2196-根据描述创建二叉树
给你一个二维整数数组 descriptions ,其中 descriptions[i] = [parenti, childi, isLefti]
表示 parenti 是 childi 在 二叉树 中的 父节点 ,二叉树中各节点的值 互不相同 。此外:
- 如果
isLefti == 1,那么childi就是parenti的左子节点。 - 如果
isLefti == 0,那么childi就是parenti的右子节点。
请你根据 descriptions 的描述来构造二叉树并返回其 根节点 。
测试用例会保证可以构造出 有效 的二叉树。
示例 1:
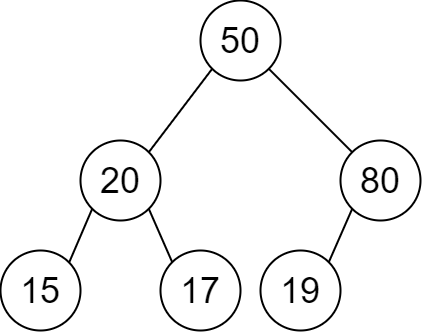
**输入:** descriptions = [[20,15,1],[20,17,0],[50,20,1],[50,80,0],[80,19,1]]
**输出:** [50,20,80,15,17,19]
**解释:** 根节点是值为 50 的节点,因为它没有父节点。
结果二叉树如上图所示。
示例 2:
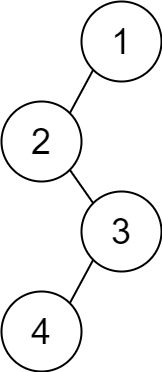
**输入:** descriptions = [[1,2,1],[2,3,0],[3,4,1]]
**输出:** [1,2,null,null,3,4]
**解释:** 根节点是值为 1 的节点,因为它没有父节点。
结果二叉树如上图所示。
提示:
1 <= descriptions.length <= 104descriptions[i].length == 31 <= parenti, childi <= 1050 <= isLefti <= 1descriptions所描述的二叉树是一棵有效二叉树
方法一:哈希表
思路与算法
由于数组 descriptions 中用节点的数值表示对应节点,因此为了方便查找,我们用哈希表 nodes 来维护数值到对应节点的映射。
我们可以遍历数组 descriptions 来创建二叉树。具体地,当我们遍历到三元组 [p, c, \textit{left}] 时,我们首先判断 nodes 中是否存在 p 与 c 对应的树节点,如果没有则我们新建一个数值为对应值的节点。随后,我们根据 left 的真假将 p 对应的节点的左或右子节点设为 c 对应的节点。当遍历完成后,我们就重建出了目标二叉树。
除此之外,我们还需要寻找二叉树的根节点。这个过程也可以在遍历和建树的过程中完成。我们可以同样用一个哈希表 isRoot 维护数值与是否为根节点的映射。在遍历时,我们需要将 isRoot}[c] 设为 false(因为该节点有父节点);而如果 p 在 isRoot 中不存在,则说明 p 暂时没有父节点,我们可以将 isRoot}[c] 设为 true。最终在遍历完成后,一定有且仅有一个元素 root 在 isRoot 中的数值为 true,此时对应的 node}[i] 为二叉树的根节点,我们返回该节点作为答案。
代码
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution: |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 为数组 descriptions 的长度。即为遍历构造二叉树并寻找根节点的时间复杂度。
空间复杂度:O(n),即为哈希表的空间开销。