给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:

**输入:** root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
**输出:** 3
示例 2:
**输入:** root = [1,null,2]
**输出:** 2
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 104] 区间内。
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
📺 视频题解

📖 文字题解
方法一:深度优先搜索
思路与算法
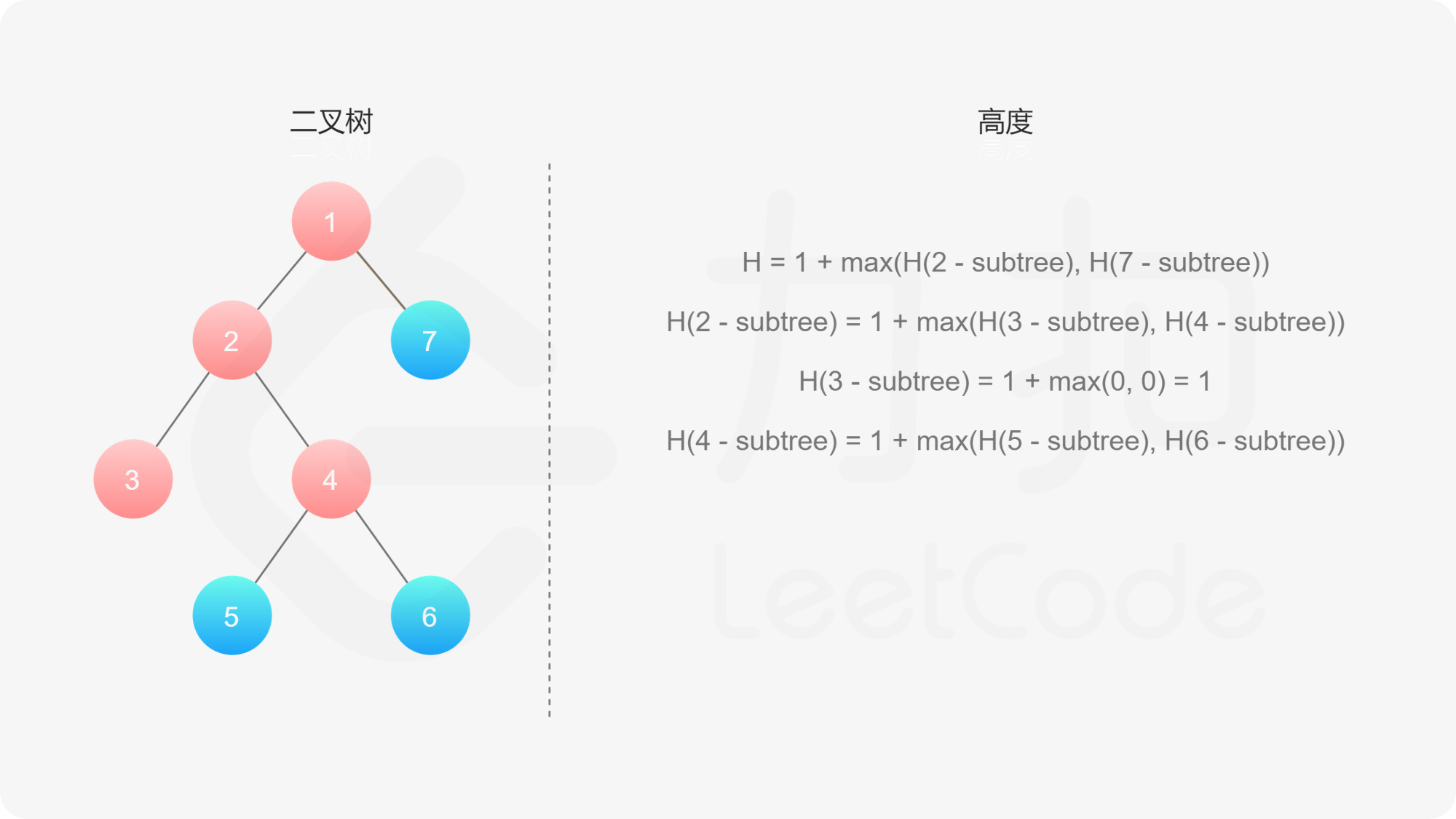
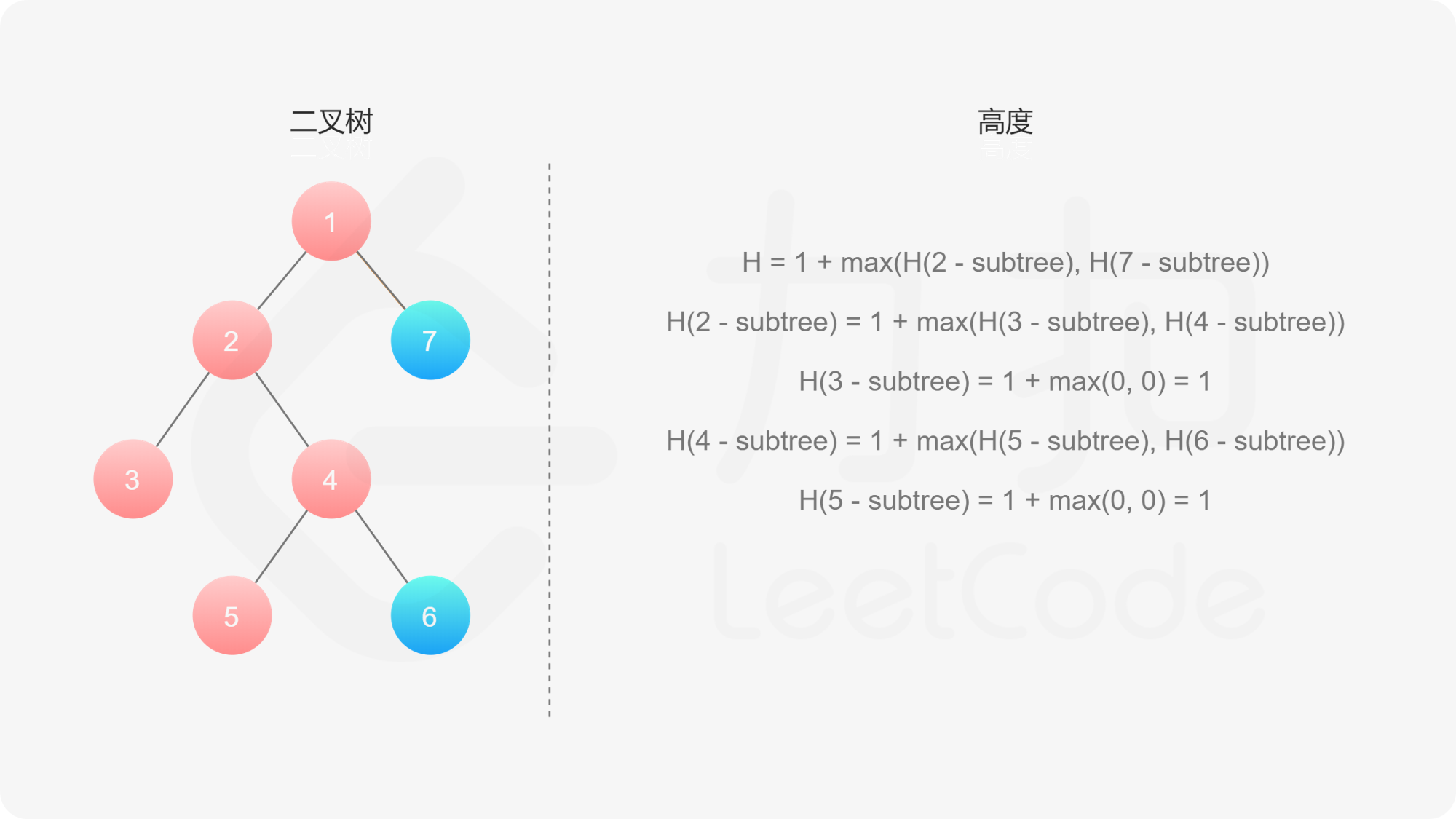
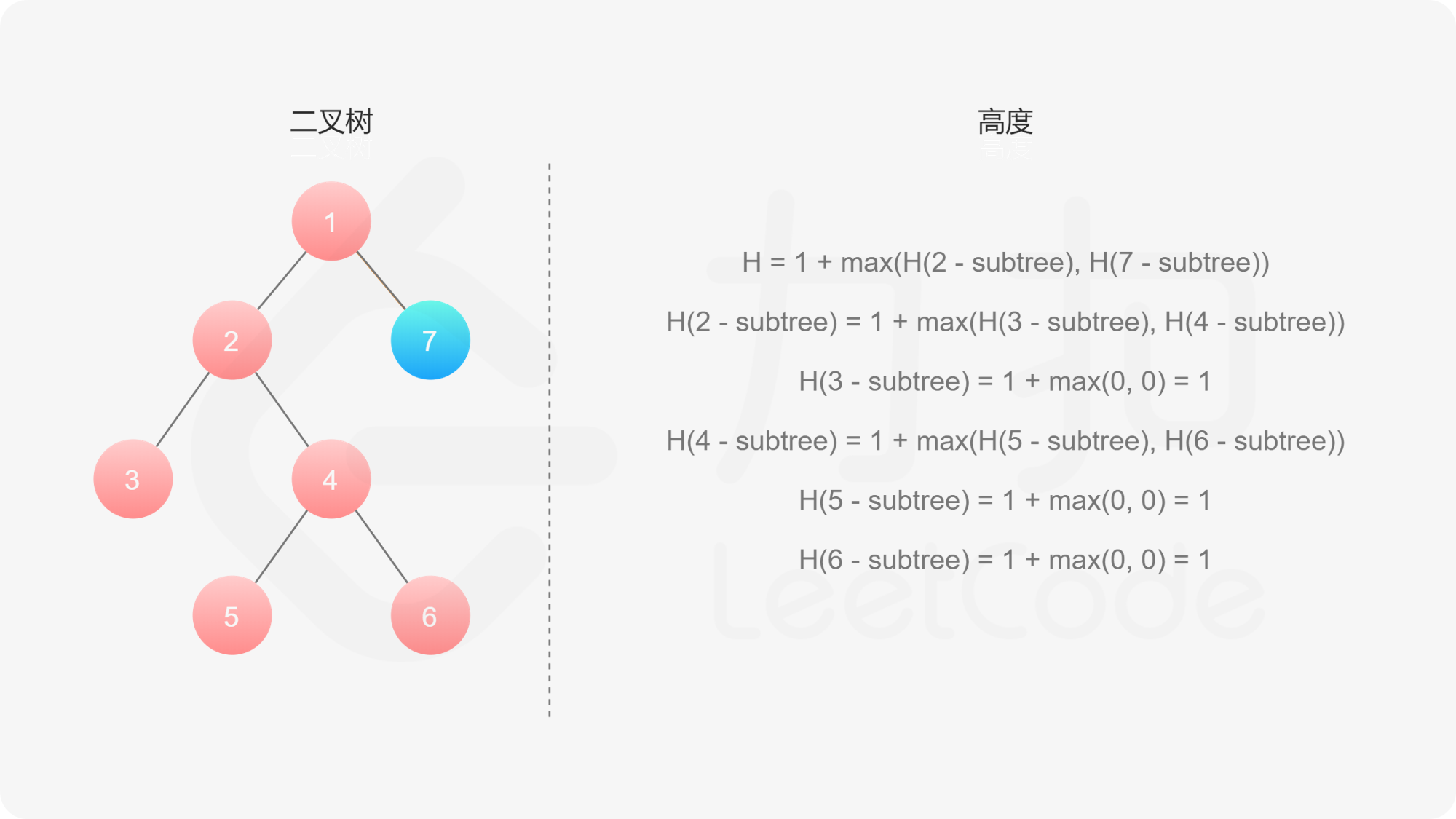
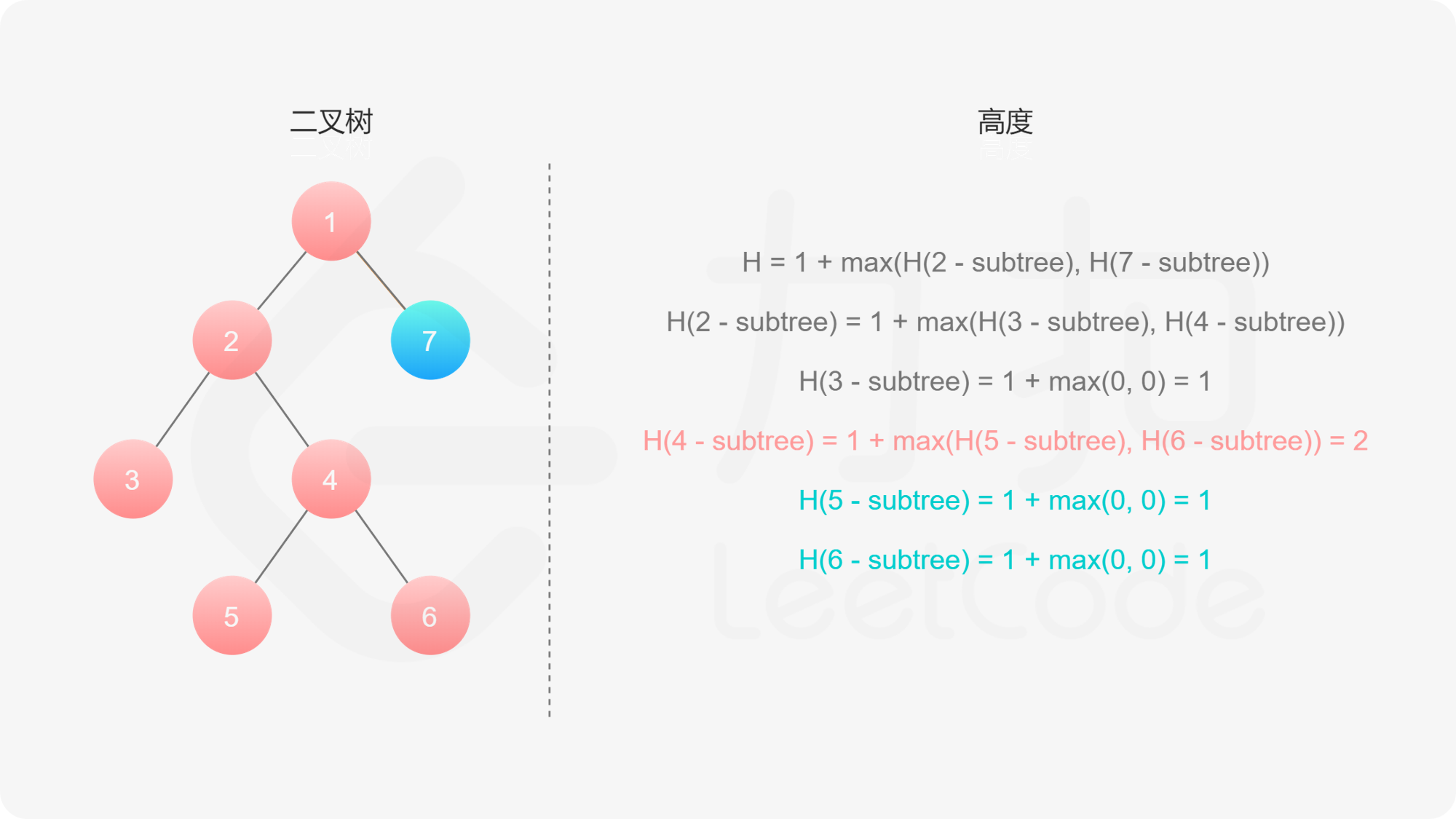
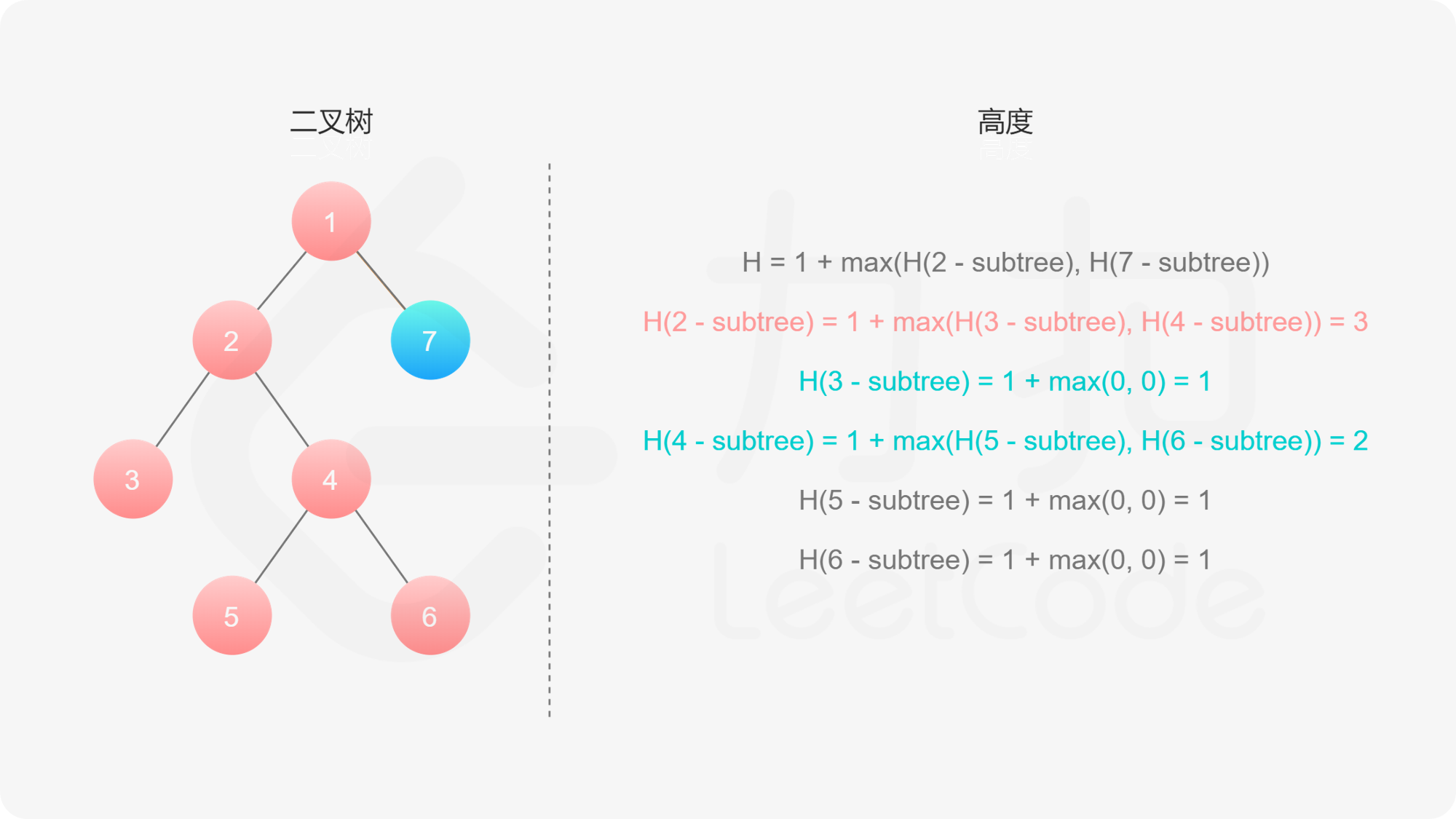
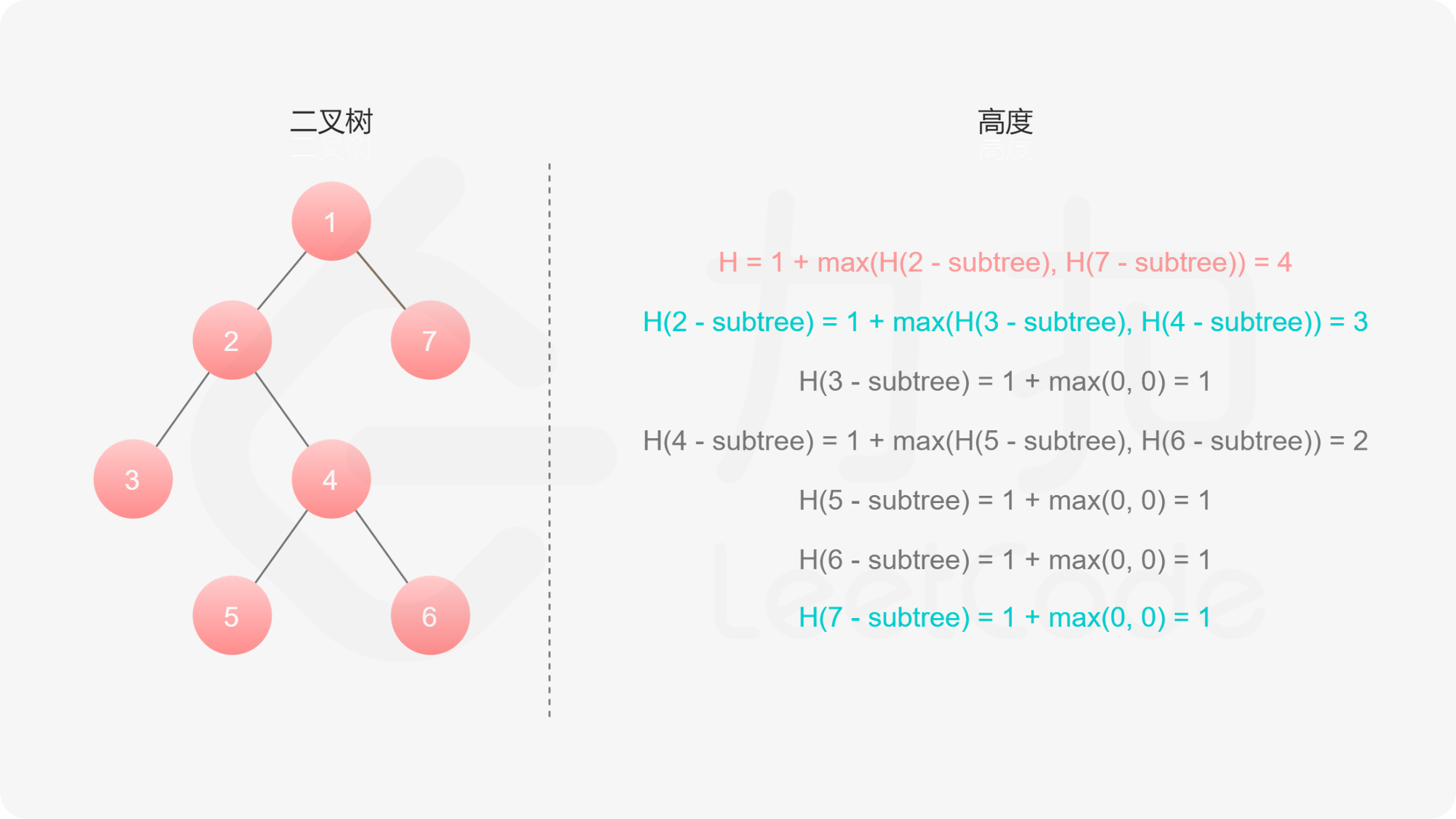
如果我们知道了左子树和右子树的最大深度 $l$ 和 $r$,那么该二叉树的最大深度即为
$$
\max(l,r) + 1
$$
而左子树和右子树的最大深度又可以以同样的方式进行计算。因此我们可以用「深度优先搜索」的方法来计算二叉树的最大深度。具体而言,在计算当前二叉树的最大深度时,可以先递归计算出其左子树和右子树的最大深度,然后在 $O(1)$ 时间内计算出当前二叉树的最大深度。递归在访问到空节点时退出。
< ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
return max(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
};
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
} else {
int leftHeight = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightHeight = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
}
}
|
[sol1-Python]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| class Solution:
def maxDepth(self, root):
if root is None:
return 0
else:
left_height = self.maxDepth(root.left)
right_height = self.maxDepth(root.right)
return max(left_height, right_height) + 1
|
[sol1-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
return max(maxDepth(root.Left), maxDepth(root.Right)) + 1
}
func max(a, b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
|
[sol1-C]1
2
3
4
| int maxDepth(struct TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
return fmax(maxDepth(root->left), maxDepth(root->right)) + 1;
}
|
复杂度分析
方法二:广度优先搜索
思路与算法
我们也可以用「广度优先搜索」的方法来解决这道题目,但我们需要对其进行一些修改,此时我们广度优先搜索的队列里存放的是「当前层的所有节点」。每次拓展下一层的时候,不同于广度优先搜索的每次只从队列里拿出一个节点,我们需要将队列里的所有节点都拿出来进行拓展,这样能保证每次拓展完的时候队列里存放的是当前层的所有节点,即我们是一层一层地进行拓展,最后我们用一个变量 $\textit{ans}$ 来维护拓展的次数,该二叉树的最大深度即为 $\textit{ans}$。
[sol2-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr) return 0;
queue<TreeNode*> Q;
Q.push(root);
int ans = 0;
while (!Q.empty()) {
int sz = Q.size();
while (sz > 0) {
TreeNode* node = Q.front();Q.pop();
if (node->left) Q.push(node->left);
if (node->right) Q.push(node->right);
sz -= 1;
}
ans += 1;
}
return ans;
}
};
|
[sol2-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
int ans = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
while (size > 0) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
size--;
}
ans++;
}
return ans;
}
}
|
[sol2-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| func maxDepth(root *TreeNode) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
queue := []*TreeNode{}
queue = append(queue, root)
ans := 0
for len(queue) > 0 {
sz := len(queue)
for sz > 0 {
node := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
if node.Left != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Left)
}
if node.Right != nil {
queue = append(queue, node.Right)
}
sz--
}
ans++
}
return ans
}
|
[sol2-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| struct QueNode {
struct TreeNode *p;
struct QueNode *next;
};
void init(struct QueNode **p, struct TreeNode *t) {
(*p) = (struct QueNode *)malloc(sizeof(struct QueNode));
(*p)->p = t;
(*p)->next = NULL;
}
int maxDepth(struct TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL) return 0;
struct QueNode *left, *right;
init(&left, root);
right = left;
int ans = 0, sz = 1, tmp = 0;
while (left != NULL) {
tmp = 0;
while (sz > 0) {
if (left->p->left != NULL) {
init(&right->next, left->p->left);
right = right->next;
tmp++;
}
if (left->p->right != NULL) {
init(&right->next, left->p->right);
right = right->next;
tmp++;
}
left = left->next;
sz--;
}
sz += tmp;
ans++;
}
return ans;
}
|
复杂度分析

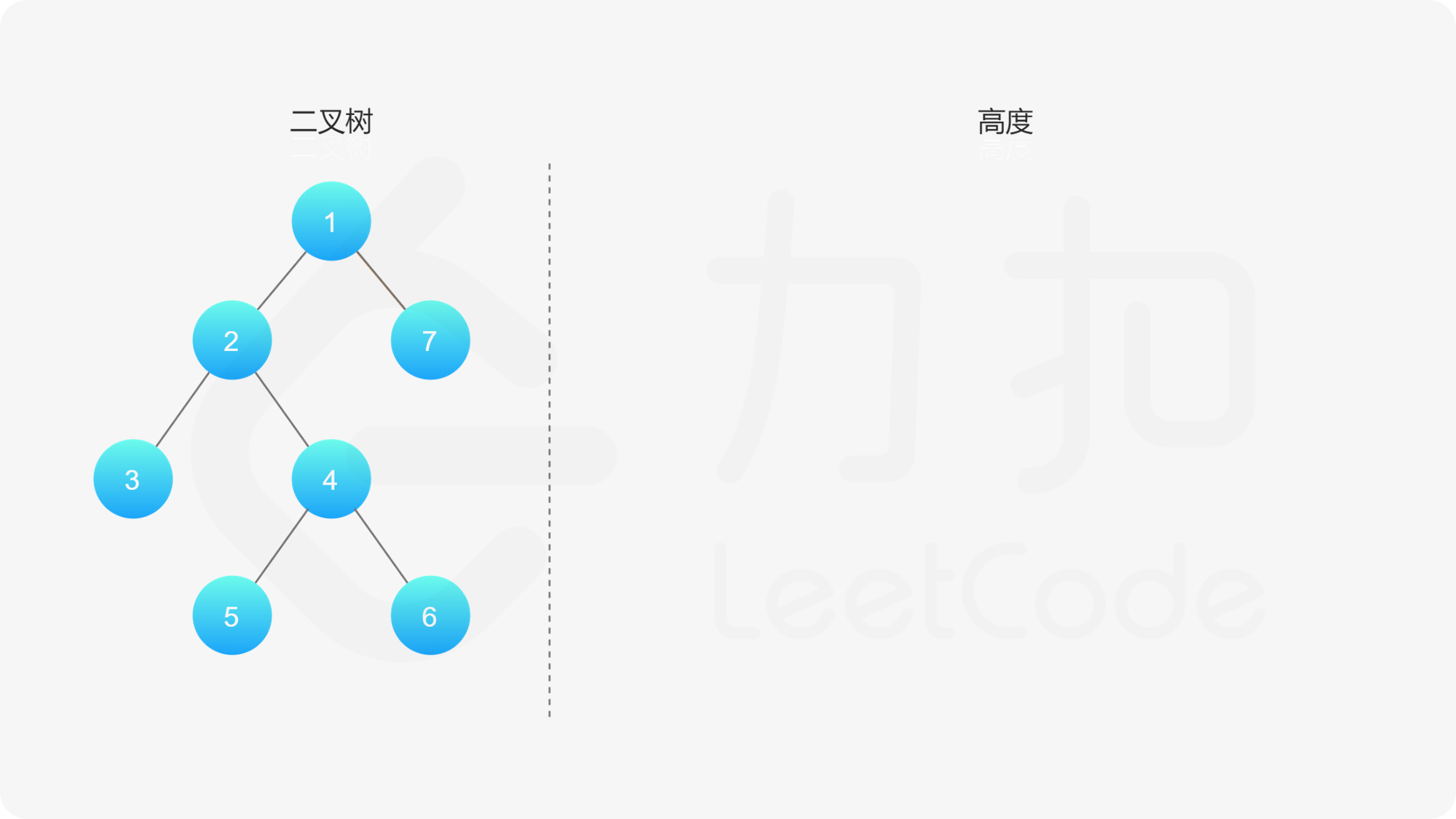 ,
,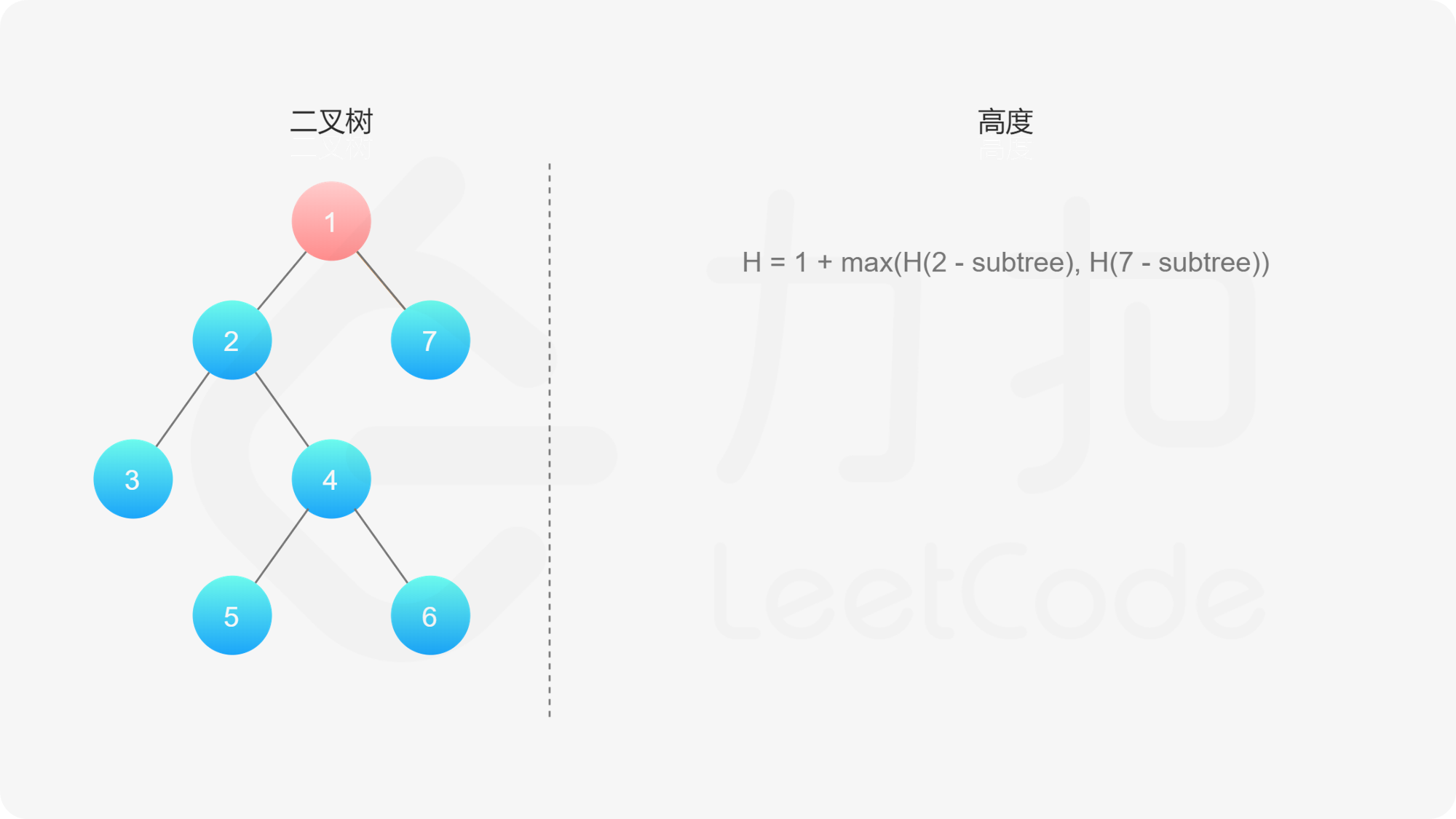 ,
,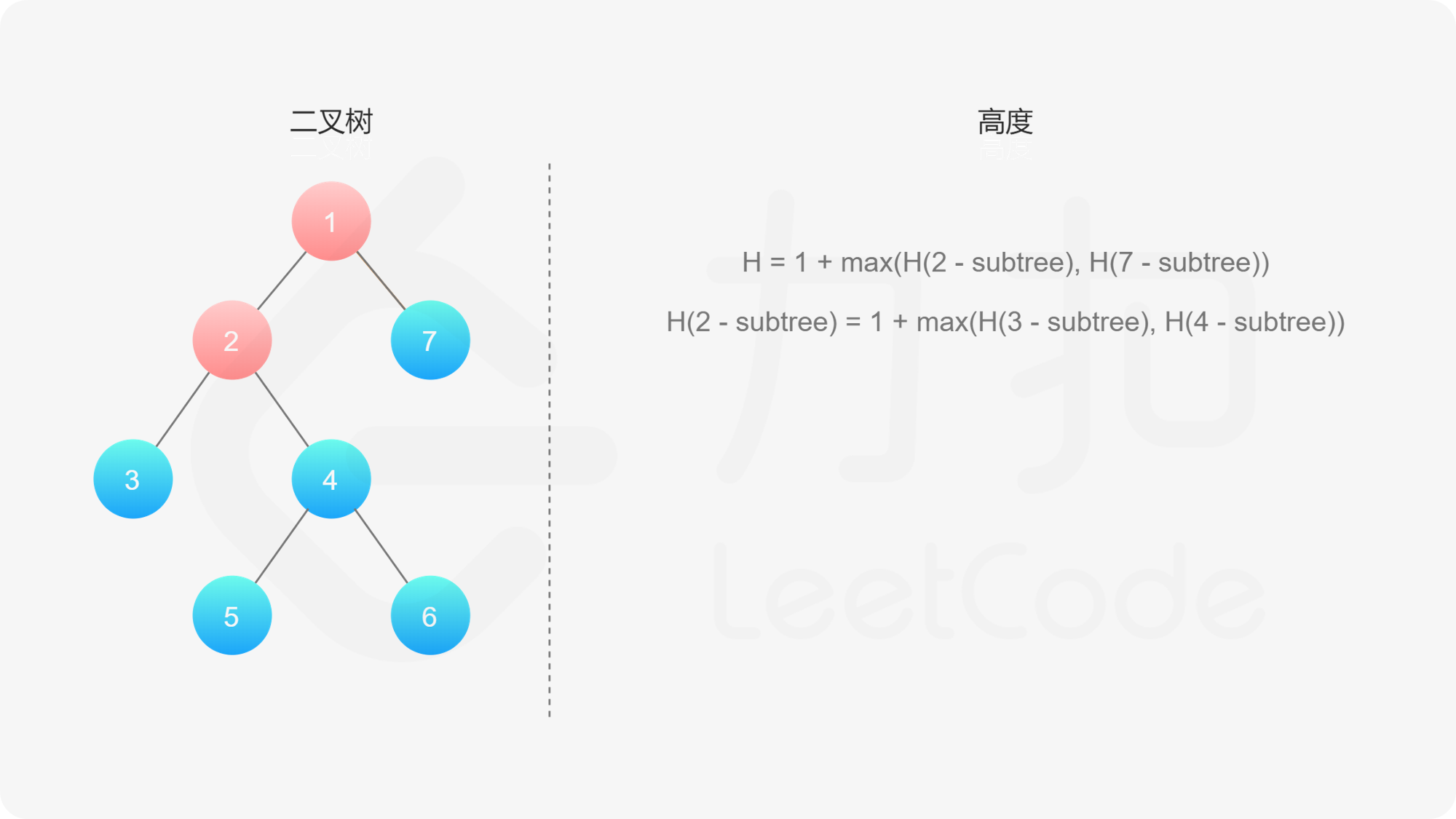 ,
,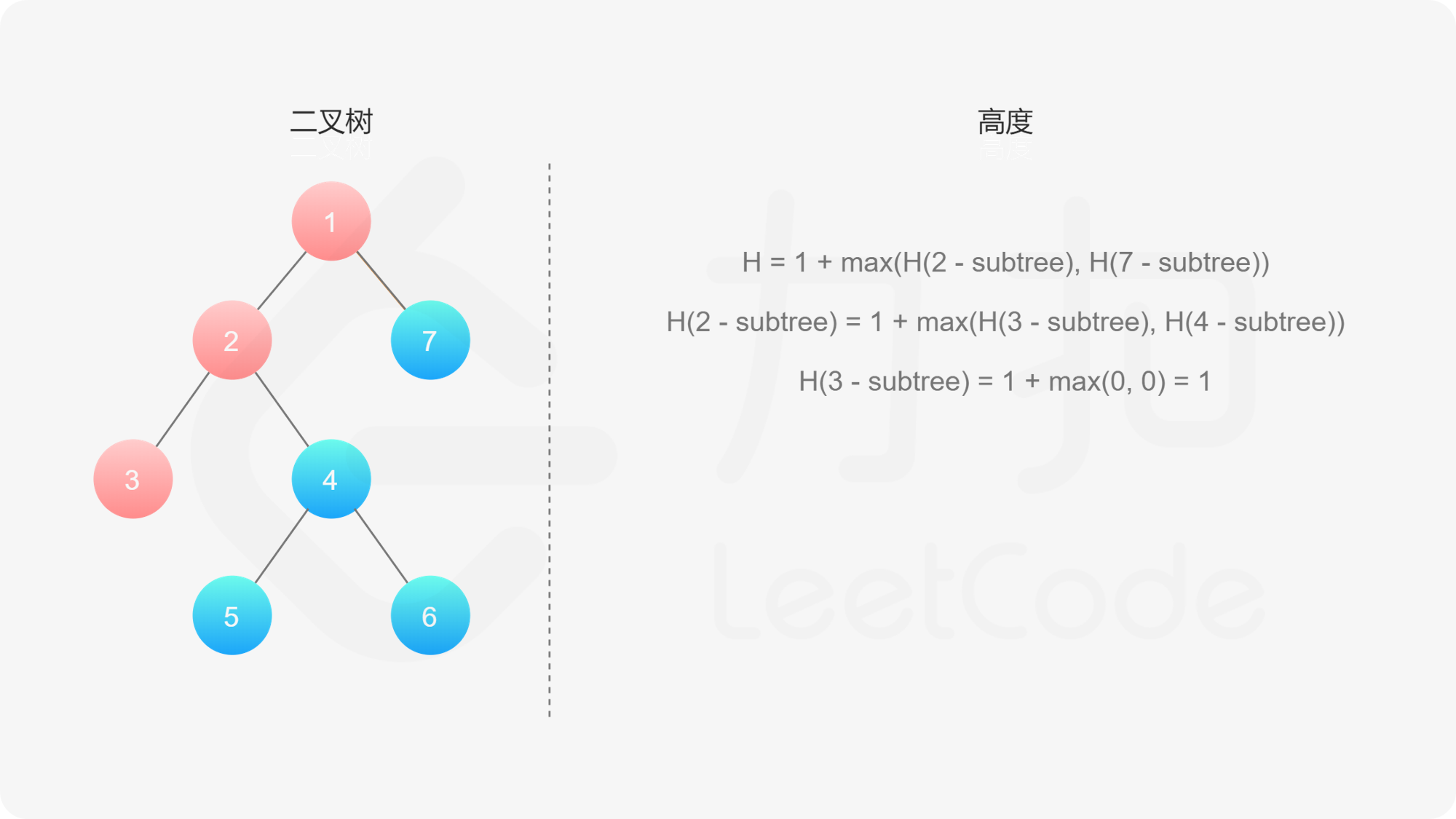 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>