,只需开辟长度为 distance}+1 的数组 depths,其中 depths}[i] 表示与 P 之间的距离为 i 的叶子节点数目。
代码
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 class Solution {public : pair<vector<int >, int > dfs (TreeNode* root, int distance) { vector<int > depths (distance + 1 , 0 ) ; bool isLeaf = (!root->left && !root->right); if (isLeaf) { depths[0 ] = 1 ; return make_pair (depths, 0 ); } vector<int > leftDepths (distance + 1 , 0 ) , rightDepths (distance + 1 , 0 ) ; int leftCount = 0 , rightCount = 0 ; if (root->left) { tie (leftDepths, leftCount) = dfs (root->left, distance); } if (root->right) { tie (rightDepths, rightCount) = dfs (root->right, distance); } for (int i = 0 ; i < distance; i++) { depths[i + 1 ] += leftDepths[i]; depths[i + 1 ] += rightDepths[i]; } int cnt = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= distance; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j + i + 2 <= distance; j++) { cnt += (leftDepths[i] * rightDepths[j]); } } return make_pair (depths, cnt + leftCount + rightCount); } int countPairs (TreeNode* root, int distance) auto [depths, ret] = dfs (root, distance); return ret; } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 class Solution { public int countPairs (TreeNode root, int distance) { Pair pair = dfs(root, distance); return pair.count; } public Pair dfs (TreeNode root, int distance) { int [] depths = new int [distance + 1 ]; boolean isLeaf = root.left == null && root.right == null ; if (isLeaf) { depths[0 ] = 1 ; return new Pair (depths, 0 ); } int [] leftDepths = new int [distance + 1 ]; int [] rightDepths = new int [distance + 1 ]; int leftCount = 0 , rightCount = 0 ; if (root.left != null ) { Pair leftPair = dfs(root.left, distance); leftDepths = leftPair.depths; leftCount = leftPair.count; } if (root.right != null ) { Pair rightPair = dfs(root.right, distance); rightDepths = rightPair.depths; rightCount = rightPair.count; } for (int i = 0 ; i < distance; i++) { depths[i + 1 ] += leftDepths[i]; depths[i + 1 ] += rightDepths[i]; } int cnt = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i <= distance; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j + i + 2 <= distance; j++) { cnt += leftDepths[i] * rightDepths[j]; } } return new Pair (depths, cnt + leftCount + rightCount); } } class Pair { int [] depths; int count; public Pair (int [] depths, int count) { this .depths = depths; this .count = count; } }
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution : def countPairs (self, root: TreeNode, distance: int ) -> int : def dfs (root: TreeNode, distance: int ) -> (List [int ], int ): depths = [0 ] * (distance + 1 ) isLeaf = not root.left and not root.right if isLeaf: depths[0 ] = 1 return (depths, 0 ) leftDepths, rightDepths = [0 ] * (distance + 1 ), [0 ] * (distance + 1 ) leftCount = rightCount = 0 if root.left: leftDepths, leftCount = dfs(root.left, distance) if root.right: rightDepths, rightCount = dfs(root.right, distance) for i in range (distance): depths[i + 1 ] += leftDepths[i] depths[i + 1 ] += rightDepths[i] cnt = 0 for i in range (distance + 1 ): for j in range (distance - i - 1 ): cnt += leftDepths[i] * rightDepths[j] return (depths, cnt + leftCount + rightCount) _, ret = dfs(root, distance) return ret
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N \cdot \textit{distance}^2),其中 N 为树中节点的数量。对于每个节点,我们至多需要遍历 O(\textit{distance}^2) 种好叶子节点对。
空间复杂度:O(H \cdot \textit{distance}),其中 H 为树的高度。对于每个节点,我们都需要额外开辟 O(\textit{distance}) 的空间,而栈的最大深度为 O(H)。