给你一个整数 n ,请你找出并返回第 n 个 丑数 。
丑数 就是只包含质因数 2、3 和/或 5 的正整数。
示例 1:
**输入:** n = 10
**输出:** 12
**解释:** [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12] 是由前 10 个丑数组成的序列。
示例 2:
**输入:** n = 1
**输出:** 1
**解释:** 1 通常被视为丑数。
提示:
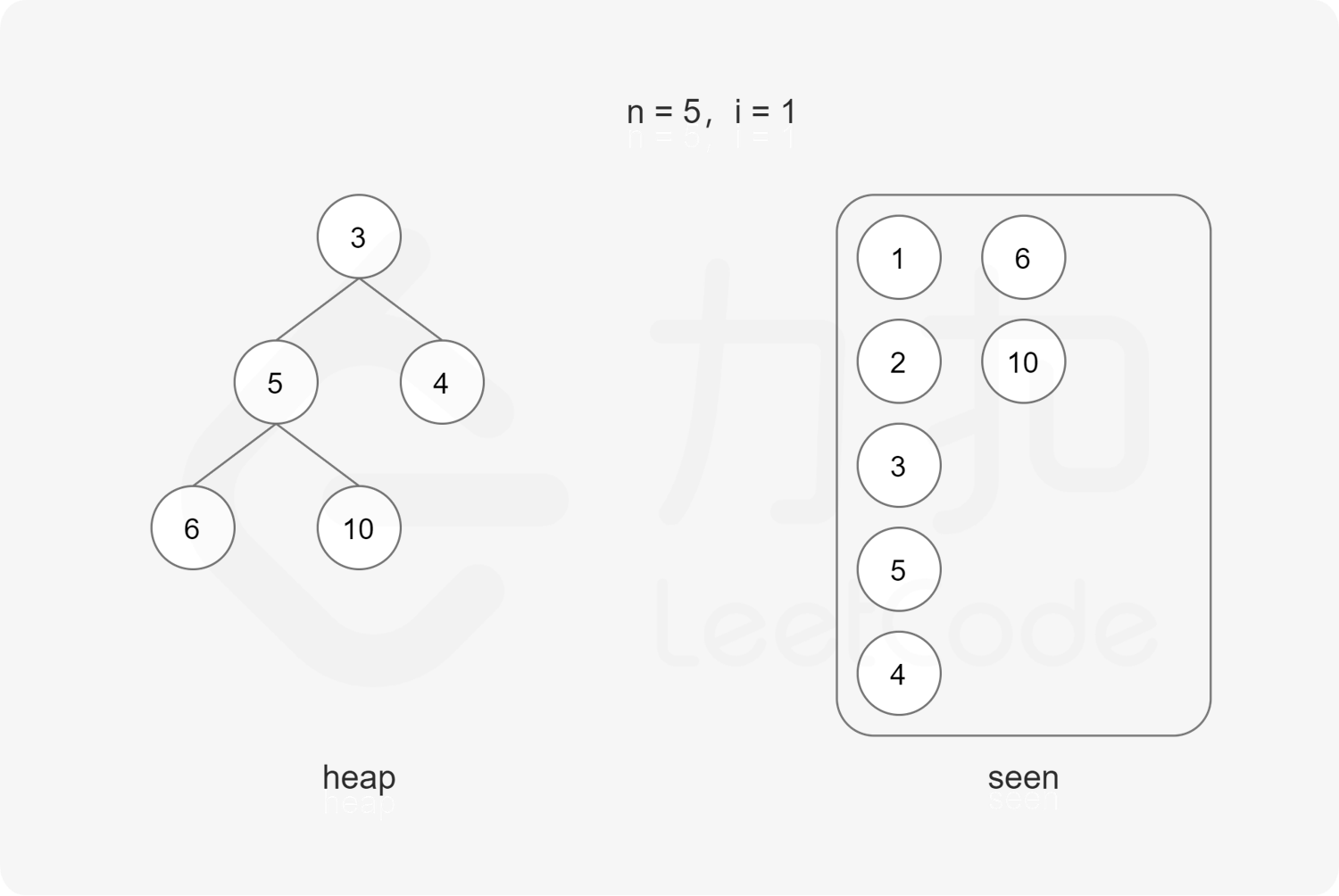
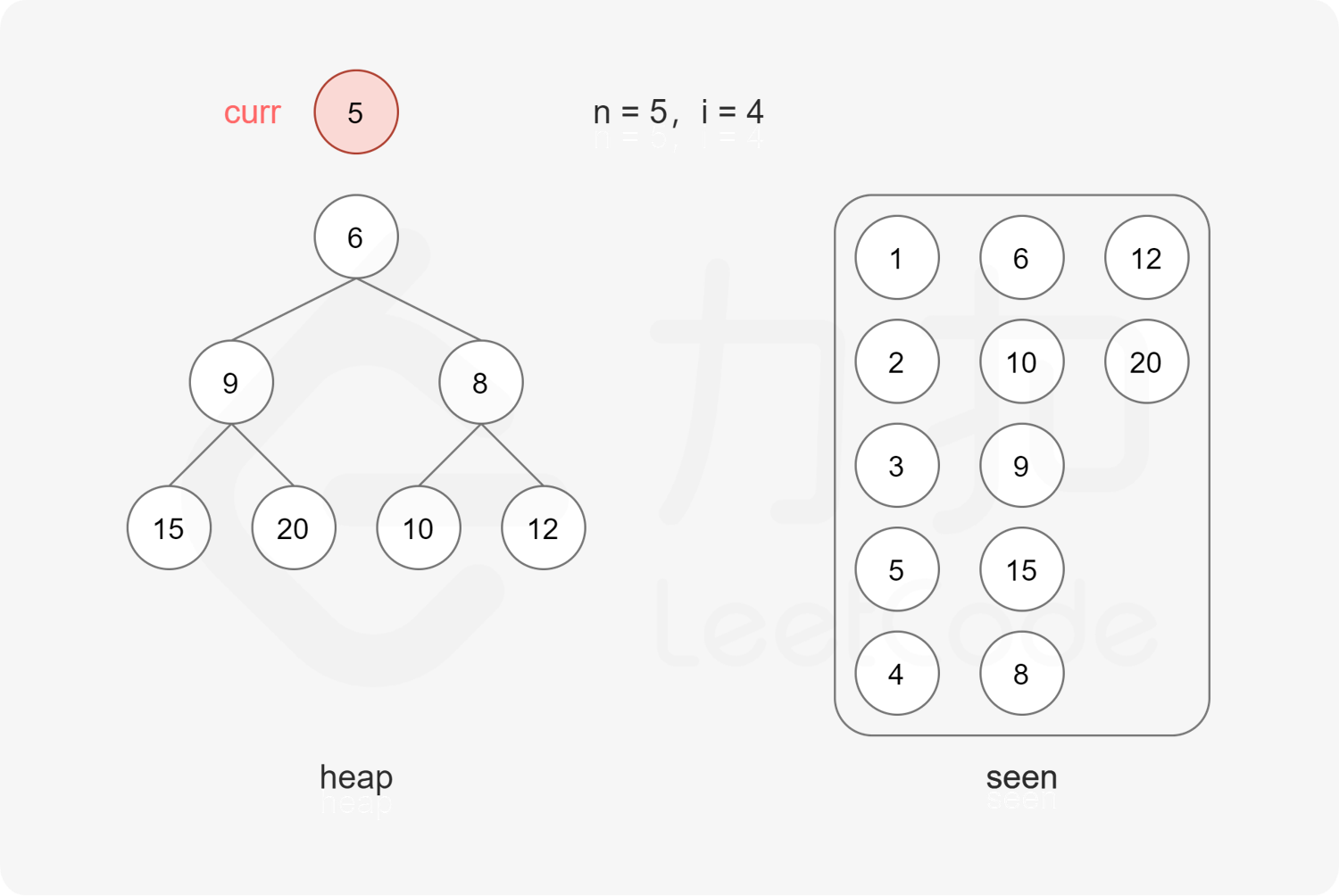
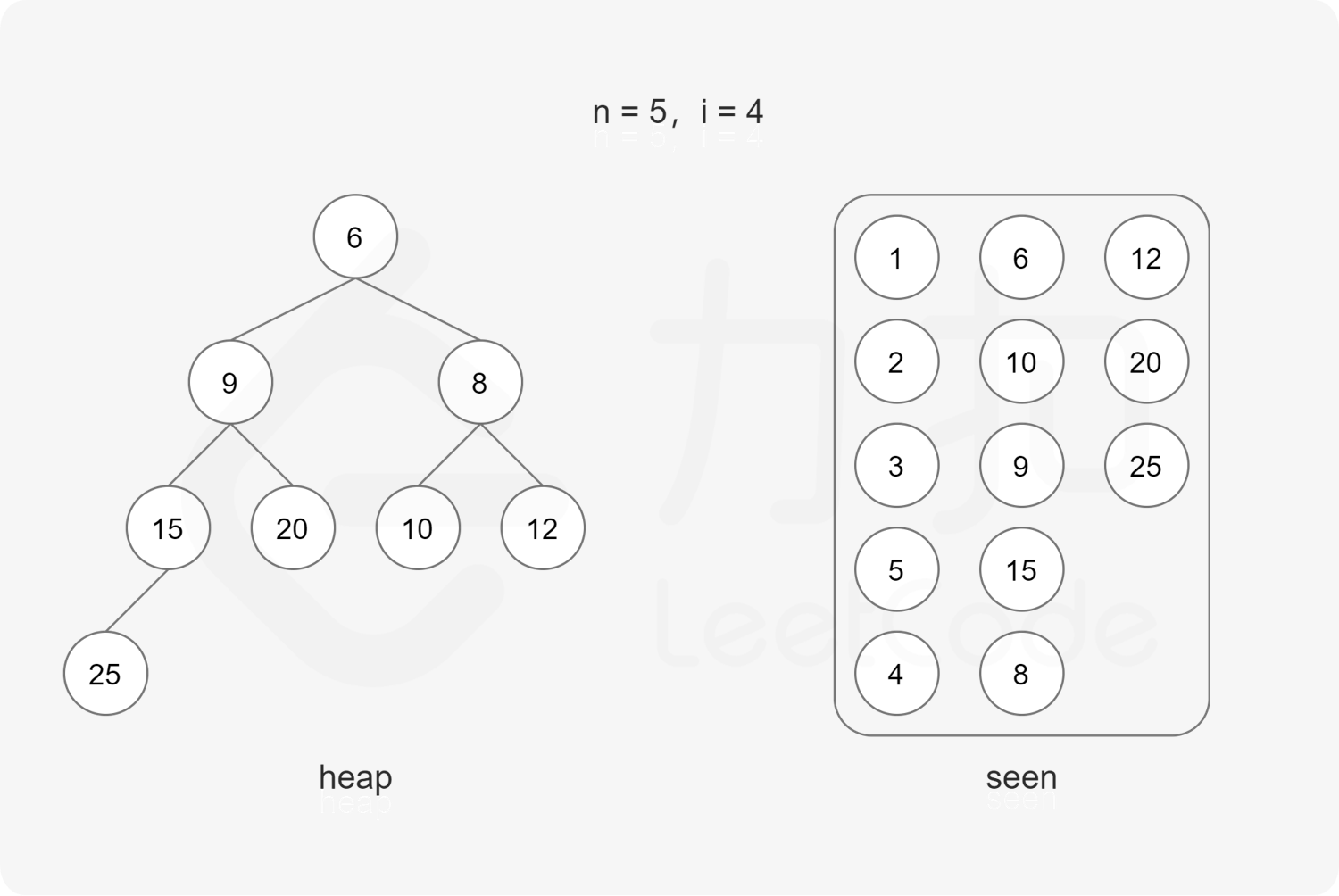
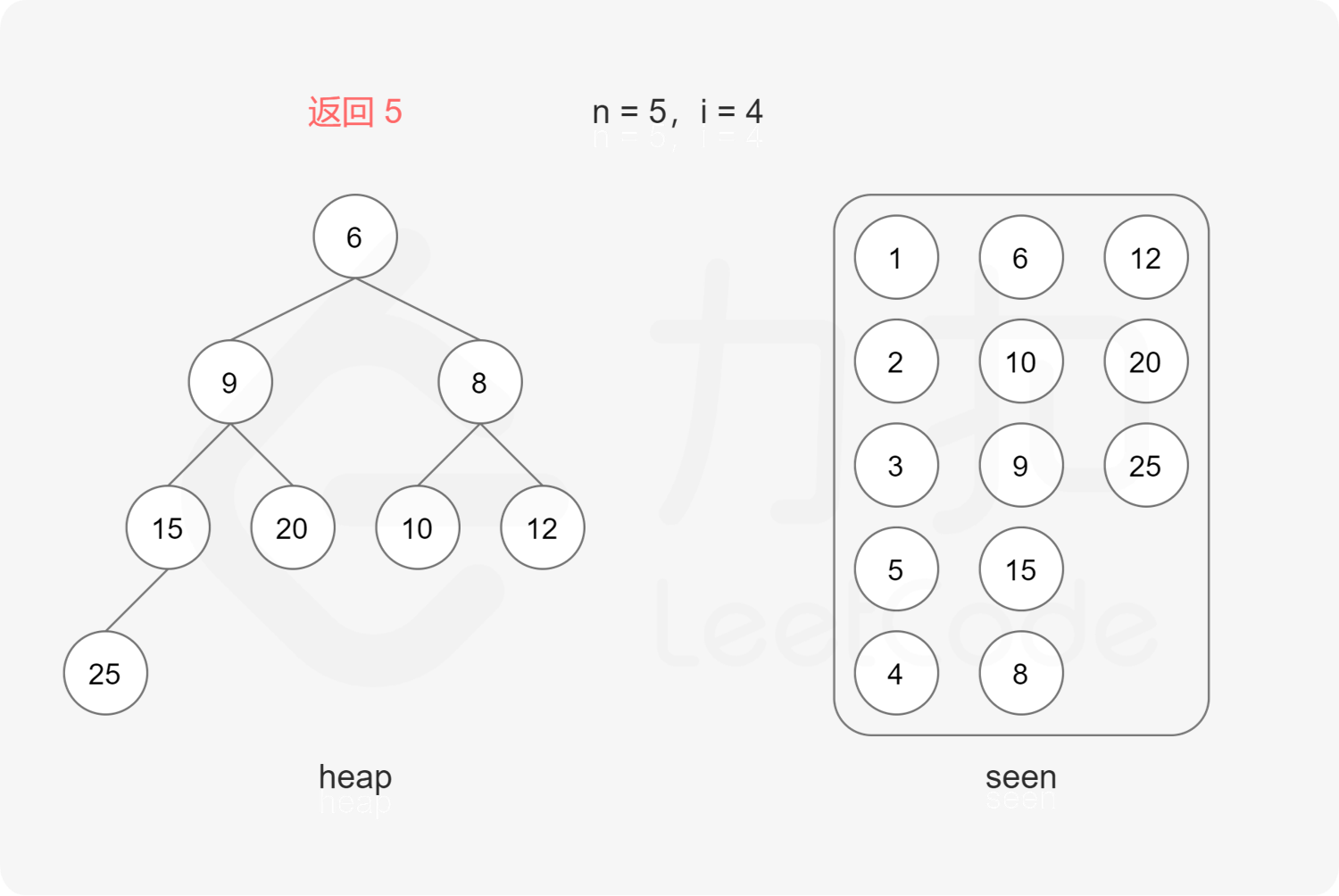
方法一:最小堆 要得到从小到大的第 $n$ 个丑数,可以使用最小堆 实现。
初始时堆为空。首先将最小的丑数 $1$ 加入堆。
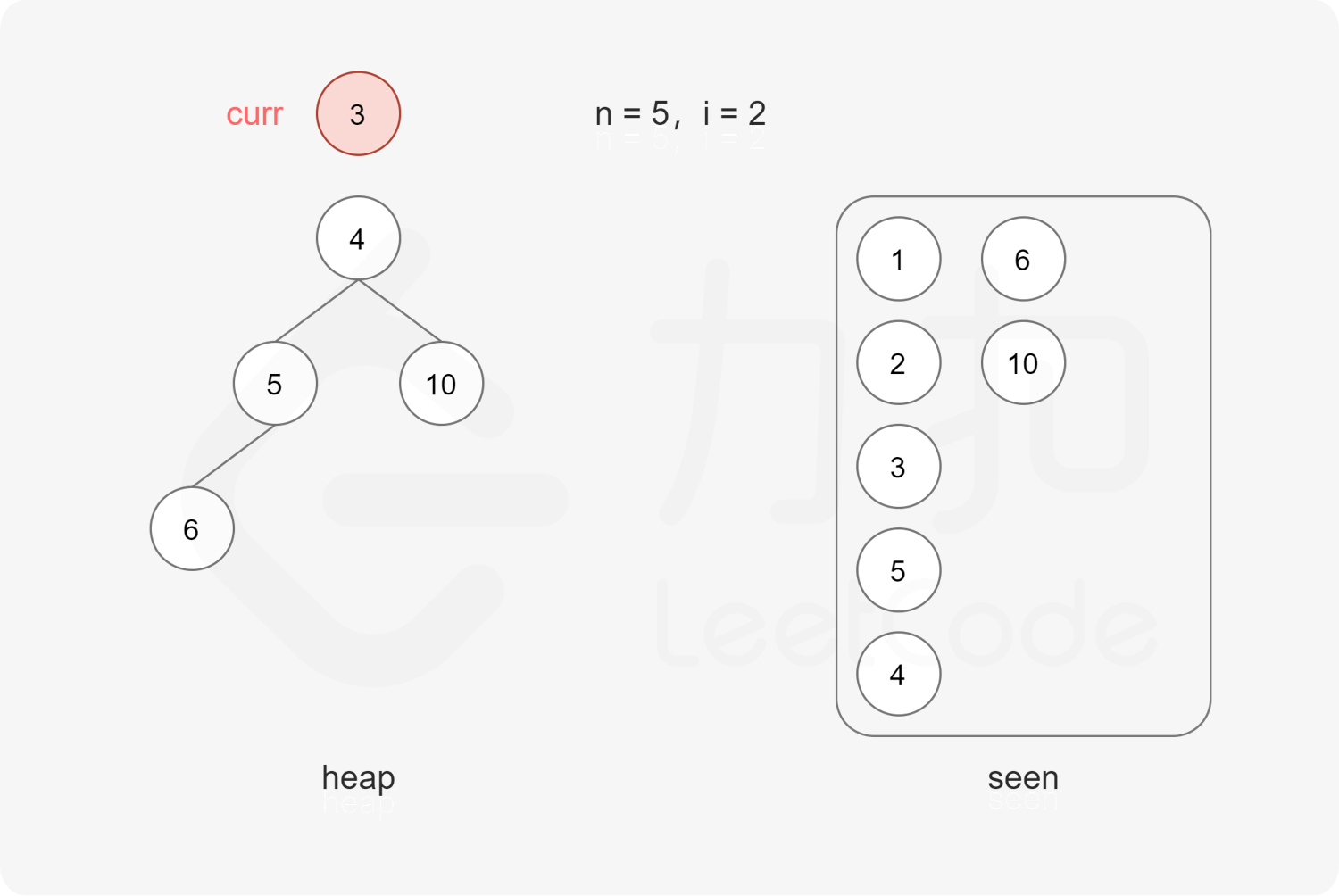
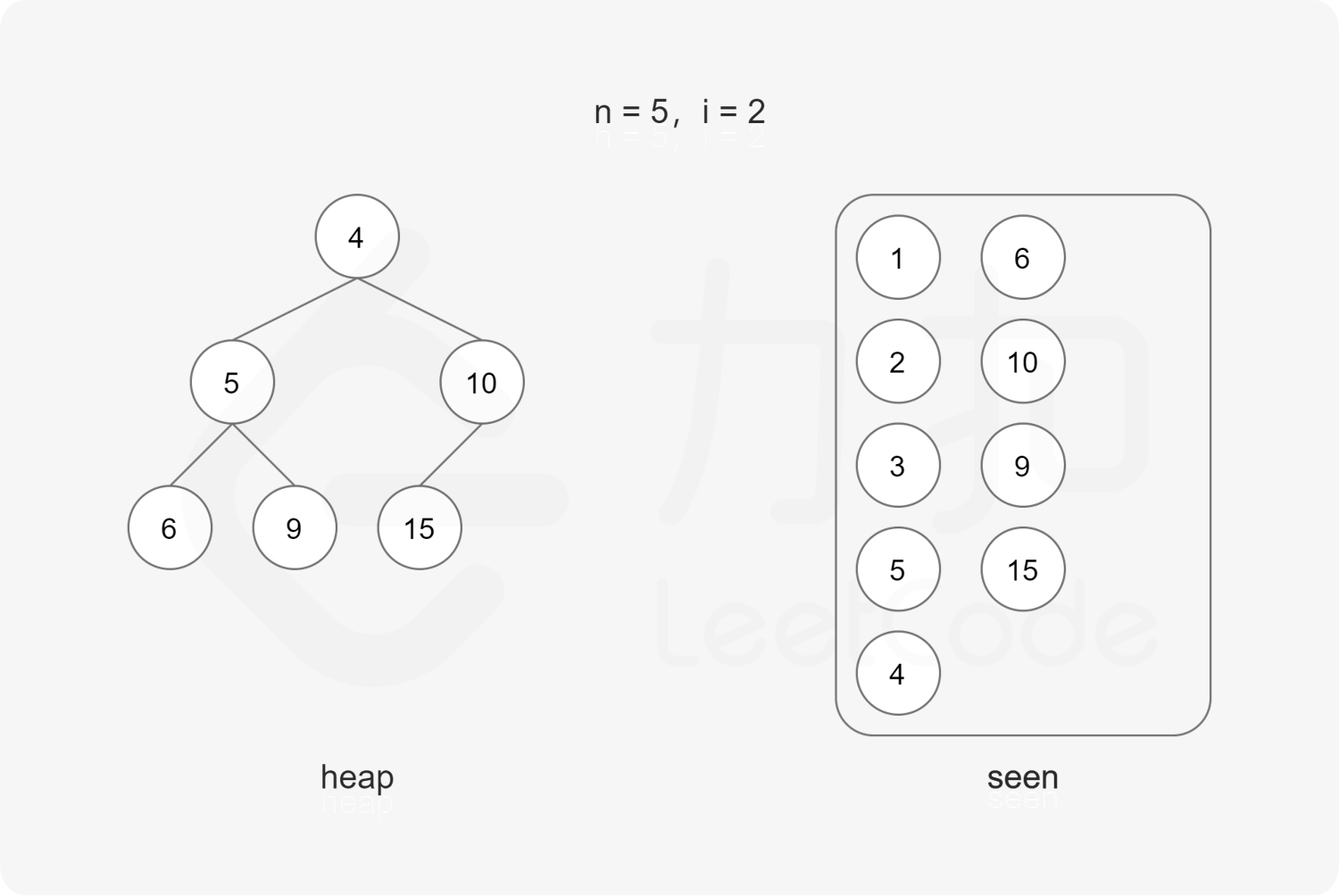
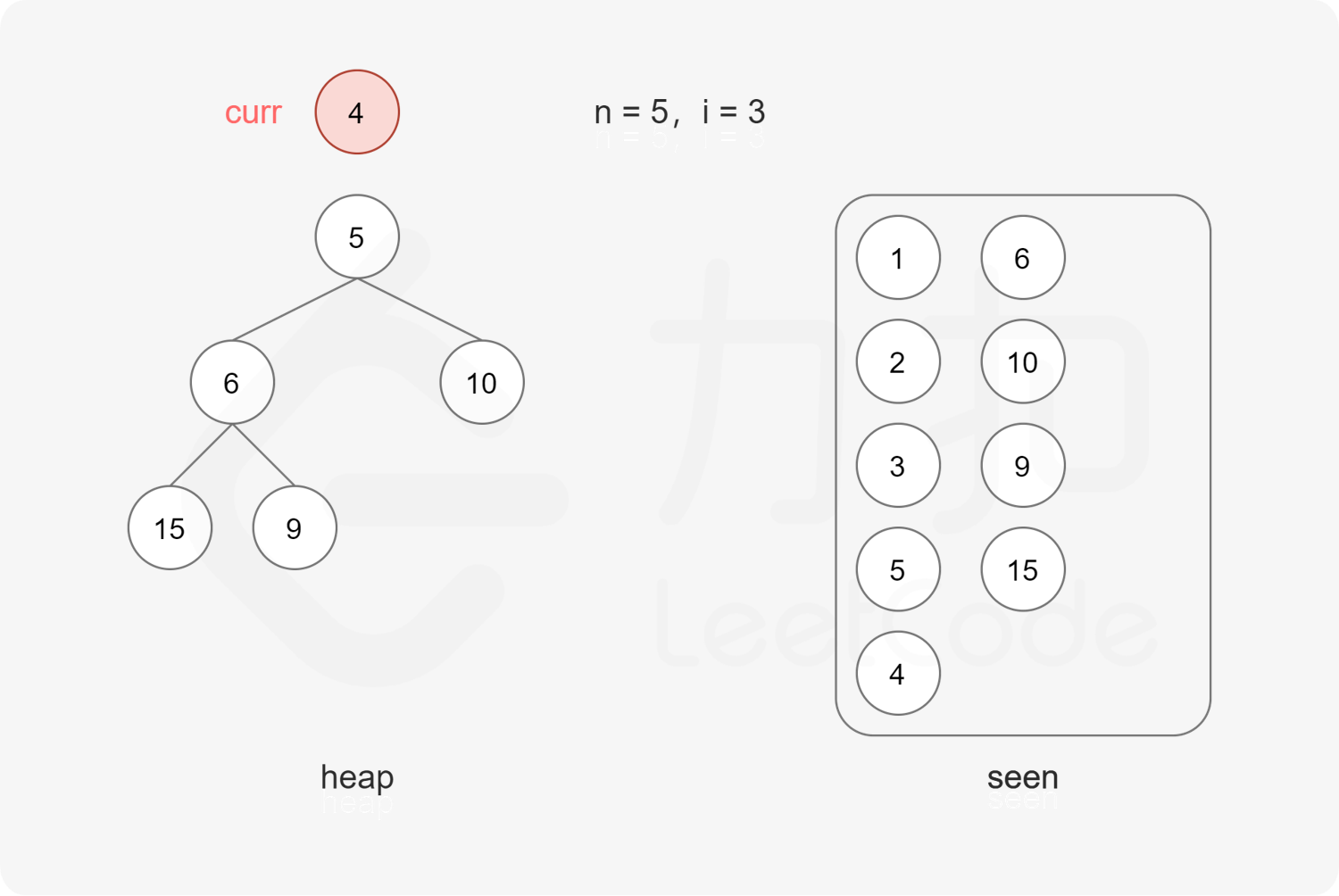
每次取出堆顶元素 $x$,则 $x$ 是堆中最小的丑数,由于 $2x, 3x, 5x$ 也是丑数,因此将 $2x, 3x, 5x$ 加入堆。
上述做法会导致堆中出现重复元素的情况。为了避免重复元素,可以使用哈希集合去重,避免相同元素多次加入堆。
在排除重复元素的情况下,第 $n$ 次从最小堆中取出的元素即为第 $n$ 个丑数。
<
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int nthUglyNumber (int n) { int [] factors = {2 , 3 , 5 }; Set<Long> seen = new HashSet <Long>(); PriorityQueue<Long> heap = new PriorityQueue <Long>(); seen.add(1L ); heap.offer(1L ); int ugly = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { long curr = heap.poll(); ugly = (int ) curr; for (int factor : factors) { long next = curr * factor; if (seen.add(next)) { heap.offer(next); } } } return ugly; } }
[sol1-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Solution { public int NthUglyNumber (int n int [] factors = {2 , 3 , 5 }; ISet<long > seen = new HashSet<long >(); PriorityQueue<long , long > heap = new PriorityQueue<long , long >(); seen.Add(1 ); heap.Enqueue(1 , 1 ); int ugly = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { long curr = heap.Dequeue(); ugly = (int ) curr; foreach (int factor in factors) { long next = curr * factor; if (seen.Add(next)) { heap.Enqueue(next, next); } } } return ugly; } }
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 var nthUglyNumber = function (n ) { const factors = [2 , 3 , 5 ]; const seen = new Set (); const heap = new MinHeap (); seen.add (1 ); heap.insert (1 ); let ugly = 0 ; for (let i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { ugly = heap.pop (); for (const factor of factors) { const next = ugly * factor; if (!seen.has (next)) { seen.add (next); heap.insert (next); } } } return ugly; }; class MinHeap { constructor ( this .heap = []; } getParentIndex (i ) { return (i - 1 ) >> 1 ; } getLeftIndex (i ) { return i * 2 + 1 ; } getRightIndex (i ) { return i * 2 + 2 ; } shiftUp (index ) { if (index === 0 ) { return ; } const parentIndex = this .getParentIndex (index); if (this .heap [parentIndex] > this .heap [index]){ this .swap (parentIndex, index); this .shiftUp (parentIndex); } } swap (i1, i2 ) { const temp = this .heap [i1]; this .heap [i1]= this .heap [i2]; this .heap [i2] = temp; } insert (value ) { this .heap .push (value); this .shiftUp (this .heap .length - 1 ); } pop ( this .heap [0 ] = this .heap .pop (); this .shiftDown (0 ); return this .heap [0 ]; } shiftDown (index ) { const leftIndex = this .getLeftIndex (index); const rightIndex = this .getRightIndex (index); if (this .heap [leftIndex] < this .heap [index]) { this .swap (leftIndex, index); this .shiftDown (leftIndex); } if (this .heap [rightIndex] < this .heap [index]){ this .swap (rightIndex, index); this .shiftDown (rightIndex); } } peek ( return this .heap [0 ]; } size ( return this .heap .length ; } }
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 var factors = []int {2 , 3 , 5 }type hp struct { sort.IntSlice }func (h *hp) interface {}) { h.IntSlice = append (h.IntSlice, v.(int )) }func (h *hp) interface {} { a := h.IntSlice; v := a[len (a)-1 ]; h.IntSlice = a[:len (a)-1 ]; return v }func nthUglyNumber (n int ) int { h := &hp{sort.IntSlice{1 }} seen := map [int ]struct {}{1 : {}} for i := 1 ; ; i++ { x := heap.Pop(h).(int ) if i == n { return x } for _, f := range factors { next := x * f if _, has := seen[next]; !has { heap.Push(h, next) seen[next] = struct {}{} } } } }
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution : def nthUglyNumber (self, n: int ) -> int : factors = [2 , 3 , 5 ] seen = {1 } heap = [1 ] for i in range (n - 1 ): curr = heapq.heappop(heap) for factor in factors: if (nxt := curr * factor) not in seen: seen.add(nxt) heapq.heappush(heap, nxt) return heapq.heappop(heap)
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 class Solution {public : int nthUglyNumber (int n) vector<int > factors = {2 , 3 , 5 }; unordered_set<long > seen; priority_queue<long , vector<long >, greater<long >> heap; seen.insert (1L ); heap.push (1L ); int ugly = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { long curr = heap.top (); heap.pop (); ugly = (int )curr; for (int factor : factors) { long next = curr * factor; if (!seen.count (next)) { seen.insert (next); heap.push (next); } } } return ugly; } };
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 #define HASH_FIND_LONG(head, findint, out) HASH_FIND(hh, head, findint, sizeof(long), out) #define HASH_ADD_LONG(head, intfield, add) HASH_ADD(hh, head, intfield, sizeof(long), add) struct HashTable { long key; UT_hash_handle hh; }; void insert (struct HashTable** hashTable, long ikey) { struct HashTable * tmp ; HASH_FIND_LONG(*hashTable, &ikey, tmp); if (tmp == NULL ) { tmp = malloc (sizeof (struct HashTable)); tmp->key = ikey; HASH_ADD_LONG(*hashTable, key, tmp); } } bool count (struct HashTable** hashTable, long ikey) { struct HashTable * tmp ; HASH_FIND_LONG(*hashTable, &ikey, tmp); return tmp == NULL ; } struct Heap { long * heap; int heapSize; bool (*cmp)(long , long ); }; void init (struct Heap* obj, int n, bool (*cmp)(long , long )) { obj->heap = malloc (sizeof (long ) * (n + 1 )); obj->heapSize = 0 ; obj->cmp = cmp; } bool cmp1 (long a, long b) { return a > b; } void swap (long * a, long * b) { long tmp = *a; *a = *b, *b = tmp; } void push (struct Heap* obj, long x) { int p = ++(obj->heapSize), q = p >> 1 ; obj->heap[p] = x; while (q) { if (!obj->cmp(obj->heap[q], obj->heap[p])) { break ; } swap(&(obj->heap[q]), &(obj->heap[p])); p = q, q = p >> 1 ; } } void pop (struct Heap* obj) { swap(&(obj->heap[1 ]), &(obj->heap[(obj->heapSize)--])); int p = 1 , q = p << 1 ; while (q <= obj->heapSize) { if (q + 1 <= obj->heapSize) { if (obj->cmp(obj->heap[q], obj->heap[q + 1 ])) { q++; } } if (!obj->cmp(obj->heap[p], obj->heap[q])) { break ; } swap(&(obj->heap[q]), &(obj->heap[p])); p = q, q = p << 1 ; } } long top (struct Heap* obj) { return obj->heap[1 ]; } bool empty (struct Heap* obj) { return obj->heapSize == 0 ; } int nthUglyNumber (int n) { int factors[3 ] = {2 , 3 , 5 }; struct HashTable * hashTable =NULL ; insert(&hashTable, 1 ); struct Heap * heap =malloc (sizeof (struct Heap)); init(heap, n * 3 , cmp1); push(heap, 1 ); int ugly = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { long curr = top(heap); pop(heap); ugly = (int )curr; for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 ; i++) { long next = curr * factors[i]; if (count(&hashTable, next)) { insert(&hashTable, next); push(heap, next); } } } return ugly; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:$O(n \log n)$。得到第 $n$ 个丑数需要进行 $n$ 次循环,每次循环都要从最小堆中取出 $1$ 个元素以及向最小堆中加入最多 $3$ 个元素,因此每次循环的时间复杂度是 $O(\log (3n) + 3 \log (3n))=O(\log n)$,总时间复杂度是 $O(n \log n)$。
空间复杂度:$O(n)$。空间复杂度主要取决于最小堆和哈希集合的大小,最小堆和哈希集合的大小都不会超过 $3n$。
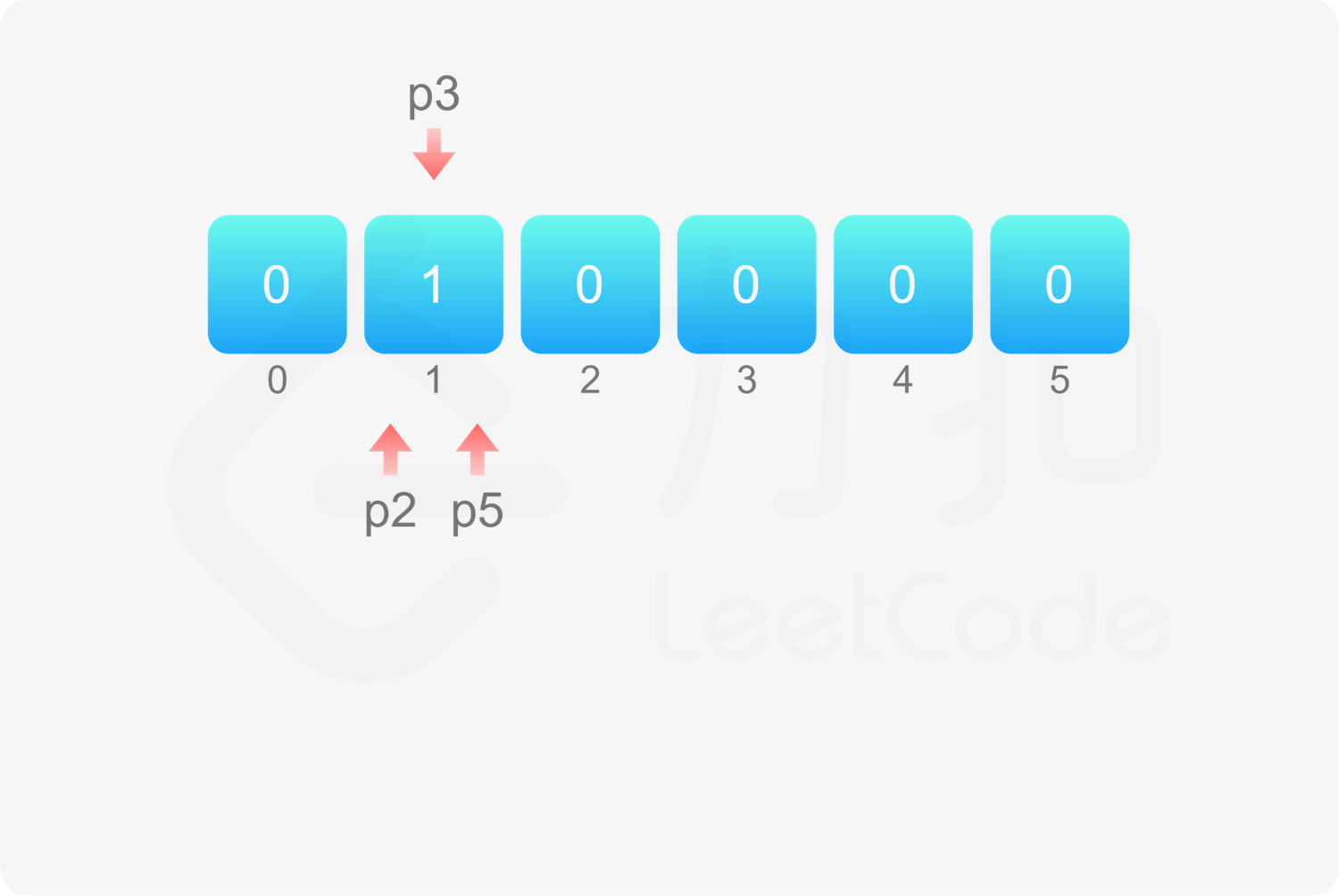
方法二:动态规划 方法一使用最小堆,会预先存储较多的丑数,维护最小堆的过程也导致时间复杂度较高。可以使用动态规划的方法进行优化。
定义数组 $\textit{dp}$,其中 $\textit{dp}[i]$ 表示第 $i$ 个丑数,第 $n$ 个丑数即为 $\textit{dp}[n]$。
由于最小的丑数是 $1$,因此 $\textit{dp}[1]=1$。
如何得到其余的丑数呢?定义三个指针 $p_2,p_3,p_5$,表示下一个丑数是当前指针指向的丑数乘以对应的质因数。初始时,三个指针的值都是 $1$。
当 $2 \le i \le n$ 时,令 $\textit{dp}[i]=\min(\textit{dp}[p_2] \times 2, \textit{dp}[p_3] \times 3, \textit{dp}[p_5] \times 5)$,然后分别比较 $\textit{dp}[i]$ 和 $\textit{dp}[p_2] \times 2,\textit{dp}[p_3] \times 3,\textit{dp}[p_5] \times 5$ 是否相等,如果相等则将对应的指针加 $1$。
正确性证明
对于 $i>1$,在计算 $\textit{dp}[i]$ 时,指针 $p_x(x \in {2,3,5})$ 的含义是使得 $\textit{dp}[j] \times x>\textit{dp}[i-1]$ 的最小的下标 $j$,即当 $j \ge p_x$ 时 $\textit{dp}[j] \times x>\textit{dp}[i-1]$,当 $j<p_x$ 时 $\textit{dp}[j] \times x \le \textit{dp}[i-1]$。
因此,对于 $i>1$,在计算 $\textit{dp}[i]$ 时,$\textit{dp}[p_2] \times 2,\textit{dp}[p_3] \times 3,\textit{dp}[p_5] \times 5$ 都大于 $\textit{dp}[i-1]$,$\textit{dp}[p_2-1] \times 2,\textit{dp}[p_3-1] \times 3,\textit{dp}[p_5-1] \times 5$ 都小于或等于 $\textit{dp}[i-1]$。令 $\textit{dp}[i]=\min(\textit{dp}[p_2] \times 2, \textit{dp}[p_3] \times 3, \textit{dp}[p_5] \times 5)$,则 $\textit{dp}[i]>\textit{dp}[i-1]$ 且 $\textit{dp}[i]$ 是大于 $\textit{dp}[i-1]$ 的最小的丑数。
在计算 $\textit{dp}[i]$ 之后,会更新三个指针 $p_2,p_3,p_5$,更新之后的指针将用于计算 $\textit{dp}[i+1]$,同样满足 $\textit{dp}[i+1]>\textit{dp}[i]$ 且 $\textit{dp}[i+1]$ 是大于 $\textit{dp}[i]$ 的最小的丑数。
<
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution { public int nthUglyNumber (int n) { int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[1 ] = 1 ; int p2 = 1 , p3 = 1 , p5 = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { int num2 = dp[p2] * 2 , num3 = dp[p3] * 3 , num5 = dp[p5] * 5 ; dp[i] = Math.min(Math.min(num2, num3), num5); if (dp[i] == num2) { p2++; } if (dp[i] == num3) { p3++; } if (dp[i] == num5) { p5++; } } return dp[n]; } }
[sol2-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 public class Solution { public int NthUglyNumber (int n int [] dp = new int [n + 1 ]; dp[1 ] = 1 ; int p2 = 1 , p3 = 1 , p5 = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { int num2 = dp[p2] * 2 , num3 = dp[p3] * 3 , num5 = dp[p5] * 5 ; dp[i] = Math.Min(Math.Min(num2, num3), num5); if (dp[i] == num2) { p2++; } if (dp[i] == num3) { p3++; } if (dp[i] == num5) { p5++; } } return dp[n]; } }
[sol2-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 var nthUglyNumber = function (n ) { const dp = new Array (n + 1 ).fill (0 ); dp[1 ] = 1 ; let p2 = 1 , p3 = 1 , p5 = 1 ; for (let i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { const num2 = dp[p2] * 2 , num3 = dp[p3] * 3 , num5 = dp[p5] * 5 ; dp[i] = Math .min (Math .min (num2, num3), num5); if (dp[i] === num2) { p2++; } if (dp[i] === num3) { p3++; } if (dp[i] === num5) { p5++; } } return dp[n]; };
[sol2-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 func nthUglyNumber (n int ) int { dp := make ([]int , n+1 ) dp[1 ] = 1 p2, p3, p5 := 1 , 1 , 1 for i := 2 ; i <= n; i++ { x2, x3, x5 := dp[p2]*2 , dp[p3]*3 , dp[p5]*5 dp[i] = min(min(x2, x3), x5) if dp[i] == x2 { p2++ } if dp[i] == x3 { p3++ } if dp[i] == x5 { p5++ } } return dp[n] } func min (a, b int ) int { if a < b { return a } return b }
[sol2-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 class Solution : def nthUglyNumber (self, n: int ) -> int : dp = [0 ] * (n + 1 ) dp[1 ] = 1 p2 = p3 = p5 = 1 for i in range (2 , n + 1 ): num2, num3, num5 = dp[p2] * 2 , dp[p3] * 3 , dp[p5] * 5 dp[i] = min (num2, num3, num5) if dp[i] == num2: p2 += 1 if dp[i] == num3: p3 += 1 if dp[i] == num5: p5 += 1 return dp[n]
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 class Solution {public : int nthUglyNumber (int n) vector<int > dp (n + 1 ) ; dp[1 ] = 1 ; int p2 = 1 , p3 = 1 , p5 = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { int num2 = dp[p2] * 2 , num3 = dp[p3] * 3 , num5 = dp[p5] * 5 ; dp[i] = min (min (num2, num3), num5); if (dp[i] == num2) { p2++; } if (dp[i] == num3) { p3++; } if (dp[i] == num5) { p5++; } } return dp[n]; } };
[sol2-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 int nthUglyNumber (int n) { int dp[n + 1 ]; dp[1 ] = 1 ; int p2 = 1 , p3 = 1 , p5 = 1 ; for (int i = 2 ; i <= n; i++) { int num2 = dp[p2] * 2 , num3 = dp[p3] * 3 , num5 = dp[p5] * 5 ; dp[i] = fmin(fmin(num2, num3), num5); if (dp[i] == num2) { p2++; } if (dp[i] == num3) { p3++; } if (dp[i] == num5) { p5++; } } return dp[n]; }
复杂度分析
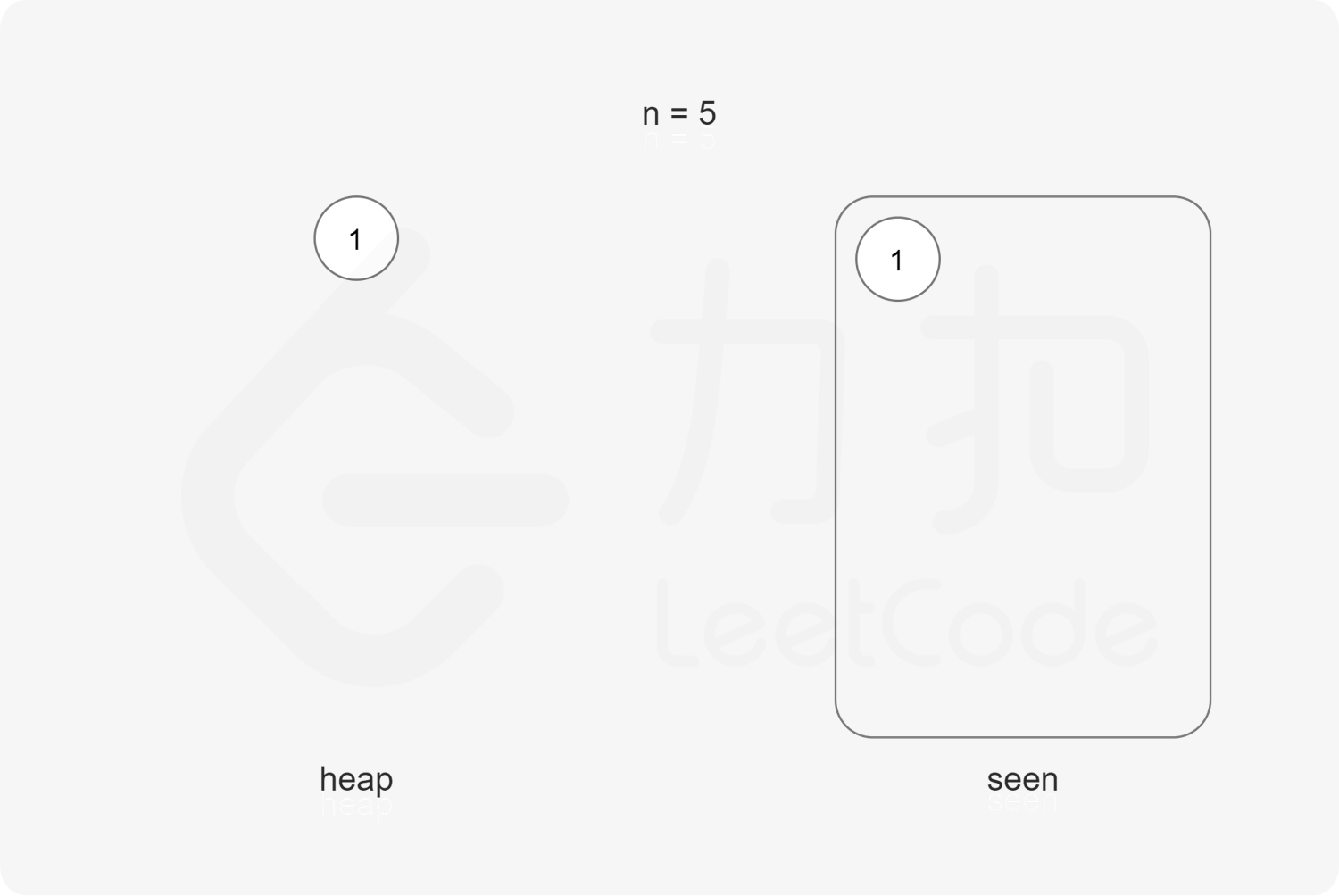 ,
,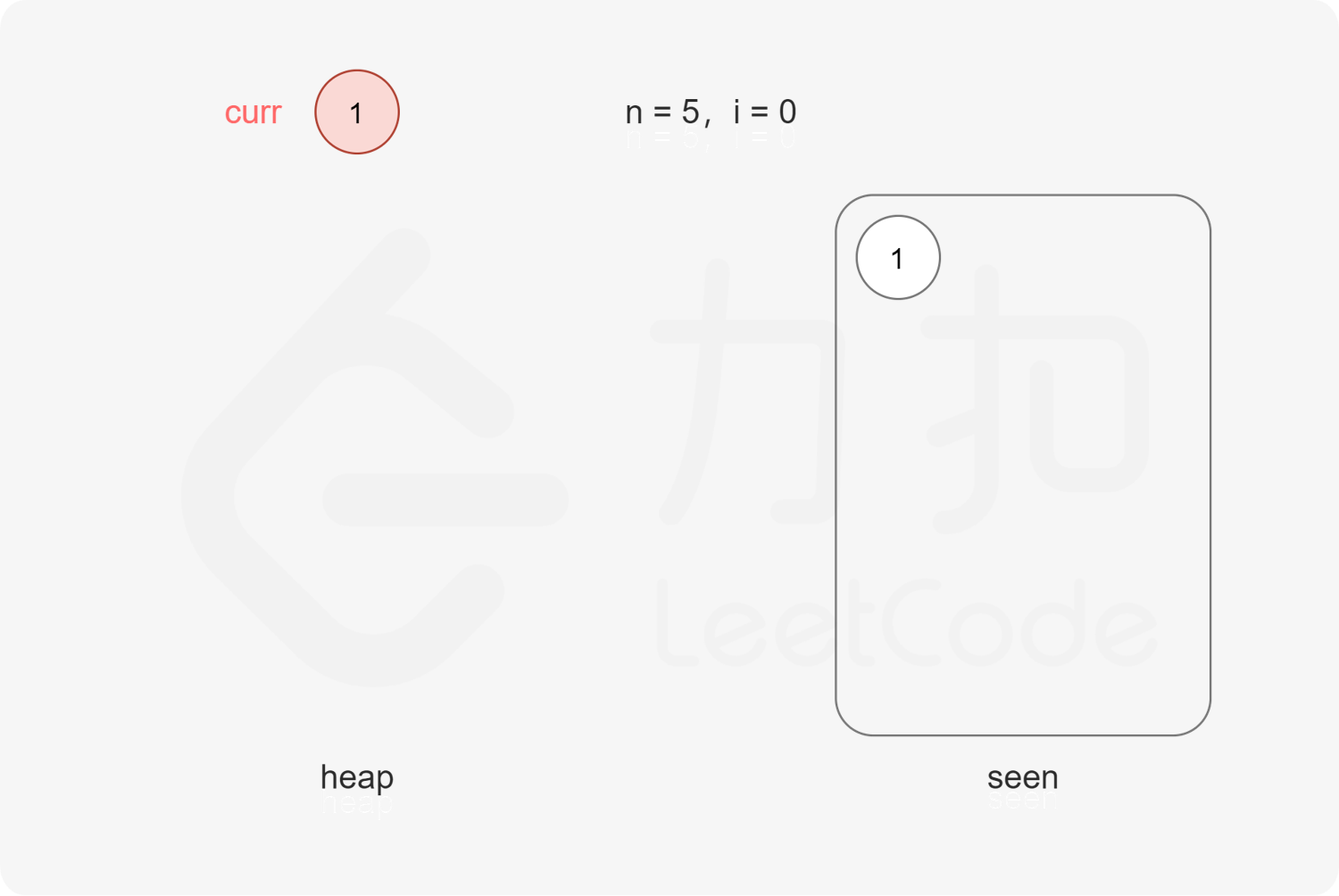 ,
,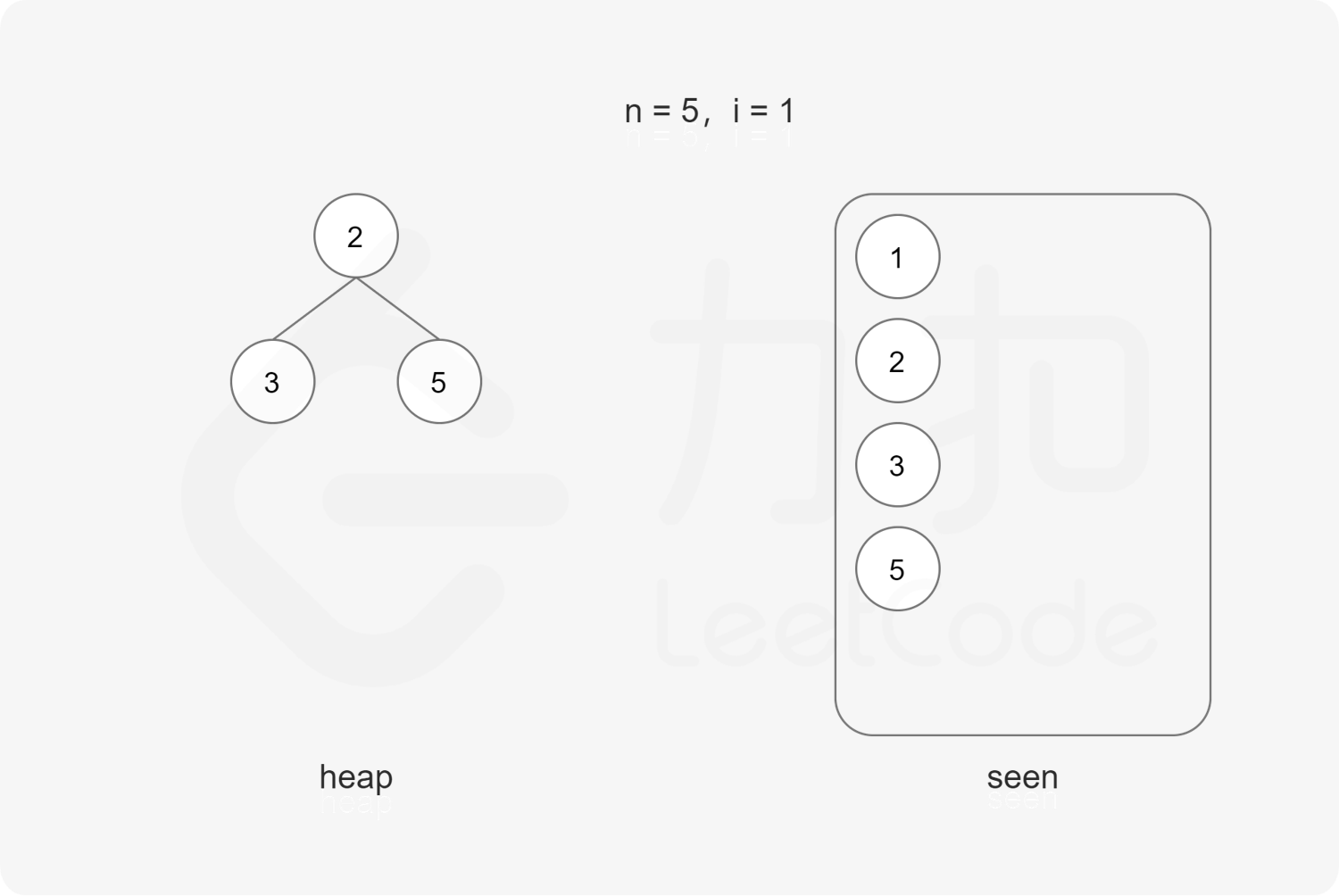 ,
,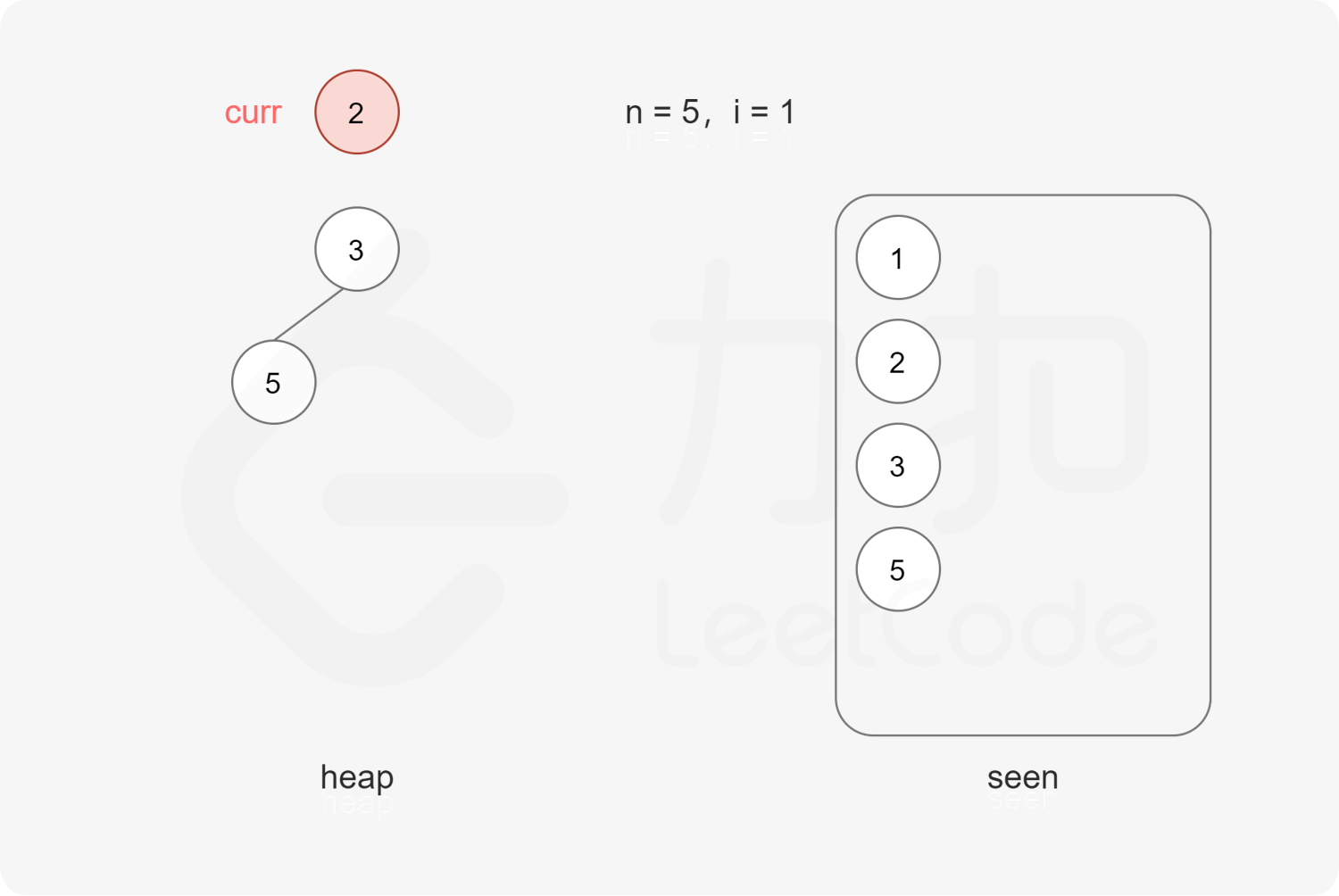 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
> ,
,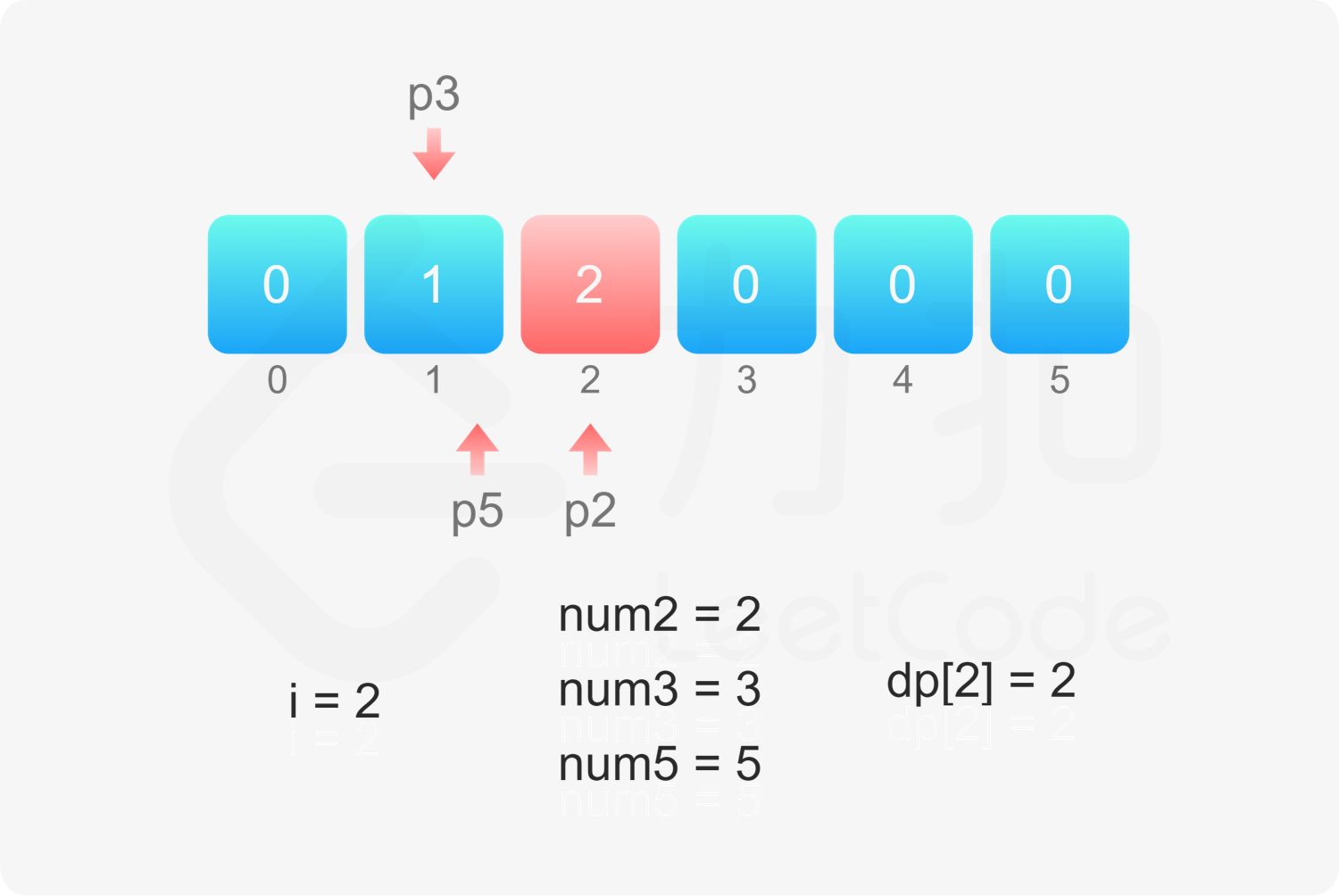 ,
,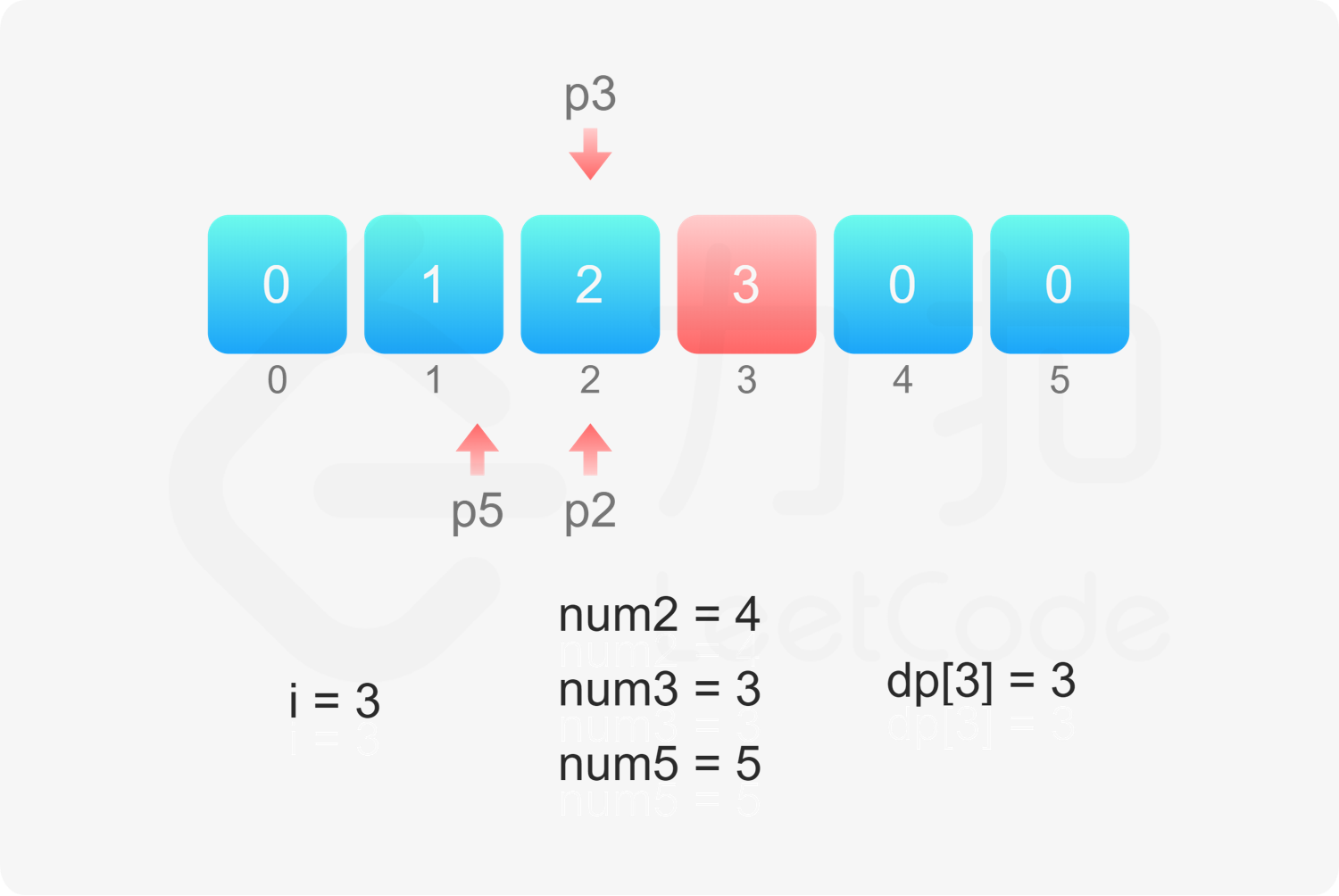 ,
,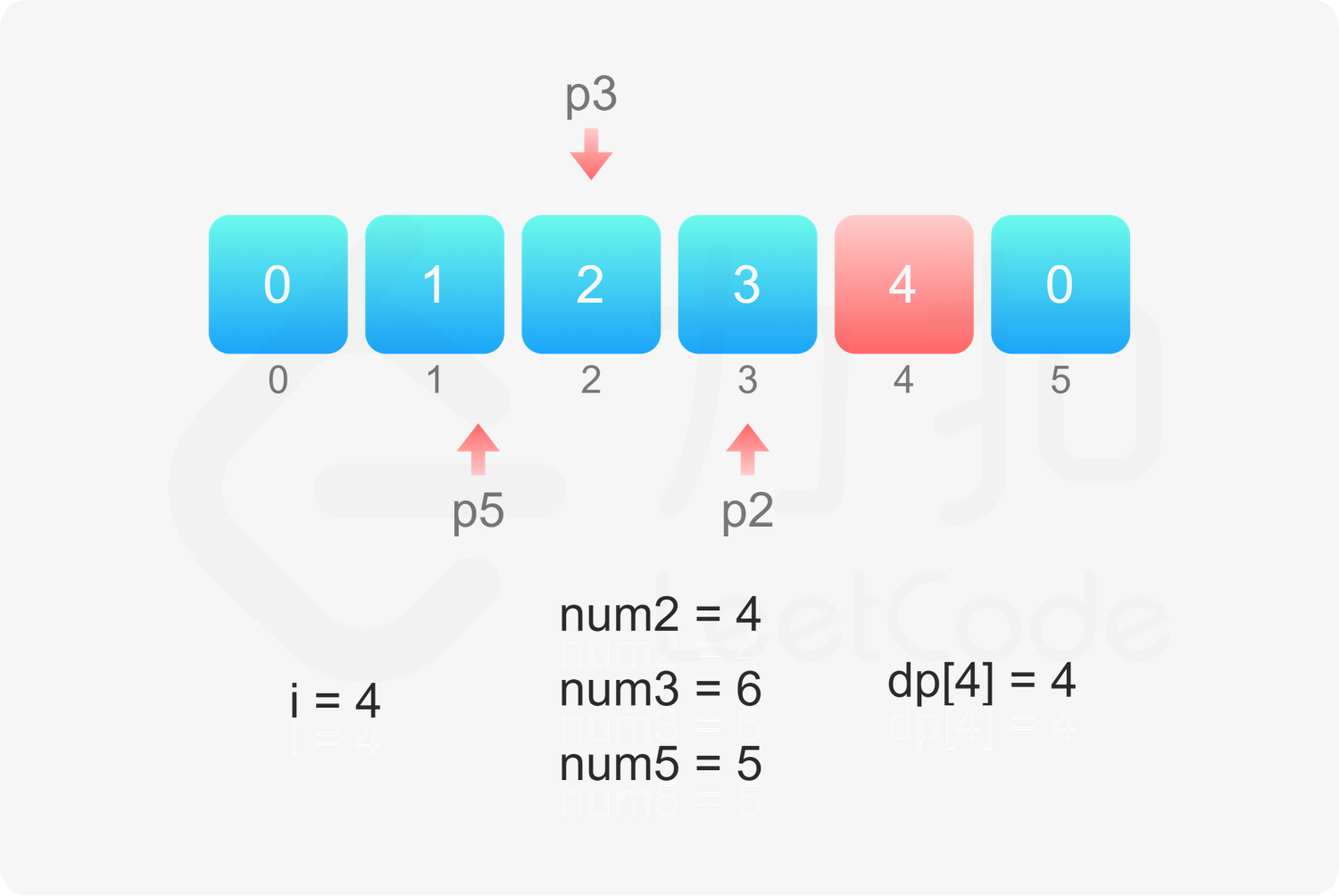 ,
,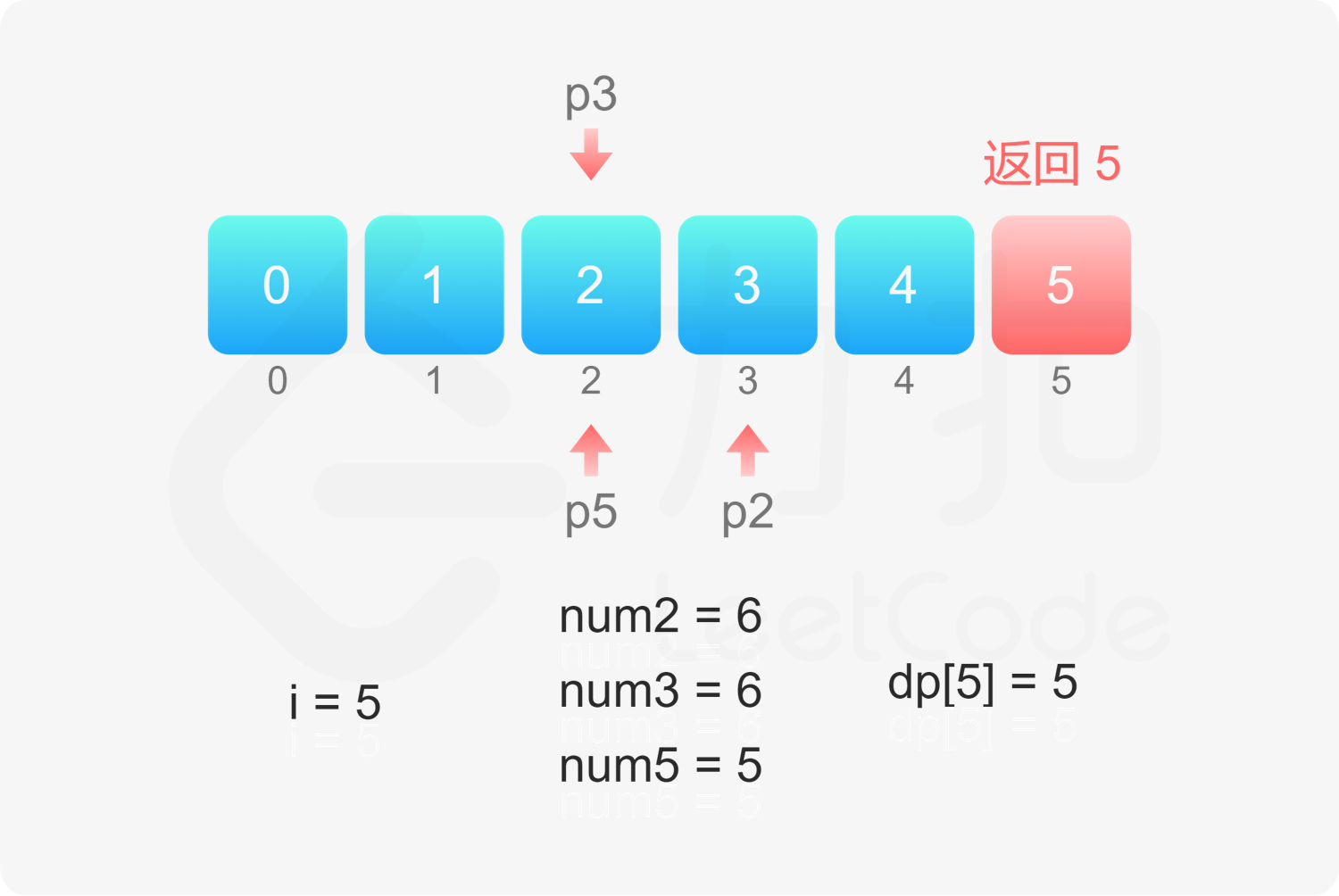 >
>