给定一个仅包含数字 2-9 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 任意顺序 返回。
给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意 1 不对应任何字母。
。该字符串初始为空。每次取电话号码的一位数字,从哈希表中获得该数字对应的所有可能的字母,并将其中的一个字母插入到已有的字母排列后面,然后继续处理电话号码的后一位数字,直到处理完电话号码中的所有数字,即得到一个完整的字母排列。然后进行回退操作,遍历其余的字母排列。
回溯算法用于寻找所有的可行解,如果发现一个解不可行,则会舍弃不可行的解。在这道题中,由于每个数字对应的每个字母都可能进入字母组合,因此不存在不可行的解,直接穷举所有的解即可。
<
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution { public List<String> letterCombinations (String digits) { List<String> combinations = new ArrayList <String>(); if (digits.length() == 0 ) { return combinations; } Map<Character, String> phoneMap = new HashMap <Character, String>() {{ put('2' , "abc" ); put('3' , "def" ); put('4' , "ghi" ); put('5' , "jkl" ); put('6' , "mno" ); put('7' , "pqrs" ); put('8' , "tuv" ); put('9' , "wxyz" ); }}; backtrack(combinations, phoneMap, digits, 0 , new StringBuffer ()); return combinations; } public void backtrack (List<String> combinations, Map<Character, String> phoneMap, String digits, int index, StringBuffer combination) { if (index == digits.length()) { combinations.add(combination.toString()); } else { char digit = digits.charAt(index); String letters = phoneMap.get(digit); int lettersCount = letters.length(); for (int i = 0 ; i < lettersCount; i++) { combination.append(letters.charAt(i)); backtrack(combinations, phoneMap, digits, index + 1 , combination); combination.deleteCharAt(index); } } } }
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 class Solution {public : vector<string> letterCombinations (string digits) { vector<string> combinations; if (digits.empty ()) { return combinations; } unordered_map<char , string> phoneMap{ {'2' , "abc" }, {'3' , "def" }, {'4' , "ghi" }, {'5' , "jkl" }, {'6' , "mno" }, {'7' , "pqrs" }, {'8' , "tuv" }, {'9' , "wxyz" } }; string combination; backtrack (combinations, phoneMap, digits, 0 , combination); return combinations; } void backtrack (vector<string>& combinations, const unordered_map<char , string>& phoneMap, const string& digits, int index, string& combination) if (index == digits.length ()) { combinations.push_back (combination); } else { char digit = digits[index]; const string& letters = phoneMap.at (digit); for (const char & letter: letters) { combination.push_back (letter); backtrack (combinations, phoneMap, digits, index + 1 , combination); combination.pop_back (); } } } };
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 var phoneMap map [string ]string = map [string ]string { "2" : "abc" , "3" : "def" , "4" : "ghi" , "5" : "jkl" , "6" : "mno" , "7" : "pqrs" , "8" : "tuv" , "9" : "wxyz" , } var combinations []string func letterCombinations (digits string ) string { if len (digits) == 0 { return []string {} } combinations = []string {} backtrack(digits, 0 , "" ) return combinations } func backtrack (digits string , index int , combination string ) if index == len (digits) { combinations = append (combinations, combination) } else { digit := string (digits[index]) letters := phoneMap[digit] lettersCount := len (letters) for i := 0 ; i < lettersCount; i++ { backtrack(digits, index + 1 , combination + string (letters[i])) } } }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 char phoneMap[11 ][5 ] = {"\0" , "\0" , "abc\0" , "def\0" , "ghi\0" , "jkl\0" , "mno\0" , "pqrs\0" , "tuv\0" , "wxyz\0" };char * digits_tmp;int digits_size;char ** combinations;int combinations_size;char * combination;int combination_size;void backtrack (int index) { if (index == digits_size) { char * tmp = malloc (sizeof (char ) * (combination_size + 1 )); memcpy (tmp, combination, sizeof (char ) * (combination_size + 1 )); combinations[combinations_size++] = tmp; } else { char digit = digits_tmp[index]; char * letters = phoneMap[digit - '0' ]; int len = strlen (letters); for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { combination[combination_size++] = letters[i]; combination[combination_size] = 0 ; backtrack(index + 1 ); combination[--combination_size] = 0 ; } } } char ** letterCombinations (char * digits, int * returnSize) { combinations_size = combination_size = 0 ; digits_tmp = digits; digits_size = strlen (digits); if (digits_size == 0 ) { *returnSize = 0 ; return combinations; } int num = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < digits_size; i++) num *= 4 ; combinations = malloc (sizeof (char *) * num); combination = malloc (sizeof (char *) * digits_size); backtrack(0 ); *returnSize = combinations_size; return combinations; }
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution : def letterCombinations (self, digits: str ) -> List [str ]: if not digits: return list () phoneMap = { "2" : "abc" , "3" : "def" , "4" : "ghi" , "5" : "jkl" , "6" : "mno" , "7" : "pqrs" , "8" : "tuv" , "9" : "wxyz" , } def backtrack (index: int ): if index == len (digits): combinations.append("" .join(combination)) else : digit = digits[index] for letter in phoneMap[digit]: combination.append(letter) backtrack(index + 1 ) combination.pop() combination = list () combinations = list () backtrack(0 ) return combinations
[sol1-Python3_oneliner] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution : def letterCombinations (self, digits: str ) -> List [str ]: if not digits: return list () phoneMap = { "2" : "abc" , "3" : "def" , "4" : "ghi" , "5" : "jkl" , "6" : "mno" , "7" : "pqrs" , "8" : "tuv" , "9" : "wxyz" , } groups = (phoneMap[digit] for digit in digits) return ["" .join(combination) for combination in itertools.product(*groups)]
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(3^m \times 4^n)$,其中 $m$ 是输入中对应 $3$ 个字母的数字个数(包括数字 $2$、$3$、$4$、$5$、$6$、$8$),$n$ 是输入中对应 $4$ 个字母的数字个数(包括数字 $7$、$9$),$m+n$ 是输入数字的总个数。当输入包含 $m$ 个对应 $3$ 个字母的数字和 $n$ 个对应 $4$ 个字母的数字时,不同的字母组合一共有 $3^m \times 4^n$ 种,需要遍历每一种字母组合。
空间复杂度:$O(m+n)$,其中 $m$ 是输入中对应 $3$ 个字母的数字个数,$n$ 是输入中对应 $4$ 个字母的数字个数,$m+n$ 是输入数字的总个数。除了返回值以外,空间复杂度主要取决于哈希表以及回溯过程中的递归调用层数,哈希表的大小与输入无关,可以看成常数,递归调用层数最大为 $m+n$。
 ,
, ,
,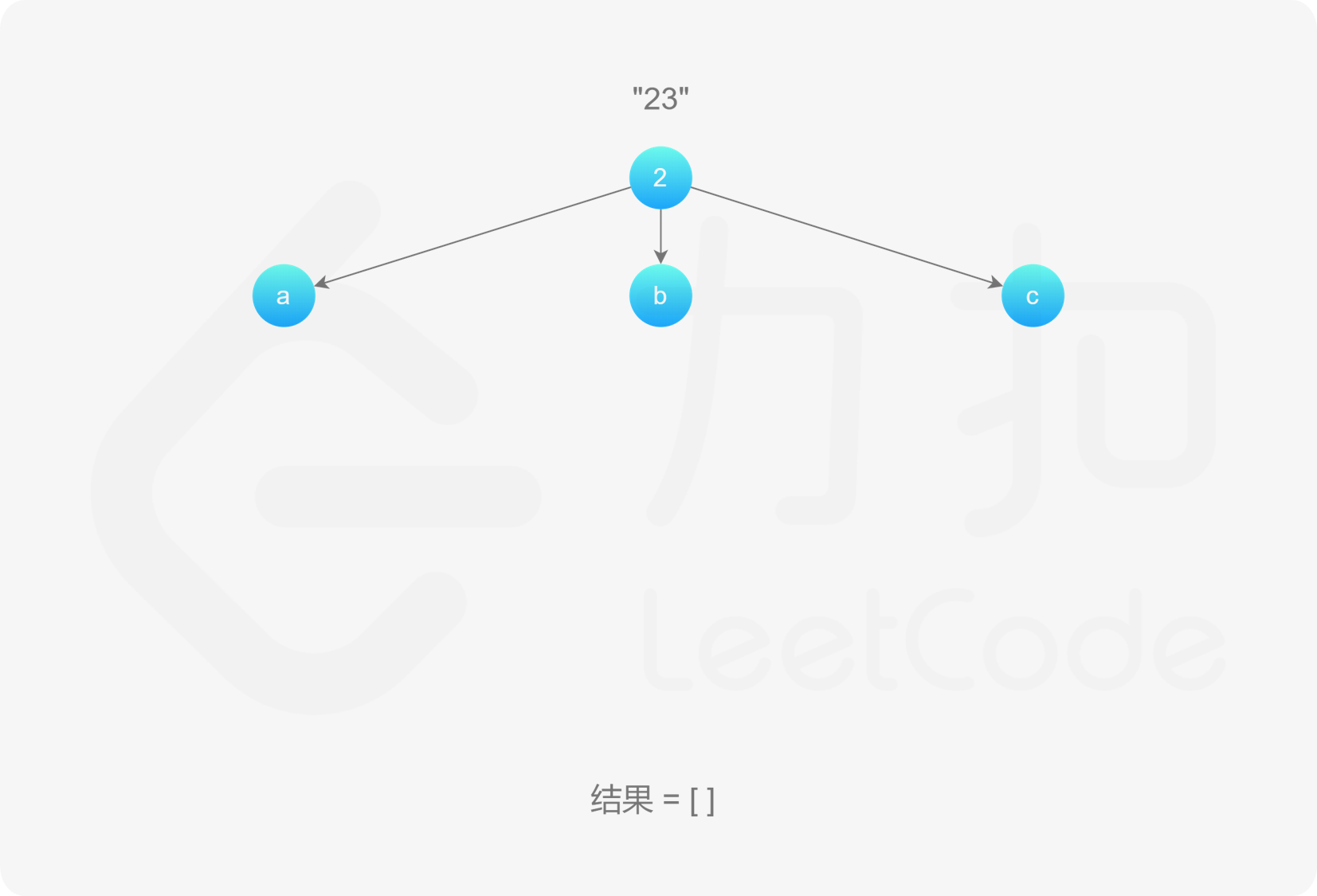 ,
,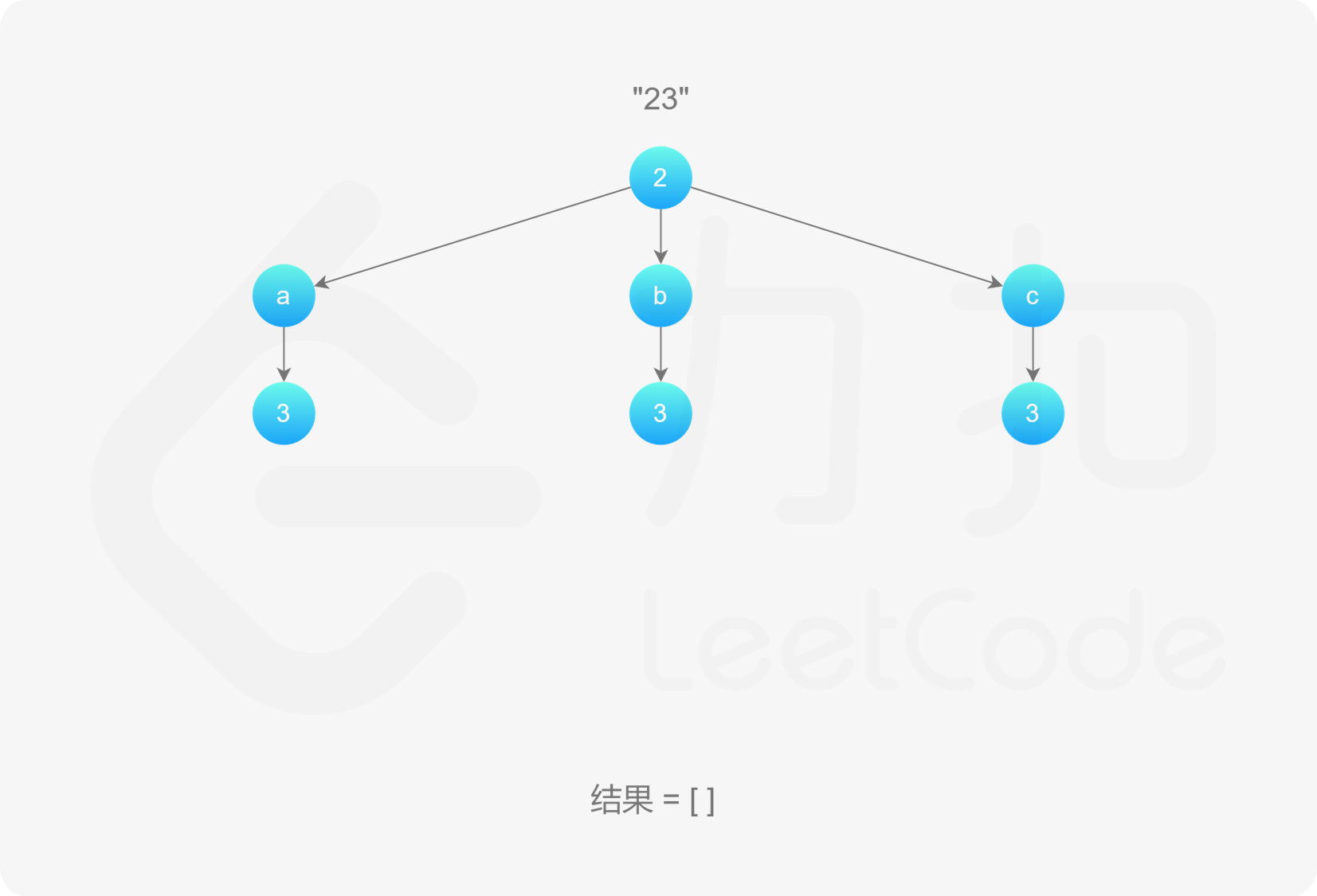 ,
,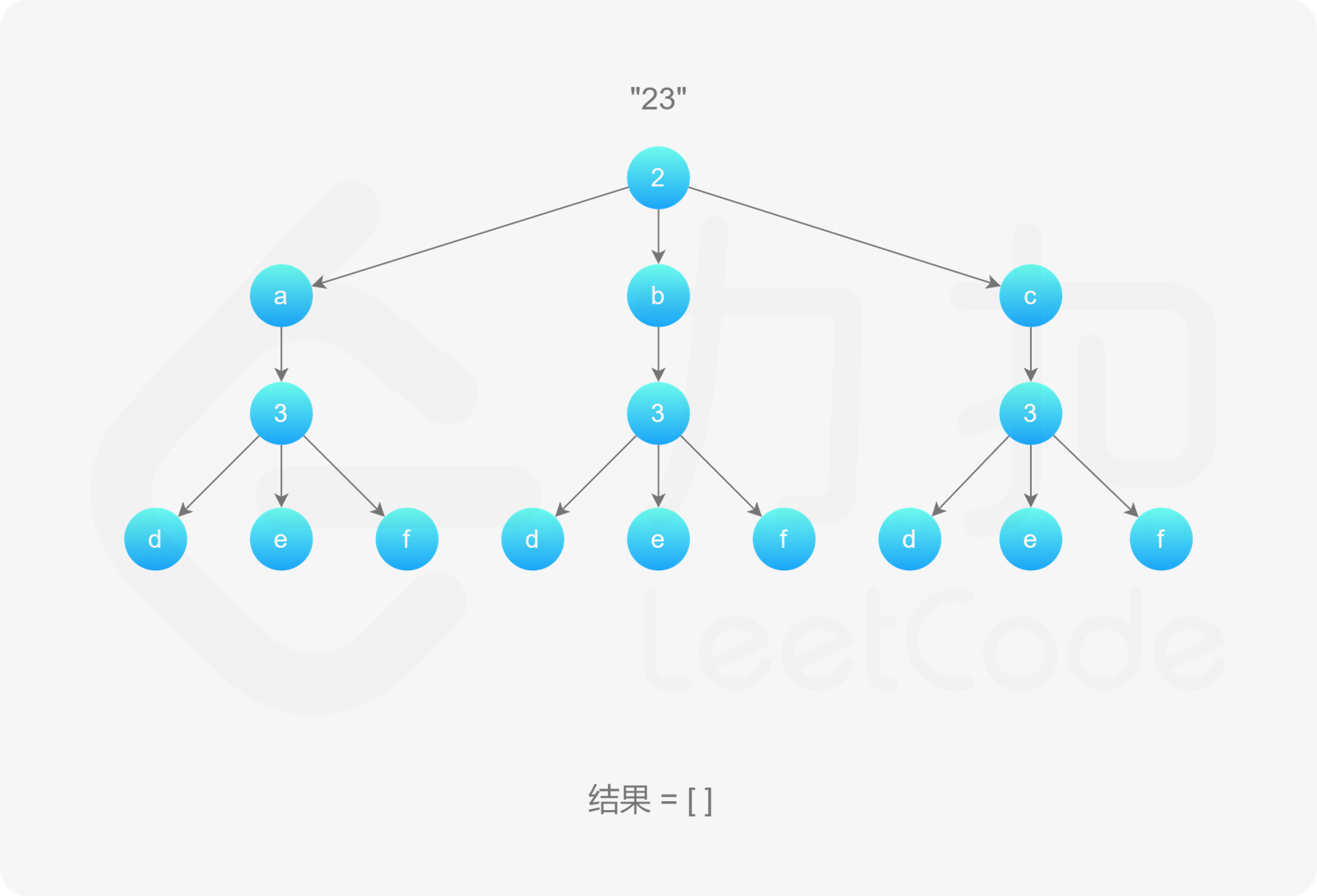 ,
,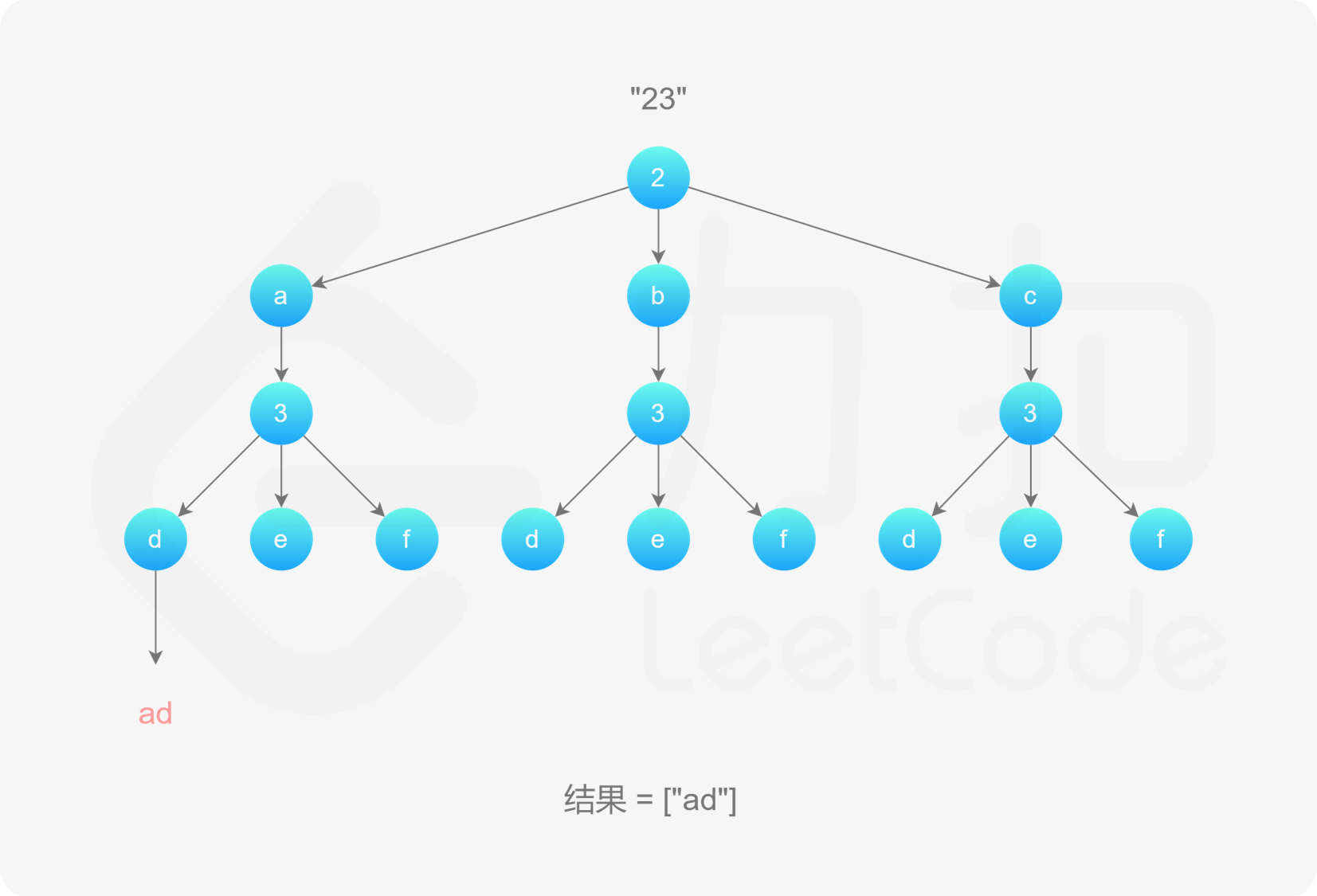 ,
,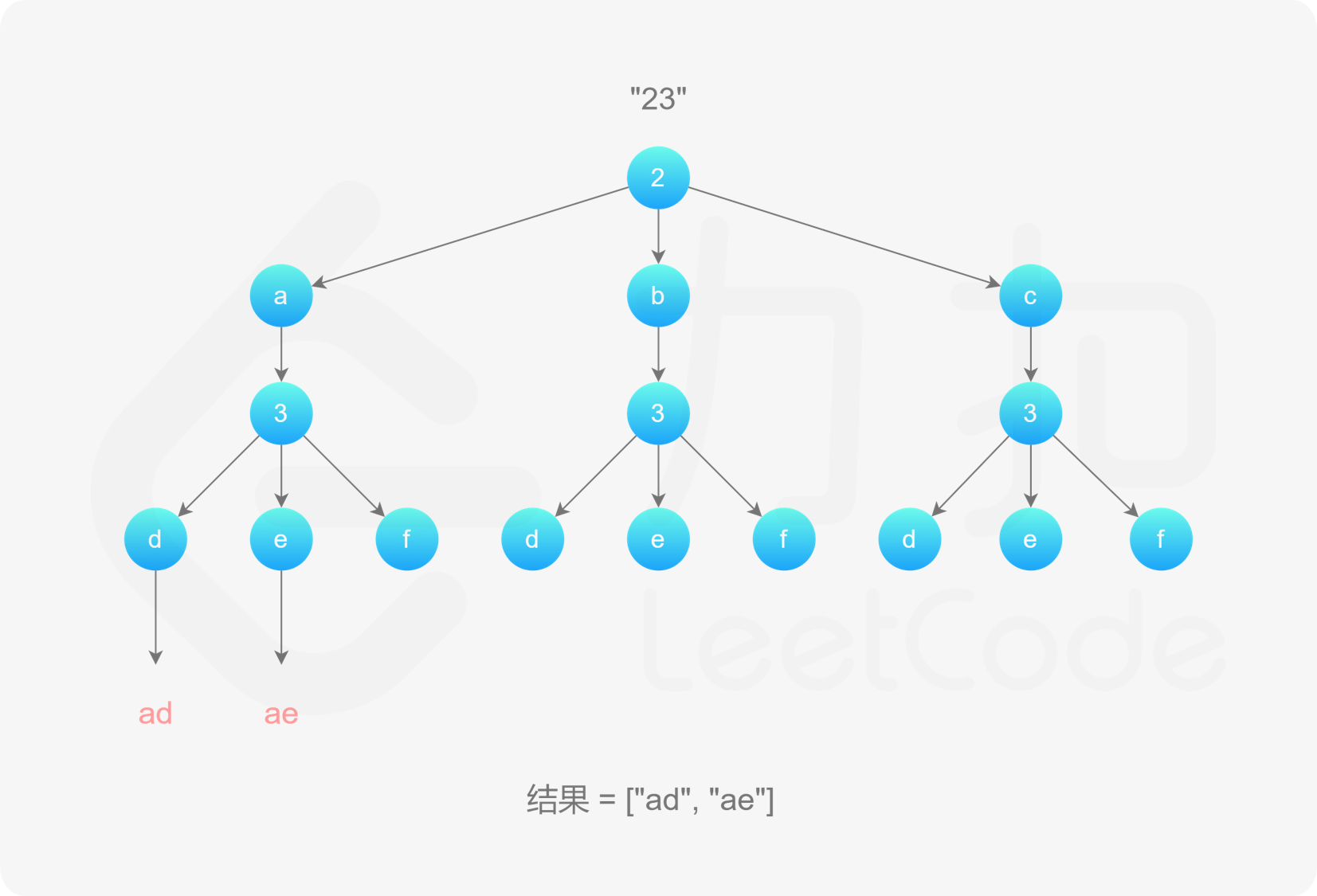 ,
,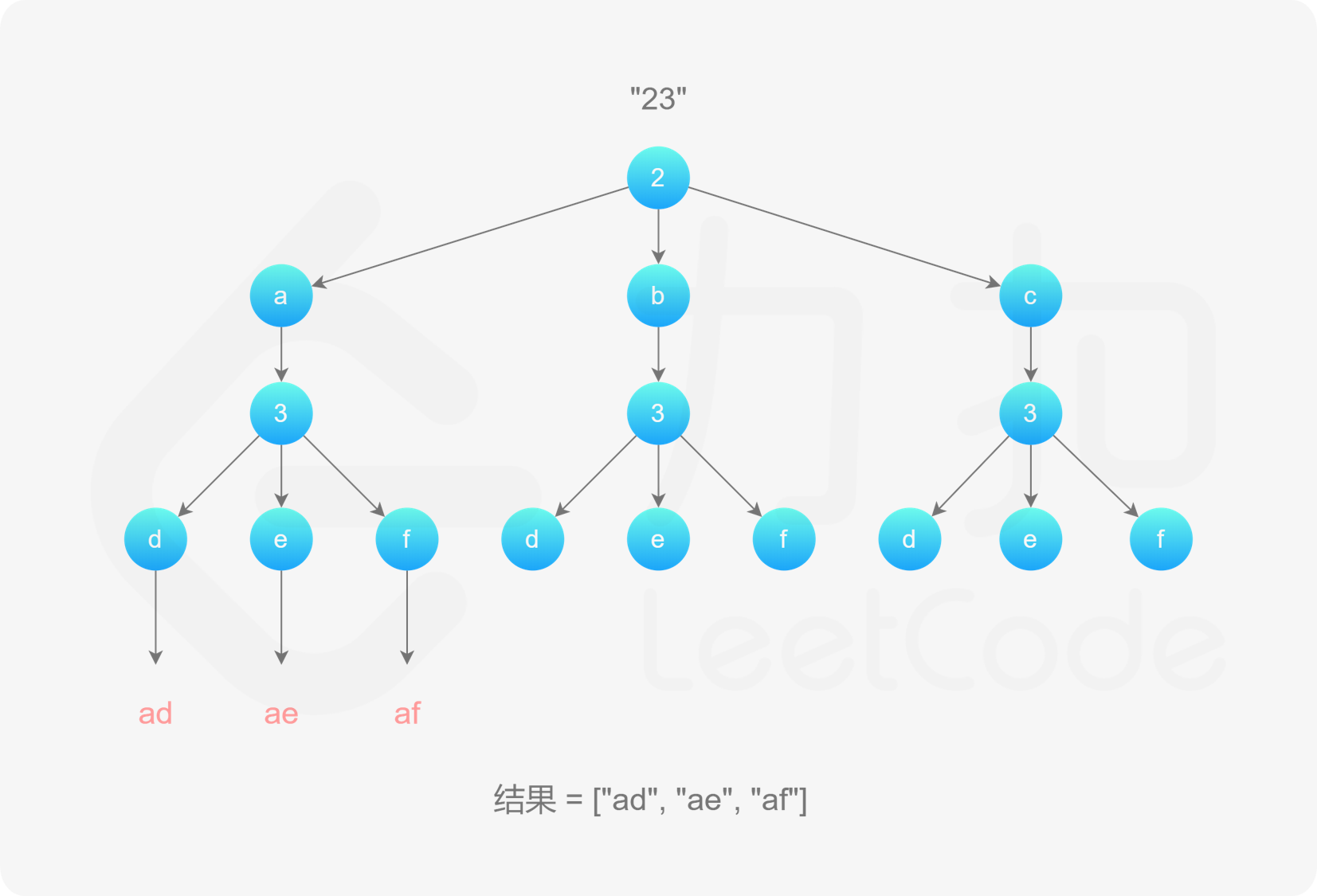 ,
,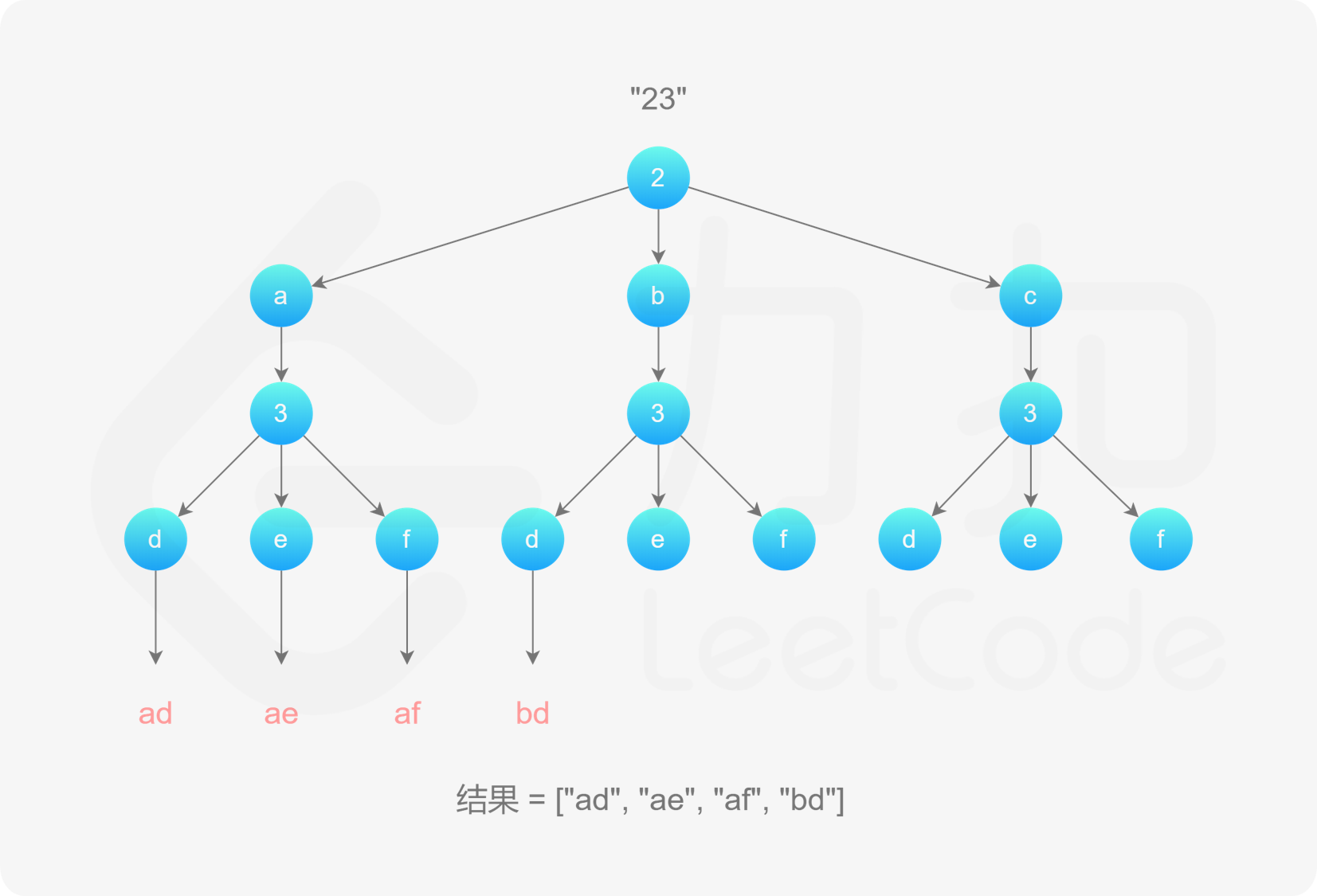 ,
,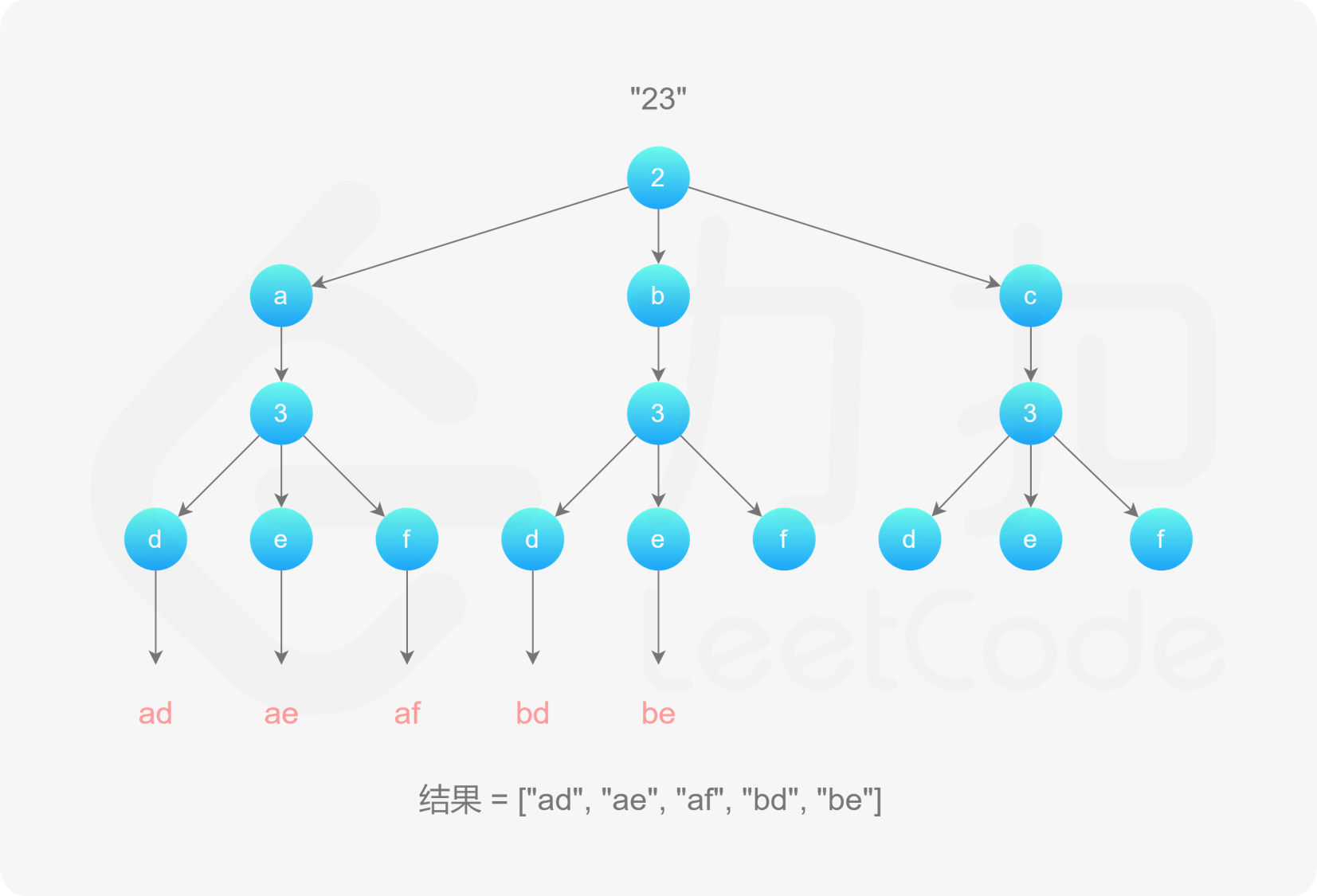 ,
,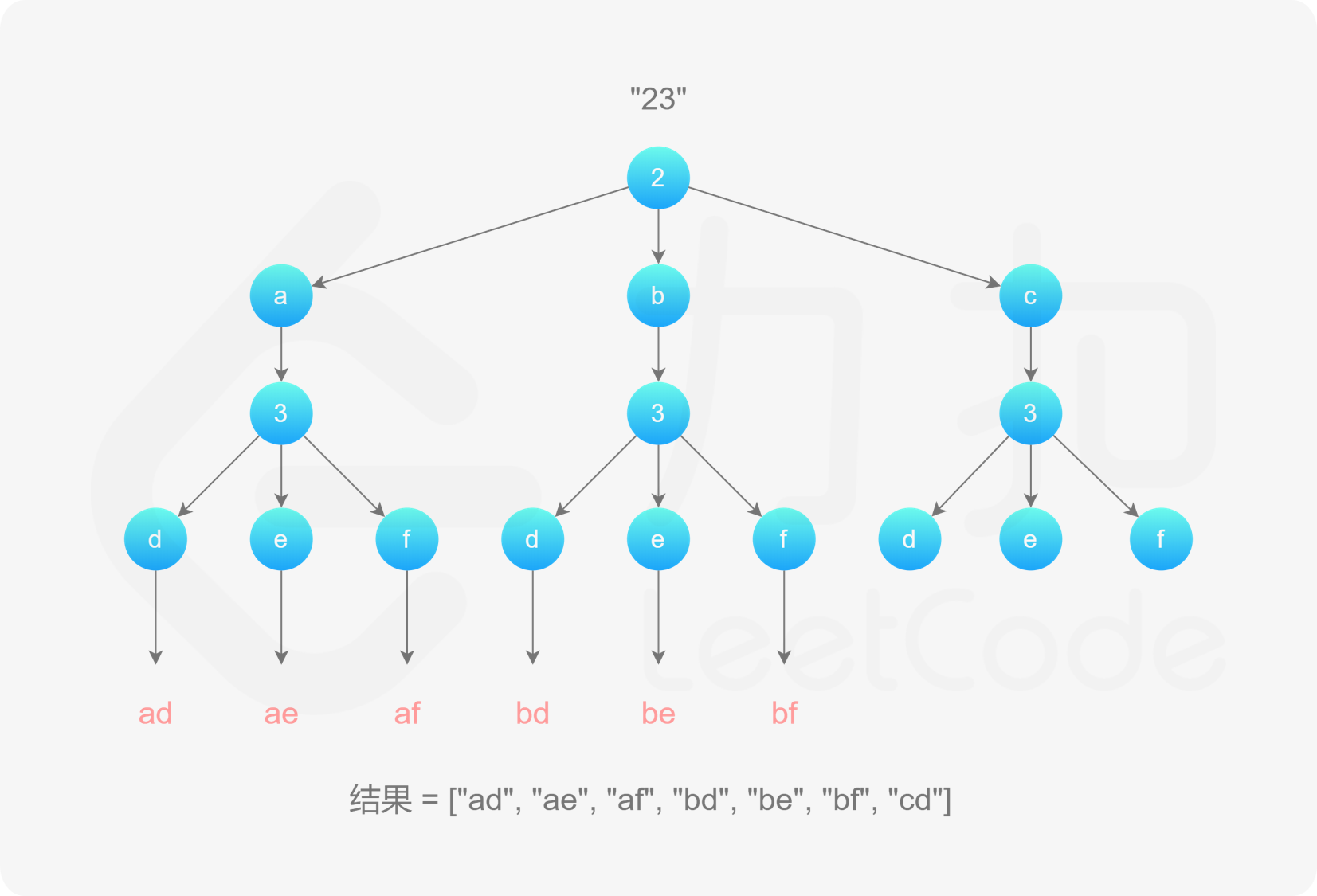 ,
,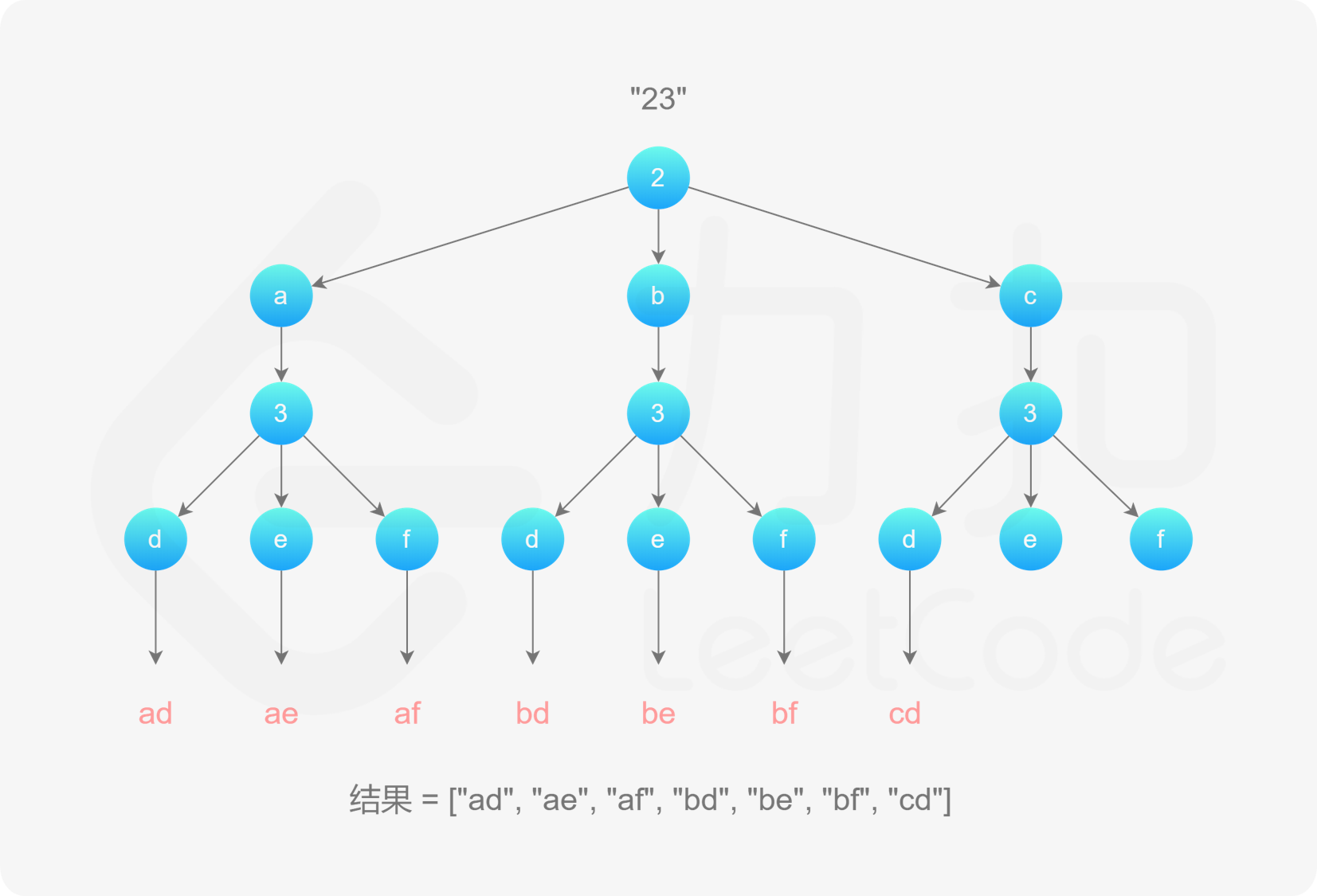 ,
,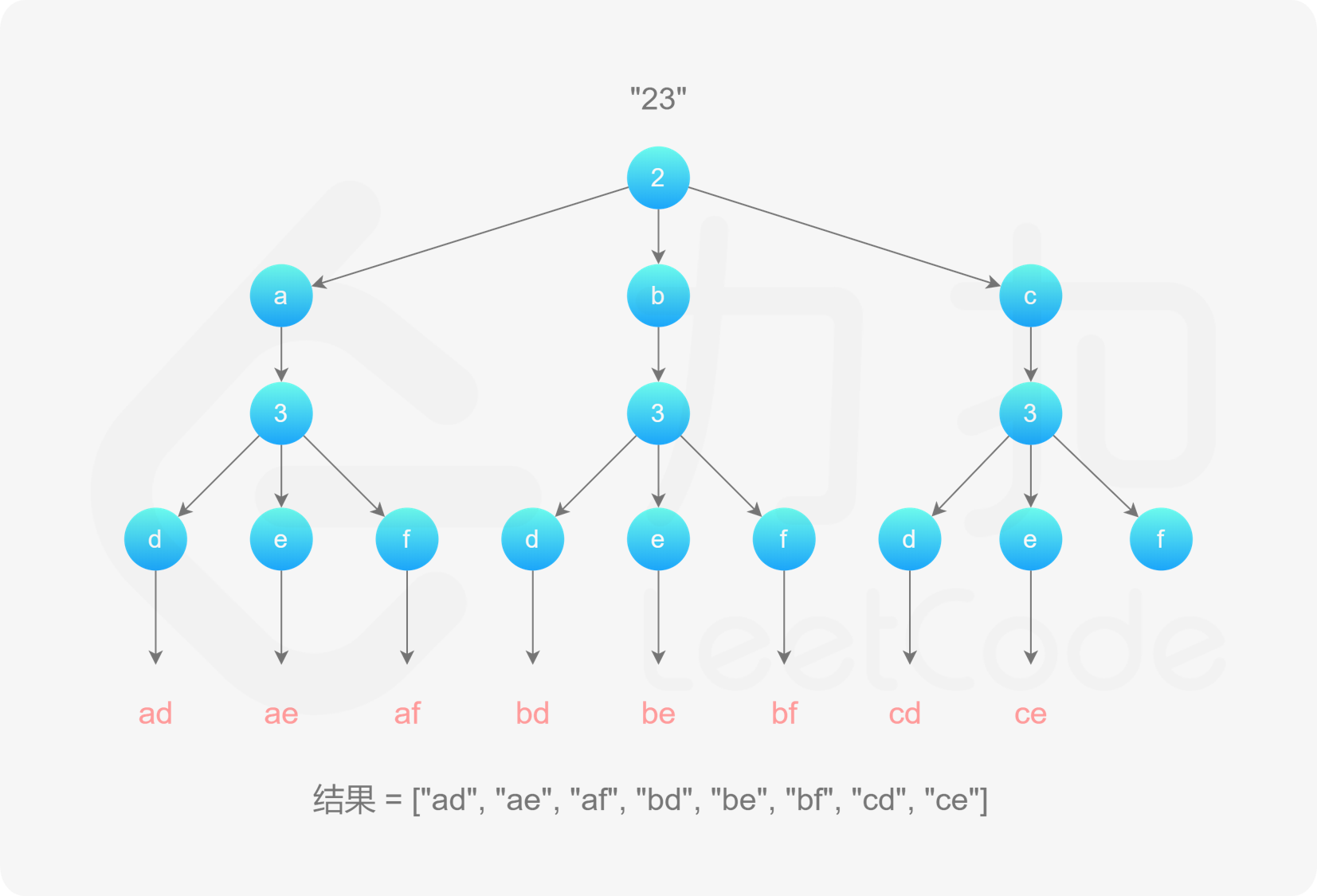 ,
,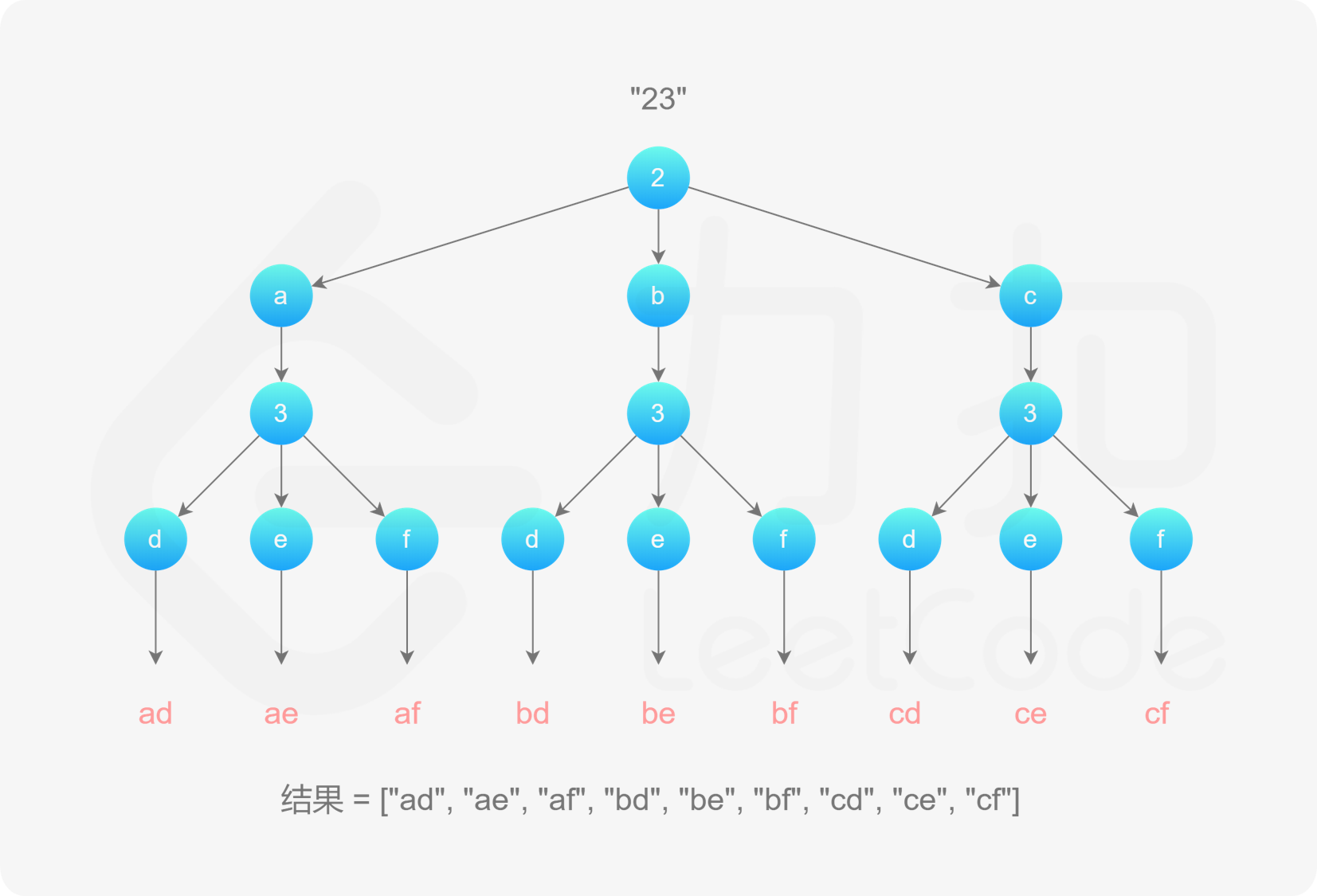 >
>