给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
叶子节点 是指没有子节点的节点。
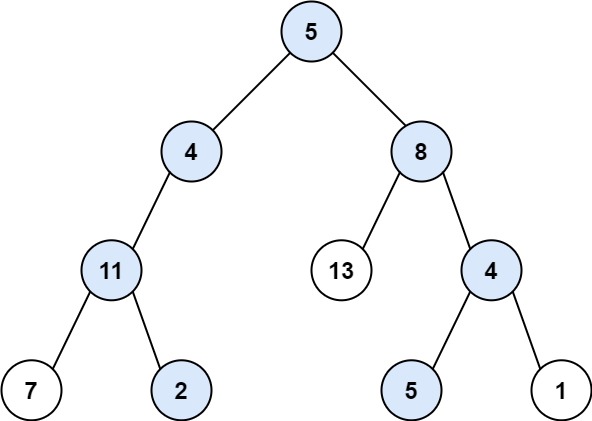
示例 1:

**输入:** root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
**输出:** [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
示例 2:

**输入:** root = [1,2,3], targetSum = 5
**输出:** []
示例 3:
**输入:** root = [1,2], targetSum = 0
**输出:** []
提示:
- 树中节点总数在范围
[0, 5000] 内
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000-1000 <= targetSum <= 1000
前言
注意到本题的要求是,找到所有满足从「根节点」到某个「叶子节点」经过的路径上的节点之和等于目标和的路径。核心思想是对树进行一次遍历,在遍历时记录从根节点到当前节点的路径和,以防止重复计算。
方法一:深度优先搜索
思路及算法
我们可以采用深度优先搜索的方式,枚举每一条从根节点到叶子节点的路径。当我们遍历到叶子节点,且此时路径和恰为目标和时,我们就找到了一条满足条件的路径。
代码
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<int> path;
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return;
}
path.emplace_back(root->val);
targetSum -= root->val;
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr && targetSum == 0) {
ret.emplace_back(path);
}
dfs(root->left, targetSum);
dfs(root->right, targetSum);
path.pop_back();
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root, targetSum);
return ret;
}
};
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root, targetSum);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
path.offerLast(root.val);
targetSum -= root.val;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == 0) {
ret.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(path));
}
dfs(root.left, targetSum);
dfs(root.right, targetSum);
path.pollLast();
}
}
|
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
ret = list()
path = list()
def dfs(root: TreeNode, targetSum: int):
if not root:
return
path.append(root.val)
targetSum -= root.val
if not root.left and not root.right and targetSum == 0:
ret.append(path[:])
dfs(root.left, targetSum)
dfs(root.right, targetSum)
path.pop()
dfs(root, targetSum)
return ret
|
[sol1-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| func pathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) (ans [][]int) {
path := []int{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int)
dfs = func(node *TreeNode, left int) {
if node == nil {
return
}
left -= node.Val
path = append(path, node.Val)
defer func() { path = path[:len(path)-1] }()
if node.Left == nil && node.Right == nil && left == 0 {
ans = append(ans, append([]int(nil), path...))
return
}
dfs(node.Left, left)
dfs(node.Right, left)
}
dfs(root, targetSum)
return
}
|
[sol1-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| int** ret;
int retSize;
int* retColSize;
int* path;
int pathSize;
void dfs(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
path[pathSize++] = root->val;
targetSum -= root->val;
if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL && targetSum == 0) {
int* tmp = malloc(sizeof(int) * pathSize);
memcpy(tmp, path, sizeof(int) * pathSize);
ret[retSize] = tmp;
retColSize[retSize++] = pathSize;
}
dfs(root->left, targetSum);
dfs(root->right, targetSum);
pathSize--;
}
int** pathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) {
ret = malloc(sizeof(int*) * 2001);
retColSize = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2001);
path = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2001);
retSize = pathSize = 0;
dfs(root, targetSum);
*returnColumnSizes = retColSize;
*returnSize = retSize;
return ret;
}
|
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(N^2)$,其中 $N$ 是树的节点数。在最坏情况下,树的上半部分为链状,下半部分为完全二叉树,并且从根节点到每一个叶子节点的路径都符合题目要求。此时,路径的数目为 $O(N)$,并且每一条路径的节点个数也为 $O(N)$,因此要将这些路径全部添加进答案中,时间复杂度为 $O(N^2)$。
空间复杂度:$O(N)$,其中 $N$ 是树的节点数。空间复杂度主要取决于栈空间的开销,栈中的元素个数不会超过树的节点数。
方法二:广度优先搜索
思路及算法
我们也可以采用广度优先搜索的方式,遍历这棵树。当我们遍历到叶子节点,且此时路径和恰为目标和时,我们就找到了一条满足条件的路径。
为了节省空间,我们使用哈希表记录树中的每一个节点的父节点。每次找到一个满足条件的节点,我们就从该节点出发不断向父节点迭代,即可还原出从根节点到当前节点的路径。
代码
[sol2-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
| class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ret;
unordered_map<TreeNode*, TreeNode*> parent;
void getPath(TreeNode* node) {
vector<int> tmp;
while (node != nullptr) {
tmp.emplace_back(node->val);
node = parent[node];
}
reverse(tmp.begin(), tmp.end());
ret.emplace_back(tmp);
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return ret;
}
queue<TreeNode*> que_node;
queue<int> que_sum;
que_node.emplace(root);
que_sum.emplace(0);
while (!que_node.empty()) {
TreeNode* node = que_node.front();
que_node.pop();
int rec = que_sum.front() + node->val;
que_sum.pop();
if (node->left == nullptr && node->right == nullptr) {
if (rec == targetSum) {
getPath(node);
}
} else {
if (node->left != nullptr) {
parent[node->left] = node;
que_node.emplace(node->left);
que_sum.emplace(rec);
}
if (node->right != nullptr) {
parent[node->right] = node;
que_node.emplace(node->right);
que_sum.emplace(rec);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
};
|
[sol2-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
Map<TreeNode, TreeNode> map = new HashMap<TreeNode, TreeNode>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) {
return ret;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queueNode = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<Integer> queueSum = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queueNode.offer(root);
queueSum.offer(0);
while (!queueNode.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queueNode.poll();
int rec = queueSum.poll() + node.val;
if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
if (rec == targetSum) {
getPath(node);
}
} else {
if (node.left != null) {
map.put(node.left, node);
queueNode.offer(node.left);
queueSum.offer(rec);
}
if (node.right != null) {
map.put(node.right, node);
queueNode.offer(node.right);
queueSum.offer(rec);
}
}
}
return ret;
}
public void getPath(TreeNode node) {
List<Integer> temp = new LinkedList<Integer>();
while (node != null) {
temp.add(node.val);
node = map.get(node);
}
Collections.reverse(temp);
ret.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(temp));
}
}
|
[sol2-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| class Solution:
def pathSum(self, root: TreeNode, targetSum: int) -> List[List[int]]:
ret = list()
parent = collections.defaultdict(lambda: None)
def getPath(node: TreeNode):
tmp = list()
while node:
tmp.append(node.val)
node = parent[node]
ret.append(tmp[::-1])
if not root:
return ret
que_node = collections.deque([root])
que_total = collections.deque([0])
while que_node:
node = que_node.popleft()
rec = que_total.popleft() + node.val
if not node.left and not node.right:
if rec == targetSum:
getPath(node)
else:
if node.left:
parent[node.left] = node
que_node.append(node.left)
que_total.append(rec)
if node.right:
parent[node.right] = node
que_node.append(node.right)
que_total.append(rec)
return ret
|
[sol2-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| type pair struct {
node *TreeNode
left int
}
func pathSum(root *TreeNode, targetSum int) (ans [][]int) {
if root == nil {
return
}
parent := map[*TreeNode]*TreeNode{}
getPath := func(node *TreeNode) (path []int) {
for ; node != nil; node = parent[node] {
path = append(path, node.Val)
}
for i, j := 0, len(path)-1; i < j; i++ {
path[i], path[j] = path[j], path[i]
j--
}
return
}
queue := []pair{{root, targetSum}}
for len(queue) > 0 {
p := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
node := p.node
left := p.left - node.Val
if node.Left == nil && node.Right == nil {
if left == 0 {
ans = append(ans, getPath(node))
}
} else {
if node.Left != nil {
parent[node.Left] = node
queue = append(queue, pair{node.Left, left})
}
if node.Right != nil {
parent[node.Right] = node
queue = append(queue, pair{node.Right, left})
}
}
}
return
}
|
[sol2-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
| int** ret;
int retSize;
int* retColSize;
int* path;
int pathSize;
typedef struct {
struct TreeNode* key;
struct TreeNode* val;
UT_hash_handle hh;
} hashTable;
hashTable* parent;
void insertHashTable(struct TreeNode* x, struct TreeNode* y) {
hashTable* rec = malloc(sizeof(hashTable));
rec->key = x;
rec->val = y;
HASH_ADD_PTR(parent, key, rec);
}
struct TreeNode* queryHashTable(struct TreeNode* x) {
hashTable* rec;
HASH_FIND_PTR(parent, &x, rec);
return rec->val;
}
void getPath(struct TreeNode* node) {
int* tmp = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2001);
int tmpSize = 0;
while (node != NULL) {
tmp[tmpSize++] = node->val;
node = queryHashTable(node);
}
for (int i = 0; i < tmpSize / 2; i++) {
int t = tmp[i];
tmp[i] = tmp[tmpSize - 1 - i], tmp[tmpSize - 1 - i] = t;
}
ret[retSize] = tmp;
retColSize[retSize++] = tmpSize;
}
int** pathSum(struct TreeNode* root, int targetSum, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes) {
ret = malloc(sizeof(int*) * 2001);
retColSize = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2001);
path = malloc(sizeof(int) * 2001);
retSize = pathSize = 0;
parent = NULL;
insertHashTable(root, NULL);
if (root == NULL) {
*returnColumnSizes = retColSize;
*returnSize = retSize;
return ret;
}
struct TreeNode* que_node[10001];
int que_sum[10001];
int left = 0, right = 0;
que_node[right] = root;
que_sum[right++] = 0;
while (left < right) {
struct TreeNode* node = que_node[left];
int rec = que_sum[left++] + node->val;
if (node->left == NULL && node->right == NULL) {
if (rec == targetSum) {
getPath(node);
}
} else {
if (node->left != NULL) {
insertHashTable(node->left, node);
que_node[right] = node->left;
que_sum[right++] = rec;
}
if (node->right != NULL) {
insertHashTable(node->right, node);
que_node[right] = node->right;
que_sum[right++] = rec;
}
}
}
*returnColumnSizes = retColSize;
*returnSize = retSize;
return ret;
}
|
复杂度分析