给定两个以字符串形式表示的非负整数 num1 和 num2,返回 num1 和 num2 的乘积,它们的乘积也表示为字符串形式。
注意: 不能使用任何内置的 BigInteger 库或直接将输入转换为整数。
示例 1:
**输入:** num1 = "2", num2 = "3"
**输出:** "6"
示例 2:
**输入:** num1 = "123", num2 = "456"
**输出:** "56088"
提示:
1 <= num1.length, num2.length <= 200num1 和 num2 只能由数字组成。num1 和 num2 都不包含任何前导零,除了数字0本身。
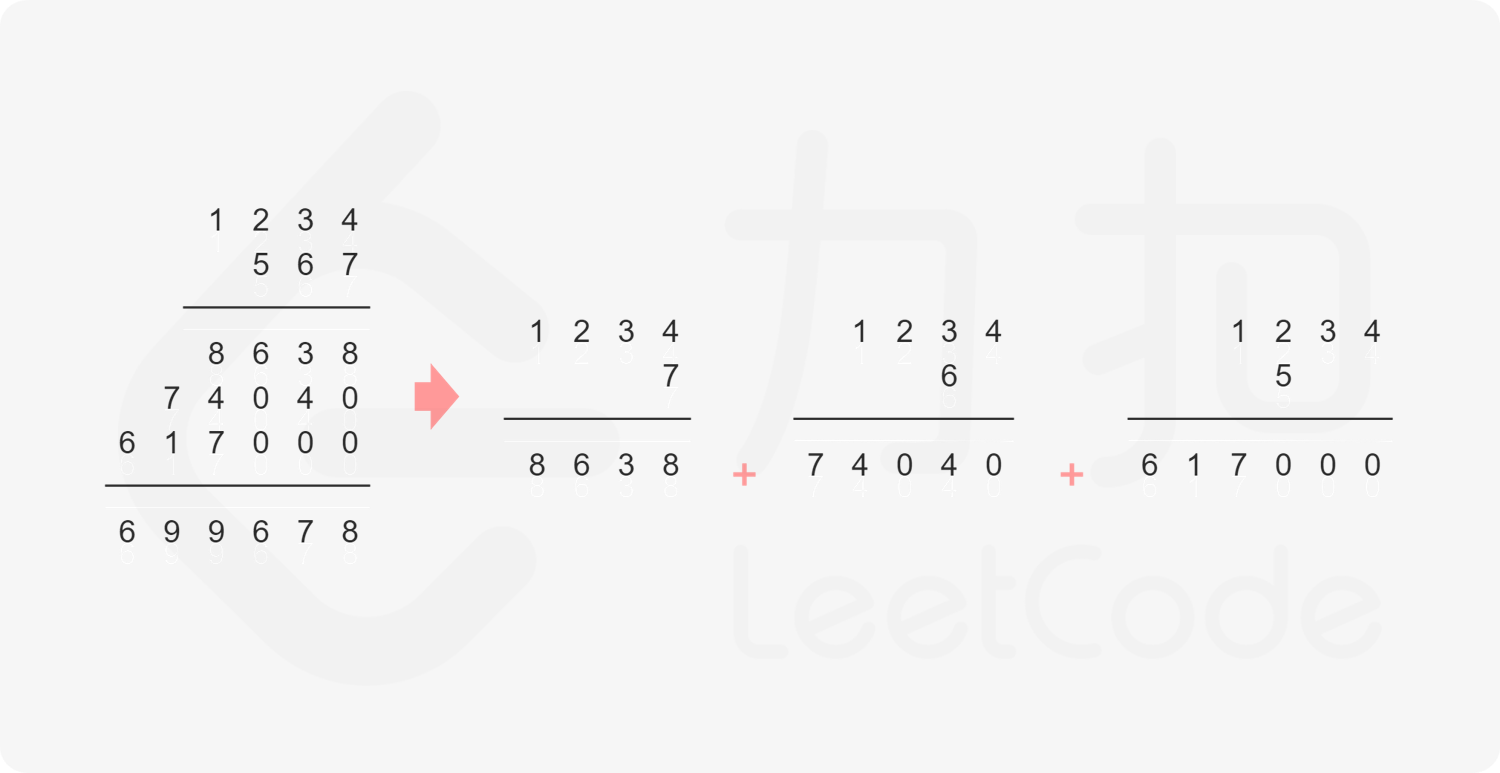
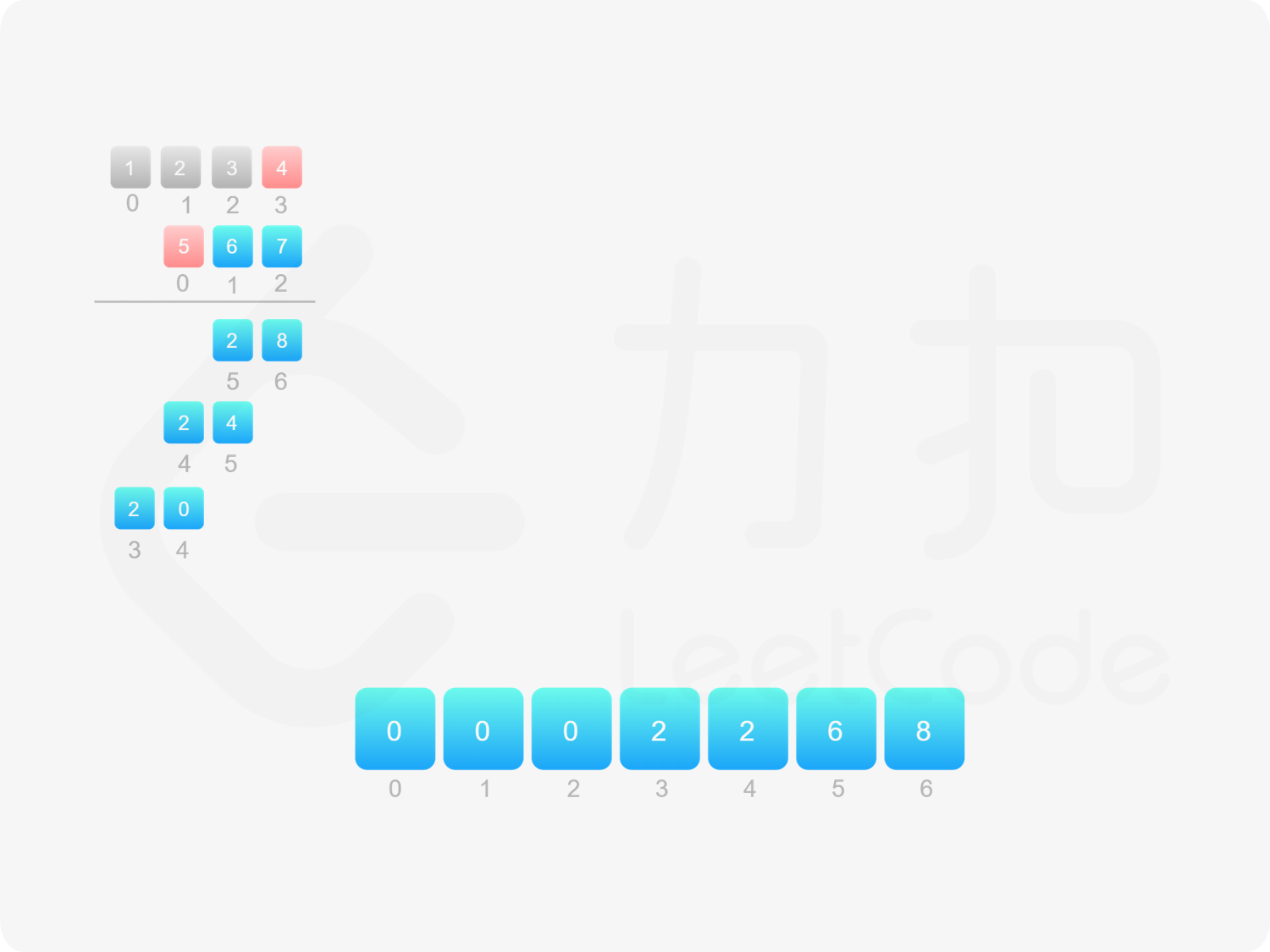
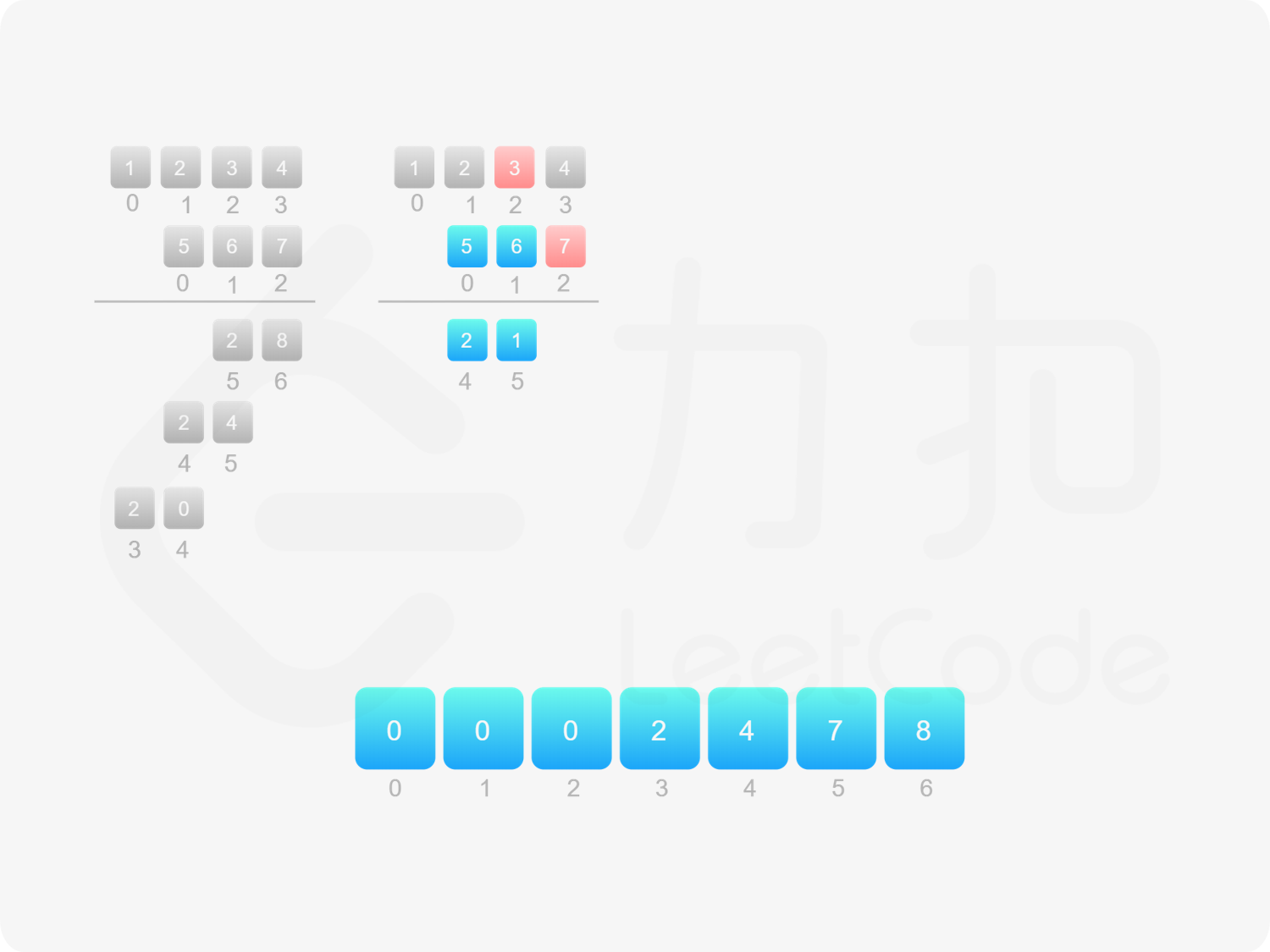
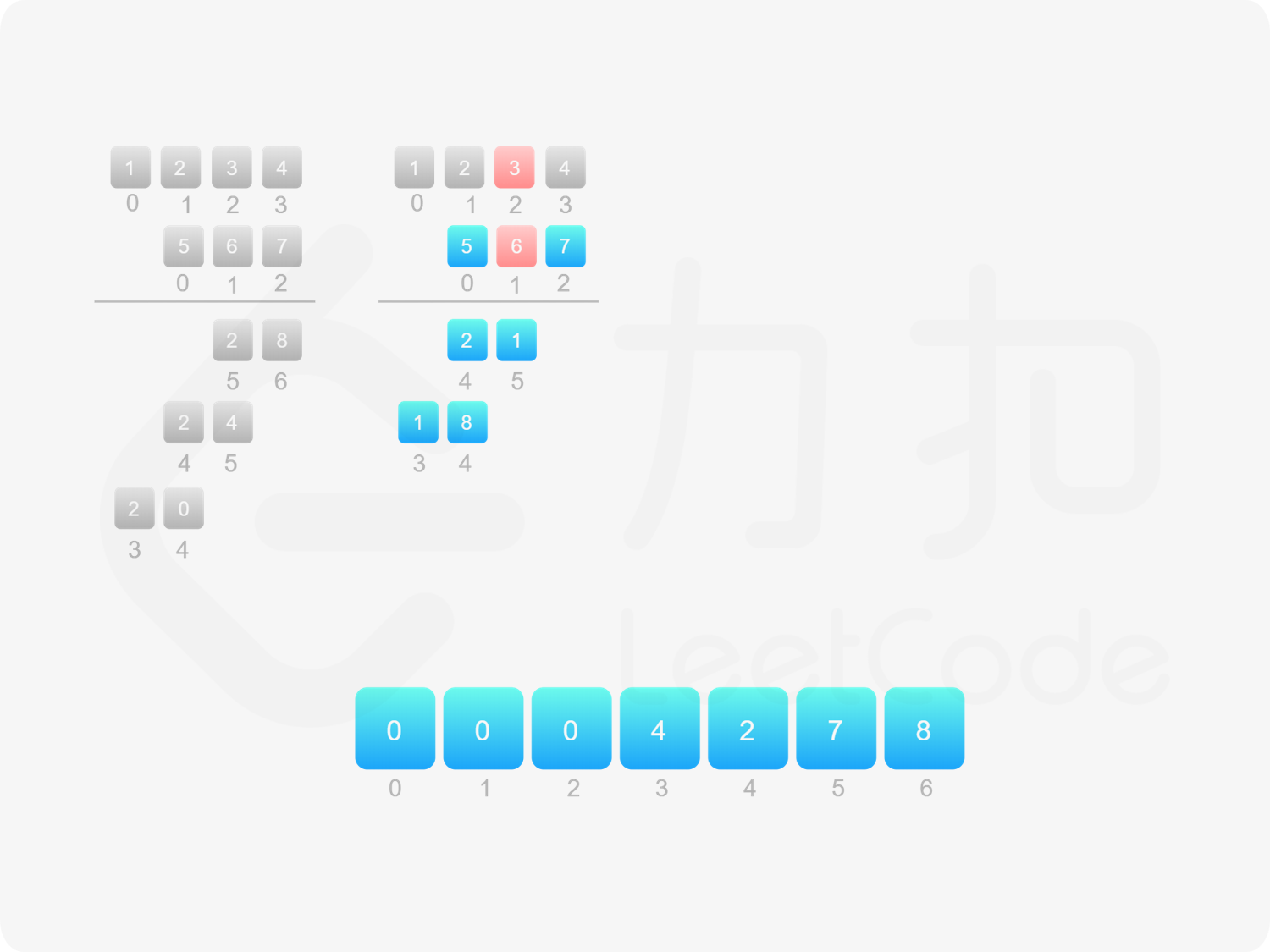
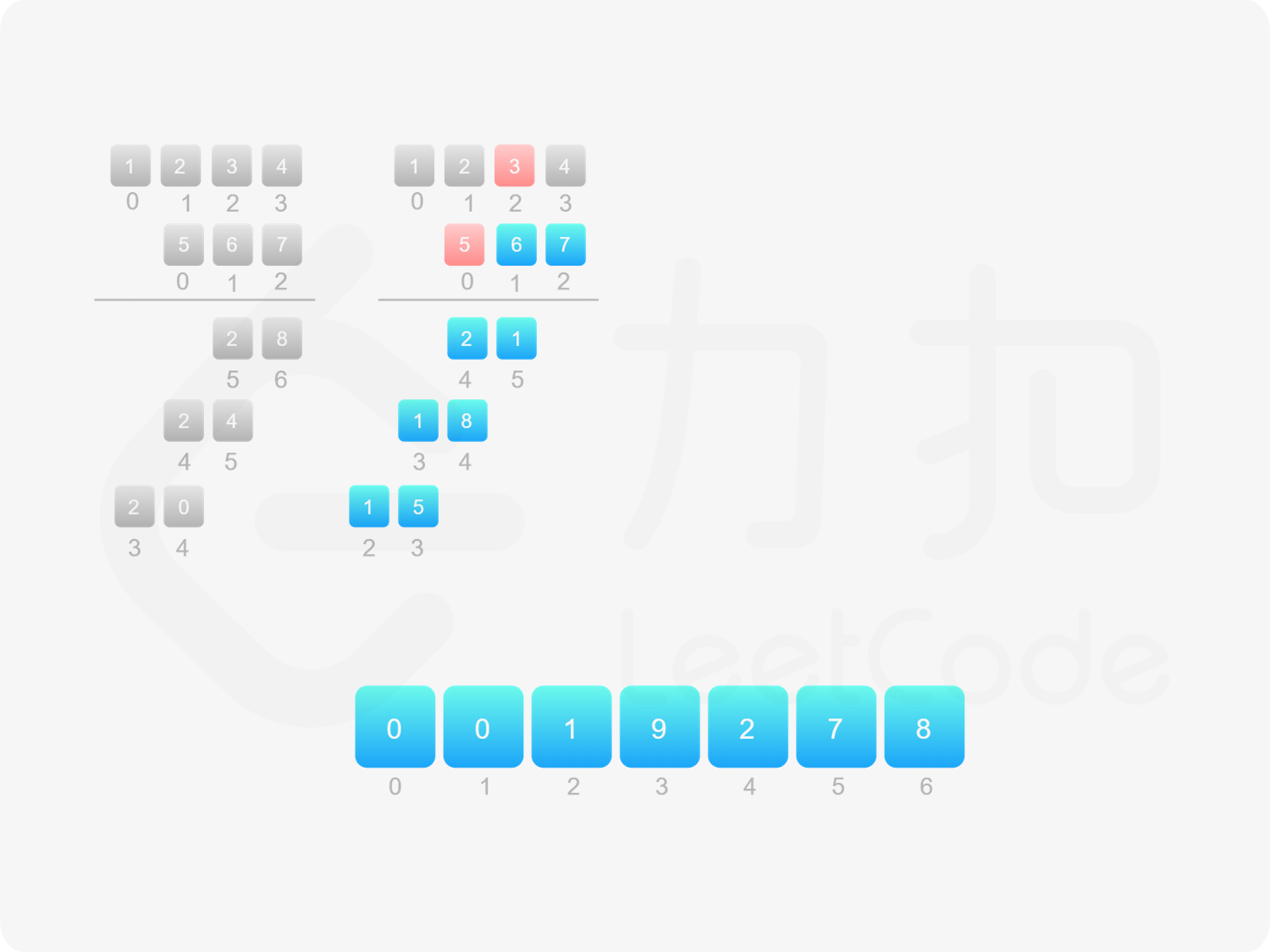
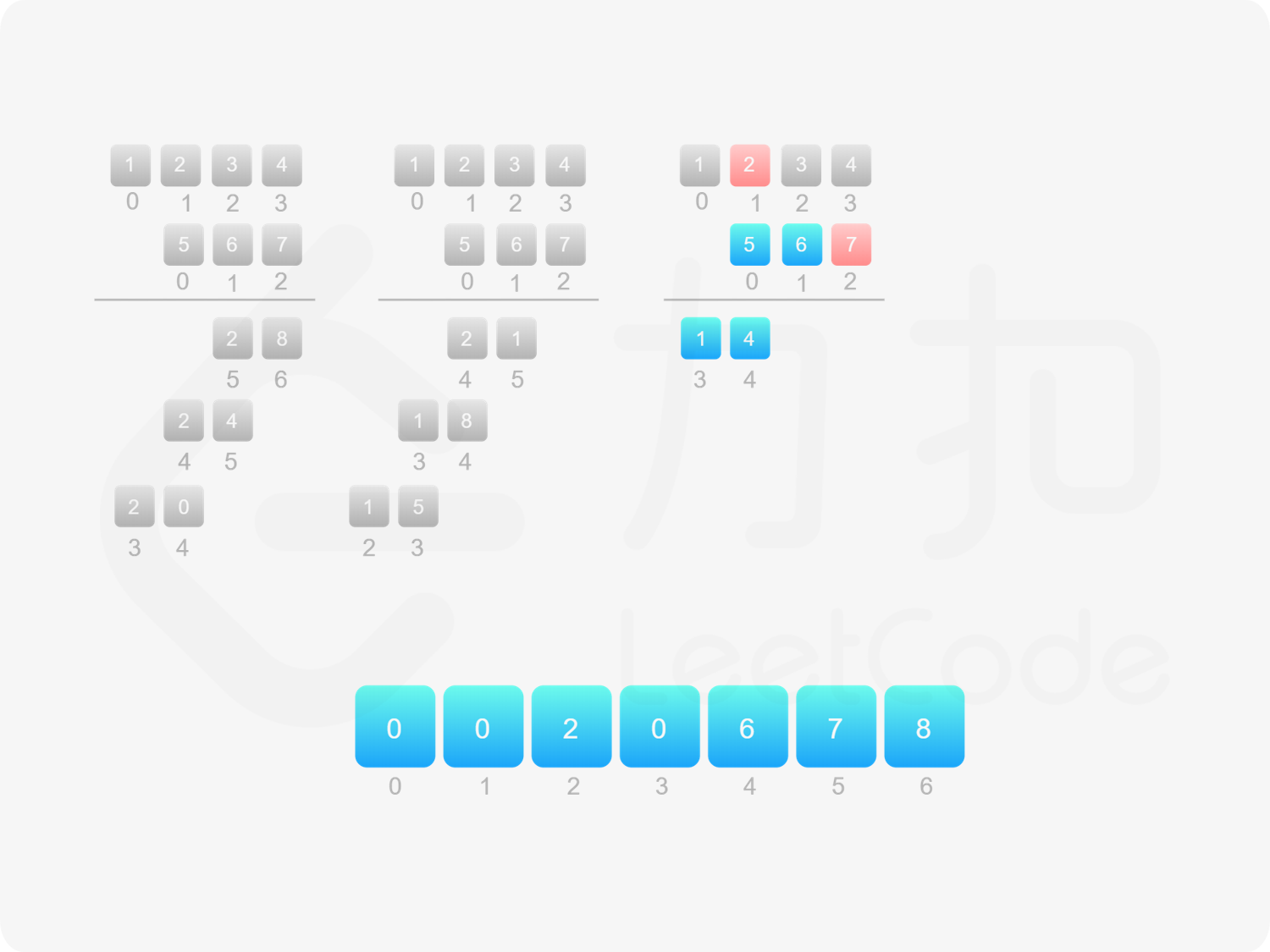
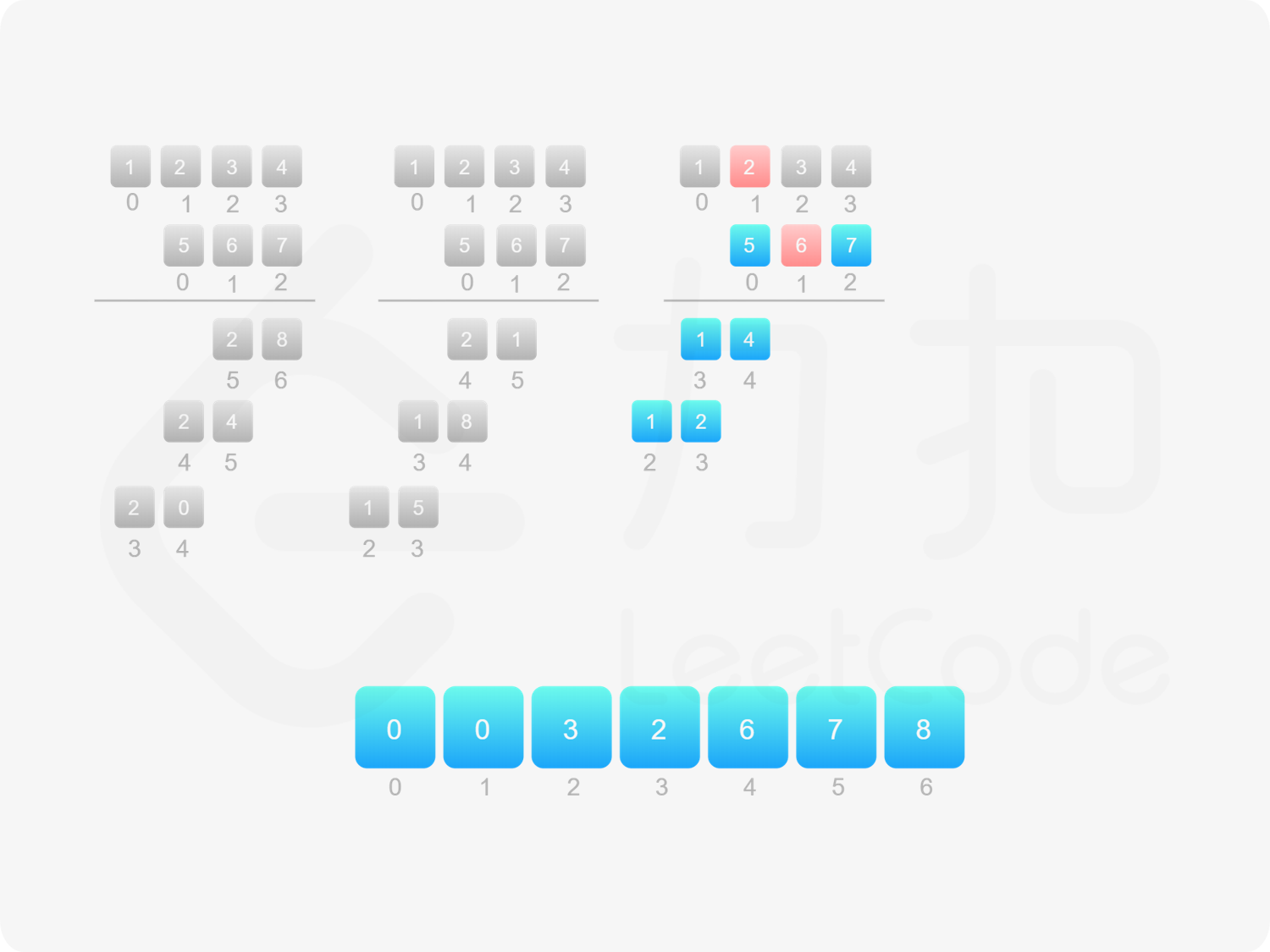
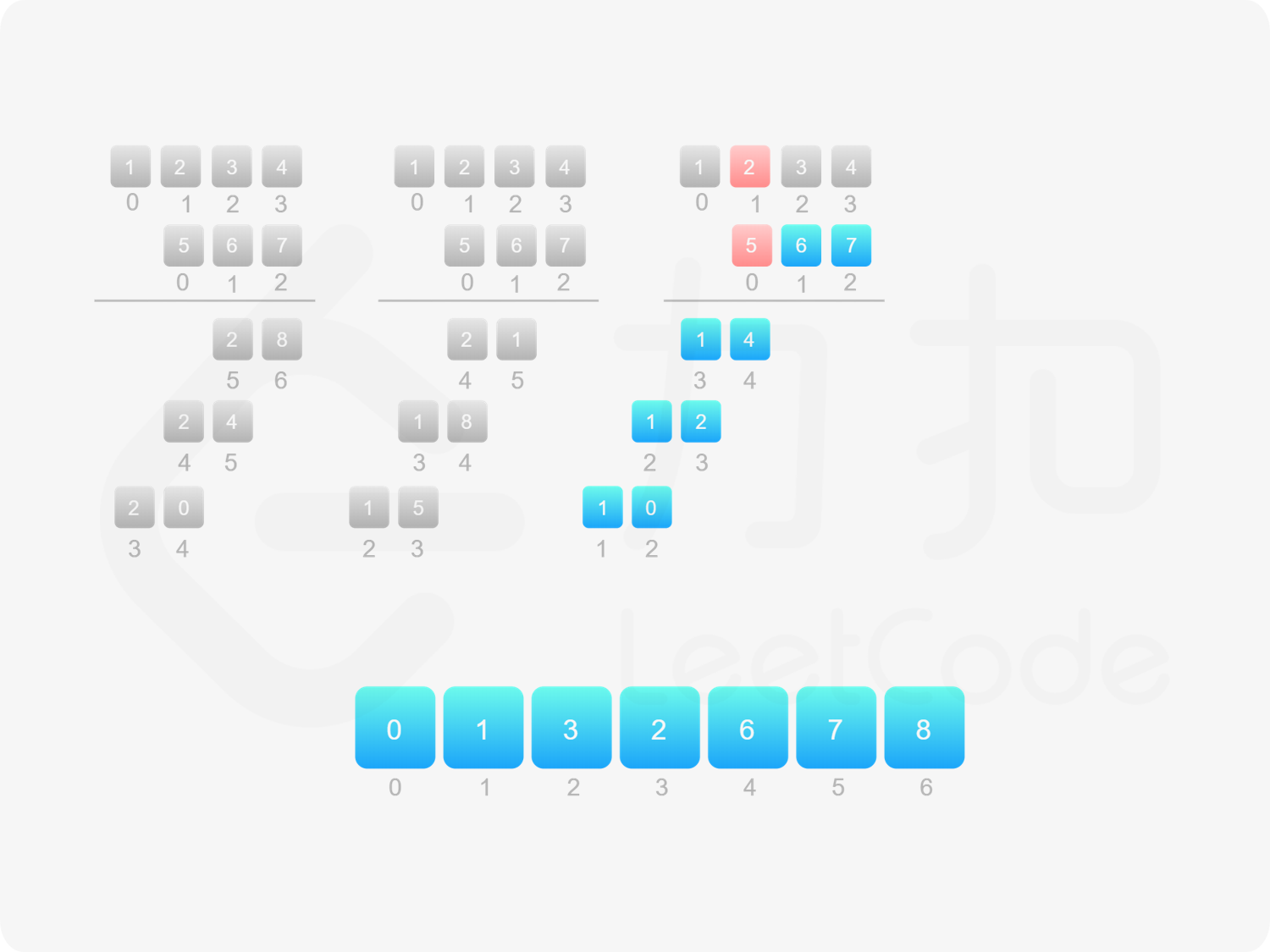
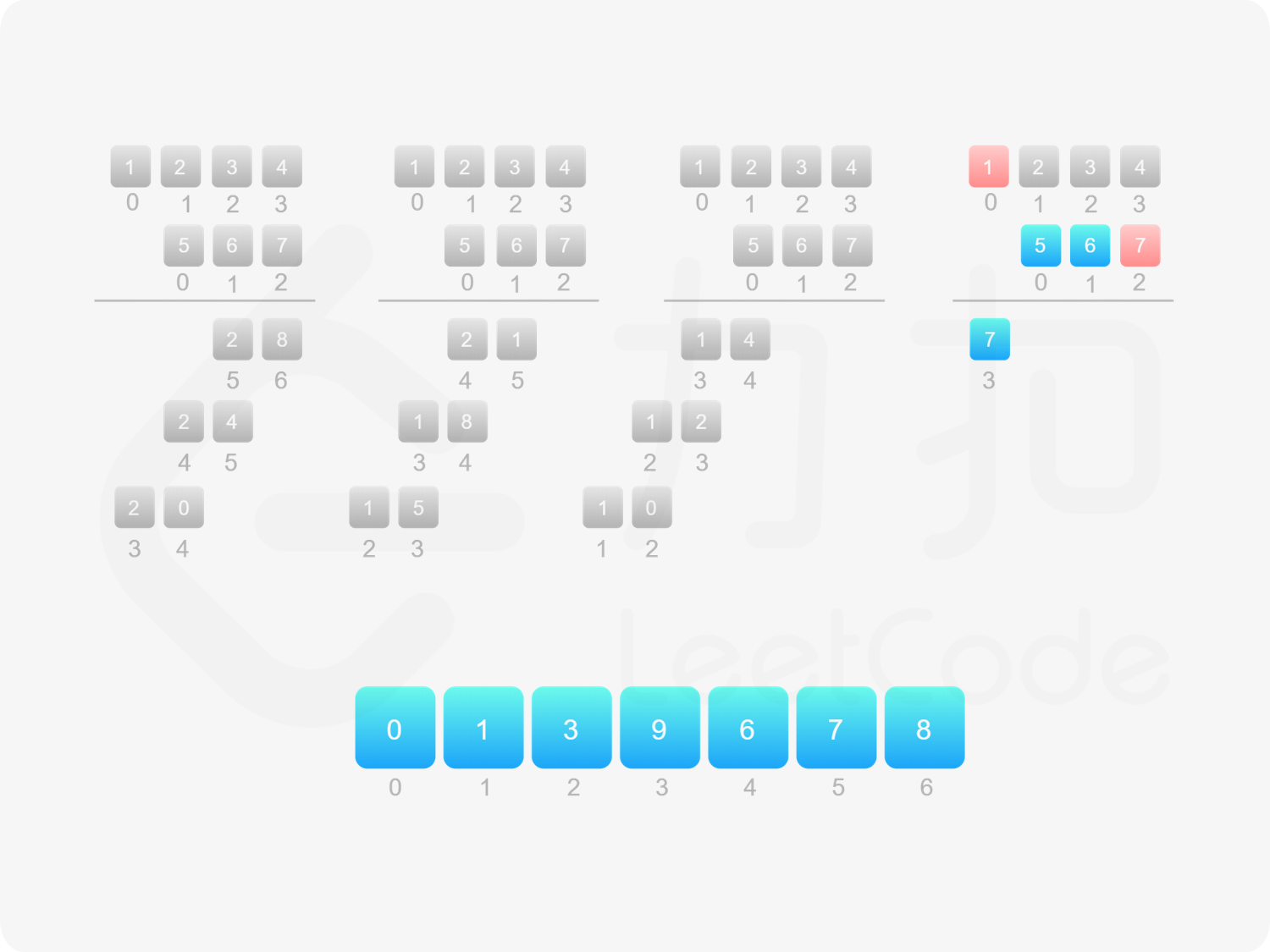
方法一:做加法 如果 $\textit{num}_1$ 和 $\textit{num}_2$ 之一是 $0$,则直接将 $0$ 作为结果返回即可。
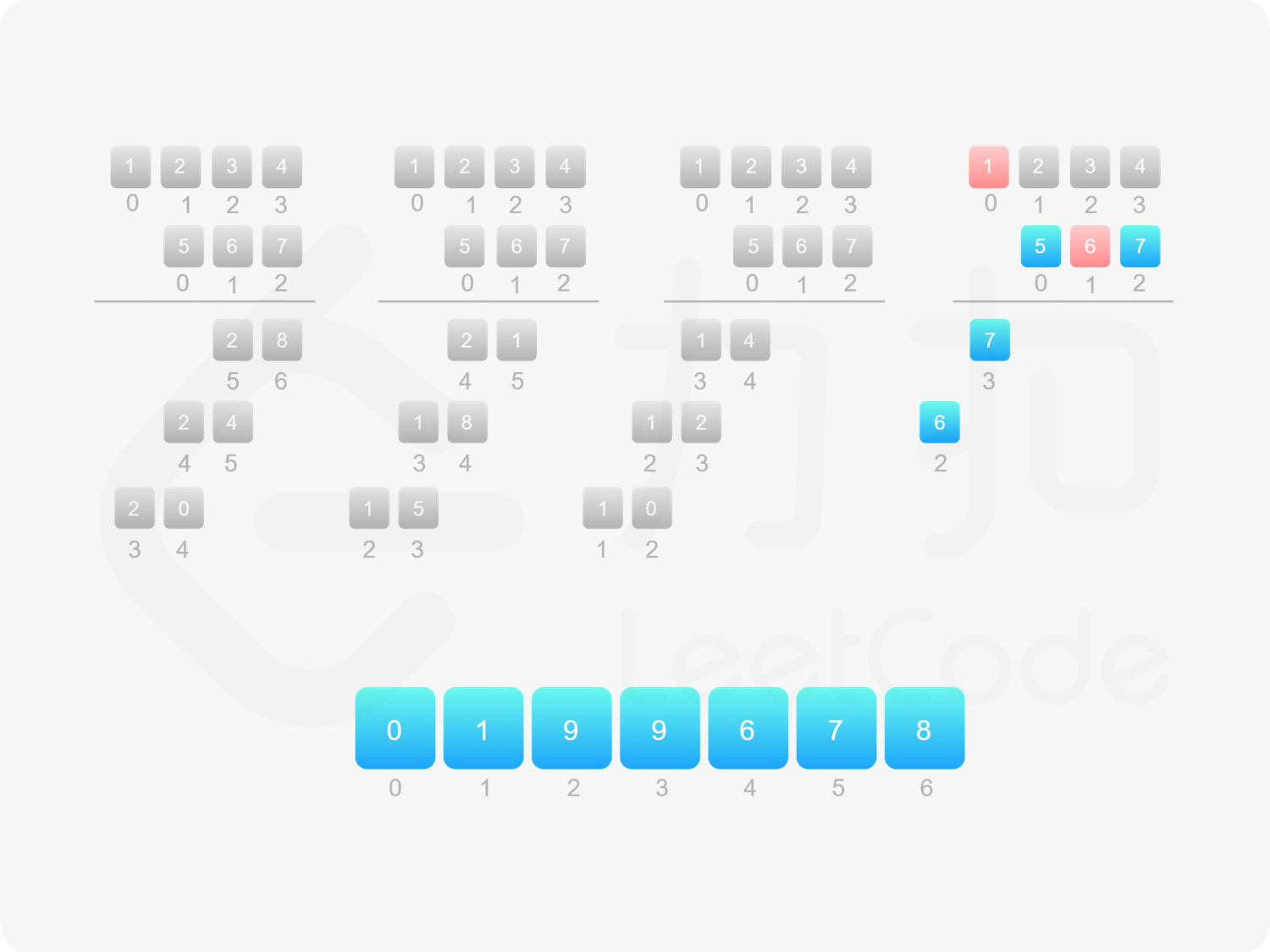
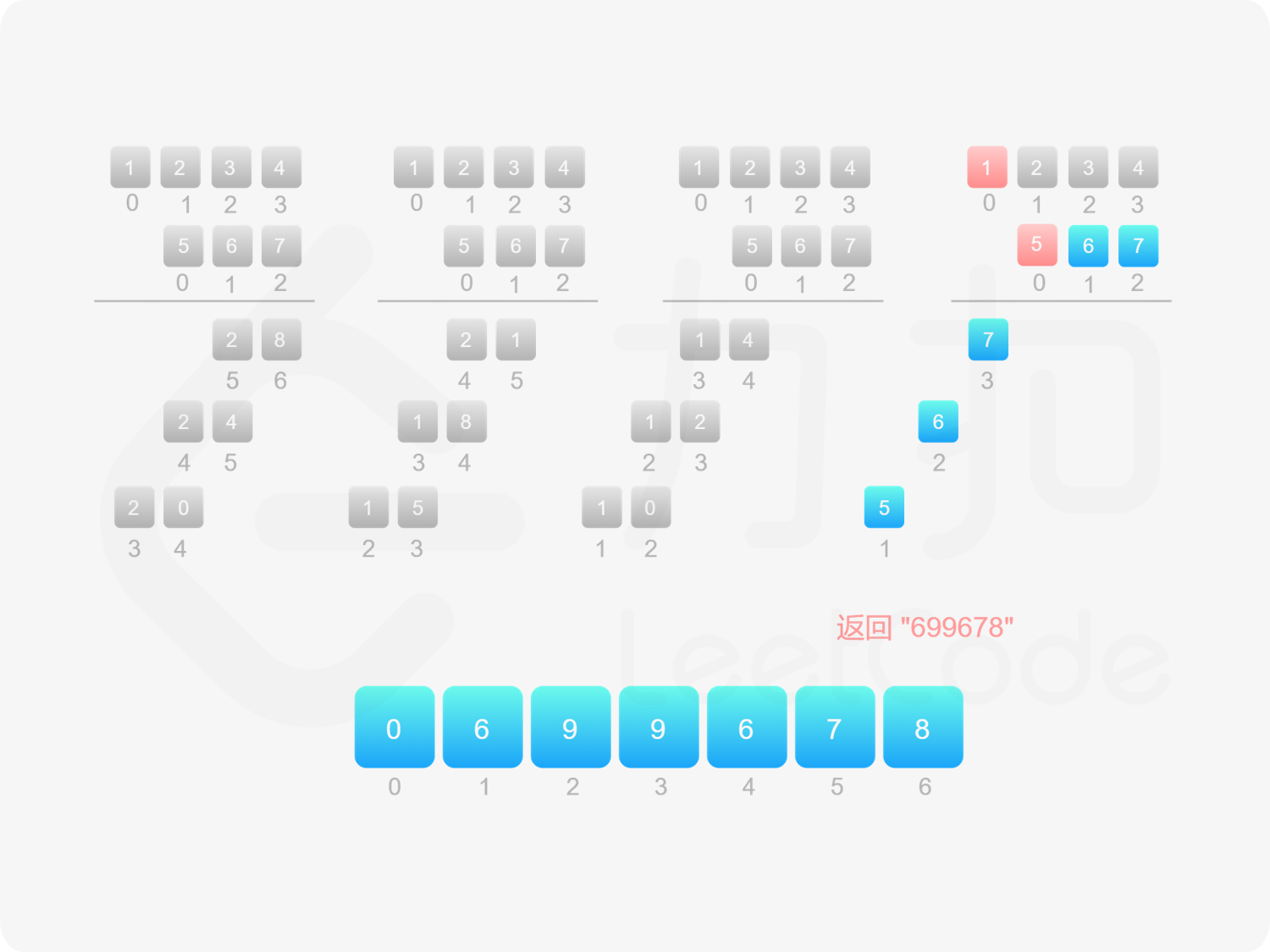
如果 $\textit{num}_1$ 和 $\textit{num}_2$ 都不是 $0$,则可以通过模拟「竖式乘法」的方法计算乘积。从右往左遍历乘数,将乘数的每一位与被乘数相乘得到对应的结果,再将每次得到的结果累加。这道题中,被乘数是 $\textit{num}_1$,乘数是 $\textit{num}_2$。
需要注意的是,$\textit{num}_2$ 除了最低位以外,其余的每一位的运算结果都需要补 $0$。
对每次得到的结果进行累加,可以使用「415. 字符串相加 」的做法。
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 class Solution { public String multiply (String num1, String num2) { if (num1.equals("0" ) || num2.equals("0" )) { return "0" ; } String ans = "0" ; int m = num1.length(), n = num2.length(); for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { StringBuffer curr = new StringBuffer (); int add = 0 ; for (int j = n - 1 ; j > i; j--) { curr.append(0 ); } int y = num2.charAt(i) - '0' ; for (int j = m - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { int x = num1.charAt(j) - '0' ; int product = x * y + add; curr.append(product % 10 ); add = product / 10 ; } if (add != 0 ) { curr.append(add % 10 ); } ans = addStrings(ans, curr.reverse().toString()); } return ans; } public String addStrings (String num1, String num2) { int i = num1.length() - 1 , j = num2.length() - 1 , add = 0 ; StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer (); while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || add != 0 ) { int x = i >= 0 ? num1.charAt(i) - '0' : 0 ; int y = j >= 0 ? num2.charAt(j) - '0' : 0 ; int result = x + y + add; ans.append(result % 10 ); add = result / 10 ; i--; j--; } ans.reverse(); return ans.toString(); } }
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 class Solution {public : string multiply (string num1, string num2) { if (num1 == "0" || num2 == "0" ) { return "0" ; } string ans = "0" ; int m = num1.size (), n = num2.size (); for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { string curr; int add = 0 ; for (int j = n - 1 ; j > i; j--) { curr.push_back (0 ); } int y = num2.at (i) - '0' ; for (int j = m - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { int x = num1.at (j) - '0' ; int product = x * y + add; curr.push_back (product % 10 ); add = product / 10 ; } while (add != 0 ) { curr.push_back (add % 10 ); add /= 10 ; } reverse (curr.begin (), curr.end ()); for (auto &c : curr) { c += '0' ; } ans = addStrings (ans, curr); } return ans; } string addStrings (string &num1, string &num2) { int i = num1.size () - 1 , j = num2.size () - 1 , add = 0 ; string ans; while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || add != 0 ) { int x = i >= 0 ? num1.at (i) - '0' : 0 ; int y = j >= 0 ? num2.at (j) - '0' : 0 ; int result = x + y + add; ans.push_back (result % 10 ); add = result / 10 ; i--; j--; } reverse (ans.begin (), ans.end ()); for (auto &c: ans) { c += '0' ; } return ans; } };
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution : def multiply (self, num1: str , num2: str ) -> str : if num1 == "0" or num2 == "0" : return "0" ans = "0" m, n = len (num1), len (num2) for i in range (n - 1 , -1 , -1 ): add = 0 y = int (num2[i]) curr = ["0" ] * (n - i - 1 ) for j in range (m - 1 , -1 , -1 ): product = int (num1[j]) * y + add curr.append(str (product % 10 )) add = product // 10 if add > 0 : curr.append(str (add)) curr = "" .join(curr[::-1 ]) ans = self.addStrings(ans, curr) return ans def addStrings (self, num1: str , num2: str ) -> str : i, j = len (num1) - 1 , len (num2) - 1 add = 0 ans = list () while i >= 0 or j >= 0 or add != 0 : x = int (num1[i]) if i >= 0 else 0 y = int (num2[j]) if j >= 0 else 0 result = x + y + add ans.append(str (result % 10 )) add = result // 10 i -= 1 j -= 1 return "" .join(ans[::-1 ])
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 func multiply (num1 string , num2 string ) string { if num1 == "0" || num2 == "0" { return "0" } ans := "0" m, n := len (num1), len (num2) for i := n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i-- { curr := "" add := 0 for j := n - 1 ; j > i; j-- { curr += "0" } y := int (num2[i] - '0' ) for j := m - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j-- { x := int (num1[j] - '0' ) product := x * y + add curr = strconv.Itoa(product % 10 ) + curr add = product / 10 } for ; add != 0 ; add /= 10 { curr = strconv.Itoa(add % 10 ) + curr } ans = addStrings(ans, curr) } return ans } func addStrings (num1, num2 string ) string { i, j := len (num1) - 1 , len (num2) - 1 add := 0 ans := "" for ; i >= 0 || j >= 0 || add != 0 ; i, j = i - 1 , j - 1 { x, y := 0 , 0 if i >= 0 { x = int (num1[i] - '0' ) } if j >= 0 { y = int (num2[j] - '0' ) } result := x + y + add ans = strconv.Itoa(result % 10 ) + ans add = result / 10 } return ans }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 char * addStrings (char * num1, char * num2) { int i = strlen (num1) - 1 , j = strlen (num2) - 1 , add = 0 ; char * ans = malloc (sizeof (char ) * (i + j + 5 )); int ansLen = 0 ; while (i >= 0 || j >= 0 || add != 0 ) { int x = i >= 0 ? num1[i] - '0' : 0 ; int y = j >= 0 ? num2[j] - '0' : 0 ; int result = x + y + add; ans[ansLen++] = result % 10 ; add = result / 10 ; i--; j--; } for (int i = 0 ; i < ansLen / 2 ; i++) { char t = ans[i]; ans[i] = ans[ansLen - 1 - i]; ans[ansLen - 1 - i] = t; } for (int i = 0 ; i < ansLen; i++) { ans[i] += '0' ; } ans[ansLen++] = 0 ; return ans; } char * multiply (char * num1, char * num2) { int m = strlen (num1), n = strlen (num2); char * ans = malloc (sizeof (char ) * 2 ); ans[0 ] = '0' , ans[1 ] = 0 ; if ((m == 1 && num1[0 ] == '0' ) || (n == 1 && num2[0 ] == '0' )) { return ans; } for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { char * curr = malloc (sizeof (char ) * (n + m + 5 )); int currLen = 0 ; int add = 0 ; for (int j = n - 1 ; j > i; j--) { curr[currLen++] = 0 ; } int y = num2[i] - '0' ; for (int j = m - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { int x = num1[j] - '0' ; int product = x * y + add; curr[currLen++] = product % 10 ; add = product / 10 ; } while (add != 0 ) { curr[currLen++] = add % 10 ; add /= 10 ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < currLen / 2 ; i++) { char t = curr[i]; curr[i] = curr[currLen - 1 - i]; curr[currLen - 1 - i] = t; } for (int i = 0 ; i < currLen; i++) { curr[i] += '0' ; } curr[currLen++] = 0 ; char * tmp = addStrings(ans, curr); free (ans), free (curr); ans = tmp; } return ans; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(mn+n^2)$,其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别是 $\textit{num}_1$ 和 $\textit{num}_2$ 的长度。需要从右往左遍历 $\textit{num}_2$,对于 $\textit{num}_2$ 的每一位,都需要和 $\textit{num}_1$ 的每一位计算乘积,因此计算乘积的总次数是 $mn$。字符串相加操作共有 $n$ 次,相加的字符串长度最长为 $m+n$,因此字符串相加的时间复杂度是 $O(mn+n^2)$。总时间复杂度是 $O(mn+n^2)$。
空间复杂度:$O(m+n)$,其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别是 $\textit{num}_1$ 和 $\textit{num}_2$ 的长度。空间复杂度取决于存储中间状态的字符串,由于乘积的最大长度为 $m+n$,因此存储中间状态的字符串的长度不会超过 $m+n$。
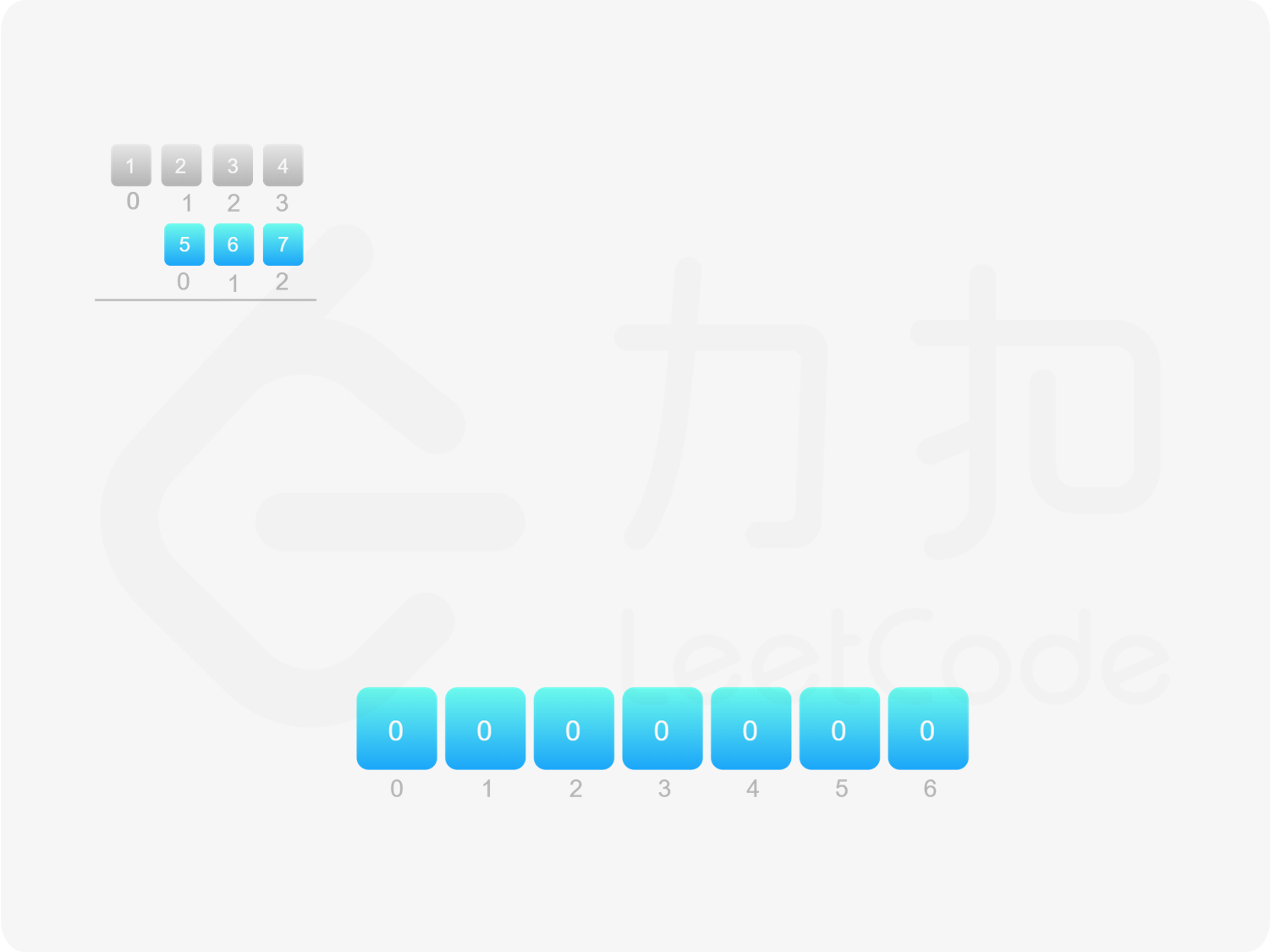
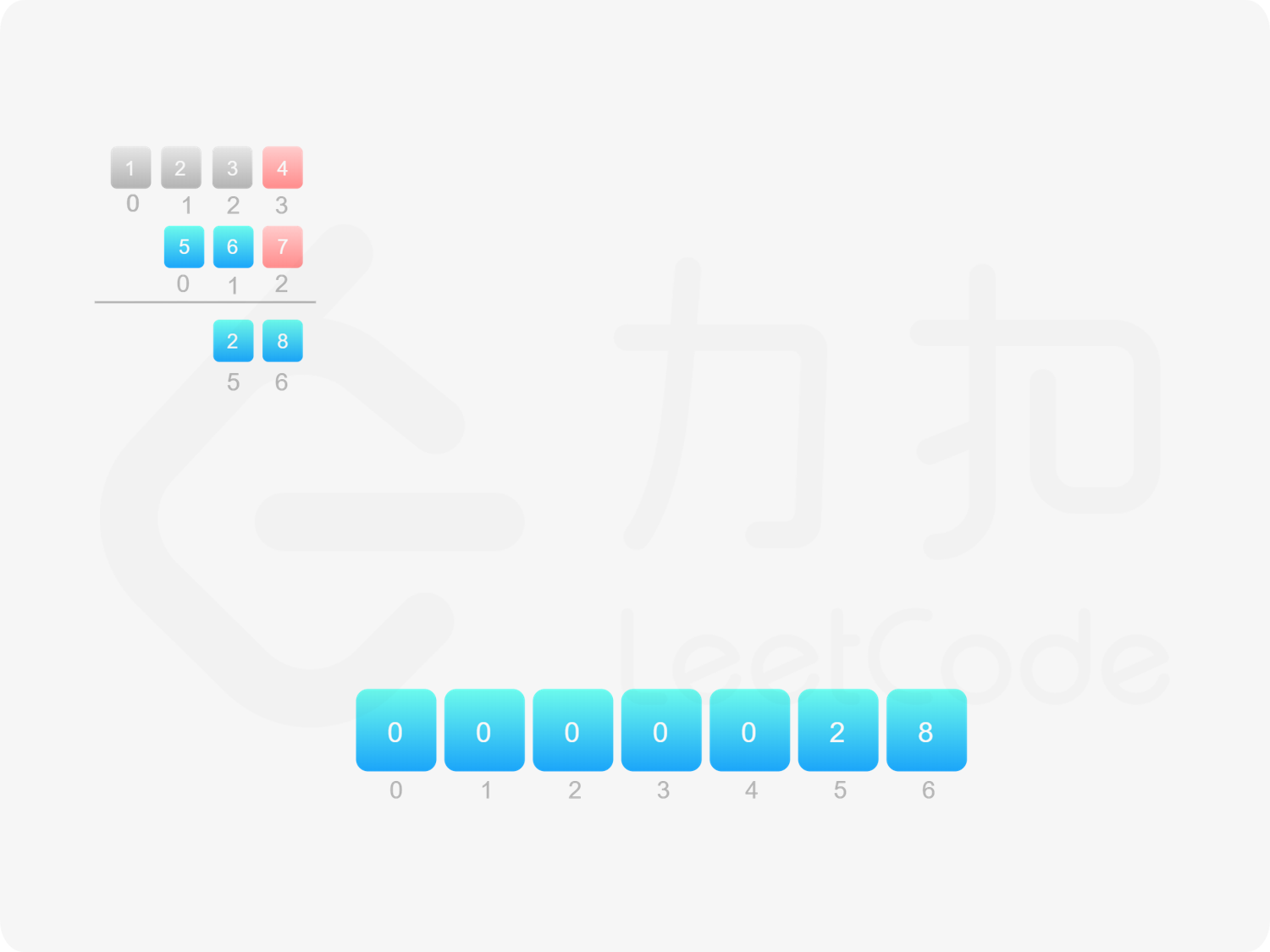
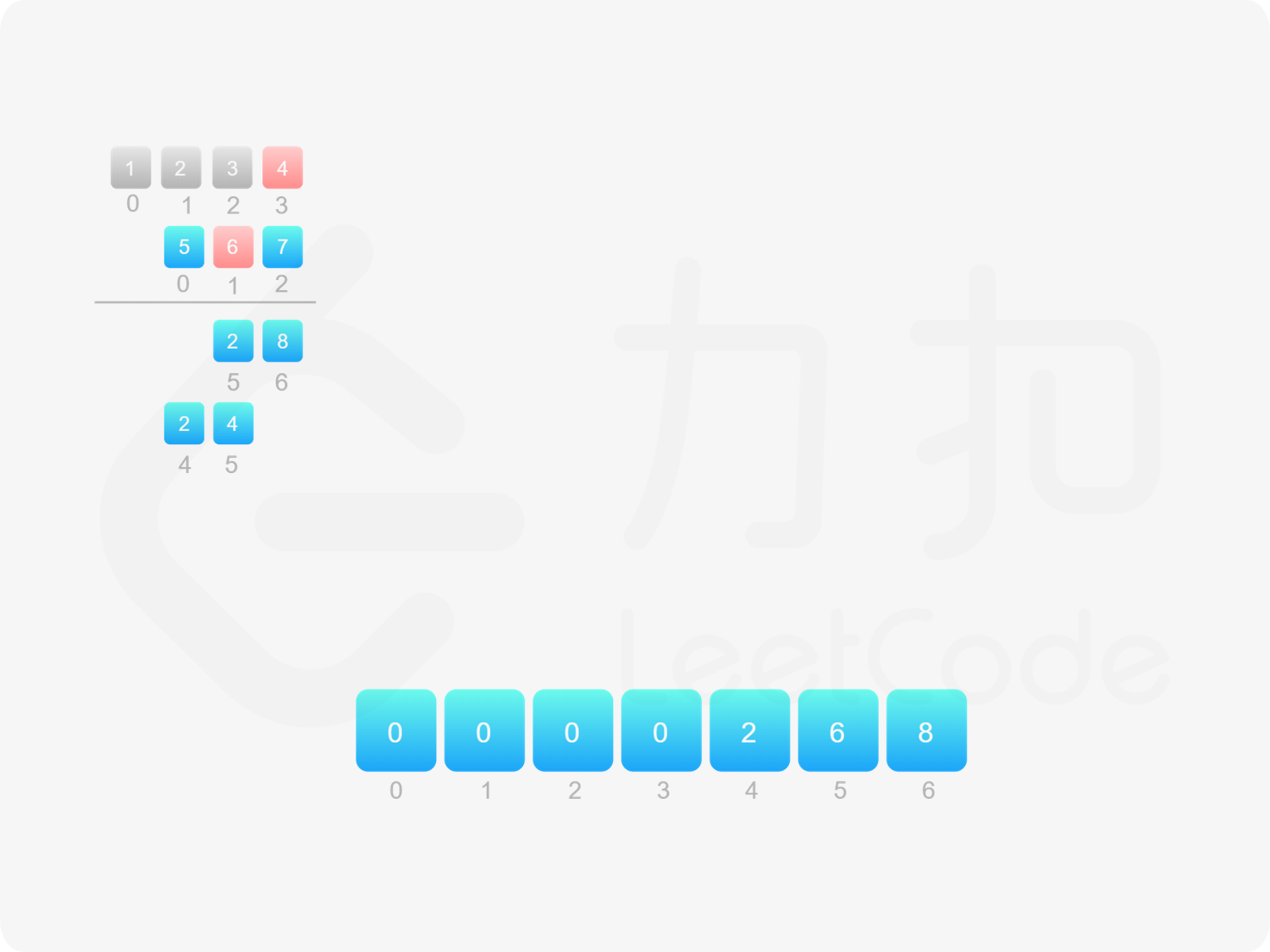
方法二:做乘法 方法一的做法是从右往左遍历乘数,将乘数的每一位与被乘数相乘得到对应的结果,再将每次得到的结果累加,整个过程中涉及到较多字符串相加的操作。如果使用数组代替字符串存储结果,则可以减少对字符串的操作。
令 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别表示 $\textit{num}_1$ 和 $\textit{num}_2$ 的长度,并且它们均不为 $0$,则 $\textit{num}_1$ 和 $\textit{num}_2$ 的乘积的长度为 $m+n-1$ 或 $m+n$。简单证明如下:
如果 $\textit{num}_1$ 和 $\textit{num}_2$ 都取最小值,则 $\textit{num}_1=10^{m-1}$,$\textit{num}_2=10^{n-1}$,$\textit{num}_1 \times \textit{num}_2=10^{m+n-2}$,乘积的长度为 $m+n-1$;
如果 $\textit{num}_1$ 和 $\textit{num}_2$ 都取最大值,则 $\textit{num}_1=10^m-1$,$\textit{num}_2=10^n-1$,$\textit{num}_1 \times \textit{num}_2=10^{m+n}-10^m-10^n+1$,乘积显然小于 $10^{m+n}$ 且大于 $10^{m+n-1}$,因此乘积的长度为 $m+n$。
由于 $\textit{num}_1$ 和 $\textit{num}_2$ 的乘积的最大长度为 $m+n$,因此创建长度为 $m+n$ 的数组 $\textit{ansArr}$ 用于存储乘积。对于任意 $0 \le i < m$ 和 $0 \le j < n$,$\textit{num}_1[i] \times \textit{num}_2[j]$ 的结果位于 $\textit{ansArr}[i+j+1]$,如果 $\textit{ansArr}[i+j+1] \ge 10$,则将进位部分加到 $\textit{ansArr}[i+j]$。
最后,将数组 $\textit{ansArr}$ 转成字符串,如果最高位是 $0$ 则舍弃最高位。
<
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public String multiply (String num1, String num2) { if (num1.equals("0" ) || num2.equals("0" )) { return "0" ; } int m = num1.length(), n = num2.length(); int [] ansArr = new int [m + n]; for (int i = m - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int x = num1.charAt(i) - '0' ; for (int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { int y = num2.charAt(j) - '0' ; ansArr[i + j + 1 ] += x * y; } } for (int i = m + n - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { ansArr[i - 1 ] += ansArr[i] / 10 ; ansArr[i] %= 10 ; } int index = ansArr[0 ] == 0 ? 1 : 0 ; StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer (); while (index < m + n) { ans.append(ansArr[index]); index++; } return ans.toString(); } }
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 class Solution {public : string multiply (string num1, string num2) { if (num1 == "0" || num2 == "0" ) { return "0" ; } int m = num1.size (), n = num2.size (); auto ansArr = vector <int >(m + n); for (int i = m - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int x = num1.at (i) - '0' ; for (int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { int y = num2.at (j) - '0' ; ansArr[i + j + 1 ] += x * y; } } for (int i = m + n - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { ansArr[i - 1 ] += ansArr[i] / 10 ; ansArr[i] %= 10 ; } int index = ansArr[0 ] == 0 ? 1 : 0 ; string ans; while (index < m + n) { ans.push_back (ansArr[index]); index++; } for (auto &c: ans) { c += '0' ; } return ans; } };
[sol2-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 class Solution : def multiply (self, num1: str , num2: str ) -> str : if num1 == "0" or num2 == "0" : return "0" m, n = len (num1), len (num2) ansArr = [0 ] * (m + n) for i in range (m - 1 , -1 , -1 ): x = int (num1[i]) for j in range (n - 1 , -1 , -1 ): ansArr[i + j + 1 ] += x * int (num2[j]) for i in range (m + n - 1 , 0 , -1 ): ansArr[i - 1 ] += ansArr[i] // 10 ansArr[i] %= 10 index = 1 if ansArr[0 ] == 0 else 0 ans = "" .join(str (x) for x in ansArr[index:]) return ans
[sol2-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 func multiply (num1 string , num2 string ) string { if num1 == "0" || num2 == "0" { return "0" } m, n := len (num1), len (num2) ansArr := make ([]int , m + n) for i := m - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i-- { x := int (num1[i]) - '0' for j := n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j-- { y := int (num2[j] - '0' ) ansArr[i + j + 1 ] += x * y } } for i := m + n - 1 ; i > 0 ; i-- { ansArr[i - 1 ] += ansArr[i] / 10 ansArr[i] %= 10 } ans := "" idx := 0 if ansArr[0 ] == 0 { idx = 1 } for ; idx < m + n; idx++ { ans += strconv.Itoa(ansArr[idx]) } return ans }
[sol2-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 char * multiply (char * num1, char * num2) { int m = strlen (num1), n = strlen (num2); char * ans = malloc (sizeof (char ) * (m + n + 3 )); memset (ans, 0 , sizeof (char ) * (m + n + 3 )); if ((m == 1 && num1[0 ] == '0' ) || (n == 1 && num2[0 ] == '0' )) { ans[0 ] = '0' , ans[1 ] = 0 ; return ans; } int * ansArr = malloc (sizeof (int ) * (m + n + 3 )); memset (ansArr, 0 , sizeof (int ) * (m + n + 3 )); for (int i = m - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int x = num1[i] - '0' ; for (int j = n - 1 ; j >= 0 ; j--) { int y = num2[j] - '0' ; ansArr[i + j + 1 ] += x * y; } } for (int i = m + n - 1 ; i > 0 ; i--) { ansArr[i - 1 ] += ansArr[i] / 10 ; ansArr[i] %= 10 ; } int index = ansArr[0 ] == 0 ? 1 : 0 ; int ansLen = 0 ; while (index < m + n) { ans[ansLen++] = ansArr[index]; index++; } for (int i = 0 ; i < ansLen; i++) ans[i] += '0' ; return ans; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(mn)$,其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别是 $\textit{num}_1$ 和 $\textit{num}_2$ 的长度。需要计算 $\textit{num}_1$ 的每一位和 $\textit{num}_2$ 的每一位的乘积。
空间复杂度:$O(m+n)$,其中 $m$ 和 $n$ 分别是 $\textit{num}_1$ 和 $\textit{num}_2$ 的长度。需要创建一个长度为 $m+n$ 的数组存储乘积。
结语 方法二还可以用另外一种方法改写。我们把两个数相乘看成是两个多项式相乘,因为任何一个数都可以表示成为
$$
的形式,也就相当于对多项式
$$
在 $x = 10$ 处求值。当两个数 $N_a$、$N_b$ 相乘的时候,我们也可以认为这两个数是两个多项式
$$
相乘的结果 $C(x) = A(x) \times B(x)$ 在 $x = 10$ 处求值。我们可以这样表示 $C(x)$:
$$
这里
$$
于是我们就可以顺序求解 $c_i$,每次 $O(i)$ 地选取下标和为 $i$ 的一组 $(a_k, b_{i - k})$。求到 $c_i$ 序列之后,再处理进位即可得到答案。对比这两种做法:
顺序求解 $c_i$ 的过程相当于集中计算 $c_i$
而方法二相当于每对 $(a_i, b_j)$ 对 $c_{i + j}$ 算贡献(注意这里的 $a_i$ 并不是题目中的 ${\it num}_1[i]$,$a_i$ 下标越小,代表的位权越小,而 ${\it num}_1[i]$ 下标越小,代表的位权越大)
它们的本质是一样的,并且时间复杂度都是 $O(\max { n, m} ^2)$。我们再仔细的观察 $c_i$ 的形式:
$$
它揭示了多项式乘法的另一面:$c_i$ 序列其实是 $a_i$ 序列和 $b_i$ 序列的卷积,即:
$$
至此,我们就可以用一种叫做快速傅立叶变换(Fast Fourier Transform,FFT)的方法来加速卷积的计算,使得时间复杂度降低到 $O(c \log c)$,这里 $c$ 是不小于 $n + m$ 的最小的 $2$ 的整数幂。由于这个方法并不在面试的考纲范围内,感兴趣的同学可以自行学习。
 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>