有一只跳蚤的家在数轴上的位置 x 处。请你帮助它从位置 0 出发,到达它的家。
跳蚤跳跃的规则如下:
它可以 往前 跳恰好 a 个位置(即往右跳)。
它可以 往后 跳恰好 b 个位置(即往左跳)。
它不能 连续 往后跳 2 次。
它不能跳到任何 forbidden 数组中的位置。
跳蚤可以往前跳 超过 它的家的位置,但是它 不能跳到负整数 的位置。
给你一个整数数组 forbidden ,其中 forbidden[i] 是跳蚤不能跳到的位置,同时给你整数 a, b 和 xx 的可行方案,请你返回 -1 。
示例 1:
**输入:** forbidden = [14,4,18,1,15], a = 3, b = 15, x = 9
**输出:** 3
**解释:** 往前跳 3 次(0 -> 3 -> 6 -> 9),跳蚤就到家了。
示例 2:
**输入:** forbidden = [8,3,16,6,12,20], a = 15, b = 13, x = 11
**输出:** -1
示例 3:
**输入:** forbidden = [1,6,2,14,5,17,4], a = 16, b = 9, x = 7
**输出:** 2
**解释:** 往前跳一次(0 -> 16),然后往回跳一次(16 -> 7),跳蚤就到家了。
提示:
1 <= forbidden.length <= 10001 <= a, b, forbidden[i] <= 20000 <= x <= 2000forbidden 中所有位置互不相同。位置 x 不在 forbidden 中。
方法一:广度优先搜索 思路
求最短路径一般需要用广度优先搜索,但是此题中的图是个无限图,如果不限制搜索的范围,无法处理无解的情况。因此,解决此题的关键是找出搜索的范围,其中下限已经由题目给出,不能跳到负整数的位置,我们还需要找出搜索的上限,下面分情况讨论:
a = b。此时为了次数最少,跳蚤没有必要向后跳,只需要一直往前跳。当它超过 x 却没有遇到 x,表示它再也跳不到 x 了,此时的上限可以设置为 x。
a > b。题目规定,跳蚤不能连续往后跳 2 次,因此这只跳蚤运动轨迹中,任意连续的两次跳跃,总的行程一定是在前进的,前进了 a-b 的距离。即使它某一步是在后退,这一步的前一步和后一步(如果有的话)一定是在前进。此时跳蚤运动的上限为 x+b,在这个上限的情况下,跳蚤往回跳一步可以到达 x。在大于这个上限的情况下,即使跳蚤马上往回跳一步,所处的位置也大于 x,而且跳蚤接下来前进的次数必然会大于等于后退的次数,再也无法到达 x。因此在这种情况下,上限为 x+b。
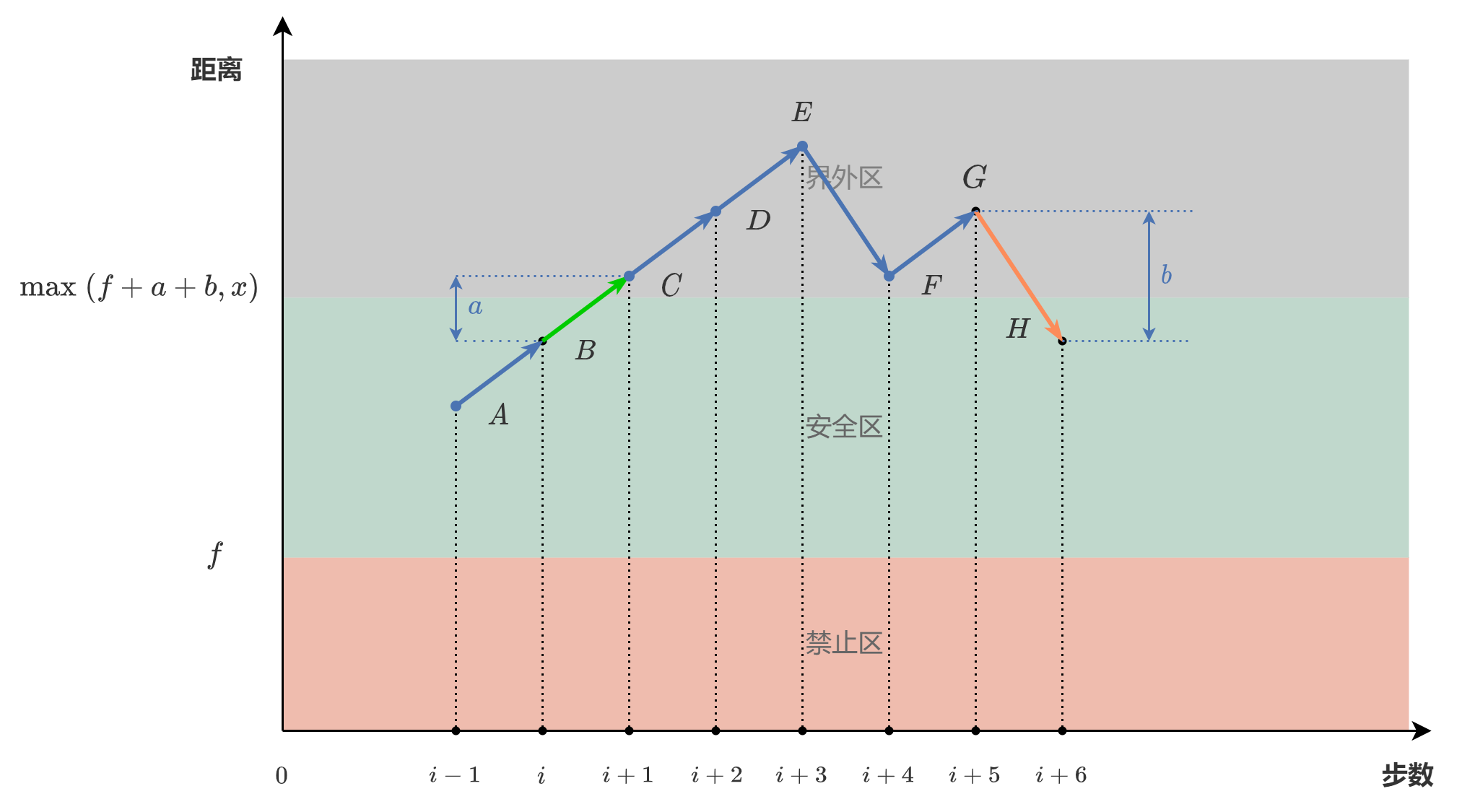
a < b。在这种情况下,上限为 \max(\max(\textit{forbidden})+a+b, x)。接下来证明这一点。为了方便,记 \max(\textit{forbidden}) = f。首先,需要将数轴上大于等于 0 的位置分为三个区域:
[0, f],禁止区。所有 forbidden 中的位置都位于这个区域。
(f, \max(f+a+b, x)],安全区,它的右边界是 a < b 情况下我们想要证明的广度优先搜索的上限。
(\max(f+a+b, x), +\infin),界外区。
这三个区域合起来组成了数轴上大于等于 0 的所有部分,注意 x 可能位于禁止区或者安全区,但不会是 forbidden 数组中的元素。假设某个步数最少的路径中,点 C 是第一个进入界外区(前进进入)的点,而点 H 是第一个离开界外区(后退离开)的点。因为 x 只可能位于禁止区或者安全区,因此如果这条路径存在点 C,那么必然存在点 H。如下图,横坐标为步数,纵坐标为与原点的距离。箭头朝右上表示前进,箭头朝右下表示后退。
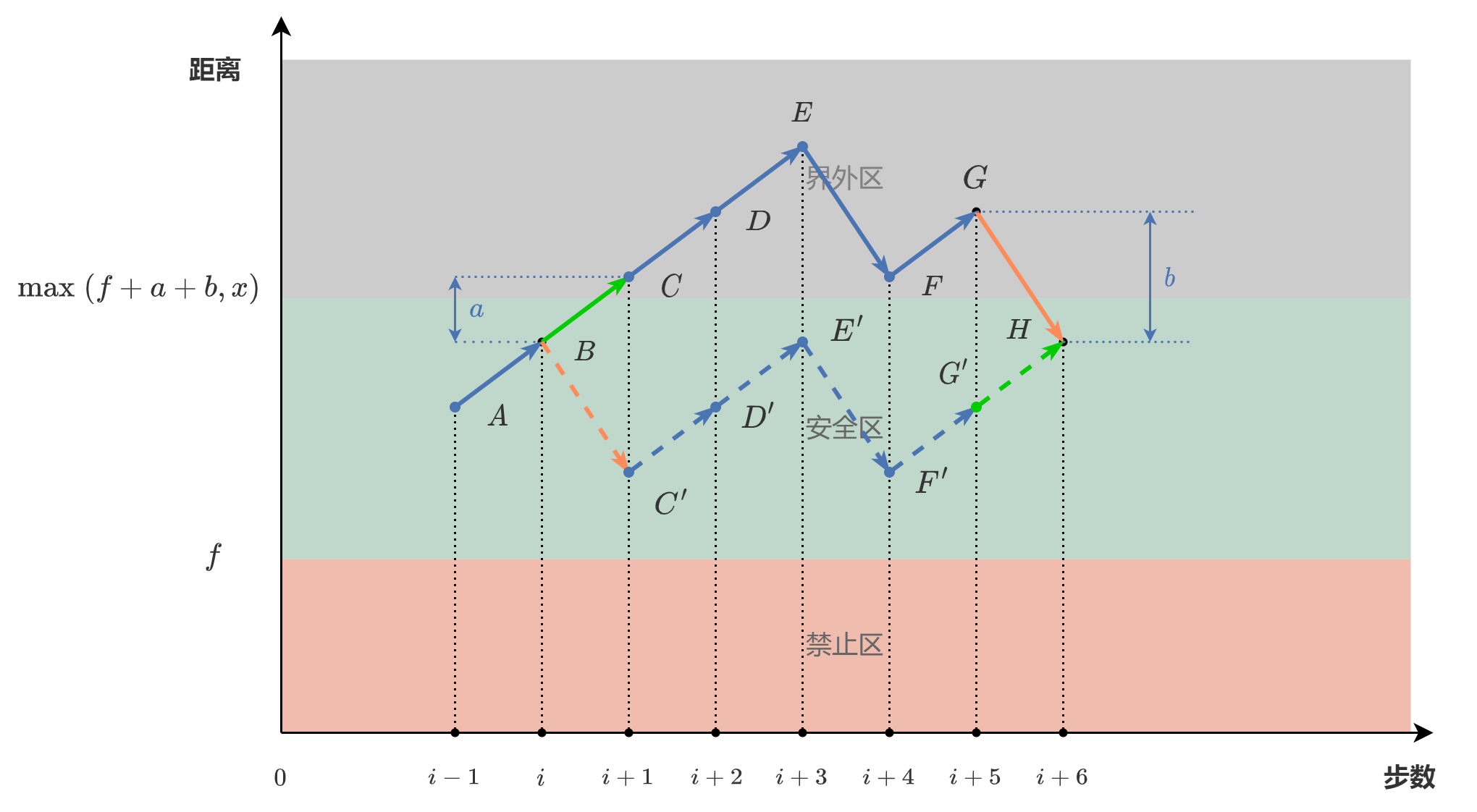
我们从以下几个方面论证这种交换的可行性:
- 交换前,点 C,D,\dots,F,G 全都位于界外区,与原点的距离大于 f + a + b。通过交换,这些点与原点的距离缩小了 a+b,仍然大于 f。因此,这些点不会落到 forbidden 中。
- 交换后不会增加这个路径的步数,也不会影响点 H 之后的点的位置。
- 交换不会造成两次倒退。交换后,前进的线段 BC 变为后退的线段 BC',但是 BC' 的前一段 AB 一定是前进的。可以利用反证法证明,如果 AB 是后退的,那么点 A 就会在界外区,因为 a < b,这样的话点 C 就不会是第一个界外区的点,因此 AB 一定是前进的。BC' 的后一段 C'D' 一定也是前进的。这里需要分为两种情况:
- CD 原本就是前进的,那么 C'D' 会保持原来前进的方向。通过交换,我们不会造成两次倒退。
- CD 原本是后退的,那么点 D 就是我们前面讨论的第一个离开界外区的点 H,因为 a < b。这样一来,我们其实是交换了前进的 BC 和后退的 CD,得到了后退的 BC' 和前进的 C'D,仍然不会造成两次倒退。
通过这样的交换,我们使得一个有效路径第一个进入界外区的点,不再位于界外区。新的路径,第一个进入界外区的点,可能位于点 C 和点 H 之间,也可能位于点 H 之后,也可能不存在这样的点。总之,我们可以不停地寻找第一个进入界外区的点,然后经过上述的交换,使得最终的路径的所有点都位于禁止区和安全区。这样,我们就证明出,如果某个输入有解,那么至少有一条最短路径,它的所有点都处于上限 \max(f+a+b, x) 之内。因此在这种情况下,上限为 \max(\max(\textit{forbidden})+a+b, x)。
综合以上三种情况,广度优先搜索的上限是 \max(\max(\textit{forbidden})+a, x) + b。
在进行广度优先搜索时,除了需要注意到上下限,不能达到 forbidden 数组中的坐标,还需要注意到达每个坐标时,都会有前进到达还是后退到达两种状态。如果是前进到达时,下一步可以选择前进或者后退;如果是后退到达时,下一步只能选择前进。因此广度优先搜索的每个元素,需要保存三个信息,坐标,方向和步数。在代码中,我们用 1 表示前进,-1 表示后退,用哈希集合 visited 来记录已经达到过的位置和方向状态。在搜索的过程中,如果坐标第一次为 x,则返回当前步数。当队列为空时,表示 x 不可到达,返回 -1。
代码
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution : def minimumJumps (self, forbidden: List [int ], a: int , b: int , x: int ) -> int : q, visited = deque([[0 , 1 , 0 ]]), set ([0 ]) lower, upper = 0 , max (max (forbidden) + a, x) + b forbiddenSet = set (forbidden) while q: position, direction, step = q.popleft() if position == x: return step nextPosition = position + a nextDirection = 1 if lower <= nextPosition <= upper and nextPosition * nextDirection not in visited and nextPosition not in forbiddenSet: visited.add(nextPosition * nextDirection) q.append([nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 ]) if direction == 1 : nextPosition = position - b nextDirection = -1 if lower <= nextPosition <= upper and nextPosition * nextDirection not in visited and nextPosition not in forbiddenSet: visited.add(nextPosition * nextDirection) q.append([nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 ]) return -1
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { public int minimumJumps (int [] forbidden, int a, int b, int x) { Queue<int []> queue = new ArrayDeque <int []>(); Set<Integer> visited = new HashSet <Integer>(); queue.offer(new int []{0 , 1 , 0 }); visited.add(0 ); int lower = 0 , upper = Math.max(Arrays.stream(forbidden).max().getAsInt() + a, x) + b; Set<Integer> forbiddenSet = new HashSet <Integer>(); for (int position : forbidden) { forbiddenSet.add(position); } while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int [] arr = queue.poll(); int position = arr[0 ], direction = arr[1 ], step = arr[2 ]; if (position == x) { return step; } int nextPosition = position + a; int nextDirection = 1 ; if (lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !visited.contains(nextPosition * nextDirection) && !forbiddenSet.contains(nextPosition)) { visited.add(nextPosition * nextDirection); queue.offer(new int []{nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 }); } if (direction == 1 ) { nextPosition = position - b; nextDirection = -1 ; if (lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !visited.contains(nextPosition * nextDirection) && !forbiddenSet.contains(nextPosition)) { visited.add(nextPosition * nextDirection); queue.offer(new int []{nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 }); } } } return -1 ; } }
[sol1-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class Solution { public int MinimumJumps (int [] forbidden, int a, int b, int x Queue<Tuple<int , int , int >> queue = new Queue<Tuple<int , int , int >>(); ISet<int > visited = new HashSet<int >(); queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<int , int , int >(0 , 1 , 0 )); visited.Add(0 ); int lower = 0 , upper = Math.Max(forbidden.Max() + a, x) + b; ISet<int > forbiddenSet = new HashSet<int >(); foreach (int position in forbidden) { forbiddenSet.Add(position); } while (queue.Count > 0 ) { Tuple<int , int , int > tuple = queue.Dequeue(); int position = tuple.Item1, direction = tuple.Item2, step = tuple.Item3; if (position == x) { return step; } int nextPosition = position + a; int nextDirection = 1 ; if (lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !visited.Contains(nextPosition * nextDirection) && !forbiddenSet.Contains(nextPosition)) { visited.Add(nextPosition * nextDirection); queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<int , int , int >(nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 )); } if (direction == 1 ) { nextPosition = position - b; nextDirection = -1 ; if (lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !visited.Contains(nextPosition * nextDirection) && !forbiddenSet.Contains(nextPosition)) { visited.Add(nextPosition * nextDirection); queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<int , int , int >(nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 )); } } } return -1 ; } }
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution {public : int minimumJumps (vector<int >& forbidden, int a, int b, int x) queue<tuple<int , int , int >> q; unordered_set<int > visited; q.emplace (0 , 1 , 0 ); visited.emplace (0 ); int lower = 0 , upper = max (*max_element (forbidden.begin (), forbidden.end ()) + a, x) + b; unordered_set<int > forbiddenSet (forbidden.begin(), forbidden.end()) ; while (!q.empty ()) { auto [position, direction, step] = q.front (); q.pop (); if (position == x) { return step; } int nextPosition = position + a; int nextDirection = 1 ; if (lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !visited.count (nextPosition * nextDirection) && !forbiddenSet.count (nextPosition)) { visited.emplace (nextPosition * nextDirection); q.emplace (nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 ); } if (direction == 1 ) { nextPosition = position - b; nextDirection = -1 ; if (lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !visited.count (nextPosition * nextDirection) && !forbiddenSet.count (nextPosition)) { visited.emplace (nextPosition * nextDirection); q.emplace (nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 ); } } } return -1 ; } };
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 typedef struct { int key; UT_hash_handle hh; } HashItem; HashItem *hashFindItem (HashItem **obj, int key) { HashItem *pEntry = NULL ; HASH_FIND_INT(*obj, &key, pEntry); return pEntry; } bool hashAddItem (HashItem **obj, int key) { if (hashFindItem(obj, key)) { return false ; } HashItem *pEntry = (HashItem *)malloc (sizeof (HashItem)); pEntry->key = key; HASH_ADD_INT(*obj, key, pEntry); return true ; } void hashFree (HashItem **obj) { HashItem *curr = NULL , *tmp = NULL ; HASH_ITER(hh, *obj, curr, tmp) { HASH_DEL(*obj, curr); free (curr); } } int minimumJumps (int * forbidden, int forbiddenSize, int a, int b, int x) { int lower = 0 , maxVal = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < forbiddenSize; i++) { maxVal = fmax(maxVal, forbidden[i]); } int upper = fmax(maxVal + a, x) + b; int queue [upper * 3 ][3 ]; HashItem *visited = NULL ; HashItem *forbiddenSet = NULL ; int head = 0 , tail = 0 ; queue [tail][0 ] = 0 ; queue [tail][1 ] = 1 ; queue [tail][2 ] = 0 ; tail++; hashAddItem(&visited, 0 ); for (int i = 0 ; i < forbiddenSize; i++) { int position = forbidden[i]; hashAddItem(&forbiddenSet, position); } while (head != tail) { int position = queue [head][0 ]; int direction = queue [head][1 ]; int step = queue [head][2 ]; head++; if (position == x) { hashFree(&visited); hashFree(&forbiddenSet); return step; } int nextPosition = position + a; int nextDirection = 1 ; if (lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !hashFindItem(&visited, nextPosition * nextDirection) && !hashFindItem(&forbiddenSet, nextPosition)) { hashAddItem(&visited, nextPosition * nextDirection); queue [tail][0 ] = nextPosition; queue [tail][1 ] = nextDirection; queue [tail][2 ] = step + 1 ; tail++; } if (direction == 1 ) { nextPosition = position - b; nextDirection = -1 ; if (lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !hashFindItem(&visited, nextPosition * nextDirection) && !hashFindItem(&forbiddenSet, nextPosition)) { hashAddItem(&visited, nextPosition * nextDirection); queue [tail][0 ] = nextPosition; queue [tail][1 ] = nextDirection; queue [tail][2 ] = step + 1 ; tail++; } } } hashFree(&visited); hashFree(&forbiddenSet); return -1 ; }
[sol1-Go] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 func minimumJumps (forbidden []int , a int , b int , x int ) int { lower := 0 maxVal := 0 for _, val := range forbidden { maxVal = max(maxVal, val); } upper := max(maxVal + a, x) + b q := [][3 ]int {[3 ]int {0 , 1 , 0 } } visited := make (map [int ]bool ) forbiddenSet := make (map [int ]bool ) visited[0 ] = true for _, position := range (forbidden) { forbiddenSet[position] = true } for len (q) > 0 { position, direction, step := q[0 ][0 ], q[0 ][1 ], q[0 ][2 ] q = q[1 :] if position == x { return step } nextPosition, nextDirection := position + a, 1 _, ok1 := visited[nextPosition * nextDirection] _, ok2 := forbiddenSet[nextPosition] if lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !ok1 && !ok2 { visited[nextPosition * nextDirection] = true q = append (q, [3 ]int {nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 }) } if direction == 1 { nextPosition, nextDirection := position - b, -1 _, ok1 := visited[nextPosition * nextDirection] _, ok2 := forbiddenSet[nextPosition] if lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !ok1 && !ok2 { visited[nextPosition * nextDirection] = true q = append (q, [3 ]int {nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 }) } } } return -1 } func max (x int , y int ) int { if x < y { return y } return x }
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 var minimumJumps = function (forbidden, a, b, x ) { const lower = 0 ; const upper = Math .max (Math .max (...forbidden) + a, x) + b; let q = [[0 , 1 , 0 ]]; const visited = new Set ([0 ]); const forbiddenSet = new Set (forbidden) while (q.length > 0 ) { let position = q[0 ][0 ]; let direction = q[0 ][1 ]; let step = q[0 ][2 ]; q.shift (); if (position == x) { return step; } let nextPosition = position + a; let nextDirection = 1 ; if (lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !visited.has (nextPosition * nextDirection) && !forbiddenSet.has (nextPosition)) { visited.add (nextPosition * nextDirection); q.push ([nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 ]); } if (direction == 1 ) { nextPosition = position - b; nextDirection = -1 ; if (lower <= nextPosition && nextPosition <= upper && !visited.has (nextPosition * nextDirection) && !forbiddenSet.has (nextPosition)) { visited.add (nextPosition * nextDirection); q.push ([nextPosition, nextDirection, step + 1 ]); } } } return -1 ; };
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(\max(\max(\textit{forbidden})+a, x) + b)。表达式为广度优先搜索的位置上限,每个位置最多会被计算两次。
空间复杂度:O(\max(\max(\textit{forbidden})+a, x) + b)。表达式为广度优先搜索的位置上限,是队列和哈希集合的空间复杂度。