给你一个长度为 n 的链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针 random ,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
构造这个链表的 深拷贝 n 个 全新 节点组成,其中每个新节点的值都设为其对应的原节点的值。新节点的 next 指针和 random复制链表中的指针都不应指向原链表中的节点 。
例如,如果原链表中有 X 和 Y 两个节点,其中 X.random --> Y 。那么在复制链表中对应的两个节点 x 和 y ,同样有x.random --> y 。
返回复制链表的头节点。
用一个由 n 个节点组成的链表来表示输入/输出中的链表。每个节点用一个 [val, random_index] 表示:
val:一个表示 Node.val 的整数。random_index:随机指针指向的节点索引(范围从 0 到 n-1);如果不指向任何节点,则为 null 。
你的代码 只 接受原链表的头节点 head 作为传入参数。
示例 1:
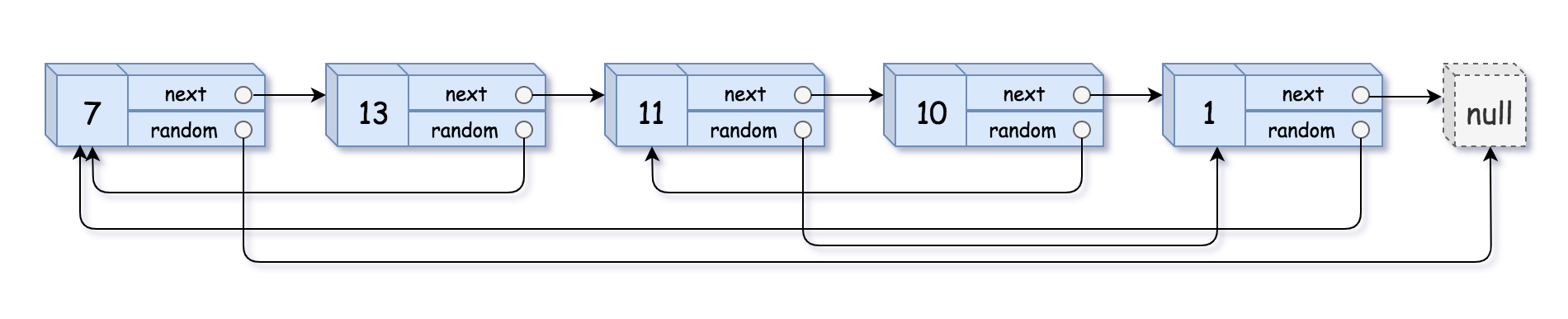
**输入:** head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
**输出:** [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
示例 2:
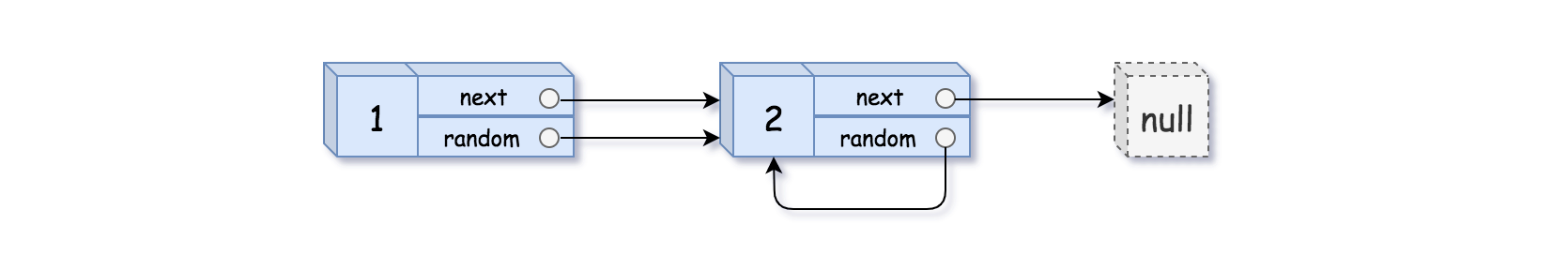
**输入:** head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
**输出:** [[1,1],[2,1]]
示例 3:
 { if (head == nullptr ) { return nullptr ; } if (!cachedNode.count (head)) { Node* headNew = new Node (head->val); cachedNode[head] = headNew; headNew->next = copyRandomList (head->next); headNew->random = copyRandomList (head->random); } return cachedNode[head]; } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 class Solution { Map<Node, Node> cachedNode = new HashMap <Node, Node>(); public Node copyRandomList (Node head) { if (head == null ) { return null ; } if (!cachedNode.containsKey(head)) { Node headNew = new Node (head.val); cachedNode.put(head, headNew); headNew.next = copyRandomList(head.next); headNew.random = copyRandomList(head.random); } return cachedNode.get(head); } }
[sol1-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public class Solution { Dictionary<Node, Node> cachedNode = new Dictionary<Node, Node>(); public Node CopyRandomList (Node head ) if (head == null ) { return null ; } if (!cachedNode.ContainsKey(head)) { Node headNew = new Node(head.val); cachedNode.Add(head, headNew); headNew.next = CopyRandomList(head.next); headNew.random = CopyRandomList(head.random); } return cachedNode[head]; } }
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 var copyRandomList = function (head, cachedNode = new Map () ) { if (head === null ) { return null ; } if (!cachedNode.has (head)) { cachedNode.set (head, {val : head.val }), Object .assign (cachedNode.get (head), {next : copyRandomList (head.next , cachedNode), random : copyRandomList (head.random , cachedNode)}) } return cachedNode.get (head); }
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 var cachedNode map [*Node]*Nodefunc deepCopy (node *Node) if node == nil { return nil } if n, has := cachedNode[node]; has { return n } newNode := &Node{Val: node.Val} cachedNode[node] = newNode newNode.Next = deepCopy(node.Next) newNode.Random = deepCopy(node.Random) return newNode } func copyRandomList (head *Node) cachedNode = map [*Node]*Node{} return deepCopy(head) }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 struct HashTable { struct Node *key , *val ; UT_hash_handle hh; } * cachedNode; struct Node* deepCopy (struct Node* head) { if (head == NULL ) { return NULL ; } struct HashTable * tmp ; HASH_FIND_PTR(cachedNode, &head, tmp); if (tmp == NULL ) { struct Node * headNew =malloc (sizeof (struct Node)); headNew->val = head->val; tmp = malloc (sizeof (struct HashTable)); tmp->key = head, tmp->val = headNew; HASH_ADD_PTR(cachedNode, key, tmp); headNew->next = deepCopy(head->next); headNew->random = deepCopy(head->random); } return tmp->val; } struct Node* copyRandomList (struct Node* head) { cachedNode = NULL ; return deepCopy(head); }
复杂度分析
方法二:迭代 + 节点拆分 思路及算法
注意到方法一需要使用哈希表记录每一个节点对应新节点的创建情况,而我们可以使用一个小技巧来省去哈希表的空间。
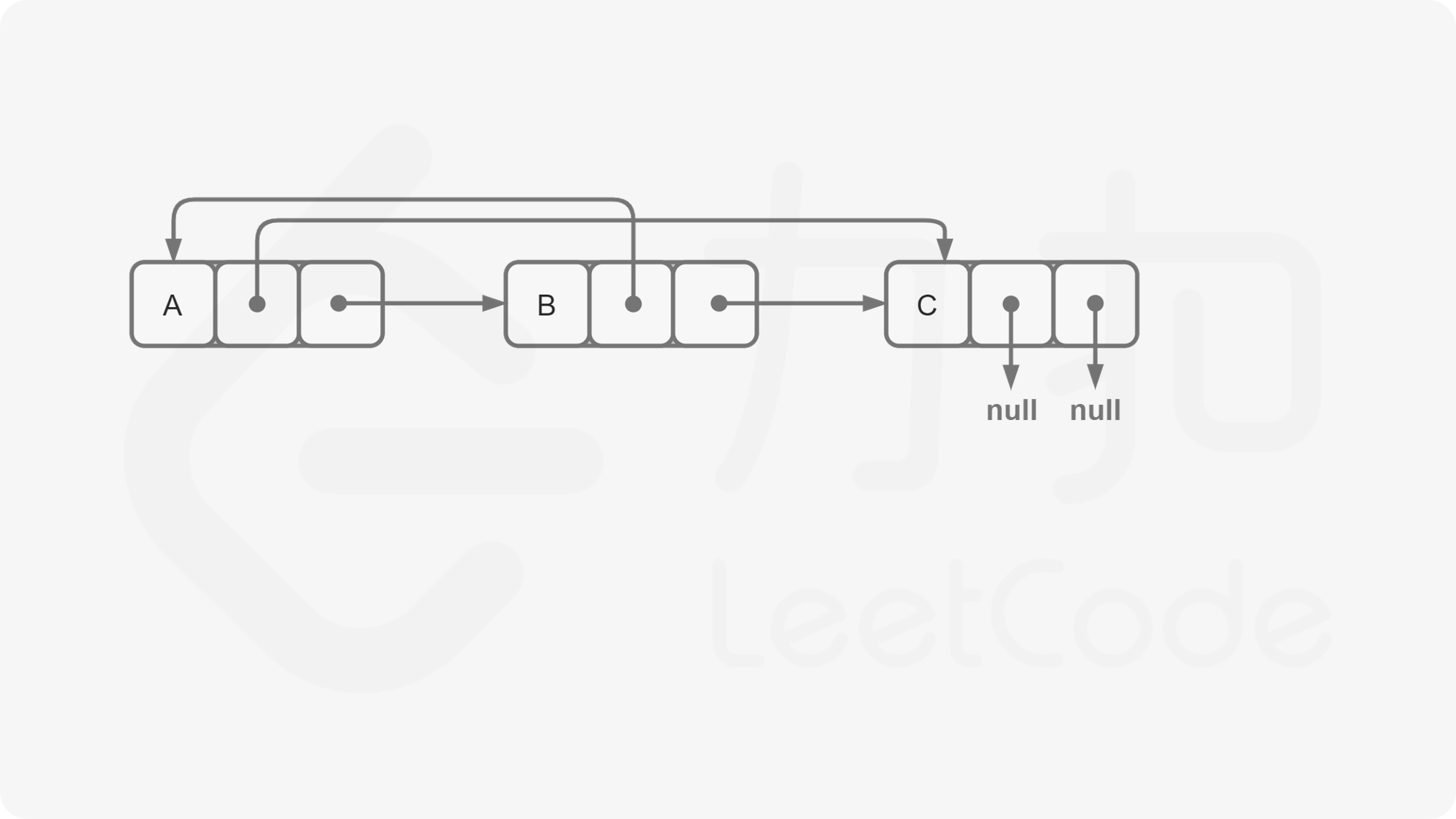
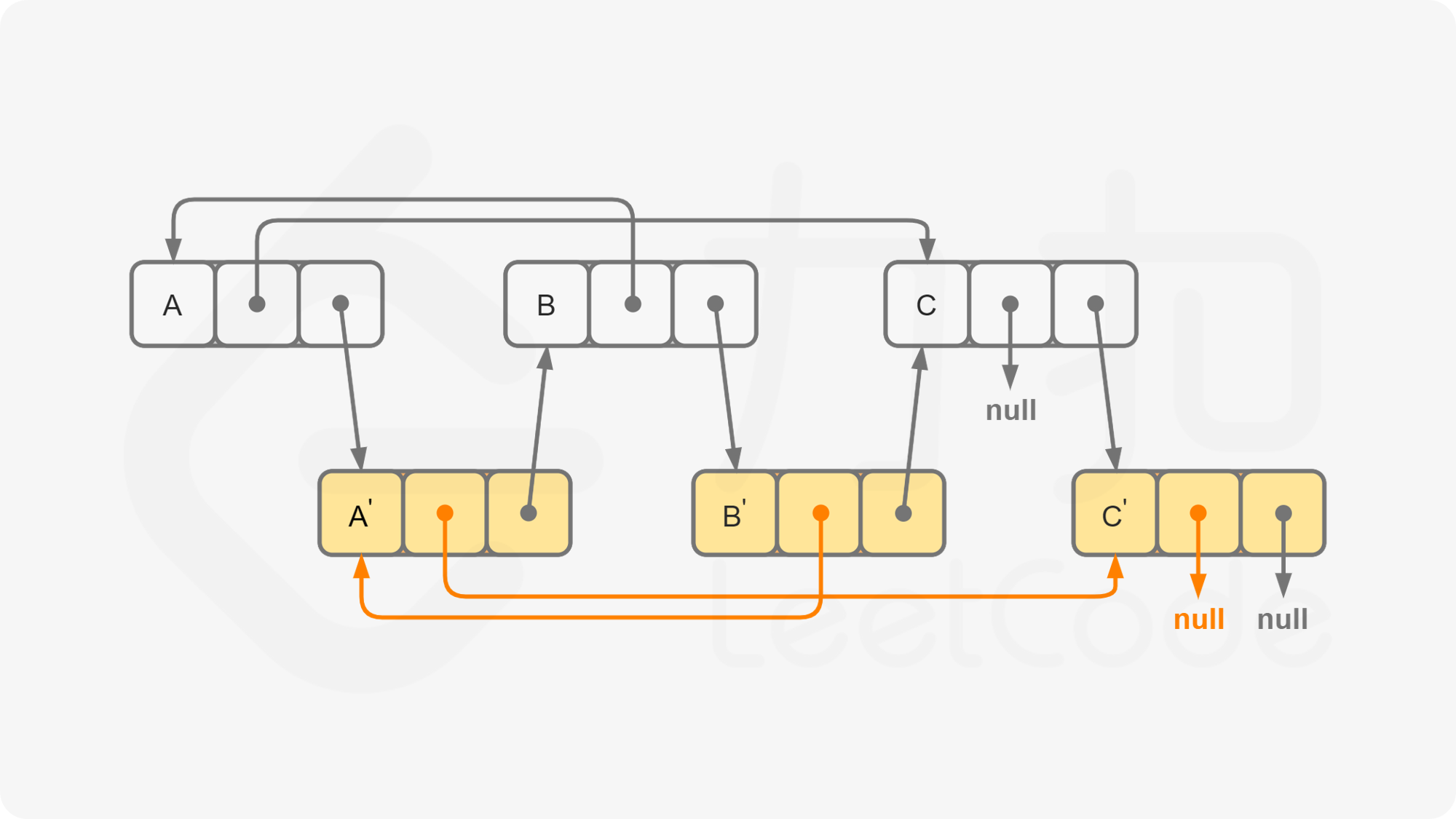
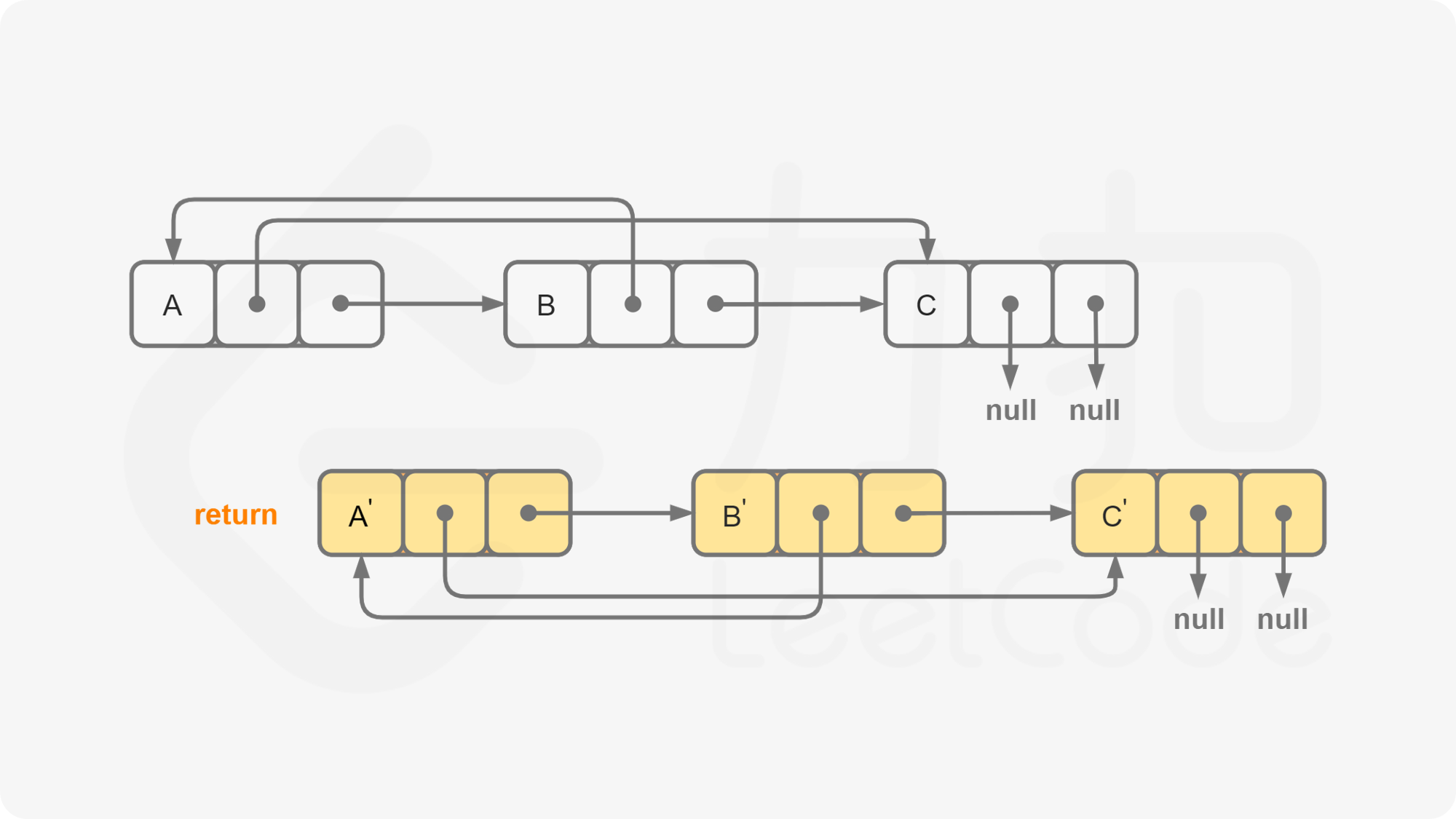
我们首先将该链表中每一个节点拆分为两个相连的节点,例如对于链表 $A \rightarrow B \rightarrow C$,我们可以将其拆分为 $A \rightarrow A’ \rightarrow B \rightarrow B’ \rightarrow C \rightarrow C’$。对于任意一个原节点 $S$,其拷贝节点 $S’$ 即为其后继节点。
这样,我们可以直接找到每一个拷贝节点 $S’$ 的随机指针应当指向的节点,即为其原节点 $S$ 的随机指针指向的节点 $T$ 的后继节点 $T’$。需要注意原节点的随机指针可能为空,我们需要特别判断这种情况。
当我们完成了拷贝节点的随机指针的赋值,我们只需要将这个链表按照原节点与拷贝节点的种类进行拆分即可,只需要遍历一次。同样需要注意最后一个拷贝节点的后继节点为空,我们需要特别判断这种情况。
<
代码
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public : Node* copyRandomList (Node* head) { if (head == nullptr ) { return nullptr ; } for (Node* node = head; node != nullptr ; node = node->next->next) { Node* nodeNew = new Node (node->val); nodeNew->next = node->next; node->next = nodeNew; } for (Node* node = head; node != nullptr ; node = node->next->next) { Node* nodeNew = node->next; nodeNew->random = (node->random != nullptr ) ? node->random->next : nullptr ; } Node* headNew = head->next; for (Node* node = head; node != nullptr ; node = node->next) { Node* nodeNew = node->next; node->next = node->next->next; nodeNew->next = (nodeNew->next != nullptr ) ? nodeNew->next->next : nullptr ; } return headNew; } };
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { public Node copyRandomList (Node head) { if (head == null ) { return null ; } for (Node node = head; node != null ; node = node.next.next) { Node nodeNew = new Node (node.val); nodeNew.next = node.next; node.next = nodeNew; } for (Node node = head; node != null ; node = node.next.next) { Node nodeNew = node.next; nodeNew.random = (node.random != null ) ? node.random.next : null ; } Node headNew = head.next; for (Node node = head; node != null ; node = node.next) { Node nodeNew = node.next; node.next = node.next.next; nodeNew.next = (nodeNew.next != null ) ? nodeNew.next.next : null ; } return headNew; } }
[sol2-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Solution { public Node CopyRandomList (Node head ) if (head == null ) { return null ; } for (Node node = head; node != null ; node = node.next.next) { Node nodeNew = new Node(node.val); nodeNew.next = node.next; node.next = nodeNew; } for (Node node = head; node != null ; node = node.next.next) { Node nodeNew = node.next; nodeNew.random = (node.random != null ) ? node.random.next : null ; } Node headNew = head.next; for (Node node = head; node != null ; node = node.next) { Node nodeNew = node.next; node.next = node.next.next; nodeNew.next = (nodeNew.next != null ) ? nodeNew.next.next : null ; } return headNew; } }
[sol2-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 var copyRandomList = function (head ) { if (head === null ) { return null ; } for (let node = head; node !== null ; node = node.next .next ) { const nodeNew = new Node (node.val , node.next , null ); node.next = nodeNew; } for (let node = head; node !== null ; node = node.next .next ) { const nodeNew = node.next ; nodeNew.random = (node.random !== null ) ? node.random .next : null ; } const headNew = head.next ; for (let node = head; node !== null ; node = node.next ) { const nodeNew = node.next ; node.next = node.next .next ; nodeNew.next = (nodeNew.next !== null ) ? nodeNew.next .next : null ; } return headNew; };
[sol2-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 func copyRandomList (head *Node) if head == nil { return nil } for node := head; node != nil ; node = node.Next.Next { node.Next = &Node{Val: node.Val, Next: node.Next} } for node := head; node != nil ; node = node.Next.Next { if node.Random != nil { node.Next.Random = node.Random.Next } } headNew := head.Next for node := head; node != nil ; node = node.Next { nodeNew := node.Next node.Next = node.Next.Next if nodeNew.Next != nil { nodeNew.Next = nodeNew.Next.Next } } return headNew }
[sol2-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 struct Node* copyRandomList (struct Node* head) { if (head == NULL ) { return NULL ; } for (struct Node* node = head; node != NULL ; node = node->next->next) { struct Node * nodeNew =malloc (sizeof (struct Node)); nodeNew->val = node->val; nodeNew->next = node->next; node->next = nodeNew; } for (struct Node* node = head; node != NULL ; node = node->next->next) { struct Node * nodeNew = nodeNew->random = (node->random != NULL ) ? node->random->next : NULL ; } struct Node * headNew = for (struct Node* node = head; node != NULL ; node = node->next) { struct Node * nodeNew = node->next = node->next->next; nodeNew->next = (nodeNew->next != NULL ) ? nodeNew->next->next : NULL ; } return headNew; }
复杂度分析
 ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>