给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个表示目标和的整数 targetSum 。判断该树中是否存在 根节点到叶子节点
的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和 targetSum 。如果存在,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:

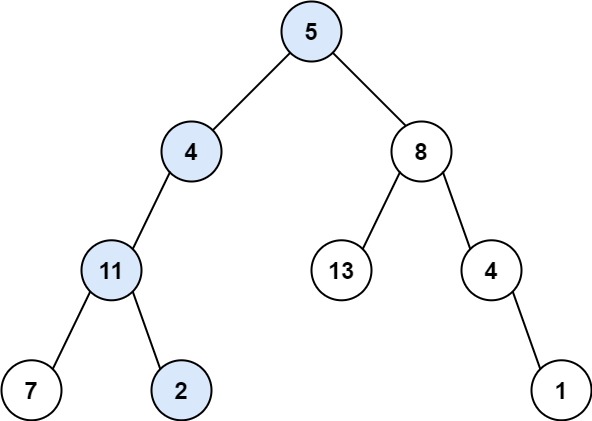
**输入:** root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1], targetSum = 22
**输出:** true
**解释:** 等于目标和的根节点到叶节点路径如上图所示。
示例 2:

**输入:** root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
**输出:** false
**解释:** 树中存在两条根节点到叶子节点的路径:
(1 --> 2): 和为 3
(1 --> 3): 和为 4
不存在 sum = 5 的根节点到叶子节点的路径。
示例 3:
**输入:** root = [], targetSum = 0
**输出:** false
**解释:** 由于树是空的,所以不存在根节点到叶子节点的路径。
提示:
- 树中节点的数目在范围
[0, 5000] 内
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
这个题要背下来!!
DFS
首先是 DFS 解法,该解法的想法是一直向下找到 叶子节点,如果到 叶子节点 时 sum == 0,说明找到了一条符合要求的路径。
我自己第一遍做的时候犯了一个错误,把递归函数写成了下面的解法:
[]1
2
3
4
| def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
if not root:
return sum == 0
return self.hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val)
|
这种代码的错误在,没有判断 root 是否为叶子节点。比如 root 为空的话,题目的意思是要返回 False 的,而上面的代码会返回 sum == 0。又比如,对于测试用例 树为 [1,2], sum = 0 时,上面的结果也会返回为 True,因为对于上述代码,只要左右任意一个孩子的为空时 sum == 0 就返回 True。
当题目中提到了 叶子节点 时,正确的做法一定要同时判断节点的 左右子树同时为空 才是叶子节点。
[]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
class Solution(object):
def hasPathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if not root: return False
if not root.left and not root.right:
return sum == root.val
return self.hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) or self.hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val)
|
[]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if(root == null){
return false;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
return root.val == sum;
}
return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
}
}
|
回溯
这里的回溯指 利用 DFS 找出从根节点到叶子节点的所有路径,只要有任意一条路径的 和 等于 sum,就返回 True。
下面的代码并非是严格意义上的回溯法,因为没有重复利用 path 变量。
[]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
class Solution(object):
def hasPathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if not root: return False
res = []
return self.dfs(root, sum, res, [root.val])
def dfs(self, root, target, res, path):
if not root: return False
if sum(path) == target and not root.left and not root.right:
return True
left_flag, right_flag = False, False
if root.left:
left_flag = self.dfs(root.left, target, res, path + [root.left.val])
if root.right:
right_flag = self.dfs(root.right, target, res, path + [root.right.val])
return left_flag or right_flag
|
BFS
BFS 使用 队列 保存遍历到每个节点时的路径和,如果该节点恰好是叶子节点,并且 路径和 正好等于 sum,说明找到了解。
[]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
class Solution:
def hasPathSum(self, root: TreeNode, sum: int) -> bool:
if not root:
return False
que = collections.deque()
que.append((root, root.val))
while que:
node, path = que.popleft()
if not node.left and not node.right and path == sum:
return True
if node.left:
que.append((node.left, path + node.left.val))
if node.right:
que.append((node.right, path + node.right.val))
return False
|
栈
除了上面的 队列 解法以外,也可以使用 栈,同时保存节点和到这个节点的路径和。但是这个解法已经不是 BFS。因为会优先访问 后进来 的节点,导致会把根节点的右子树访问结束之后,才访问左子树。
可能会有朋友好奇很少见到这种写法,为什么代码可行?答案是:栈中同时保存了 (节点,路径和),也就是说只要能把所有的节点访问一遍,那么就一定能找到正确的结果。无论是用 队列 还是 栈,都是一种 树的遍历 方式,只不过访问顺序有所有不同罢了。
[]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
class Solution(object):
def hasPathSum(self, root, sum):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type sum: int
:rtype: bool
"""
if not root:
return False
stack = []
stack.append((root, root.val))
while stack:
node, path = stack.pop()
if not node.left and not node.right and path == sum:
return True
if node.left:
stack.append((node.left, path + node.left.val))
if node.right:
stack.append((node.right, path + node.right.val))
return False
|