给你二叉树的根节点 root ,请你采用前序遍历的方式,将二叉树转化为一个由括号和整数组成的字符串,返回构造出的字符串。
空节点使用一对空括号对 "()" 表示,转化后需要省略所有不影响字符串与原始二叉树之间的一对一映射关系的空括号对。
示例 1:
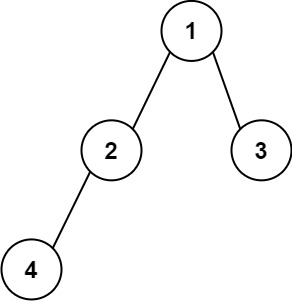
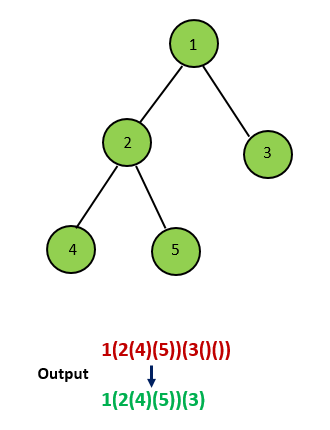
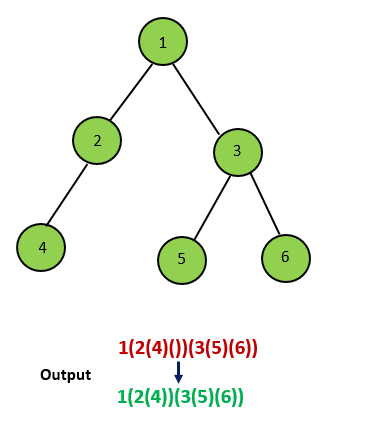
**输入:** root = [1,2,3,4]
**输出:** "1(2(4))(3)"
**解释:** 初步转化后得到 "1(2(4)())(3()())" ,但省略所有不必要的空括号对后,字符串应该是"1(2(4))(3)" 。
示例 2:
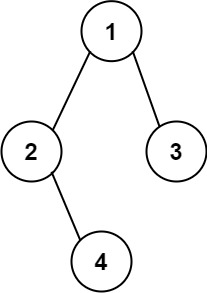
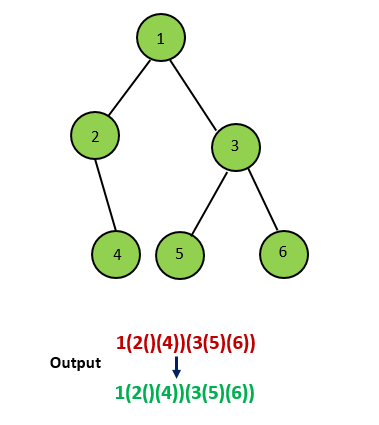
**输入:** root = [1,2,3,null,4]
**输出:** "1(2()(4))(3)"
**解释:** 和第一个示例类似,但是无法省略第一个空括号对,否则会破坏输入与输出一一映射的关系。
提示:
树中节点的数目范围是 [1, 104]
-1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
方法一:递归 我们可以使用递归的方法得到二叉树的前序遍历,并在递归时加上额外的括号。
会有以下 4 种情况:
如果当前节点只有左孩子,那我们在递归时,只需要在左孩子的结果外加上一层括号,而不需要给右孩子加上任何括号;
如果当前节点只有右孩子,那我们在递归时,需要先加上一层空的括号 `()’ 表示左孩子为空,再对右孩子进行递归,并在结果外加上一层括号。
考虑完上面的 4 种情况,我们就可以得到最终的字符串。
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 class Solution : def tree2str (self, root: Optional [TreeNode] ) -> str : if root is None : return "" if root.left is None and root.right is None : return str (root.val) if root.right is None : return f"{root.val} ({self.tree2str(root.left)} )" return f"{root.val} ({self.tree2str(root.left)} )({self.tree2str(root.right)} )"
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 class Solution {public : string tree2str (TreeNode *root) { if (root == nullptr ) { return "" ; } if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr ) { return to_string (root->val); } if (root->right == nullptr ) { return to_string (root->val) + "(" + tree2str (root->left) + ")" ; } return to_string (root->val) + "(" + tree2str (root->left) + ")(" + tree2str (root->right) + ")" ; } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 class Solution { public String tree2str (TreeNode root) { if (root == null ) { return "" ; } if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) { return Integer.toString(root.val); } if (root.right == null ) { return new StringBuffer ().append(root.val).append("(" ).append(tree2str(root.left)).append(")" ).toString(); } return new StringBuffer ().append(root.val).append("(" ).append(tree2str(root.left)).append(")(" ).append(tree2str(root.right)).append(")" ).toString(); } }
[sol1-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 public class Solution { public string Tree2str (TreeNode root ) if (root == null ) { return "" ; } if (root.left == null && root.right == null ) { return root.val.ToString(); } if (root.right == null ) { return new StringBuilder().Append(root.val).Append("(" ).Append(Tree2str(root.left)).Append(")" ).ToString(); } return new StringBuilder().Append(root.val).Append("(" ).Append(Tree2str(root.left)).Append(")(" ).Append(Tree2str(root.right)).Append(")" ).ToString(); } }
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 func tree2str (root *TreeNode) string { switch { case root == nil : return "" case root.Left == nil && root.Right == nil : return strconv.Itoa(root.Val) case root.Right == nil : return fmt.Sprintf("%d(%s)" , root.Val, tree2str(root.Left)) default : return fmt.Sprintf("%d(%s)(%s)" , root.Val, tree2str(root.Left), tree2str(root.Right)) } }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #define MAX_STR_LEN 100000 void helper (struct TreeNode* root, char * str, int * pos) { if (root == NULL ) { return ; } if (root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL ) { *pos += sprintf (str + *pos, "%d" , root->val); return ; } if (root->right == NULL ) { *pos += sprintf (str + *pos, "%d" , root->val); str[(*pos)++] = '(' ; helper(root->left, str, pos); str[(*pos)++] = ')' ; } else { *pos += sprintf (str + *pos, "%d" , root->val); str[(*pos)++] = '(' ; helper(root->left, str, pos); str[(*pos)++] = ')' ; str[(*pos)++] = '(' ; helper(root->right, str, pos); str[(*pos)++] = ')' ; } } char * tree2str (struct TreeNode* root) { char * res = (char *)malloc (sizeof (char ) * MAX_STR_LEN); int pos = 0 ; helper(root, res, &pos); res[pos] = '\0' ; return res; }
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 var tree2str = function (root ) { if (!root) { return "" ; } if (!root.left && !root.right ) { return '' + root.val ; } if (!root.right ) { return root.val + '(' + tree2str (root.left ) + ')' ; } return root.val + '(' + tree2str (root.left ) + ')(' + tree2str (root.right ) + ')' ; };
复杂度分析
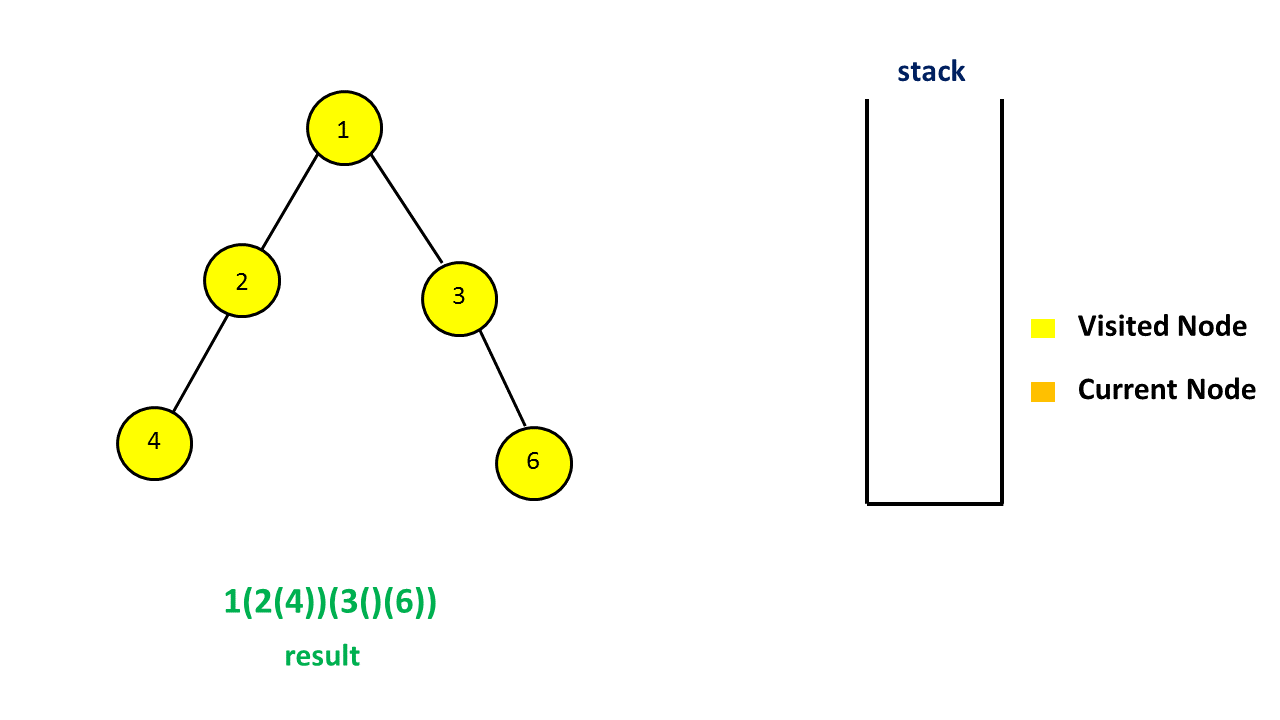
方法二:迭代 我们也可以使用迭代的方法得到二叉树的前序遍历,并在迭代时加上额外的括号。
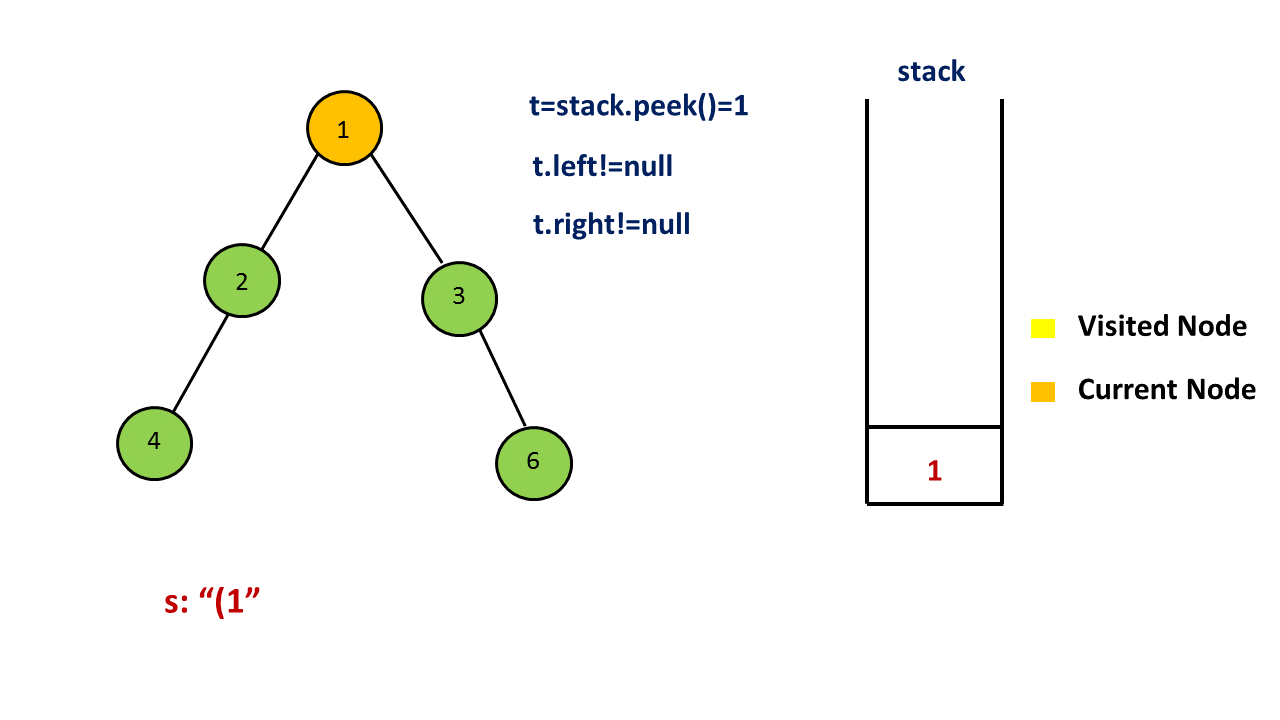
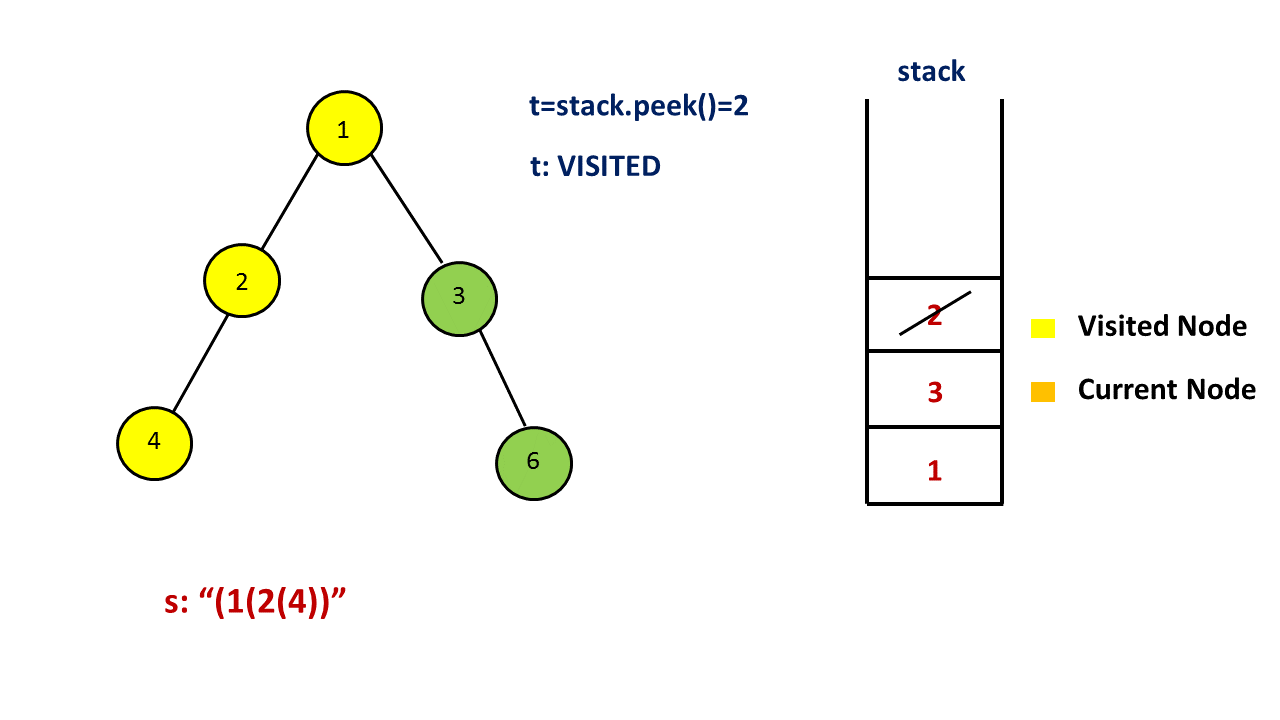
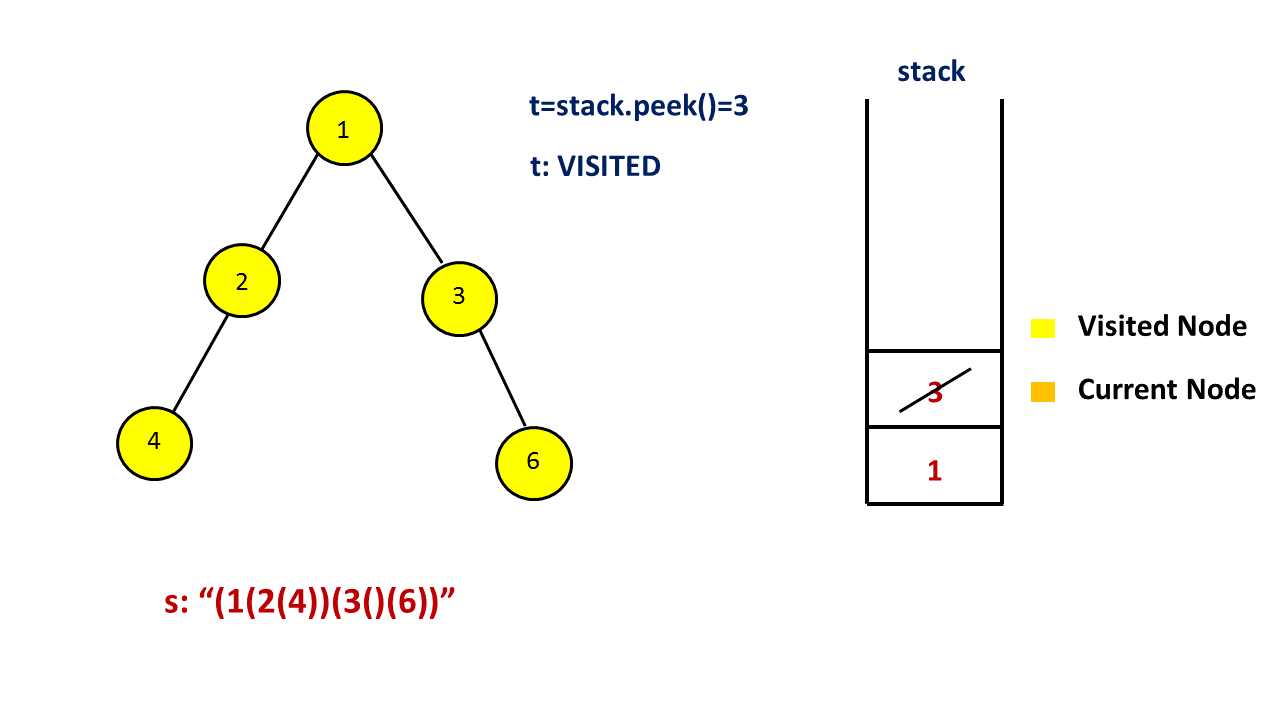
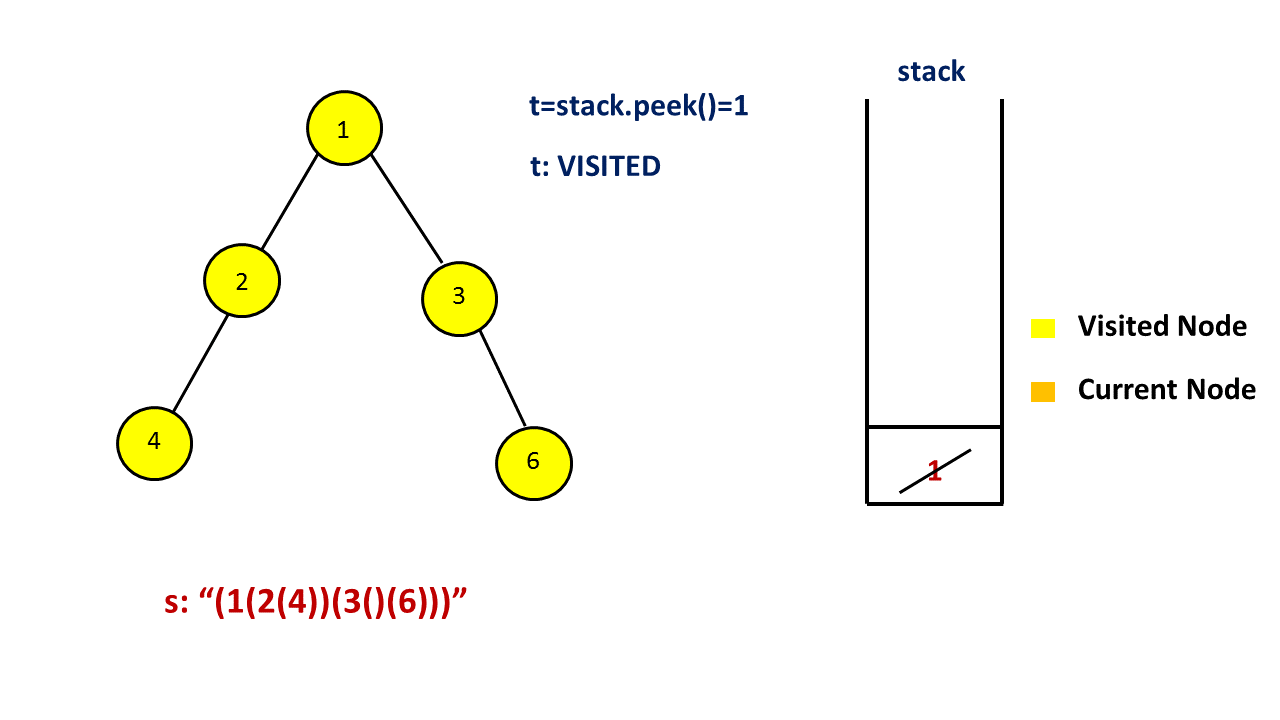
用一个栈来存储树中的一些节点,其中栈顶的元素为当前遍历到的节点,从栈底到栈顶的节点为从根到当前节点的唯一路径上的节点。和迭代得到前序遍历的方法略有不同,由于这里需要输出额外的括号,因此我们还需要用一个集合存储所有遍历过的节点,理由见下文。
首先我们把根节点入栈。对于当前栈顶的元素,如果它没有遍历过,那么就把它加入到集合中,并开始对以它为根的子树进行前序遍历。我们先在答案末尾添加一个 `(‘,表示一个节点的开始,然后判断该节点的子节点个数。
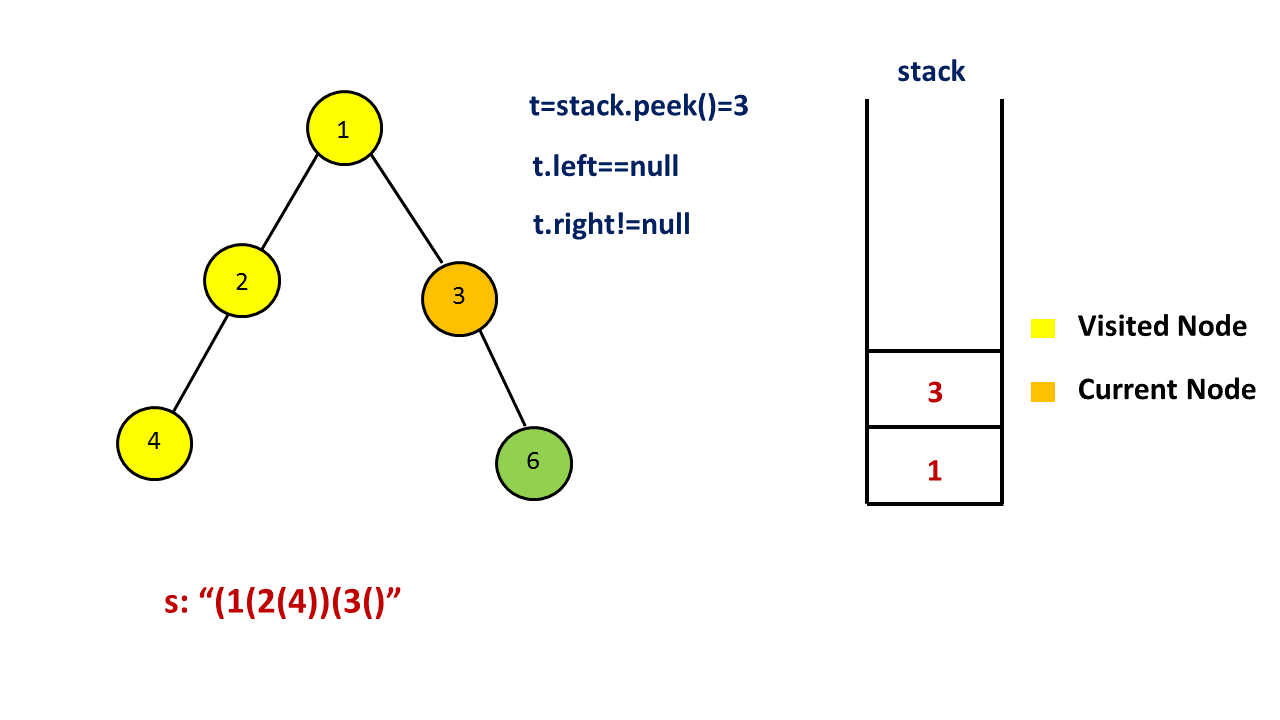
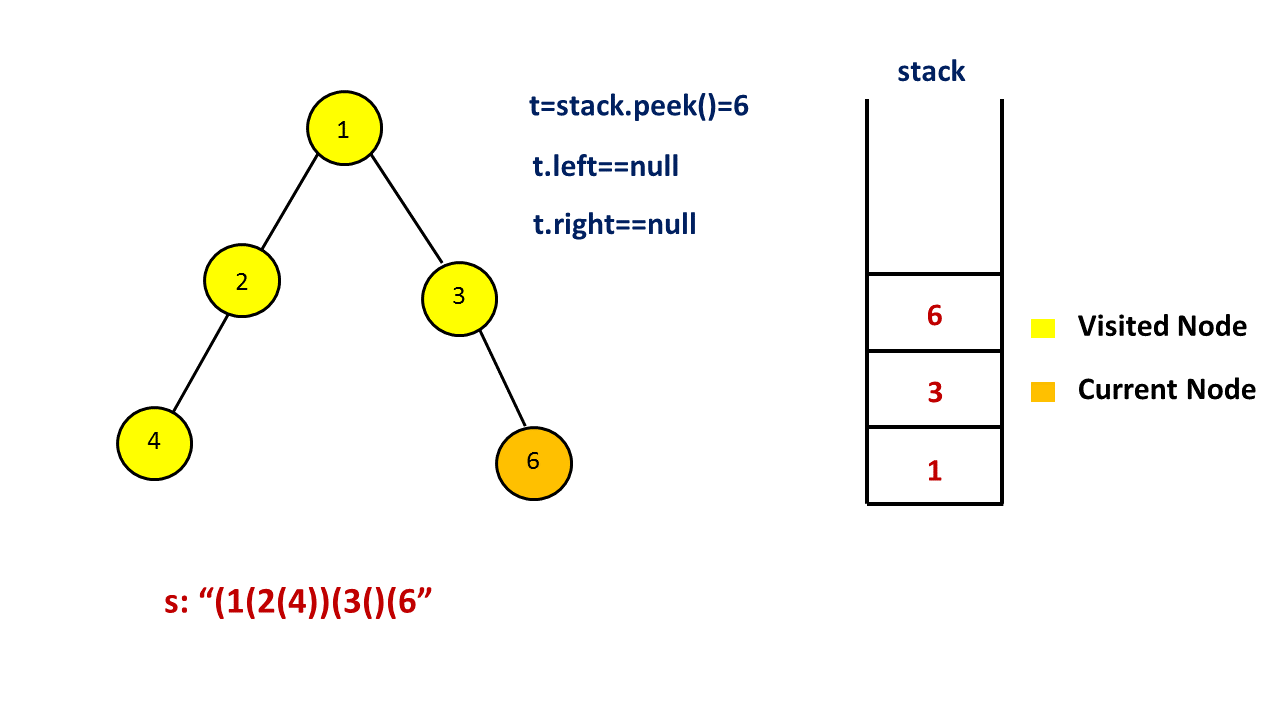
和方法一相同,这里会出现四种情况:
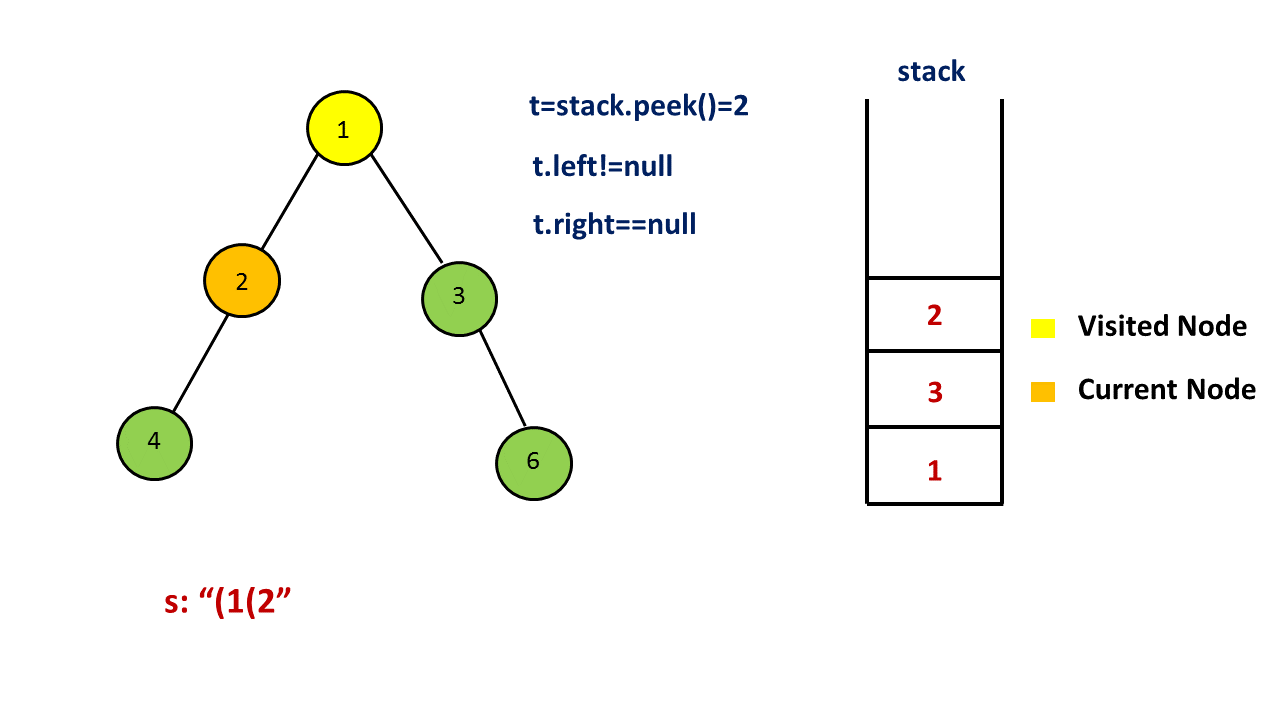
如果当前节点有两个孩子,那么我们先将右孩子入栈,再将左孩子入栈,从而保证前序遍历的顺序;
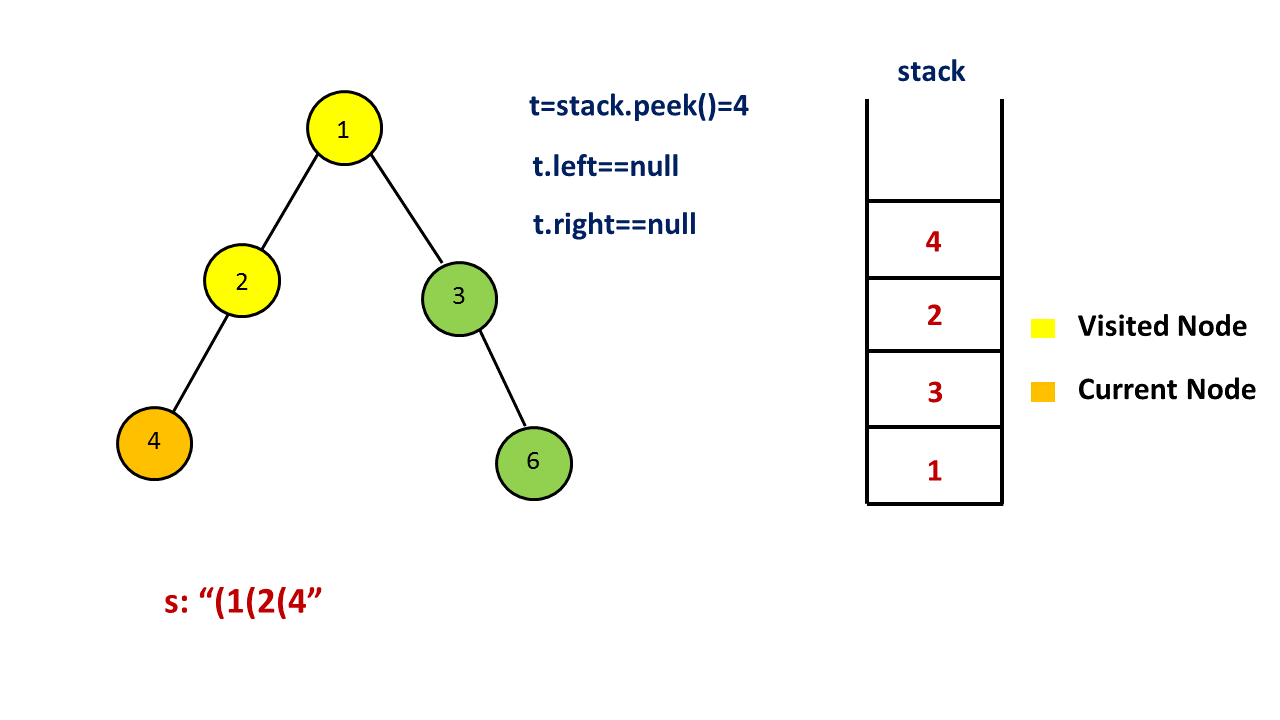
如果当前节点没有孩子,我们什么都不做;
如果当前节点只有左孩子,那么我们将左孩子入栈;
如果当前节点只有右孩子,那么需要在答案末尾添加一对 `()’ 表示空的左孩子,再将右孩子入栈。
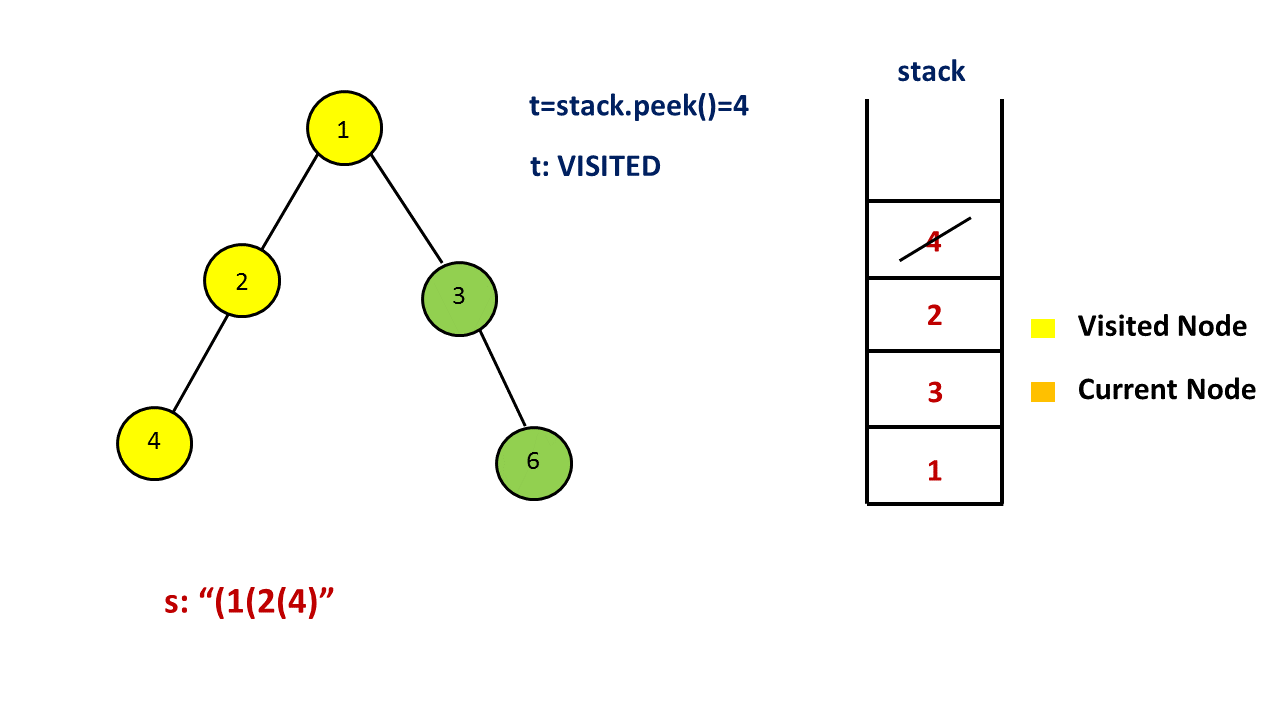
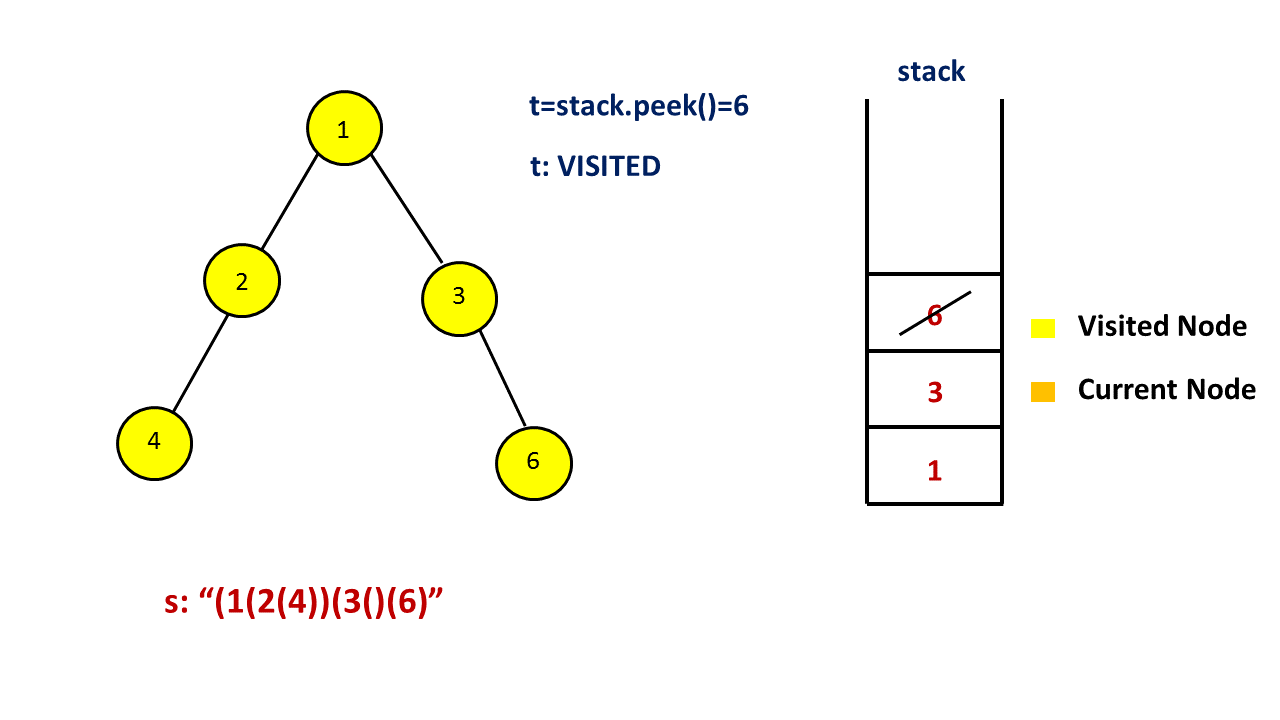
注意这四种情况中,我们都不会将当前节点出栈,原因是我们一开始添加了 (' 表示节点的开始,在以当前节点为根的子树中所有节点遍历完成之后,我们才会在答案末尾添加 )’ 表示节点的结束。因此我们需要用上面提到的集合来存储遍历过的节点,如果当前栈顶的元素遍历过,那么就需要在答案末尾添加 `)’ ,并将这个节点出栈。
<
[sol2-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 class Solution : def tree2str (self, root: Optional [TreeNode] ) -> str : ans = "" st = [root] vis = set () while st: node = st[-1 ] if node in vis: if node != root: ans += ")" st.pop() else : vis.add(node) if node != root: ans += "(" ans += str (node.val) if node.left is None and node.right: ans += "()" if node.right: st.append(node.right) if node.left: st.append(node.left) return ans
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public : string tree2str (TreeNode *root) { string ans = "" ; stack<TreeNode *> st; st.push (root); unordered_set<TreeNode *> vis; while (!st.empty ()) { auto node = st.top (); if (vis.count (node)) { if (node != root) { ans += ")" ; } st.pop (); } else { vis.insert (node); if (node != root) { ans += "(" ; } ans += to_string (node->val); if (node->left == nullptr && node->right != nullptr ) { ans += "()" ; } if (node->right != nullptr ) { st.push (node->right); } if (node->left != nullptr ) { st.push (node->left); } } } return ans; } };
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution { public String tree2str (TreeNode root) { StringBuffer ans = new StringBuffer (); Deque<TreeNode> stack = new ArrayDeque <TreeNode>(); stack.push(root); Set<TreeNode> visited = new HashSet <TreeNode>(); while (!stack.isEmpty()) { TreeNode node = stack.peek(); if (!visited.add(node)) { if (node != root) { ans.append(")" ); } stack.pop(); } else { if (node != root) { ans.append("(" ); } ans.append(node.val); if (node.left == null && node.right != null ) { ans.append("()" ); } if (node.right != null ) { stack.push(node.right); } if (node.left != null ) { stack.push(node.left); } } } return ans.toString(); } }
[sol2-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public class Solution { public string Tree2str (TreeNode root ) StringBuilder ans = new StringBuilder(); Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>(); stack.Push(root); ISet<TreeNode> visited = new HashSet<TreeNode>(); while (stack.Count > 0 ) { TreeNode node = stack.Peek(); if (!visited.Add(node)) { if (node != root) { ans.Append(")" ); } stack.Pop(); } else { if (node != root) { ans.Append("(" ); } ans.Append(node.val); if (node.left == null && node.right != null ) { ans.Append("()" ); } if (node.right != null ) { stack.Push(node.right); } if (node.left != null ) { stack.Push(node.left); } } } return ans.ToString(); } }
[sol2-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 func tree2str (root *TreeNode) string { ans := &strings.Builder{} st := []*TreeNode{root} vis := map [*TreeNode]bool {} for len (st) > 0 { node := st[len (st)-1 ] if vis[node] { if (node != root) { ans.WriteByte(')' ) } st = st[:len (st)-1 ] } else { vis[node] = true if (node != root) { ans.WriteByte('(' ) } ans.WriteString(strconv.Itoa(node.Val)) if node.Left == nil && node.Right != nil { ans.WriteString("()" ) } if node.Right != nil { st = append (st, node.Right) } if node.Left != nil { st = append (st, node.Left) } } } return ans.String() }
[sol2-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 #define MAX_STR_LEN 100000 #define MAX_NODE_SIZE 100000 typedef struct { struct TreeNode * key ; UT_hash_handle hh; } HashItem; char * tree2str (struct TreeNode* root) { char * ans = (char *)malloc (sizeof (char ) * MAX_STR_LEN); int pos = 0 ; struct TreeNode ** st =struct TreeNode **)malloc (sizeof (struct TreeNode *) * MAX_NODE_SIZE); HashItem * vis = NULL ; int top = 0 ; st[top++] = root; while (top > 0 ) { struct TreeNode * node =1 ]; HashItem * pEntry = NULL ; HASH_FIND_PTR(vis, &node, pEntry); if (pEntry != NULL ) { if (node != root) { ans[pos++] = ')' ; } top--; } else { pEntry = (HashItem *)malloc (sizeof (HashItem)); pEntry->key = node; HASH_ADD_PTR(vis, key, pEntry); if (node != root) { ans[pos++] = '(' ; } pos += sprintf (ans + pos, "%d" , node->val); if (node->left == NULL && node->right != NULL ) { pos += sprintf (ans + pos, "()" ); } if (node->right != NULL ) { st[top++] = node->right; } if (node->left != NULL ) { st[top++] = node->left; } } } ans[pos] = '\0' ; free (st); HashItem * curr, * next; HASH_ITER(hh, vis, curr, next) { HASH_DEL(vis, curr); free (curr); } return ans; }
[sol2-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 var tree2str = function (root ) { let ans = '' ; const st = [root]; const vis = new Set (); while (st.length ) { const node = st[st.length - 1 ]; if (vis.has (node)) { if (node !== root) { ans += ')' ; } st.pop (); } else { vis.add (node); if (node !== root) { ans += '(' ; } ans += '' + node.val ; if (!node.left && node.right ) { ans += '()' ; } if (node.right ) { st.push (node.right ); } if (node.left ) { st.push (node.left ); } } } return ans; };
复杂度分析