LCR 023-相交链表
给定两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交 :
[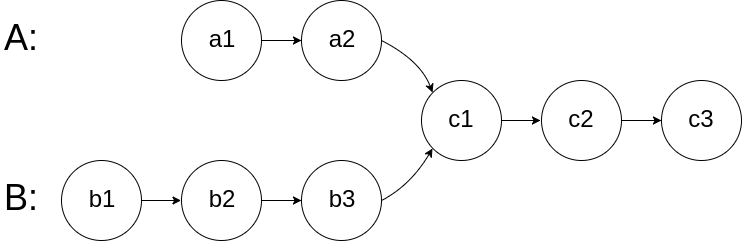](https://assets.leetcode-
cn.com/aliyun-lc-upload/uploads/2018/12/14/160_statement.png)
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意 ,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
示例 1:
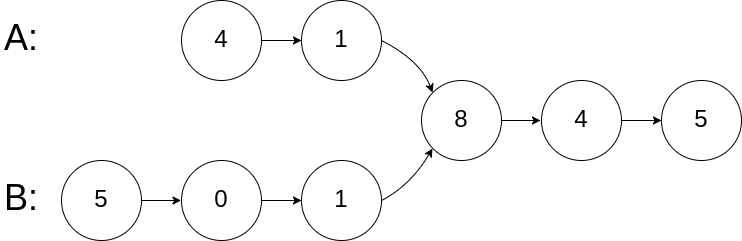
**输入:** intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
**输出:** Intersected at '8'
**解释:** 相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
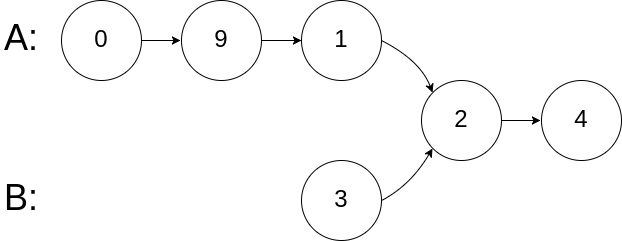
**输入:** intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
**输出:** Intersected at '2'
**解释:** 相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
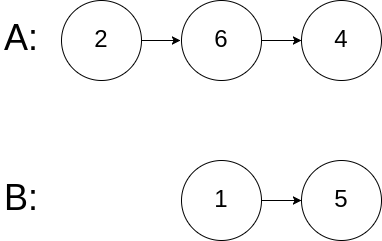
**输入:** intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
**输出:** null
**解释:** 从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
提示:
listA中节点数目为mlistB中节点数目为n0 <= m, n <= 3 * 1041 <= Node.val <= 1050 <= skipA <= m0 <= skipB <= n- 如果
listA和listB没有交点,intersectVal为0 - 如果
listA和listB有交点,intersectVal == listA[skipA + 1] == listB[skipB + 1]
进阶: 能否设计一个时间复杂度 O(n) 、仅用 O(1) 内存的解决方案?
注意:本题与主站 160 题相同:<https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-
lists/>
方法一:哈希集合
思路和算法
判断两个链表是否相交,可以使用哈希集合存储链表节点。
首先遍历链表 headA,并将链表 headA 中的每个节点加入哈希集合中。然后遍历链表 headB,对于遍历到的每个节点,判断该节点是否在哈希集合中:
如果当前节点不在哈希集合中,则继续遍历下一个节点;
如果当前节点在哈希集合中,则后面的节点都在哈希集合中,即从当前节点开始的所有节点都在两个链表的相交部分,因此在链表 headB 中遍历到的第一个在哈希集合中的节点就是两个链表相交的节点,返回该节点。
如果链表 headB 中的所有节点都不在哈希集合中,则两个链表不相交,返回 null。
代码
1 | public class Solution { |
1 | public class Solution { |
1 | var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) { |
1 | func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode { |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | struct HashTable { |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m+n),其中 m 和 n 是分别是链表 headA 和 headB 的长度。需要遍历两个链表各一次。
空间复杂度:O(m),其中 m 是链表 headA 的长度。需要使用哈希集合存储链表 headA 中的全部节点。
方法二:双指针
思路和算法
使用双指针的方法,可以将空间复杂度降至 O(1)。
只有当链表 headA 和 headB 都不为空时,两个链表才可能相交。因此首先判断链表 headA 和 headB 是否为空,如果其中至少有一个链表为空,则两个链表一定不相交,返回 null。
当链表 headA 和 headB 都不为空时,创建两个指针 pA 和 pB,初始时分别指向两个链表的头节点 headA 和 headB,然后将两个指针依次遍历两个链表的每个节点。具体做法如下:
每步操作需要同时更新指针 pA 和 pB。
如果指针 pA 不为空,则将指针 pA 移到下一个节点;如果指针 pB 不为空,则将指针 pB 移到下一个节点。
如果指针 pA 为空,则将指针 pA 移到链表 headB 的头节点;如果指针 pB 为空,则将指针 pB 移到链表 headA 的头节点。
当指针 pA 和 pB 指向同一个节点或者都为空时,返回它们指向的节点或者 null。
证明
下面提供双指针方法的正确性证明。考虑两种情况,第一种情况是两个链表相交,第二种情况是两个链表不相交。
情况一:两个链表相交
链表 headA 和 headB 的长度分别是 m 和 n。假设链表 headA 的不相交部分有 a 个节点,链表 headB 的不相交部分有 b 个节点,两个链表相交的部分有 c 个节点,则有 a+c=m,b+c=n。
如果 a=b,则两个指针会同时到达两个链表相交的节点,此时返回相交的节点;
如果 a \ne b,则指针 pA 会遍历完链表 headA,指针 pB 会遍历完链表 headB,两个指针不会同时到达链表的尾节点,然后指针 pA 移到链表 headB 的头节点,指针 pB 移到链表 headA 的头节点,然后两个指针继续移动,在指针 pA 移动了 a+c+b 次、指针 pB 移动了 b+c+a 次之后,两个指针会同时到达两个链表相交的节点,该节点也是两个指针第一次同时指向的节点,此时返回相交的节点。
情况二:两个链表不相交
链表 headA 和 headB 的长度分别是 m 和 n。考虑当 m=n 和 m \ne n 时,两个指针分别会如何移动:
如果 m=n,则两个指针会同时到达两个链表的尾节点,然后同时变成空值 null,此时返回 null;
如果 m \ne n,则由于两个链表没有公共节点,两个指针也不会同时到达两个链表的尾节点,因此两个指针都会遍历完两个链表,在指针 pA 移动了 m+n 次、指针 pB 移动了 n+m 次之后,两个指针会同时变成空值 null,此时返回 null。
代码
1 | public class Solution { |
1 | public class Solution { |
1 | var getIntersectionNode = function(headA, headB) { |
1 | func getIntersectionNode(headA, headB *ListNode) *ListNode { |
1 | class Solution { |
1 | struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) { |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m+n),其中 m 和 n 是分别是链表 headA 和 headB 的长度。两个指针同时遍历两个链表,每个指针遍历两个链表各一次。
空间复杂度:O(1)。