给定一个二叉树的 根节点 root,请找出该二叉树的 最底层 最左边 节点的值。
假设二叉树中至少有一个节点。
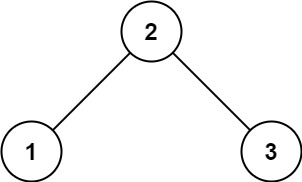
示例 1:
**输入:** root = [2,1,3]
**输出:** 1
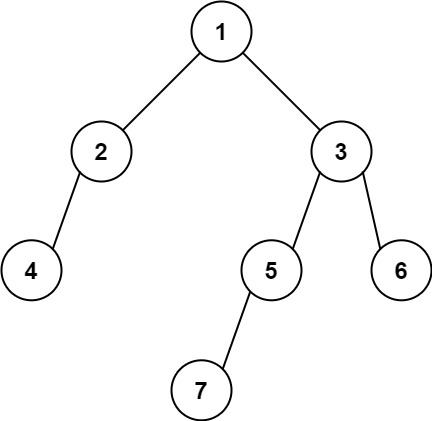
示例 2:
**输入:** [1,2,3,4,null,5,6,null,null,7]
**输出:** 7
提示:
二叉树的节点个数的范围是 [1,104]
-231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
方法一:深度优先搜索 使用 height 记录遍历到的节点的高度,curVal 记录高度在 curHeight 的最左节点的值。在深度优先搜索时,我们先搜索当前节点的左子节点,再搜索当前节点的右子节点,然后判断当前节点的高度 height 是否大于 curHeight,如果是,那么将 curVal 设置为当前结点的值,curHeight 设置为 height。
因为我们先遍历左子树,然后再遍历右子树,所以对同一高度的所有节点,最左节点肯定是最先被遍历到的。
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution : def findBottomLeftValue (self, root: Optional [TreeNode] ) -> int : curVal = curHeight = 0 def dfs (node: Optional [TreeNode], height: int ) -> None : if node is None : return height += 1 dfs(node.left, height) dfs(node.right, height) nonlocal curVal, curHeight if height > curHeight: curHeight = height curVal = node.val dfs(root, 0 ) return curVal
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution {public : void dfs (TreeNode *root, int height, int &curVal, int &curHeight) if (root == nullptr ) { return ; } height++; dfs (root->left, height, curVal, curHeight); dfs (root->right, height, curVal, curHeight); if (height > curHeight) { curHeight = height; curVal = root->val; } } int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode* root) int curVal, curHeight = 0 ; dfs (root, 0 , curVal, curHeight); return curVal; } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution { int curVal = 0 ; int curHeight = 0 ; public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) { int curHeight = 0 ; dfs(root, 0 ); return curVal; } public void dfs (TreeNode root, int height) { if (root == null ) { return ; } height++; dfs(root.left, height); dfs(root.right, height); if (height > curHeight) { curHeight = height; curVal = root.val; } } }
[sol1-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Solution { int curVal = 0 ; int curHeight = 0 ; public int FindBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root ) int curHeight = 0 ; DFS(root, 0 ); return curVal; } public void DFS (TreeNode root, int height ) if (root == null ) { return ; } height++; DFS(root.left, height); DFS(root.right, height); if (height > curHeight) { curHeight = height; curVal = root.val; } } }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 void dfs (const struct TreeNode *root, int height, int *curVal, int *curHeight) { if (root == NULL ) { return ; } height++; dfs(root->left, height, curVal, curHeight); dfs(root->right, height, curVal, curHeight); if (height > *curHeight) { *curHeight = height; *curVal = root->val; } } int findBottomLeftValue (struct TreeNode* root) { int curVal, curHeight = 0 ; dfs(root, 0 , &curVal, &curHeight); return curVal; }
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 var findBottomLeftValue = function (root ) { const dfs = (root, height ) => { if (!root) { return ; } height++; dfs (root.left , height); dfs (root.right , height); if (height > curHeight) { curHeight = height; curVal = root.val ; } } let curHeight = 0 ; dfs (root, 0 ); return curVal; };
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 func findBottomLeftValue (root *TreeNode) int ) { curHeight := 0 var dfs func (*TreeNode, int ) dfs = func (node *TreeNode, height int ) if node == nil { return } height++ dfs(node.Left, height) dfs(node.Right, height) if height > curHeight { curHeight = height curVal = node.Val } } dfs(root, 0 ) return }
复杂度分析
方法二:广度优先搜索 使用广度优先搜索遍历每一层的节点。在遍历一个节点时,需要先把它的非空右子节点放入队列,然后再把它的非空左子节点放入队列,这样才能保证从右到左遍历每一层的节点。广度优先搜索所遍历的最后一个节点的值就是最底层最左边节点的值。
[sol2-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution : def findBottomLeftValue (self, root: Optional [TreeNode] ) -> int : q = deque([root]) while q: node = q.popleft() if node.right: q.append(node.right) if node.left: q.append(node.left) ans = node.val return ans
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 class Solution {public : int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode* root) int ret; queue<TreeNode *> q; q.push (root); while (!q.empty ()) { auto p = q.front (); q.pop (); if (p->right) { q.push (p->right); } if (p->left) { q.push (p->left); } ret = p->val; } return ret; } };
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 class Solution { public int findBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root) { int ret = 0 ; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque <TreeNode>(); queue.offer(root); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { TreeNode p = queue.poll(); if (p.right != null ) { queue.offer(p.right); } if (p.left != null ) { queue.offer(p.left); } ret = p.val; } return ret; } }
[sol2-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Solution { public int FindBottomLeftValue (TreeNode root ) int ret = 0 ; Queue<TreeNode> queue = new Queue<TreeNode>(); queue.Enqueue(root); while (queue.Count > 0 ) { TreeNode p = queue.Dequeue(); if (p.right != null ) { queue.Enqueue(p.right); } if (p.left != null ) { queue.Enqueue(p.left); } ret = p.val; } return ret; } }
[sol2-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 #define MAX_NODE_SIZE 10000 int findBottomLeftValue (struct TreeNode* root) { int ret; struct TreeNode ** queue =struct TreeNode **)malloc (sizeof (struct TreeNode) * MAX_NODE_SIZE); int head = 0 ; int tail = 0 ; queue [tail++] = root; while (head != tail) { struct TreeNode *p =queue [head++]; if (p->right) { queue [tail++] = p->right; } if (p->left) { queue [tail++] = p->left; } ret = p->val; } free (queue ); return ret; }
[sol2-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 var findBottomLeftValue = function (root ) { let ret = 0 ; const queue = [root]; while (queue.length ) { const p = queue.shift (); if (p.right ) { queue.push (p.right ); } if (p.left ) { queue.push (p.left ); } ret = p.val ; } return ret; };
[sol2-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 func findBottomLeftValue (root *TreeNode) int ) { q := []*TreeNode{root} for len (q) > 0 { node := q[0 ] q = q[1 :] if node.Right != nil { q = append (q, node.Right) } if node.Left != nil { q = append (q, node.Left) } ans = node.Val } return }
复杂度分析
 ****
****