给你一个按 非递减顺序 排列的整数数组 nums 。
请你判断是否能在将 nums 分割成 一个或多个子序列 的同时满足下述 两个 条件:
每个子序列都是一个 连续递增序列 (即,每个整数 恰好 比前一个整数大 1 )。
所有子序列的长度 至少 为 3 **** 。
如果可以分割 nums 并满足上述条件,则返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
**输入:** nums = [1,2,3,3,4,5]
**输出:** true
**解释:** nums 可以分割成以下子序列:
[ _ **1**_ , _ **2**_ , _ **3**_ ,3,4,5] --> 1, 2, 3
[1,2,3, _ **3**_ , _ **4**_ , _ **5**_ ] --> 3, 4, 5
示例 2:
**输入:** nums = [1,2,3,3,4,4,5,5]
**输出:** true
**解释:** nums 可以分割成以下子序列:
[ _ **1**_ , _ **2**_ , _ **3**_ ,3, _ **4**_ ,4, _ **5**_ ,5] --> 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
[1,2,3, _ **3**_ ,4, _ **4**_ ,5, _ **5**_ ] --> 3, 4, 5
示例 3:
**输入:** nums = [1,2,3,4,4,5]
**输出:** false
**解释:** 无法将 nums 分割成长度至少为 3 的连续递增子序列。
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 104-1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000nums 按非递减顺序排列
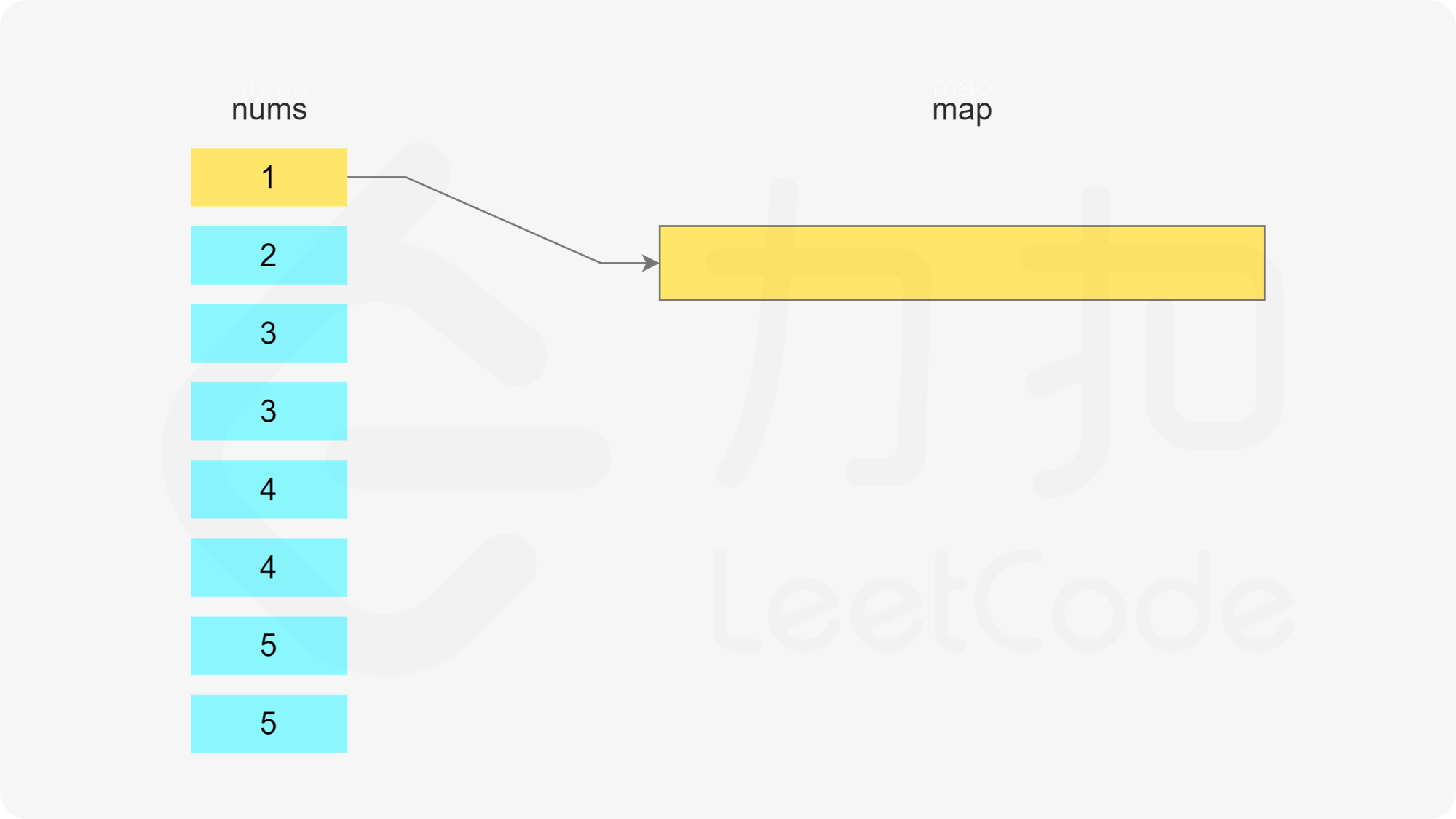
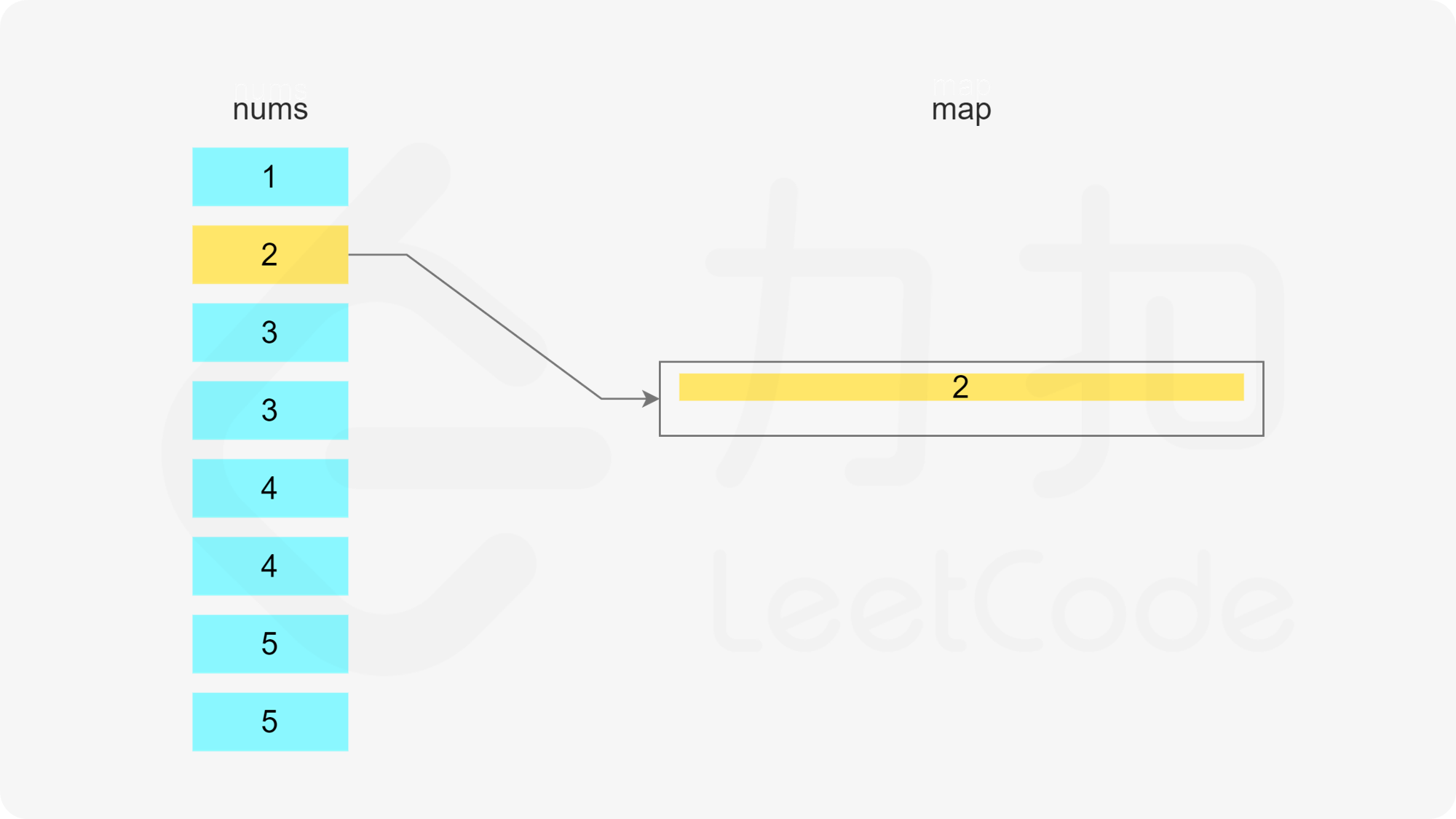
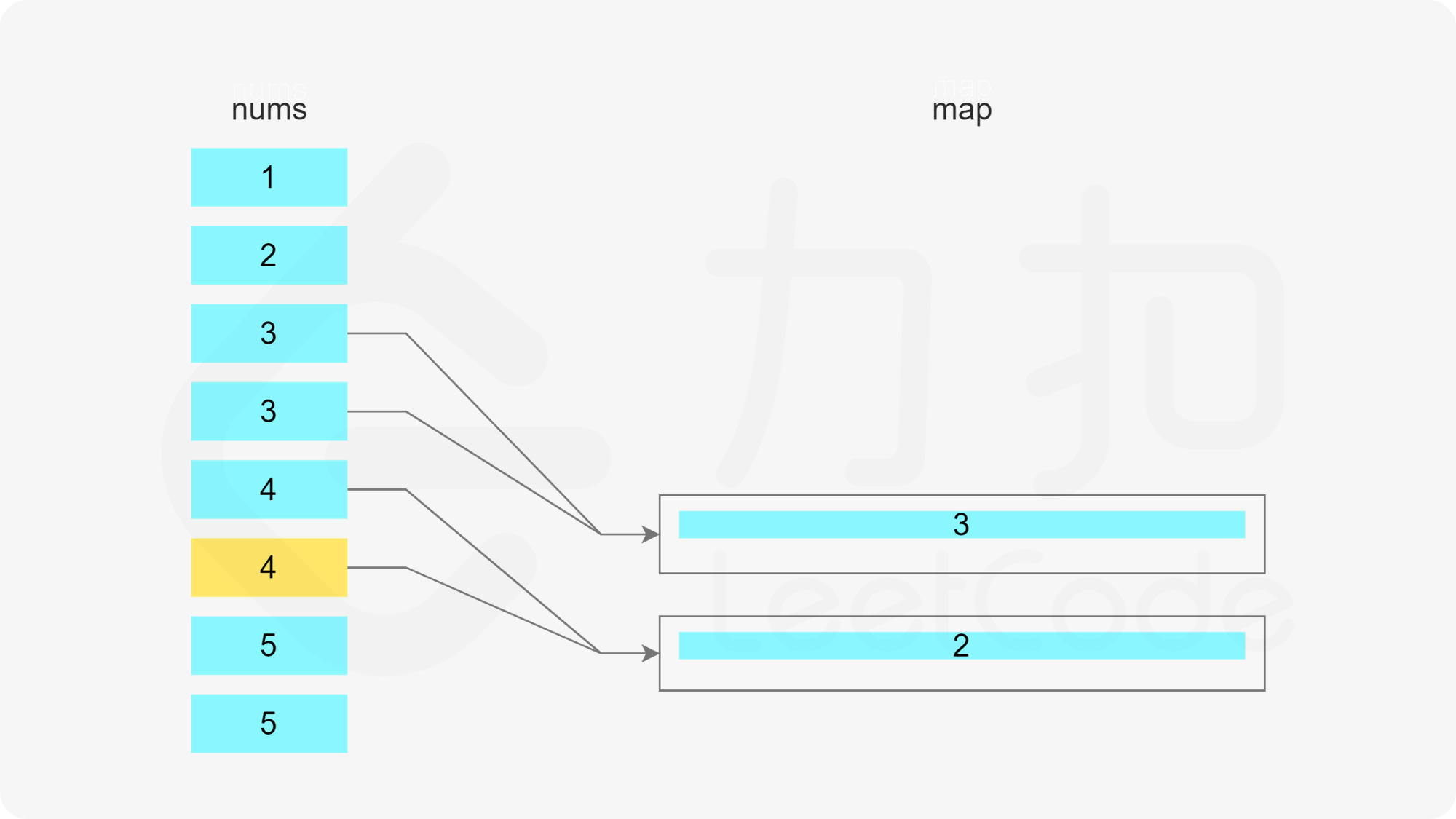
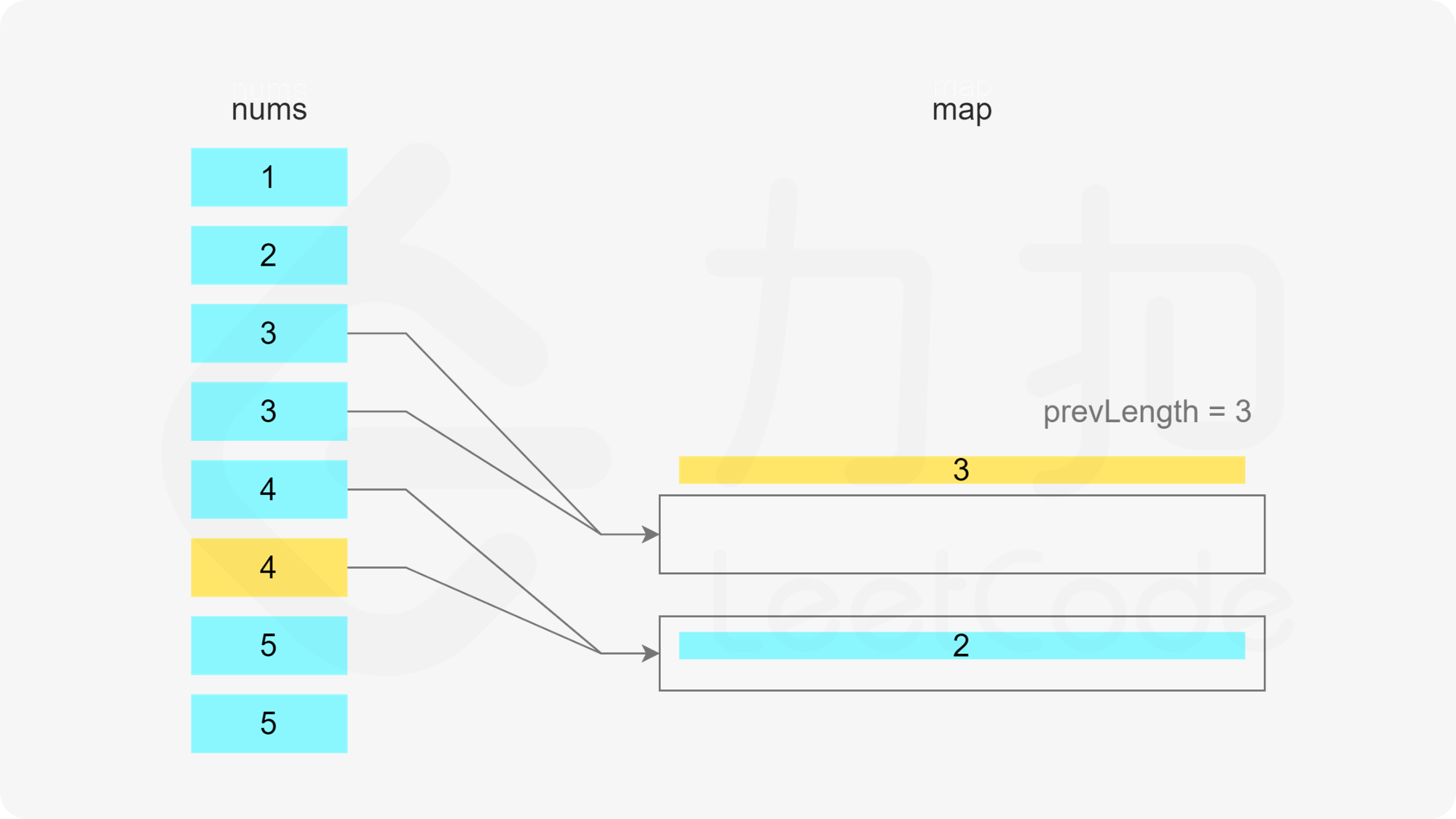
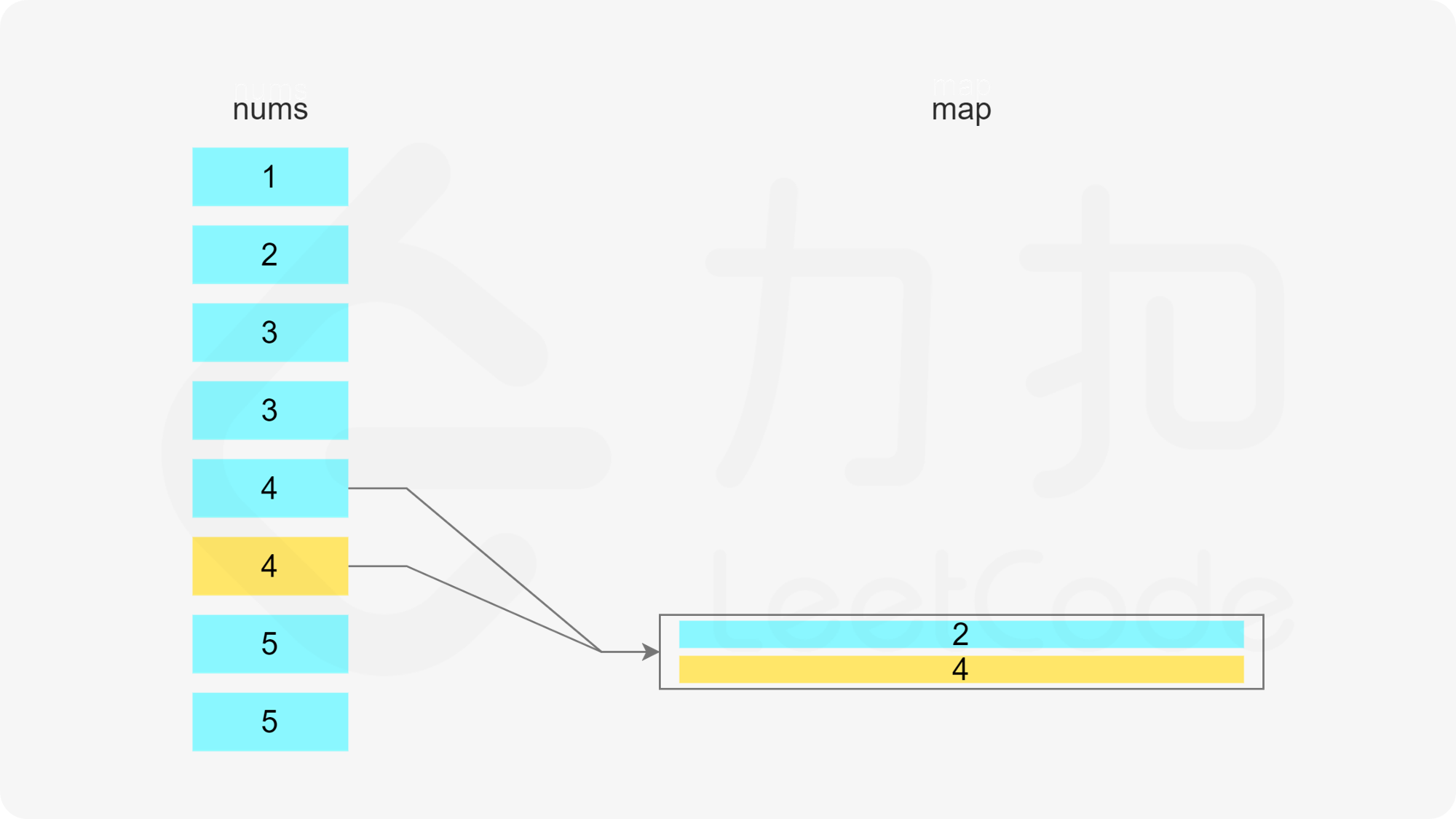
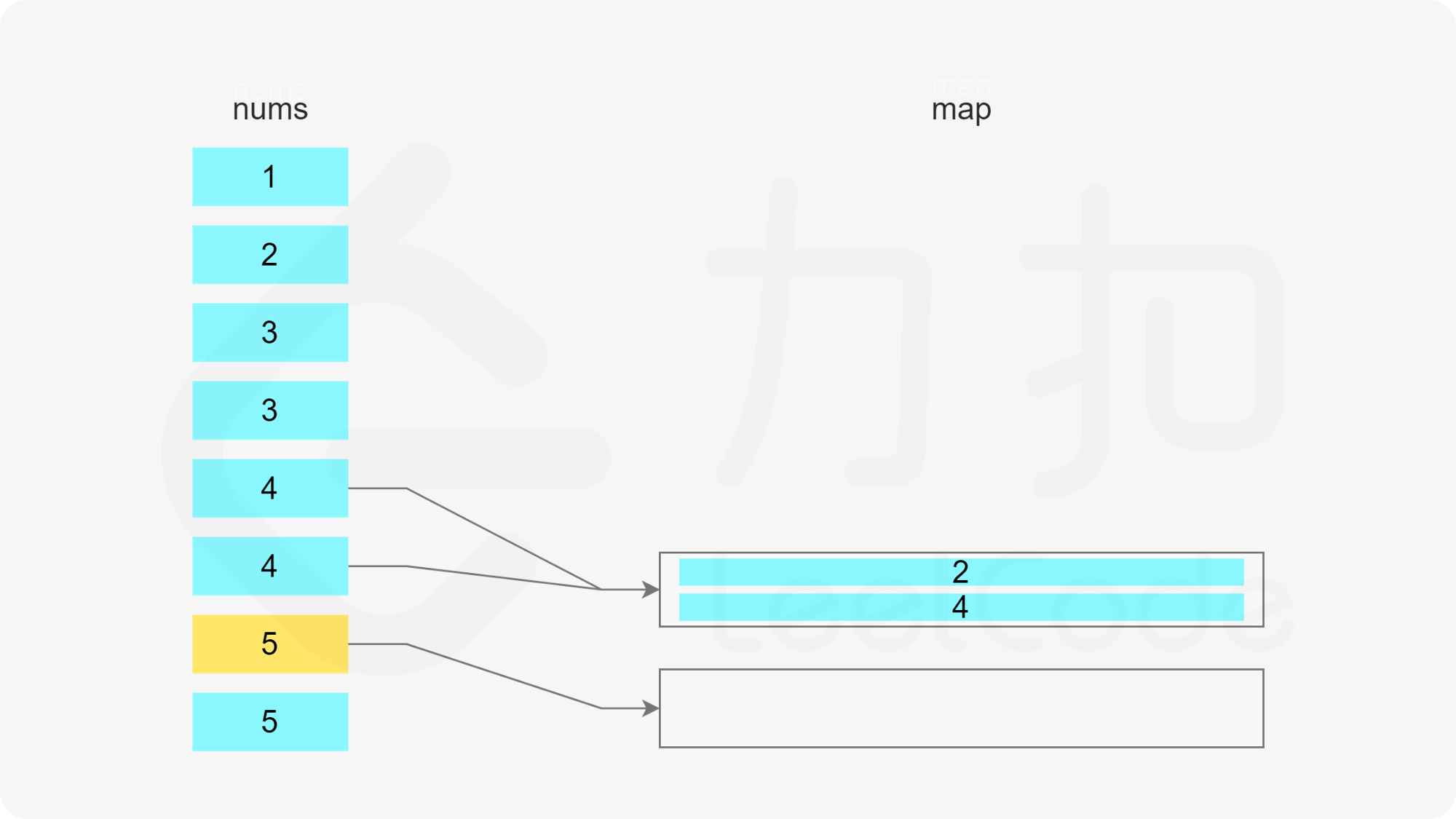
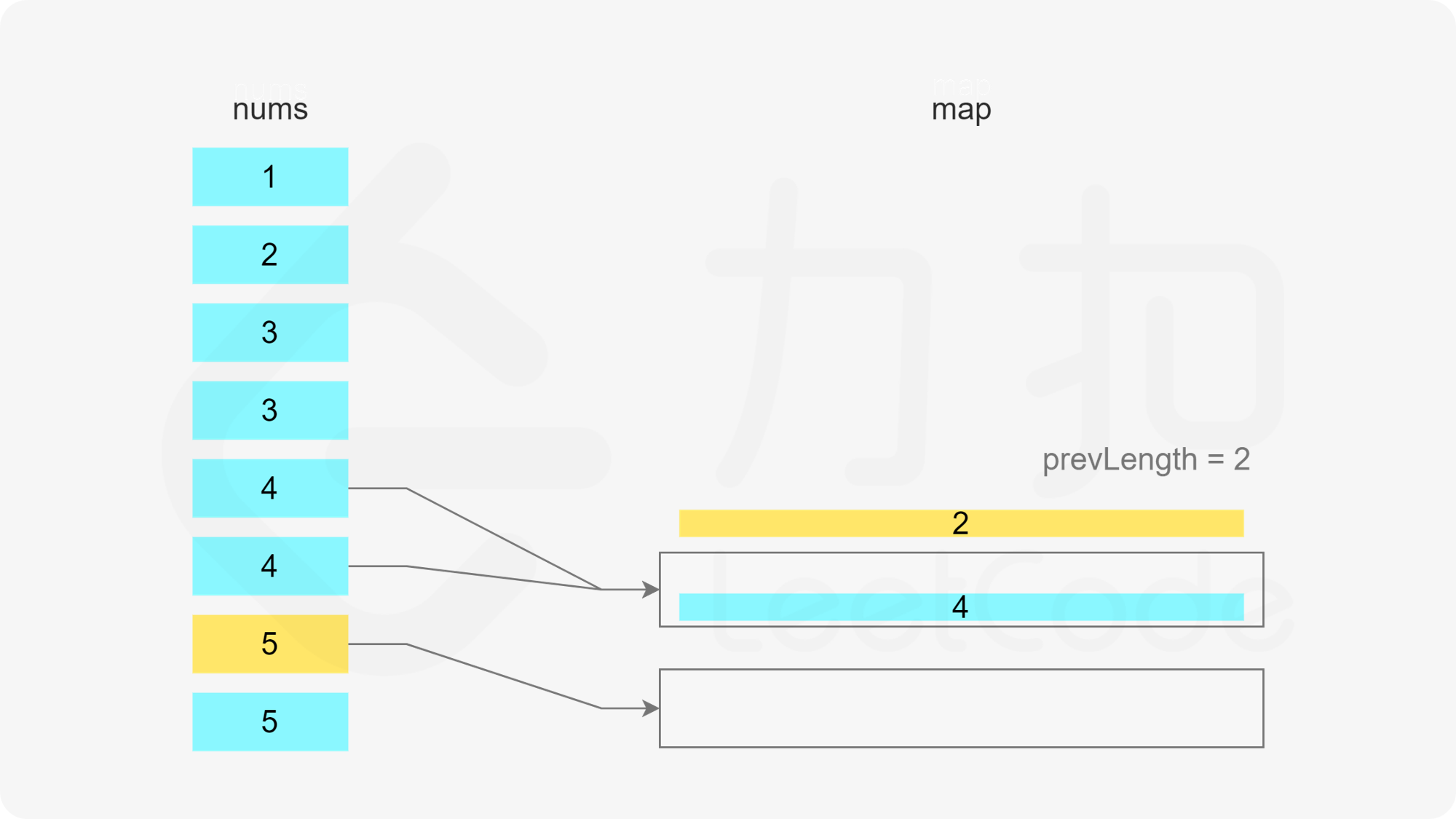
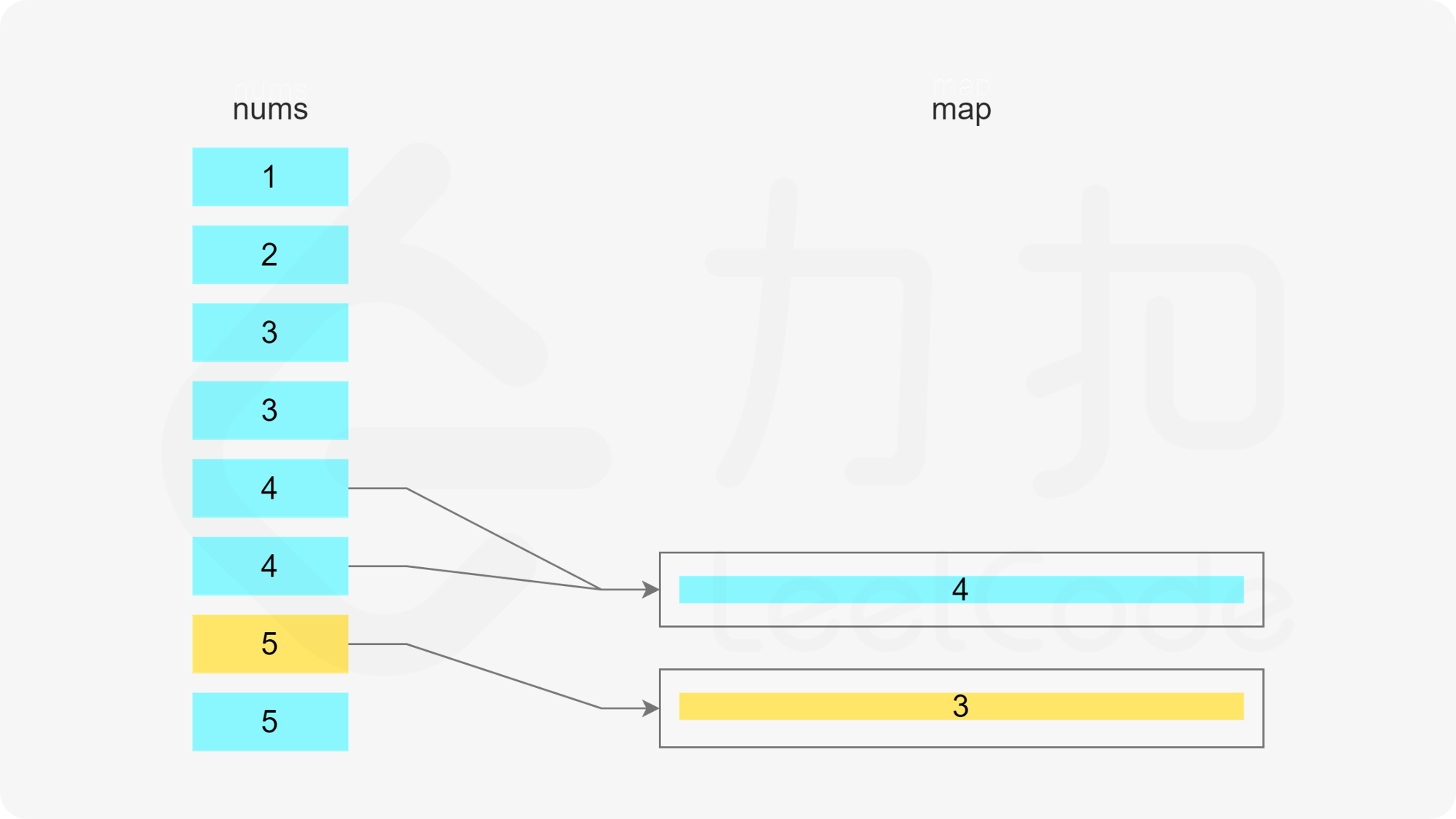
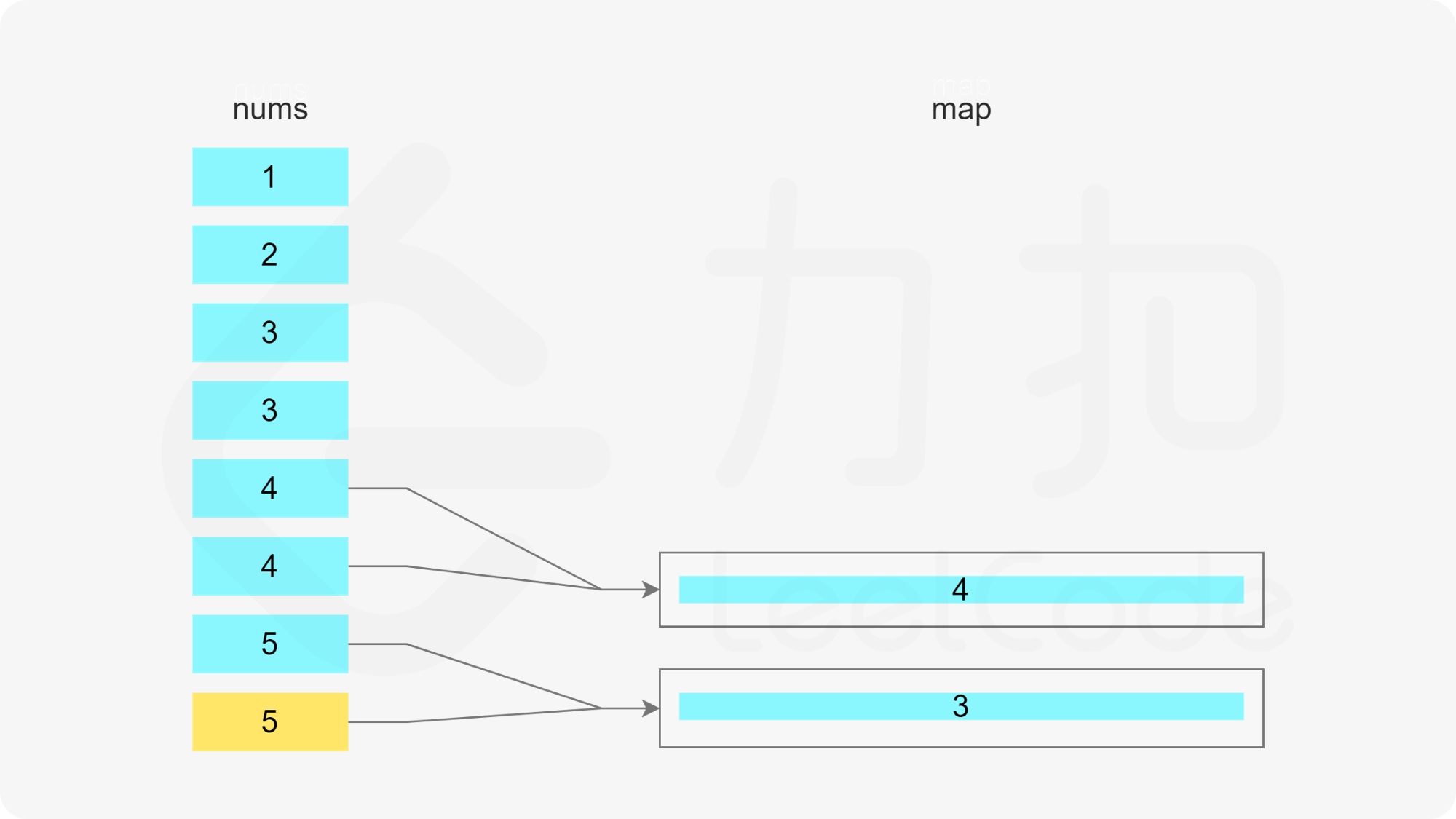
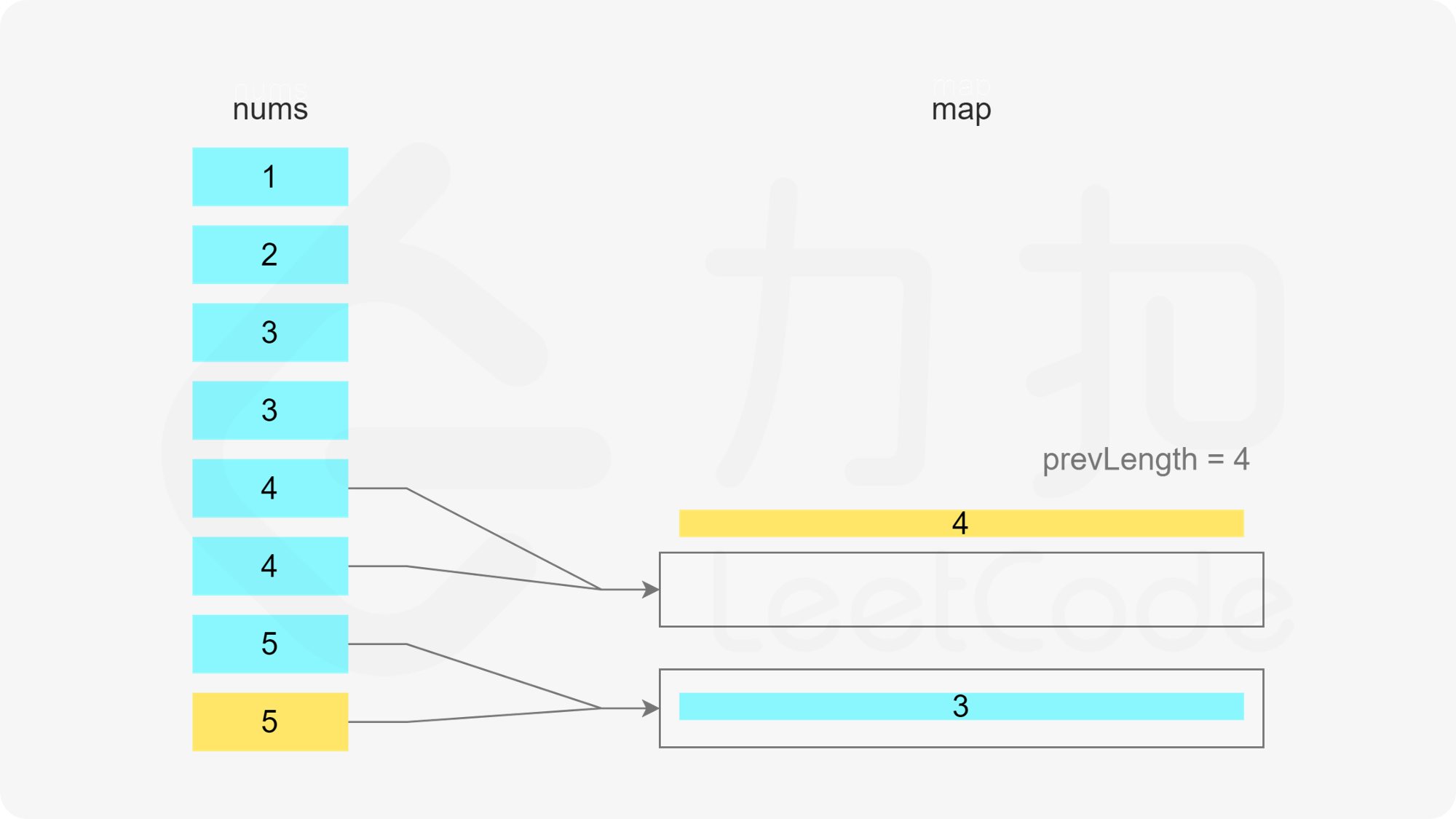
方法一:哈希表 + 最小堆 由于需要将数组分割成一个或多个由连续整数组成的子序列,因此只要知道子序列的最后一个数字和子序列的长度,就能确定子序列。
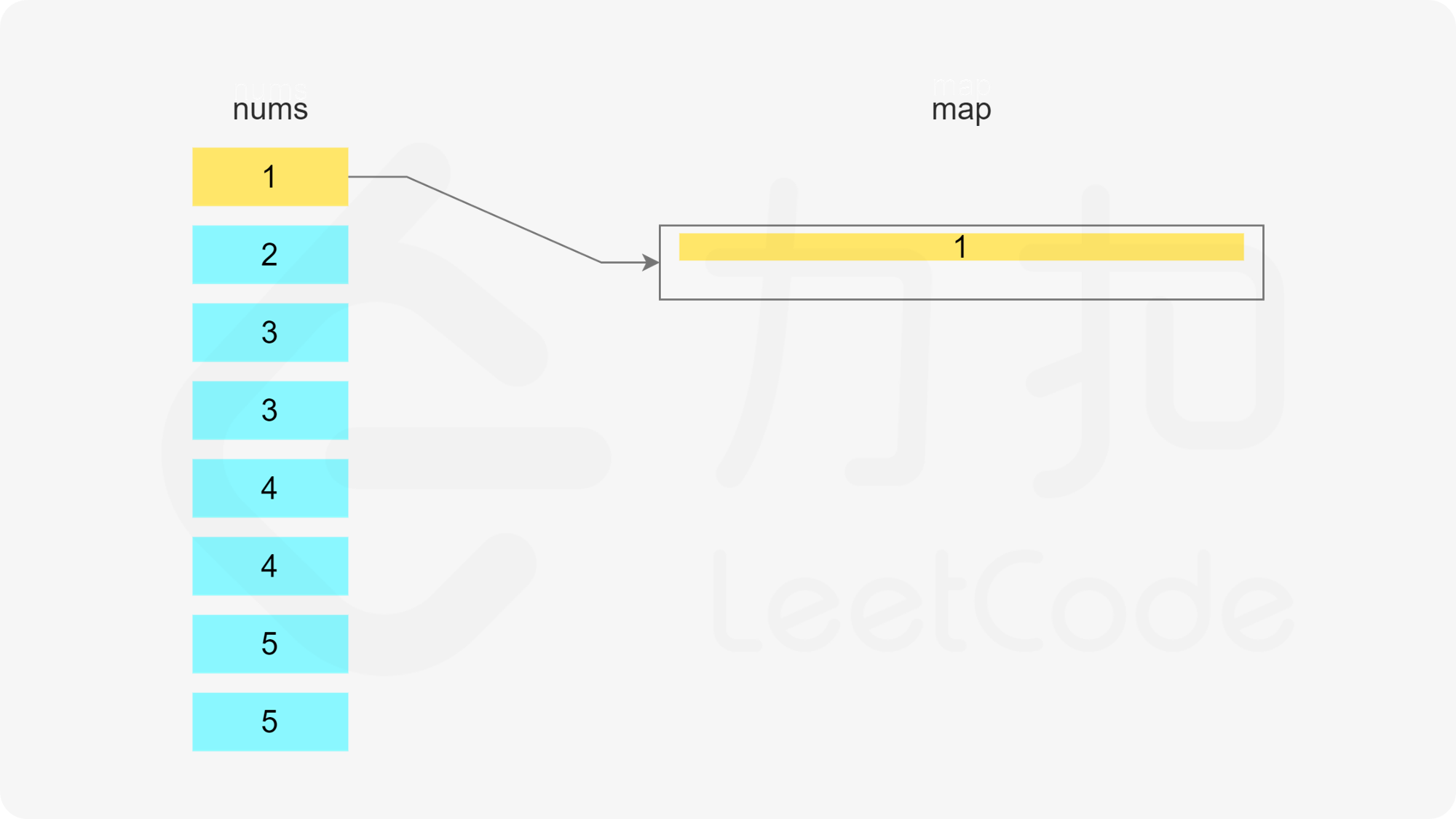
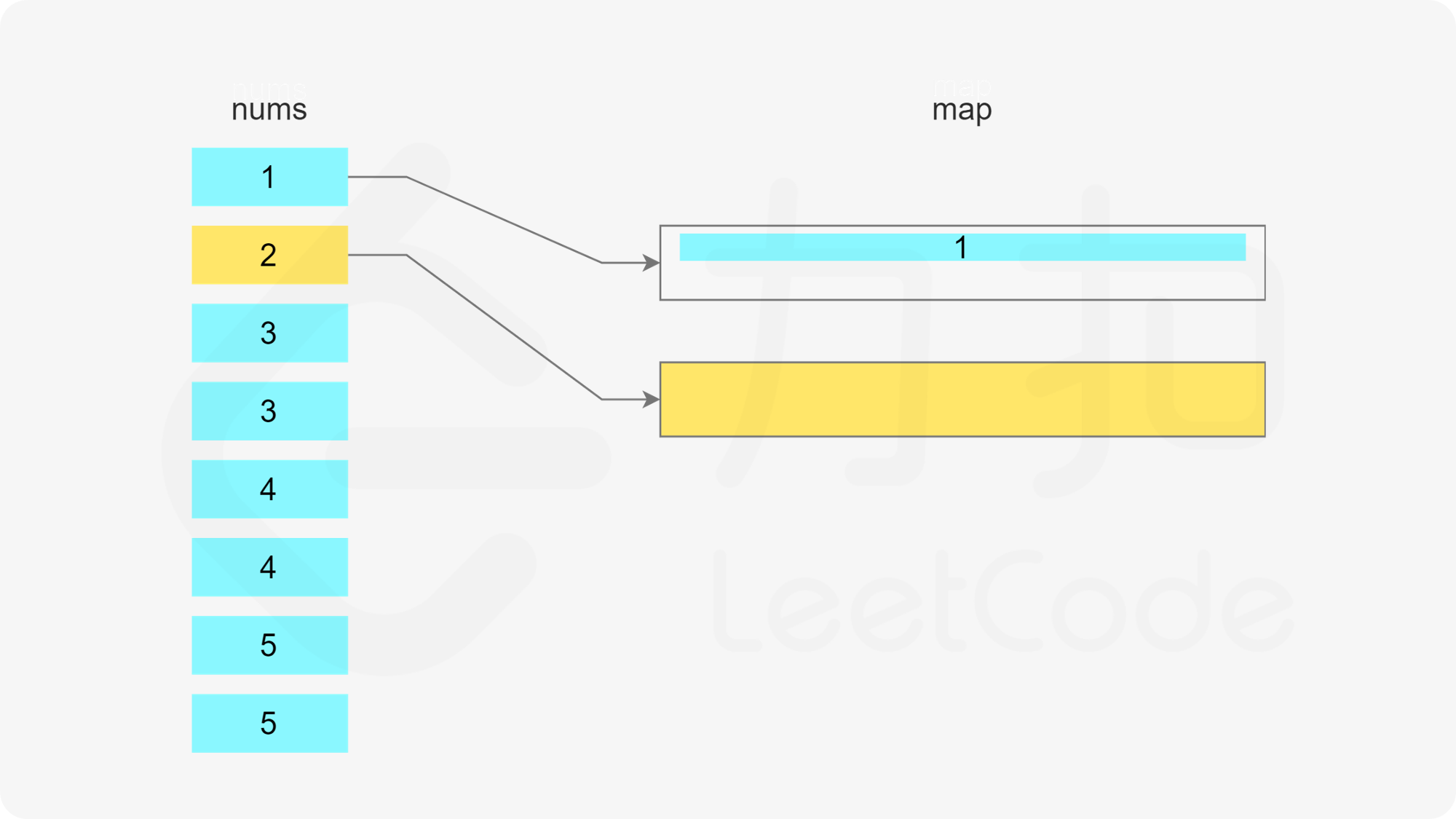
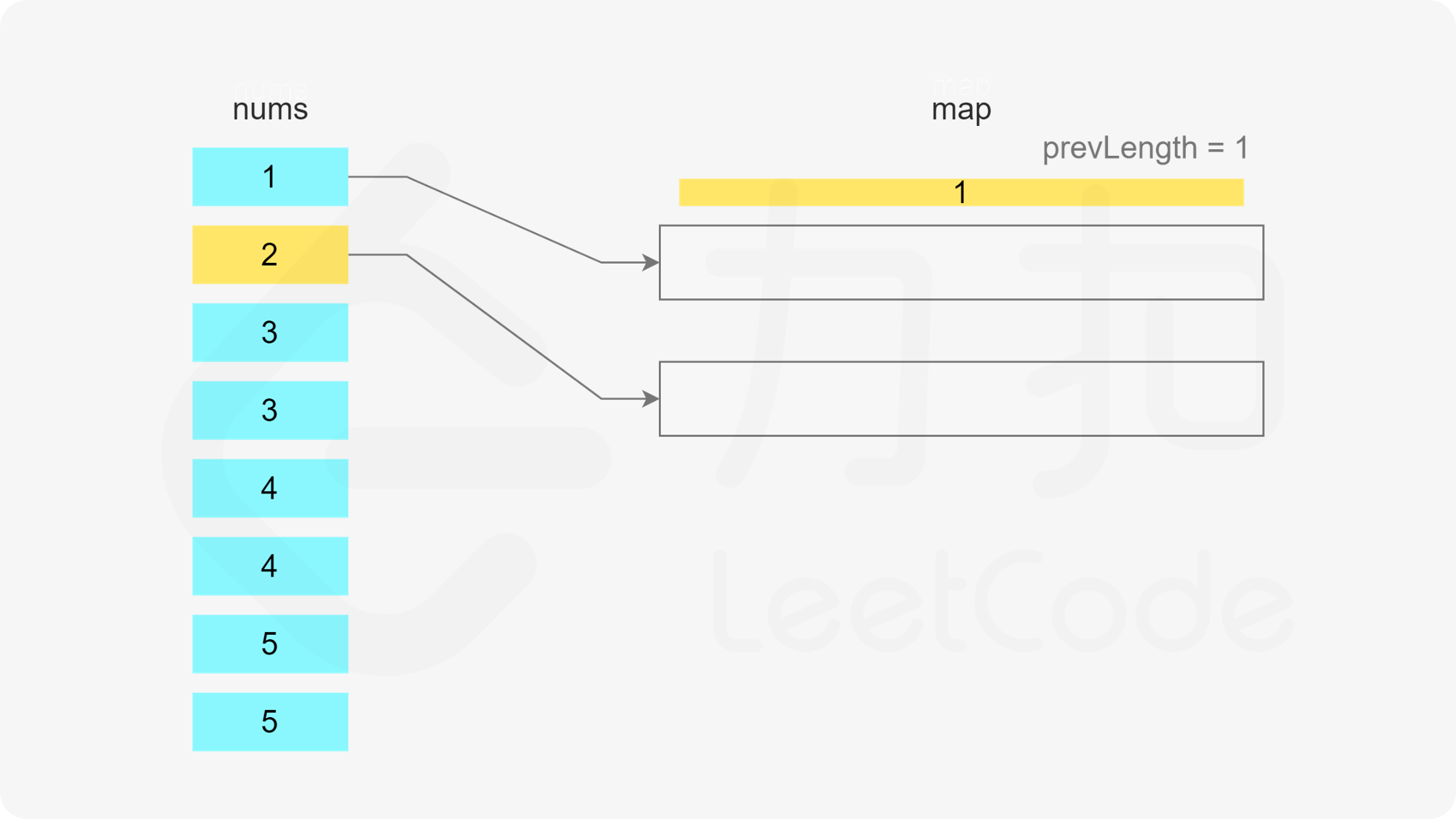
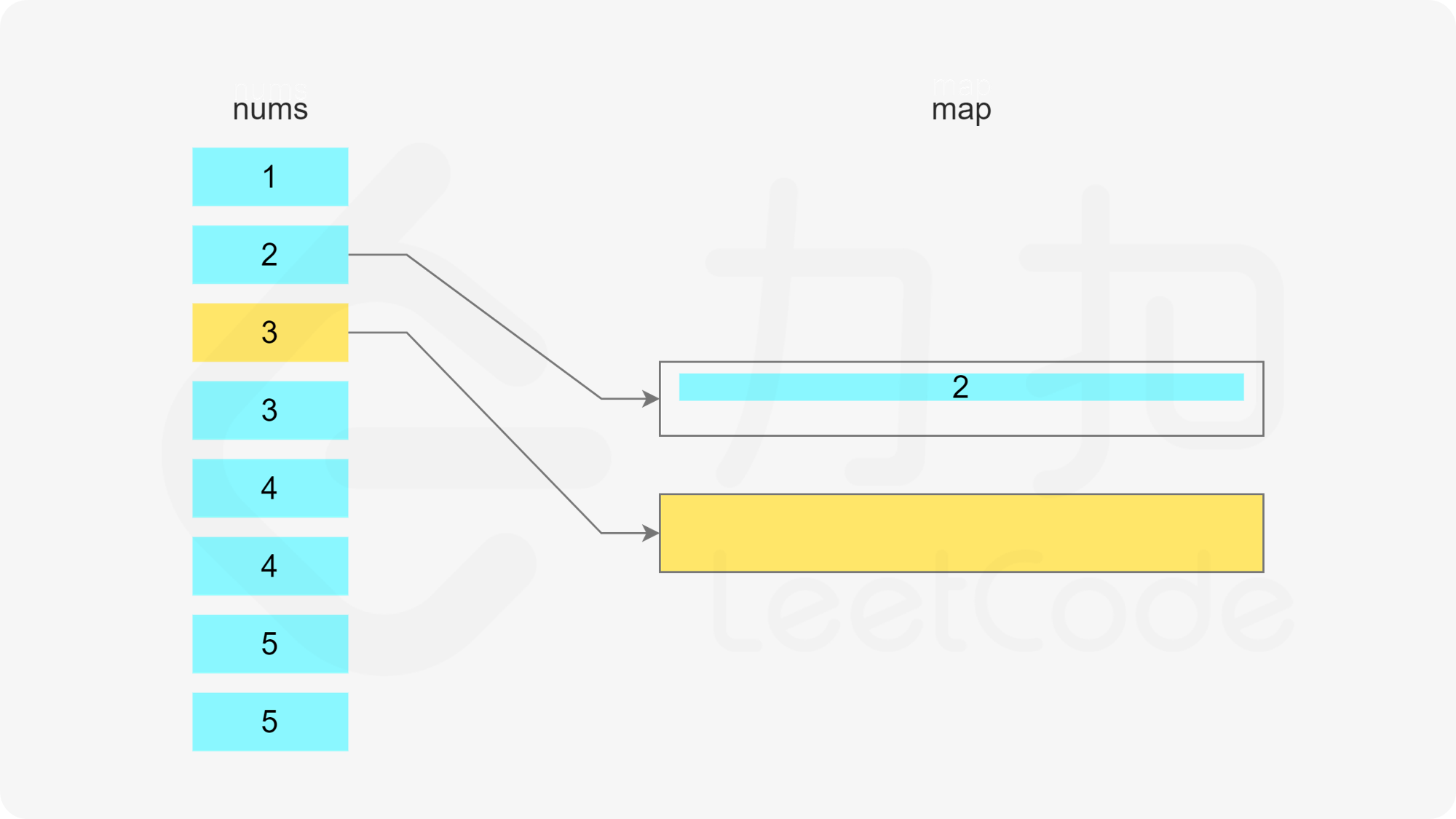
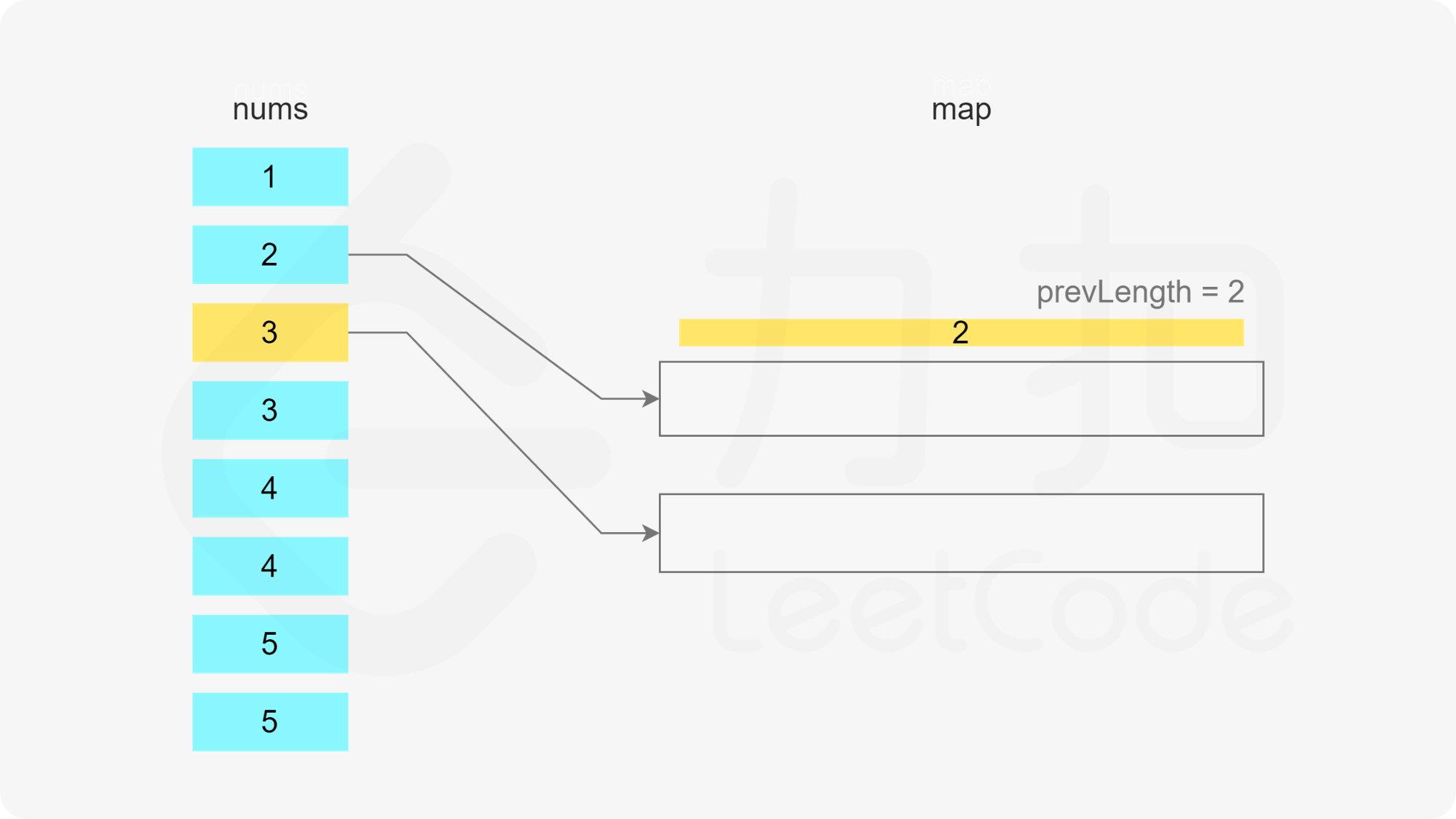
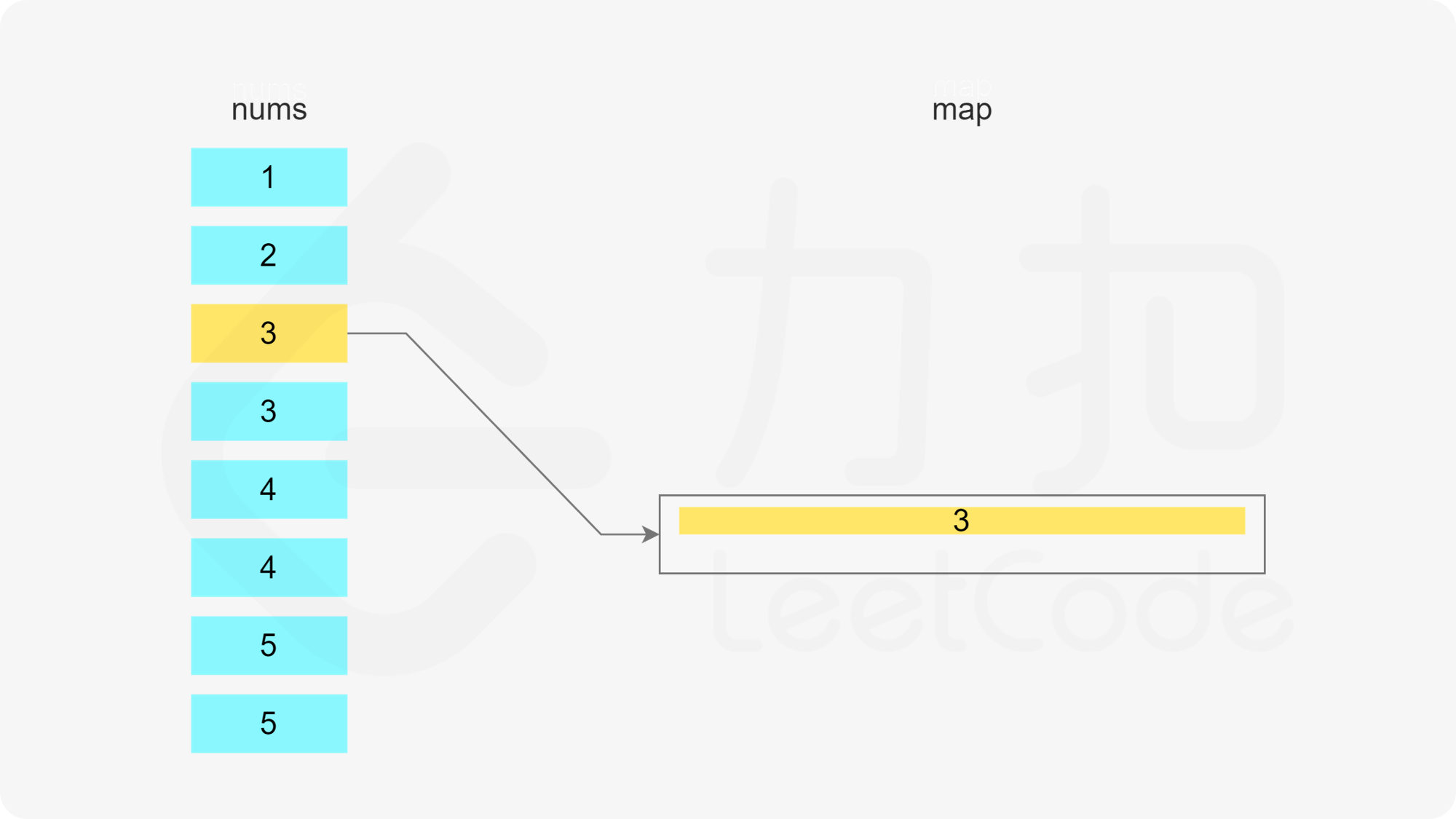
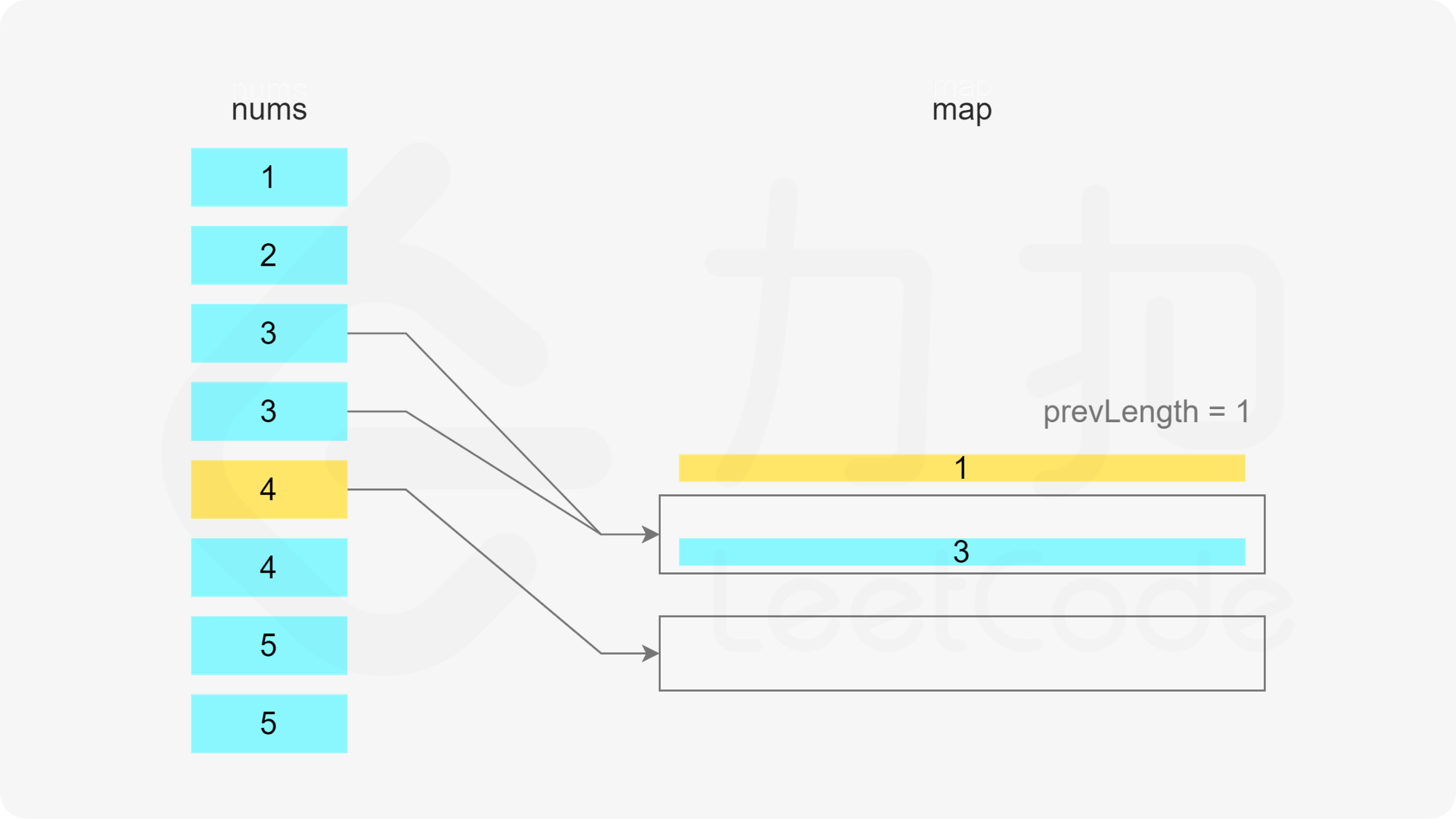
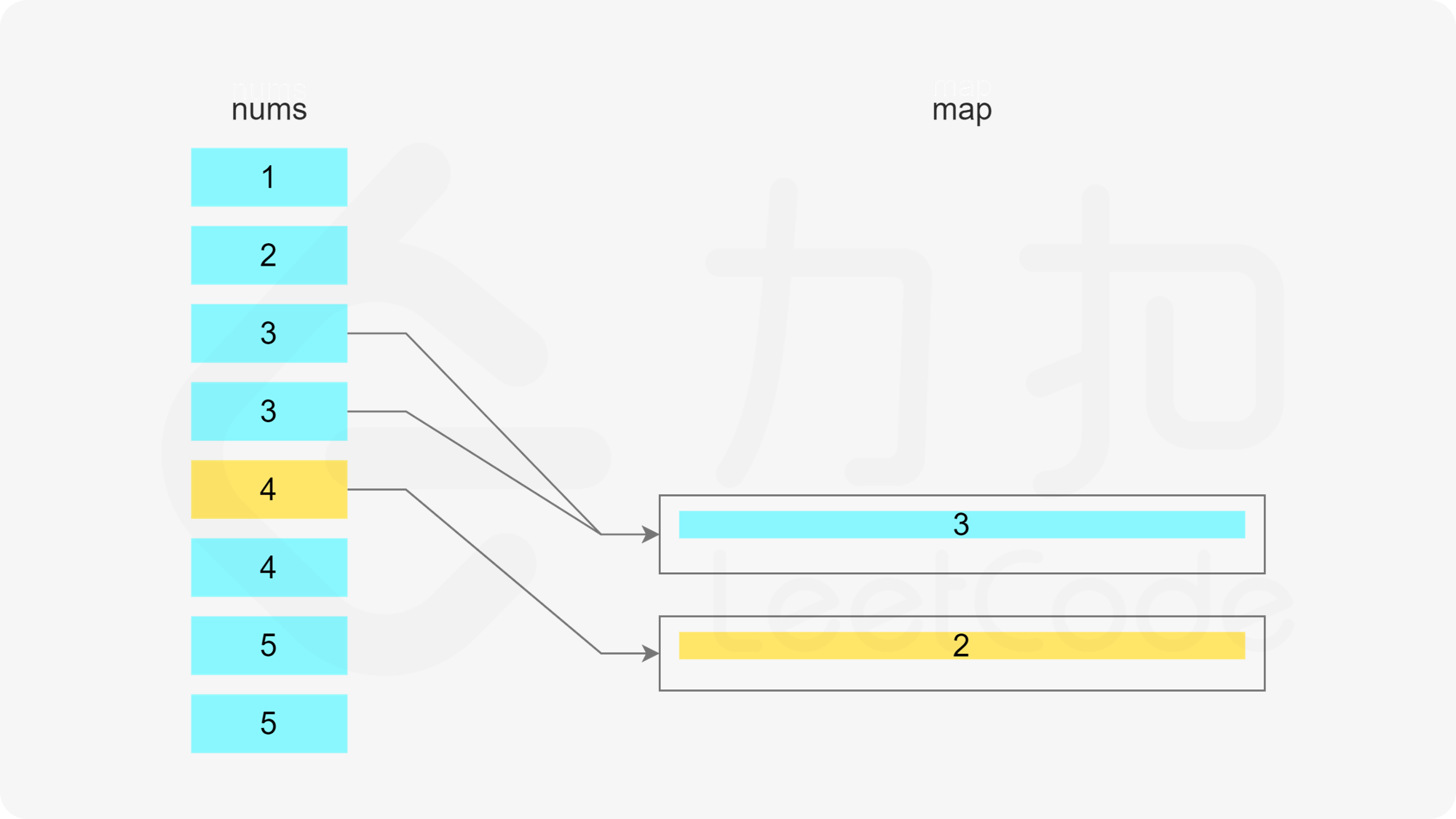
当 x 在数组中时,如果存在一个子序列以 x-1 结尾,长度为 k,则可以将 x 加入该子序列中,得到长度为 k+1 的子序列。如果不存在以 x-1 结尾的子序列,则必须新建一个只包含 x 的子序列,长度为 1。
当 x 在数组中时,如果存在多个子序列以 x-1 结尾,应该将 x 加入其中的哪一个子序列?由于题目要求每个子序列的长度至少为 3,显然应该让最短的子序列尽可能长,因此应该将 x 加入其中最短的子序列。
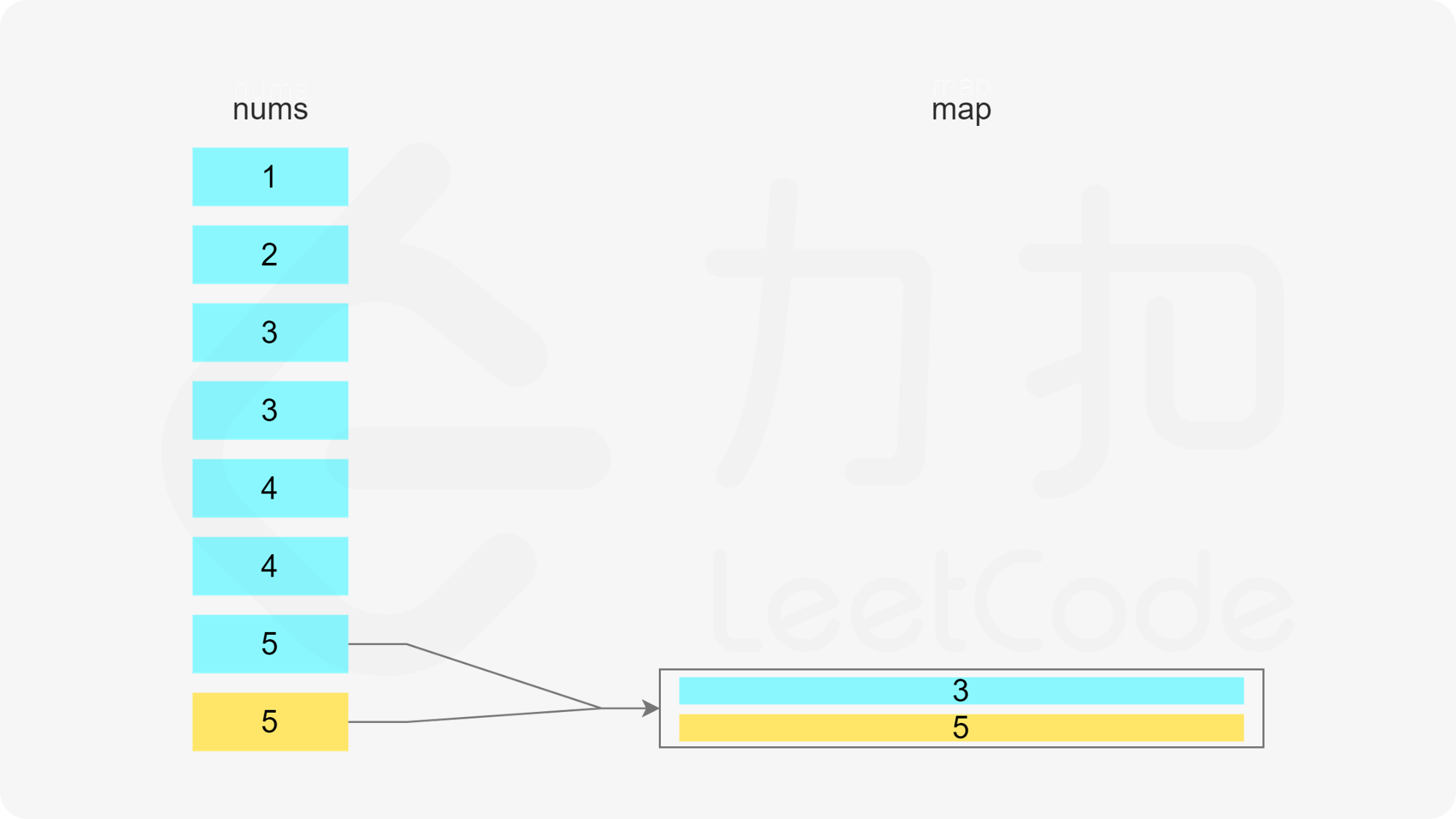
基于上述分析,可以使用哈希表和最小堆进行实现。
哈希表的键为子序列的最后一个数字,值为最小堆,用于存储所有的子序列长度,最小堆满足堆顶的元素是最小的,因此堆顶的元素即为最小的子序列长度。
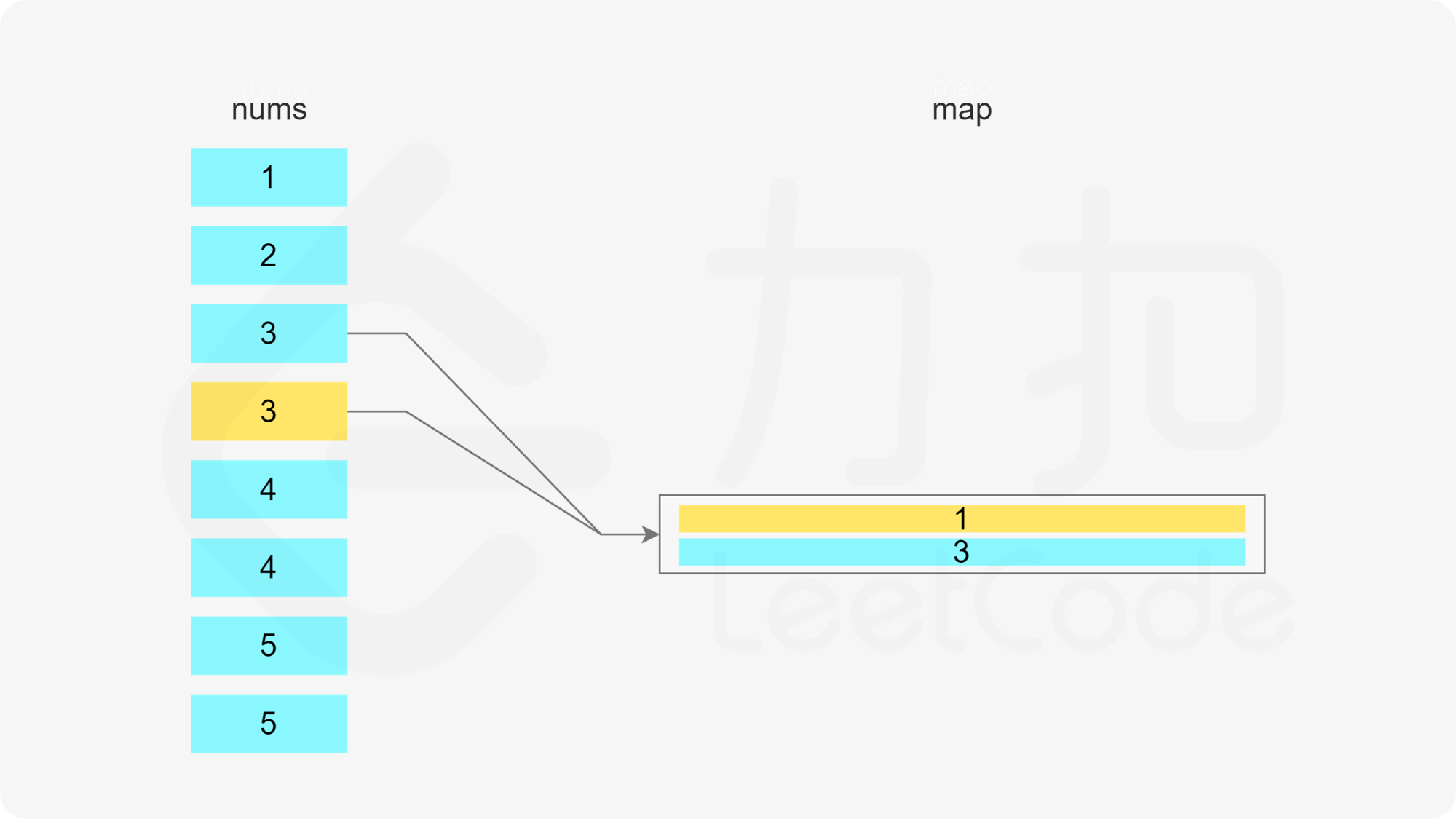
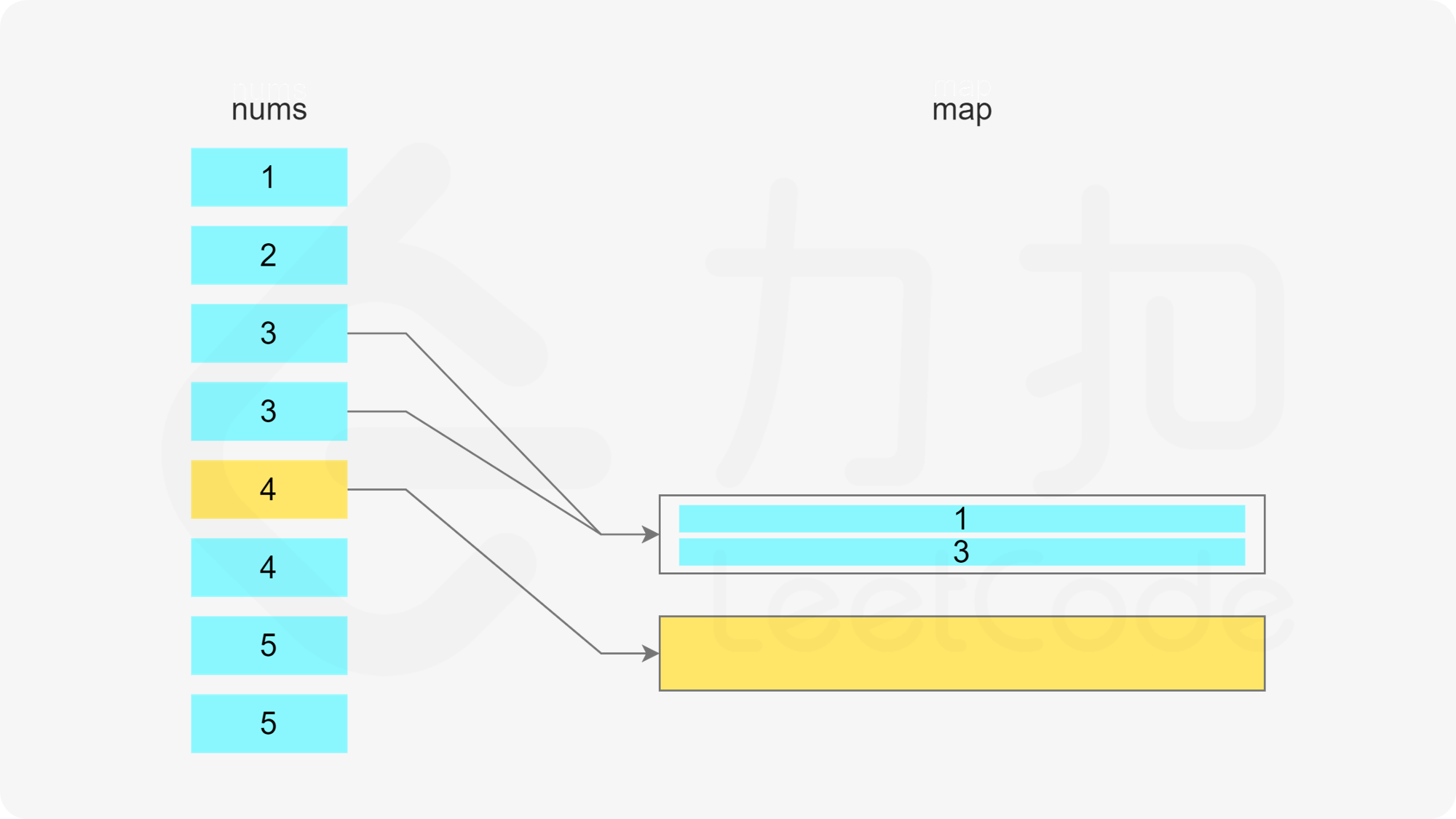
遍历数组,当遍历到元素 x 时,可以得到一个以 x 结尾的子序列。
由于数组是有序的,因此当遍历到元素 x 时,数组中所有小于 x 的元素都已经被遍历过,不会出现当前元素比之前的元素小的情况。
遍历结束之后,检查哈希表中存储的每个子序列的长度是否都不小于 3,即可判断是否可以完成分割。由于哈希表中的每条记录的值都是最小堆,堆顶元素为最小的子序列长度(以当前的键为最后一个数字的子序列),因此只要遍历每个最小堆的堆顶元素,即可判断每个子序列的长度是否都不小于 3。
<
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 class Solution { public boolean isPossible (int [] nums) { Map<Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>> map = new HashMap <Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>>(); for (int x : nums) { if (!map.containsKey(x)) { map.put(x, new PriorityQueue <Integer>()); } if (map.containsKey(x - 1 )) { int prevLength = map.get(x - 1 ).poll(); if (map.get(x - 1 ).isEmpty()) { map.remove(x - 1 ); } map.get(x).offer(prevLength + 1 ); } else { map.get(x).offer(1 ); } } Set<Map.Entry<Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>>> entrySet = map.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<Integer, PriorityQueue<Integer>> entry : entrySet) { PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = entry.getValue(); if (queue.peek() < 3 ) { return false ; } } return true ; } }
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution {public : bool isPossible (vector<int >& nums) unordered_map<int , priority_queue<int , vector<int >,greater<int >>> mp; for (auto & x : nums) { if (mp.find (x) == mp.end ()) { mp[x] = priority_queue<int , vector<int >,greater<int >>(); } if (mp.find (x - 1 ) != mp.end ()) { int prevLength = mp[x - 1 ].top (); mp[x - 1 ].pop (); if (mp[x - 1 ].empty ()) { mp.erase (x - 1 ); } mp[x].push (prevLength + 1 ); } else { mp[x].push (1 ); } } for (auto it = mp.begin (); it != mp.end (); ++it) { priority_queue<int , vector<int >,greater<int >> queue = it->second; if (queue.top () < 3 ) { return false ; } } return true ; } };
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 var isPossible = function (nums ) { const map = new Map (); for (let x of nums) { if (!map.has (x)) { map.set (x, new MinPriorityQueue ()); } if (map.has (x - 1 )) { const prevLength = map.get (x - 1 ).dequeue ()['priority' ]; if (map.get (x - 1 ).isEmpty ()) { map.delete (x - 1 ); } map.get (x).enqueue (x, prevLength + 1 ); } else { map.get (x).enqueue (x, 1 ); } } for (let [key, value] of map.entries ()) { if (value.front ()['priority' ] < 3 ) { return false ; } } return true ; };
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 class Solution : def isPossible (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> bool : mp = collections.defaultdict(list ) for x in nums: if queue := mp.get(x - 1 ): prevLength = heapq.heappop(queue) heapq.heappush(mp[x], prevLength + 1 ) else : heapq.heappush(mp[x], 1 ) return not any (queue and queue[0 ] < 3 for queue in mp.values())
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 type hp struct { sort.IntSlice }func (h *hp) interface {}) { h.IntSlice = append (h.IntSlice, v.(int )) }func (h *hp) interface {} { a := h.IntSlice; v := a[len (a)-1 ]; h.IntSlice = a[:len (a)-1 ]; return v }func (h *hp) int ) { heap.Push(h, v) }func (h *hp) int { return heap.Pop(h).(int ) }func isPossible (nums []int ) bool { lens := map [int ]*hp{} for _, v := range nums { if lens[v] == nil { lens[v] = new (hp) } if h := lens[v-1 ]; h != nil { prevLen := h.pop() if h.Len() == 0 { delete (lens, v-1 ) } lens[v].push(prevLen + 1 ) } else { lens[v].push(1 ) } } for _, h := range lens { if h.IntSlice[0 ] < 3 { return false } } return true }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n \log n),其中 n 是数组的长度。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是数组的长度。需要使用哈希表和最小堆存储以每个数结尾的各个子序列的长度,哈希表和最小堆中的元素数量不会超过数组的长度。
方法二:贪心 从方法一可以看到,对于数组中的元素 x,如果存在一个子序列以 x-1 结尾,则可以将 x 加入该子序列中。将 x 加入已有的子序列总是比新建一个只包含 x 的子序列更优,因为前者可以将一个已有的子序列的长度增加 1,而后者新建一个长度为 1 的子序列,而题目要求分割成的子序列的长度都不小于 3,因此应该尽量避免新建短的子序列。
基于此,可以通过贪心的方法判断是否可以完成分割。
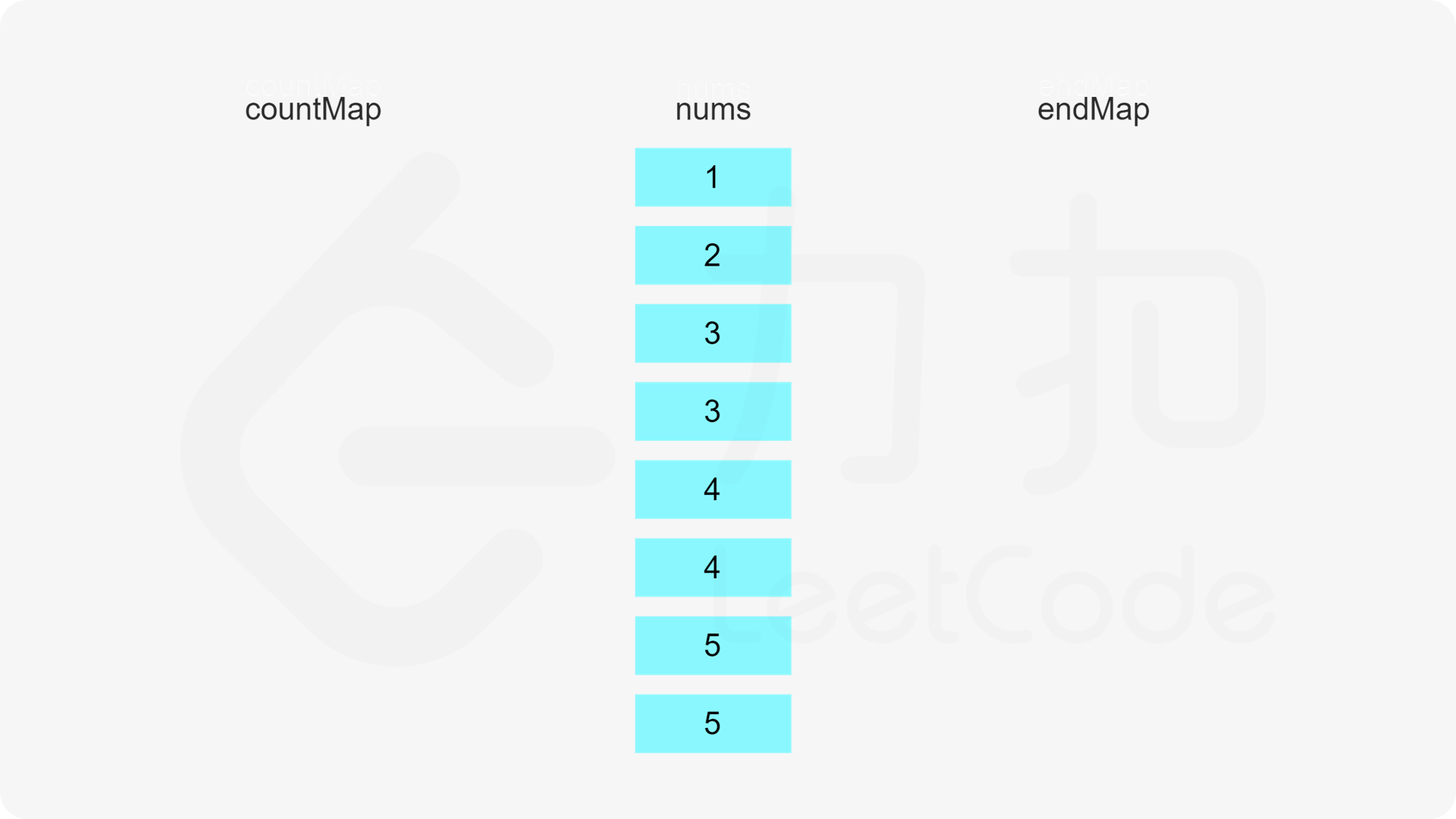
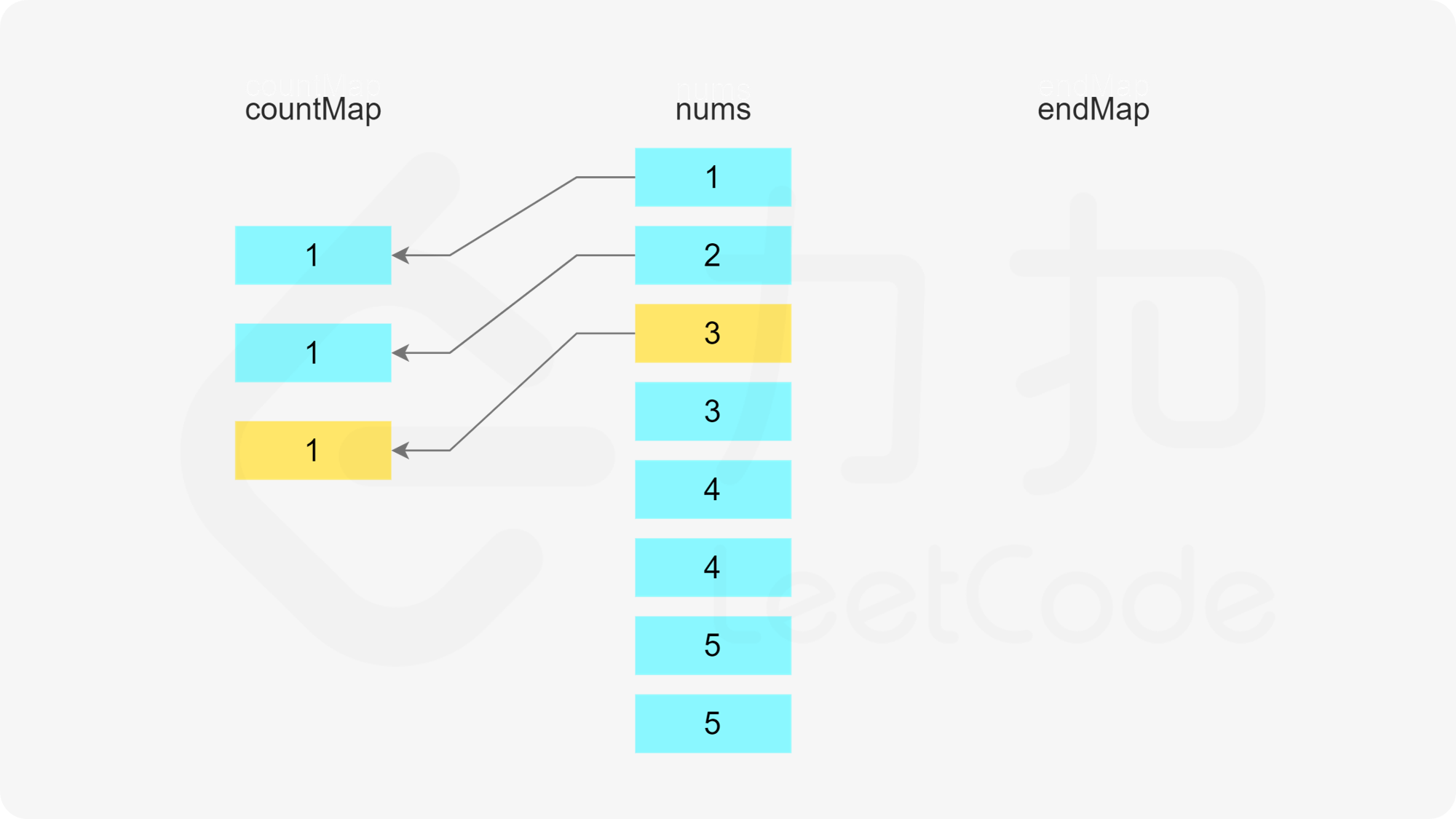
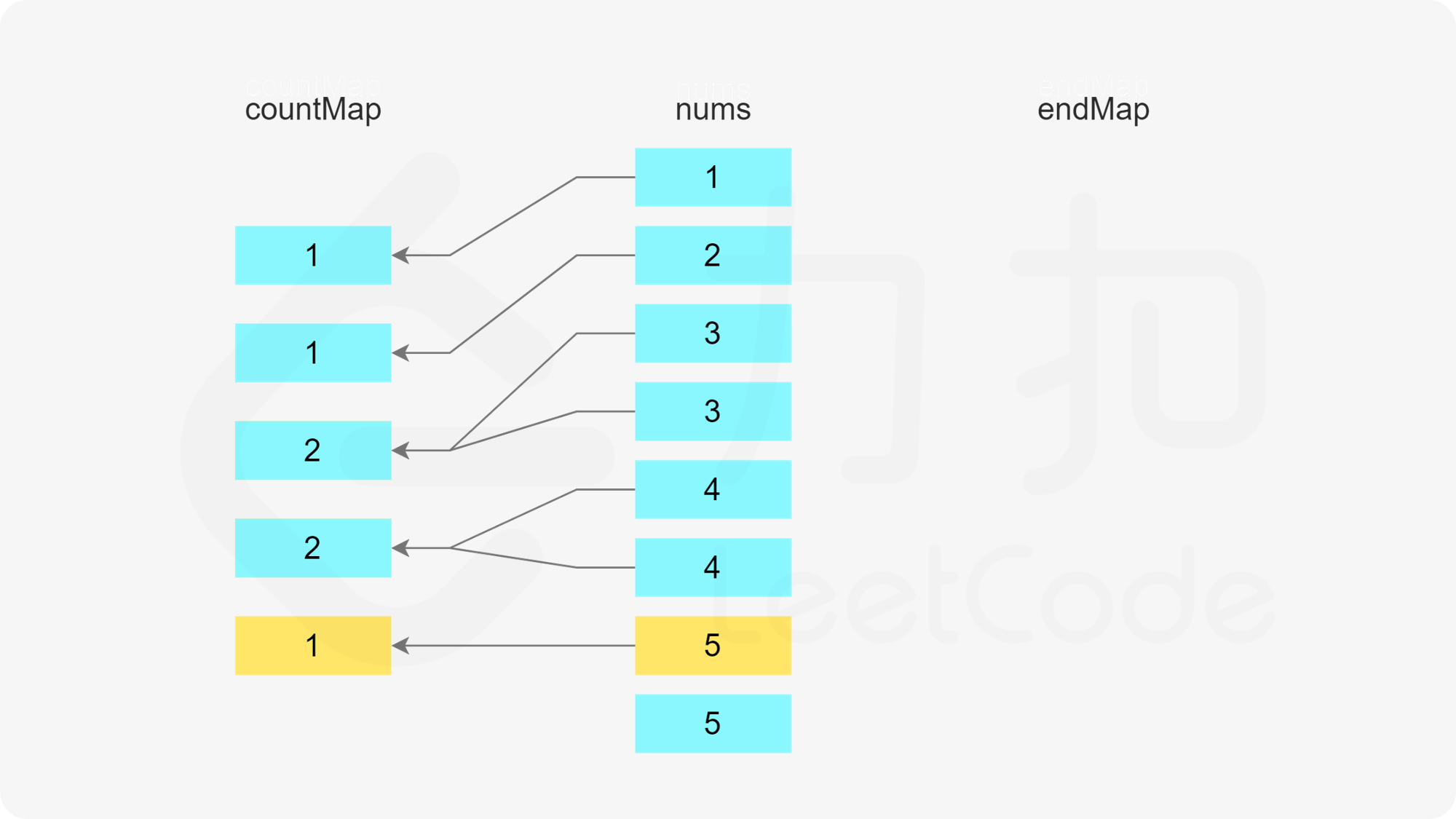
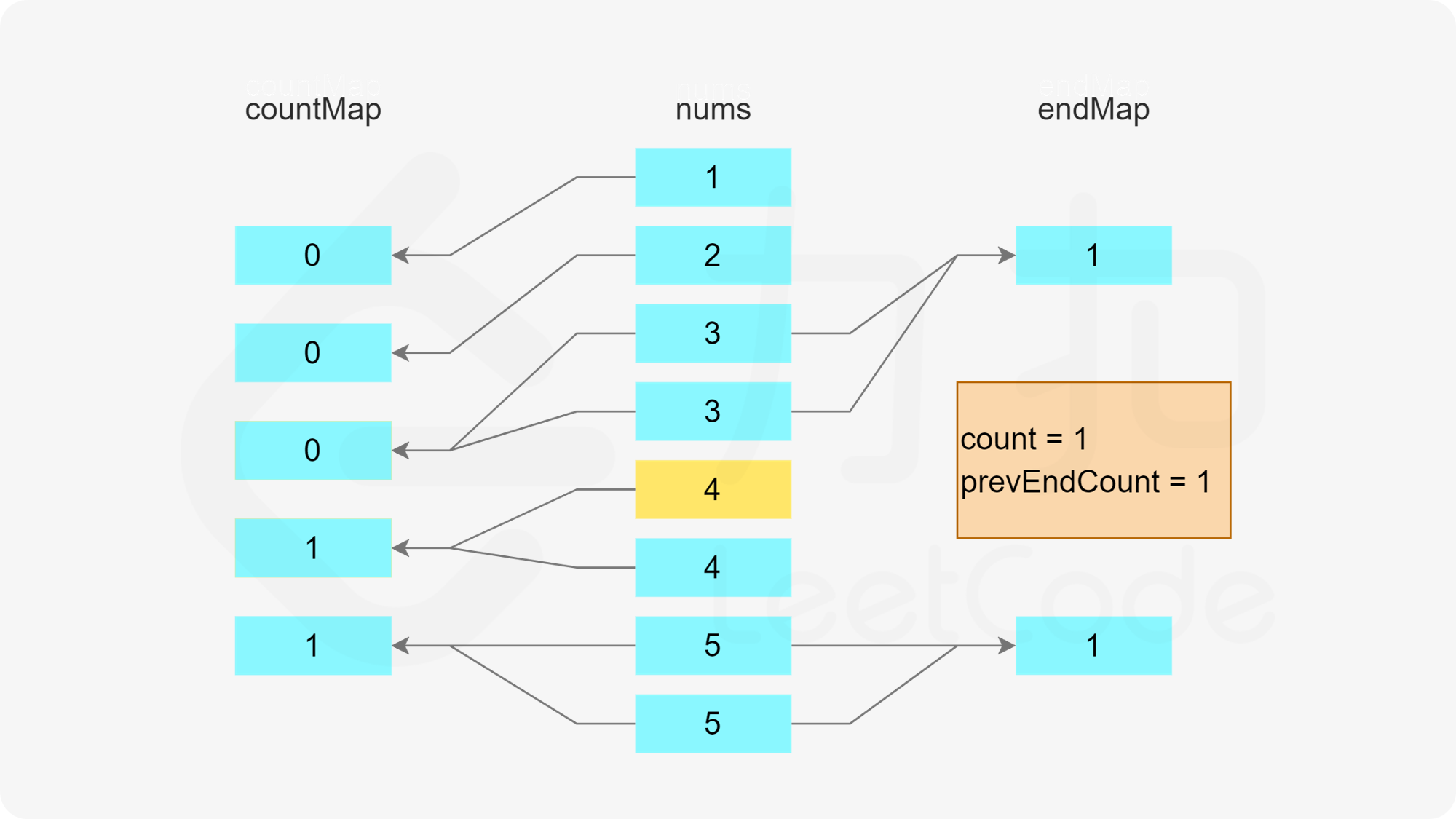
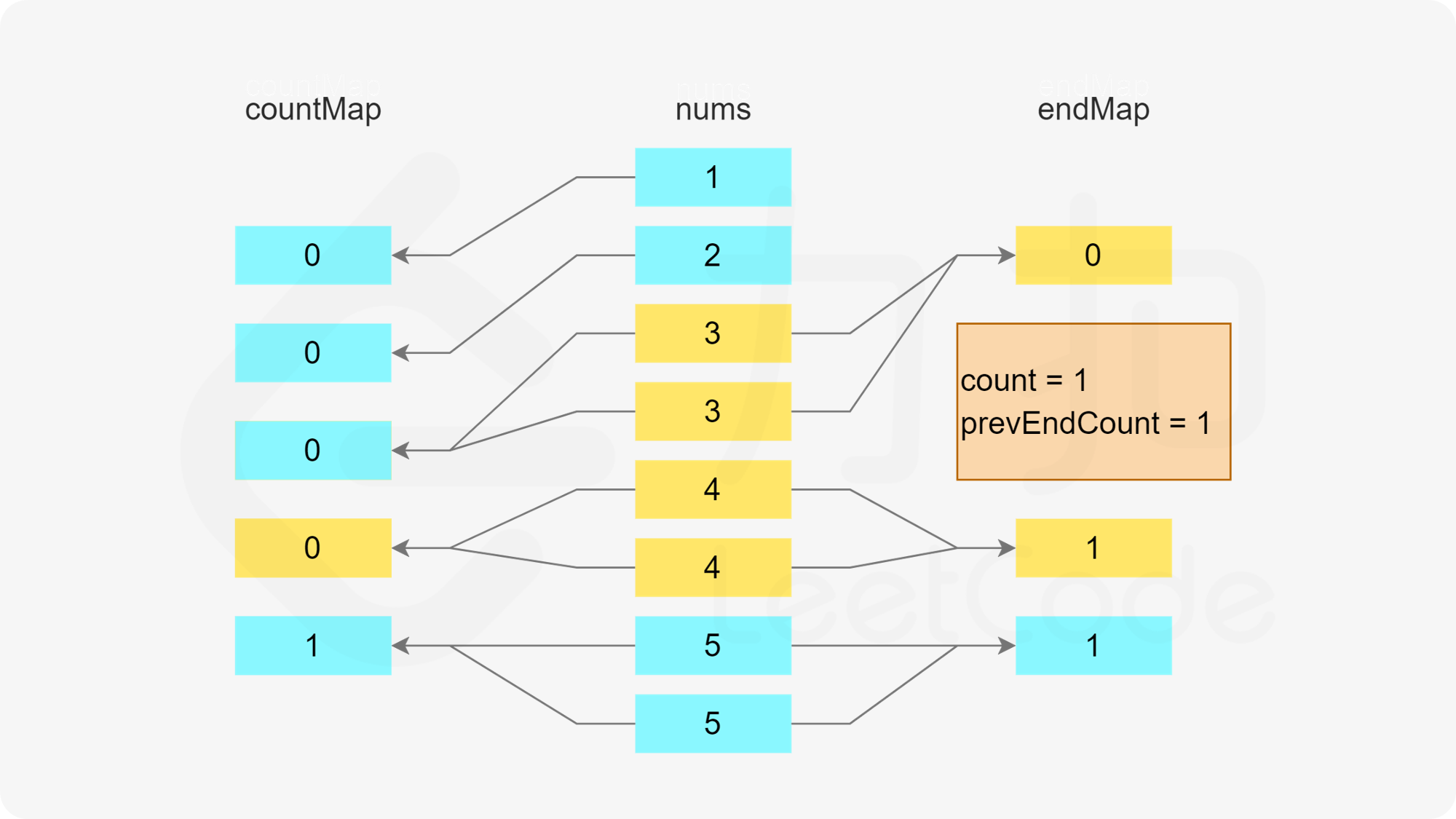
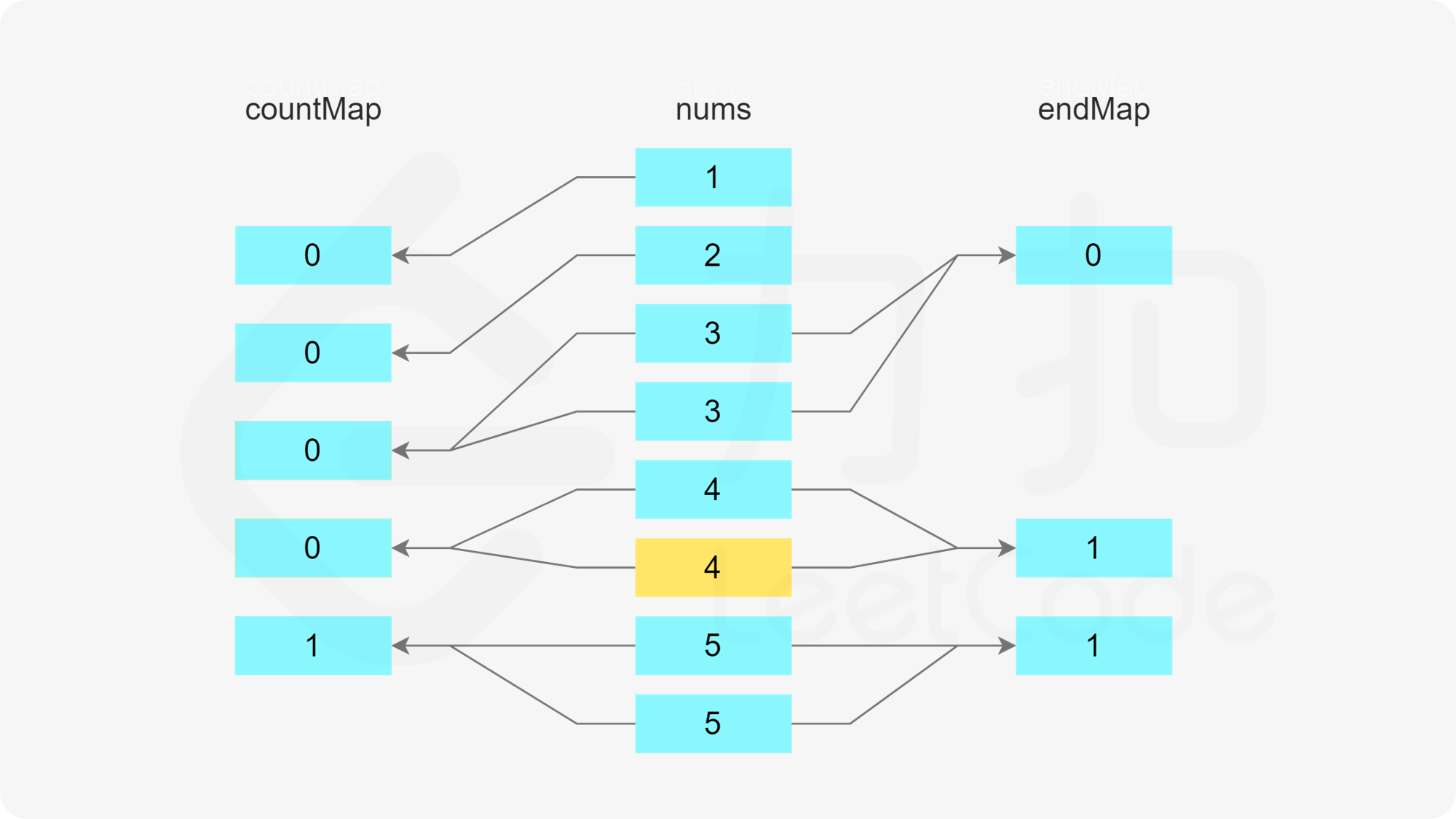
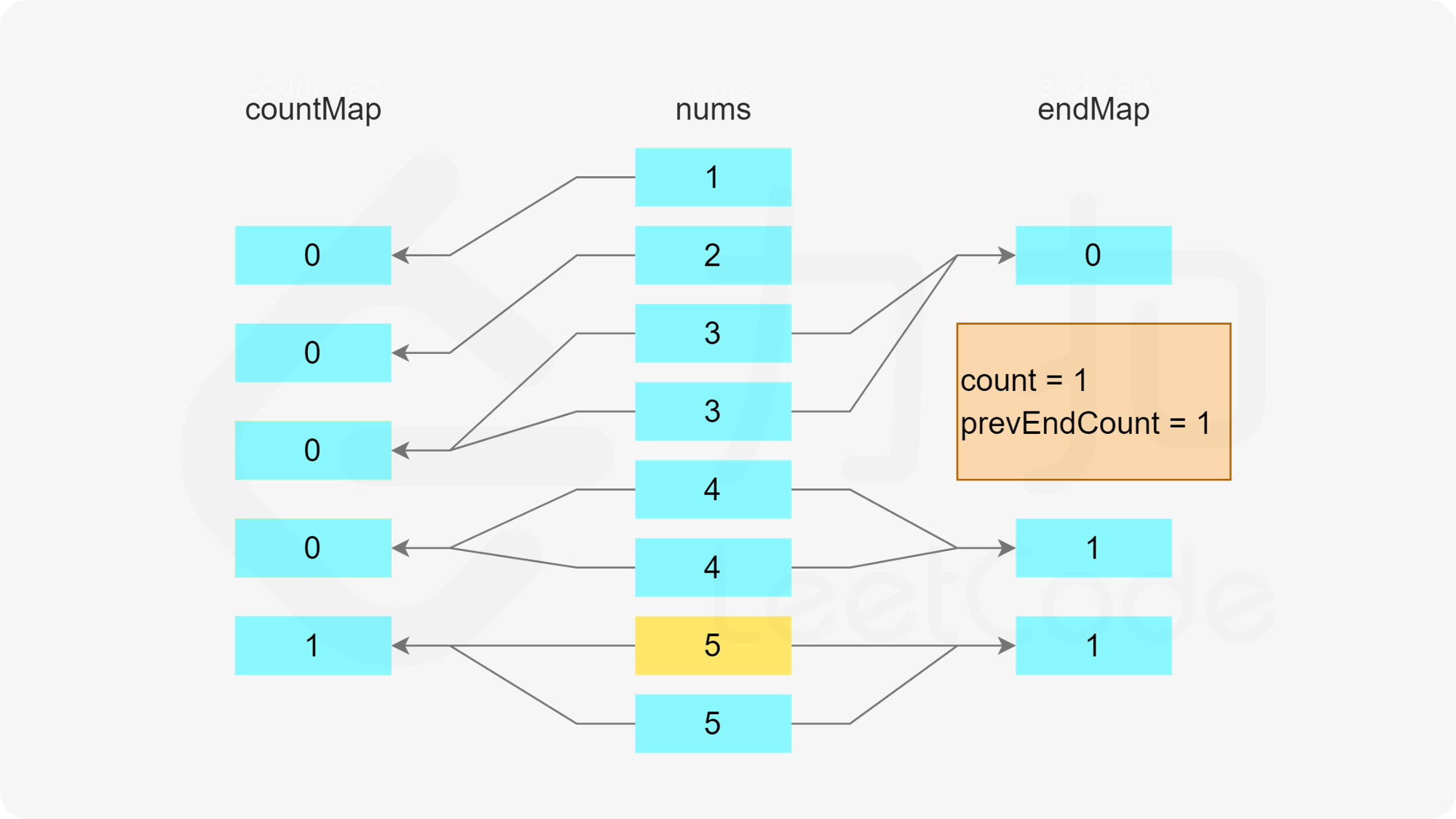
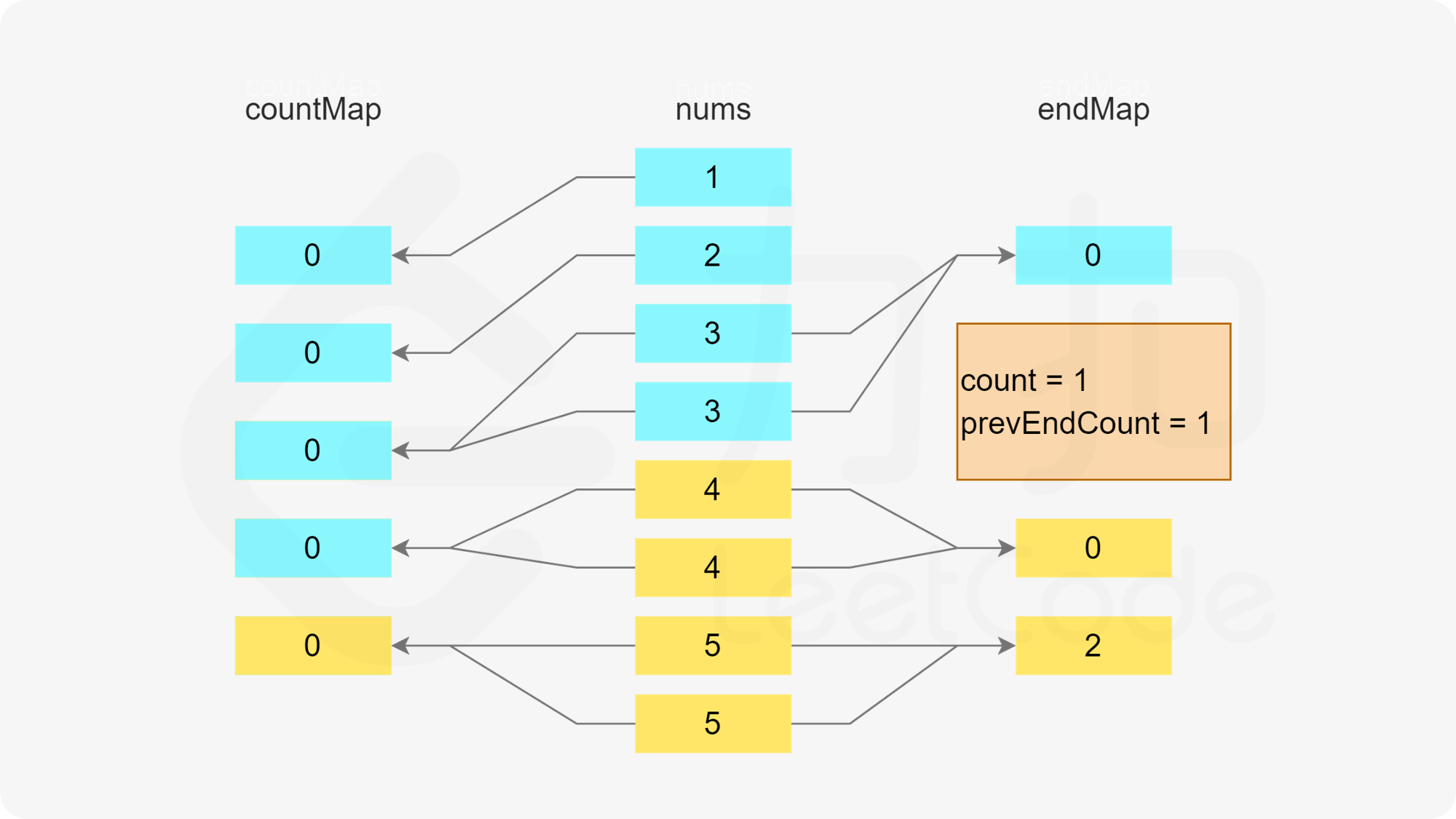
使用两个哈希表,第一个哈希表存储数组中的每个数字的剩余次数,第二个哈希表存储数组中的每个数字作为结尾的子序列的数量。
初始时,每个数字的剩余次数即为每个数字在数组中出现的次数,因此遍历数组,初始化第一个哈希表。
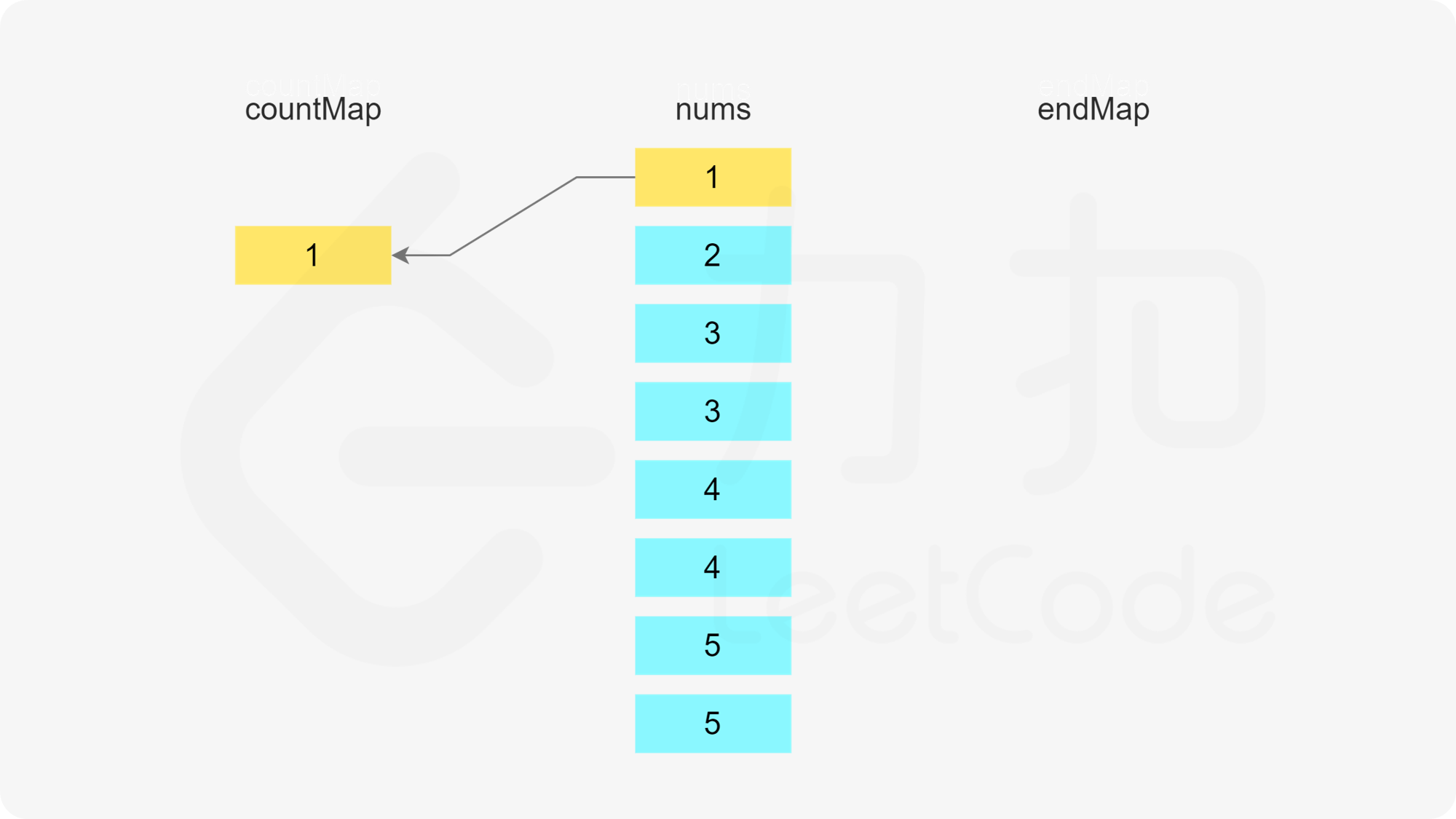
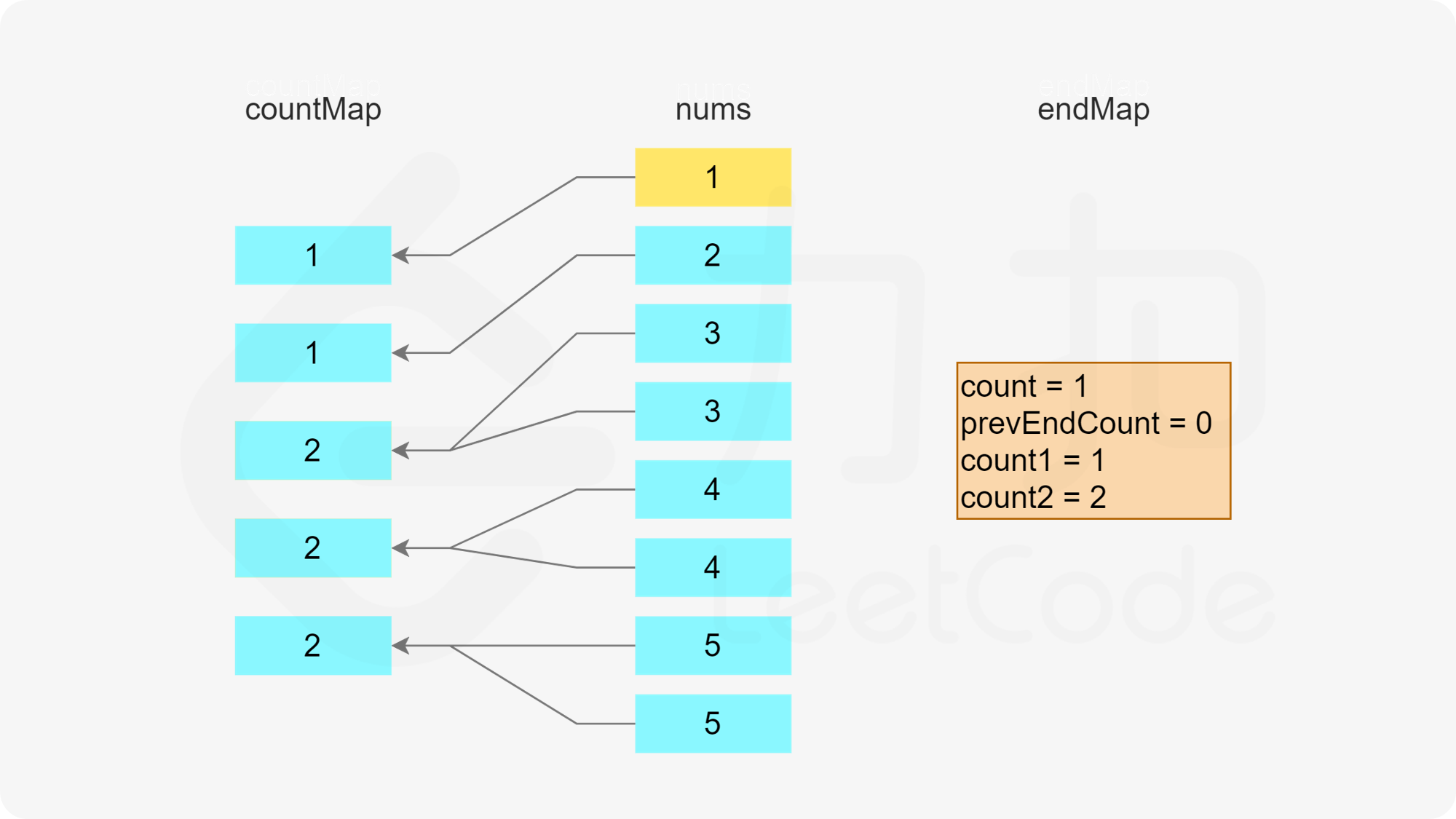
在初始化第一个哈希表之后,遍历数组,更新两个哈希表。只有当一个数字的剩余次数大于 0 时,才需要考虑这个数字是否属于某个子序列。假设当前元素是 x,进行如下操作。
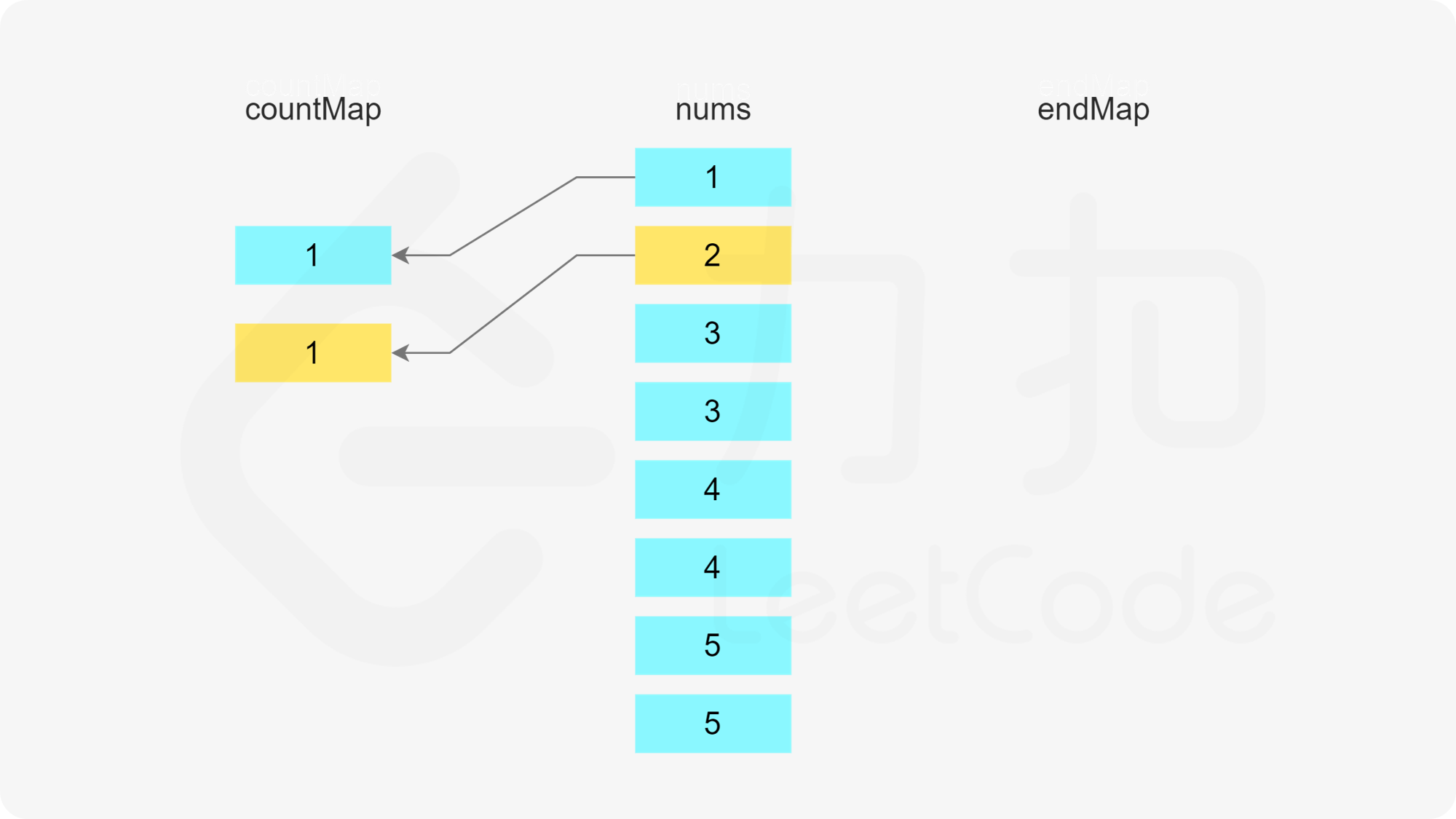
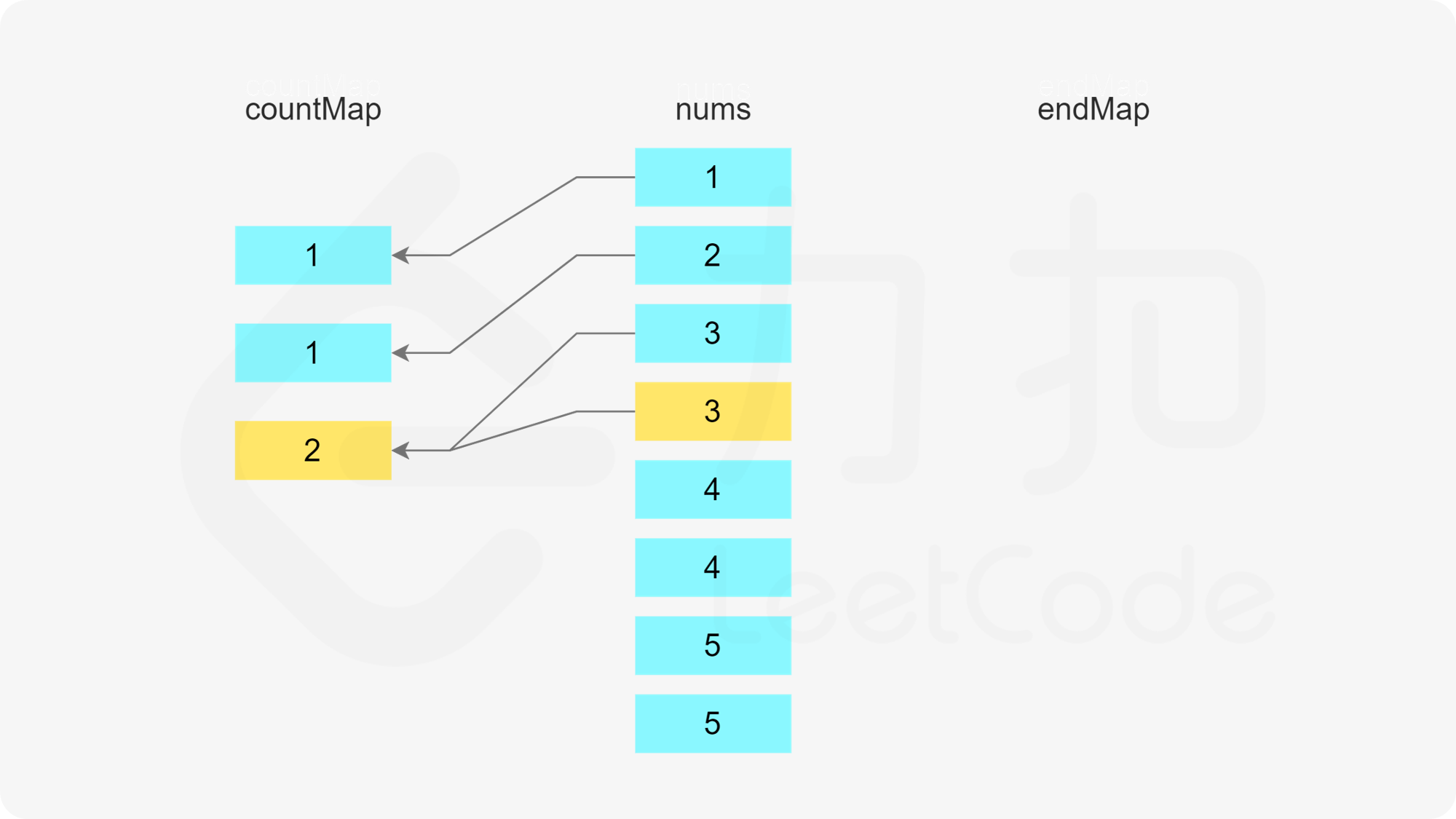
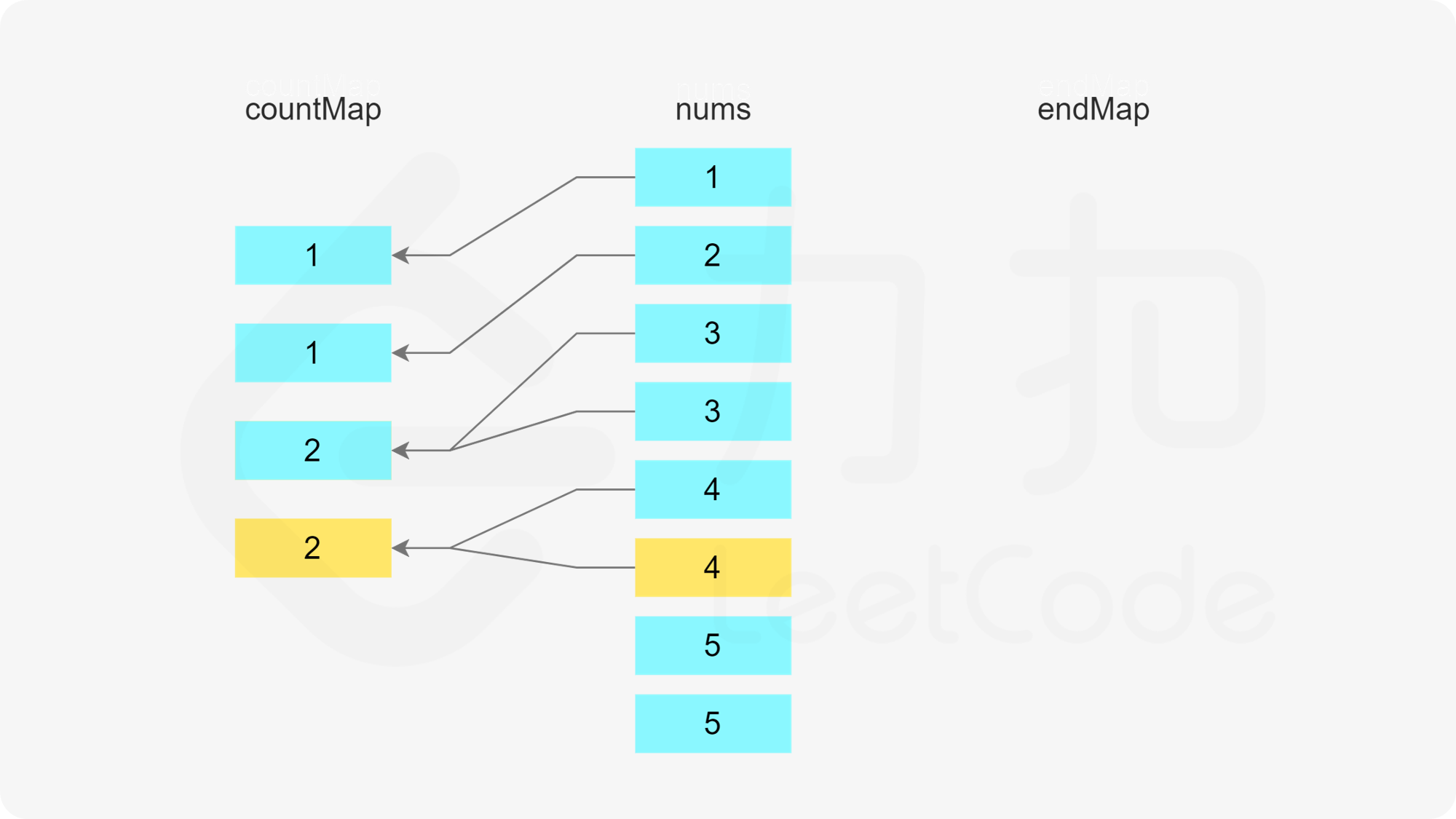
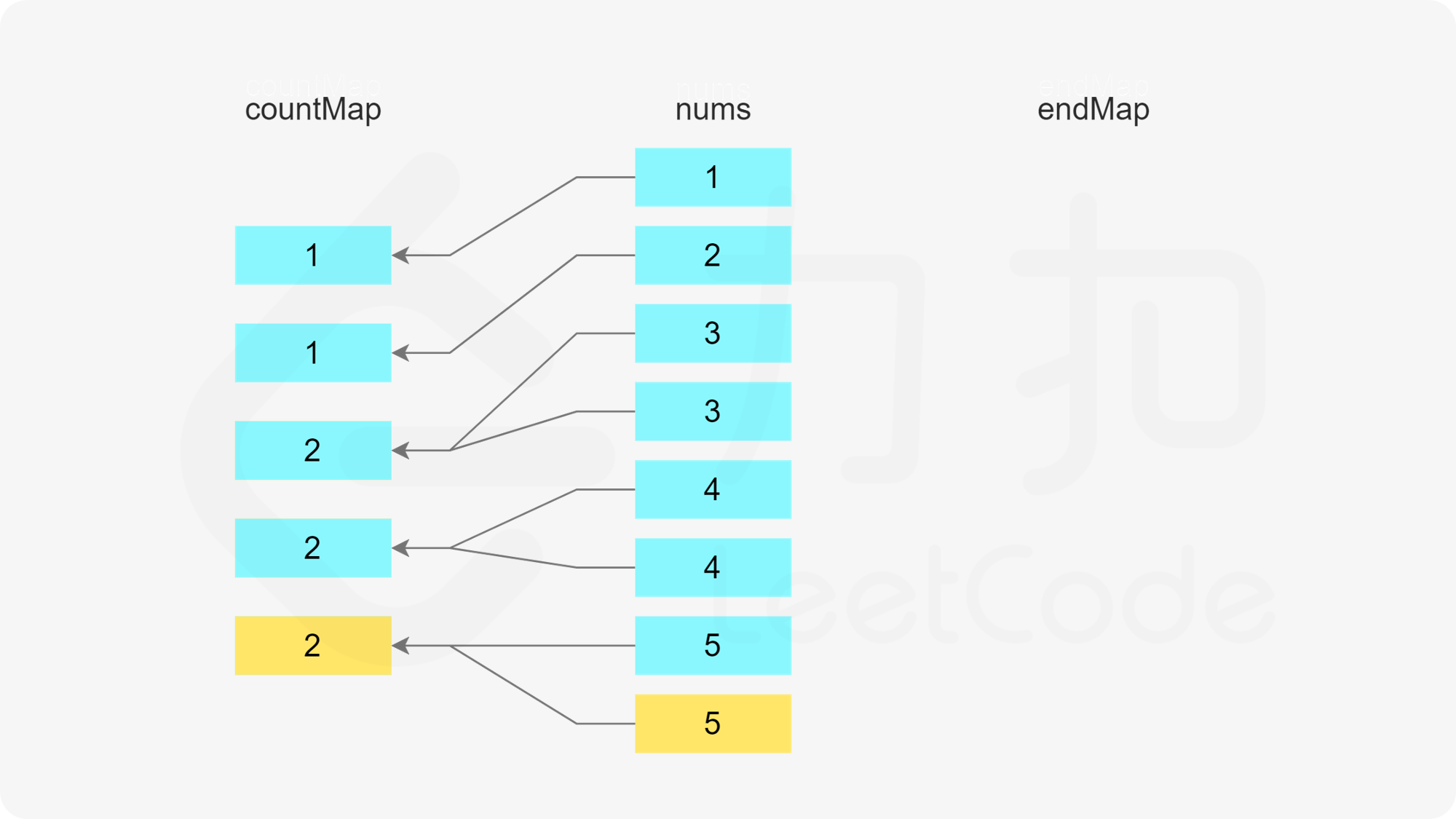
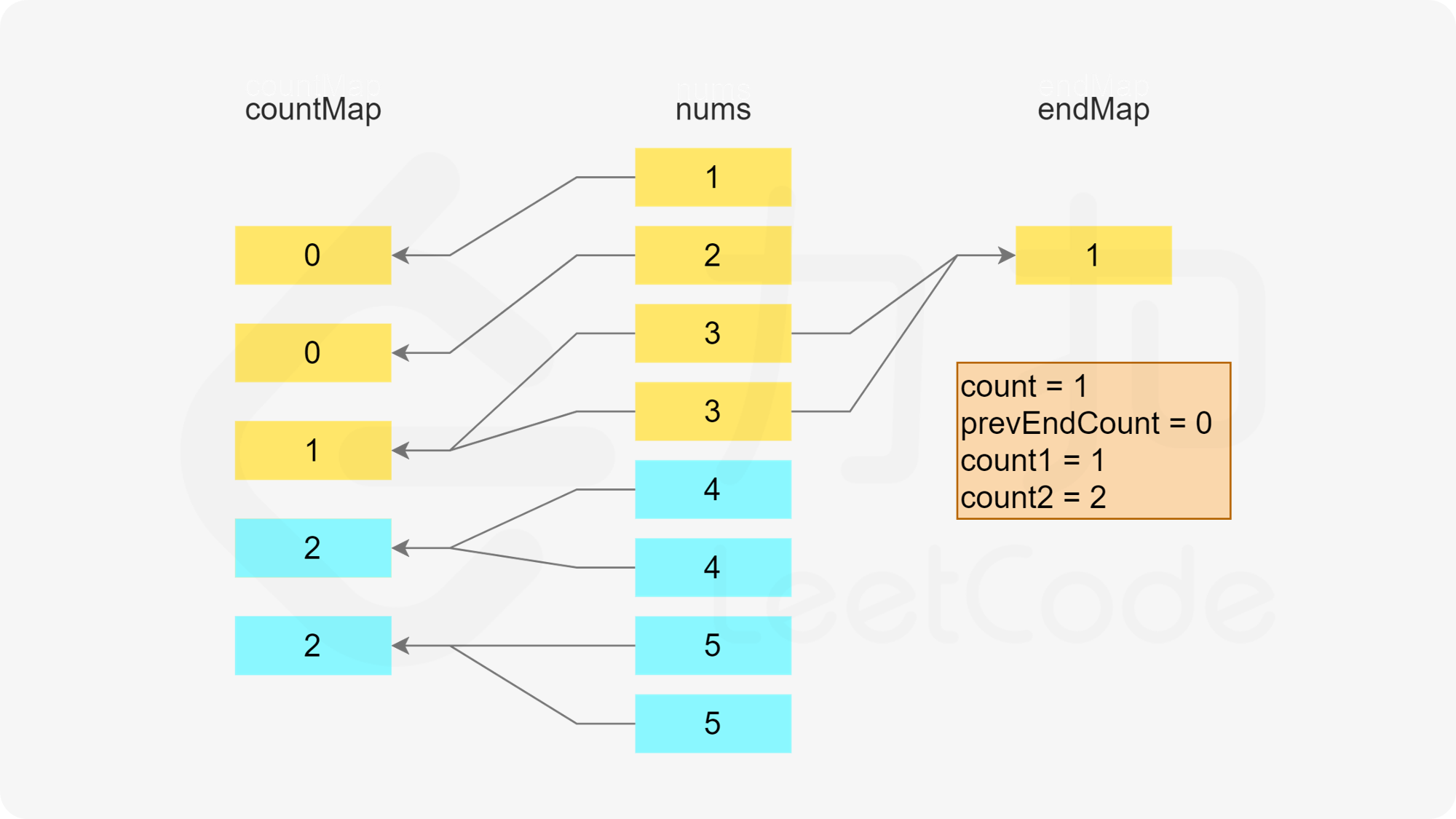
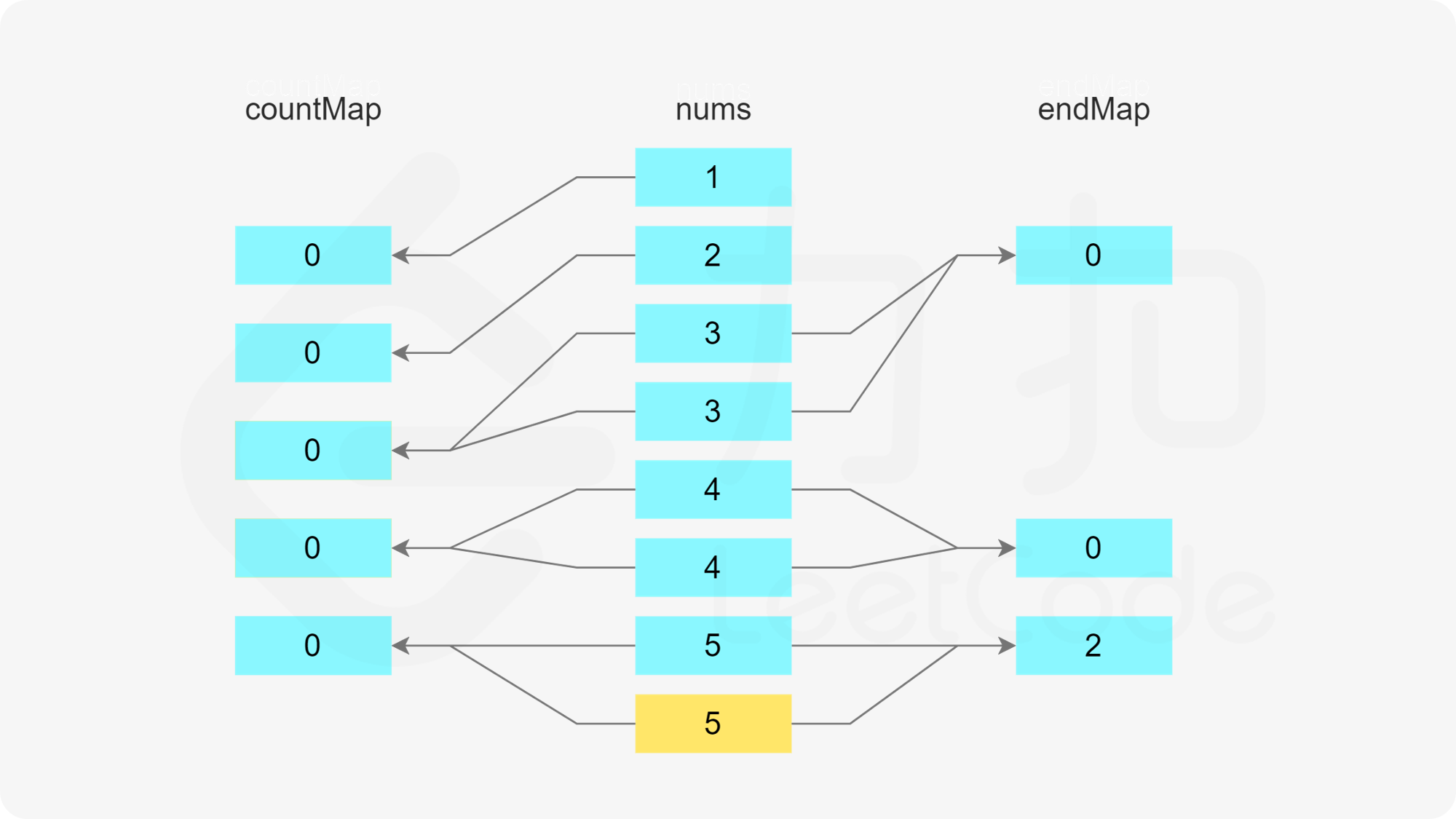
首先判断是否存在以 x-1 结尾的子序列,即根据第二个哈希表判断 x-1 作为结尾的子序列的数量是否大于 0,如果大于 0,则将元素 x 加入该子序列中。由于 x 被使用了一次,因此需要在第一个哈希表中将 x 的剩余次数减 1。又由于该子序列的最后一个数字从 x-1 变成了 x,因此需要在第二个哈希表中将 x-1 作为结尾的子序列的数量减 1,以及将 x 作为结尾的子序列的数量加 1。
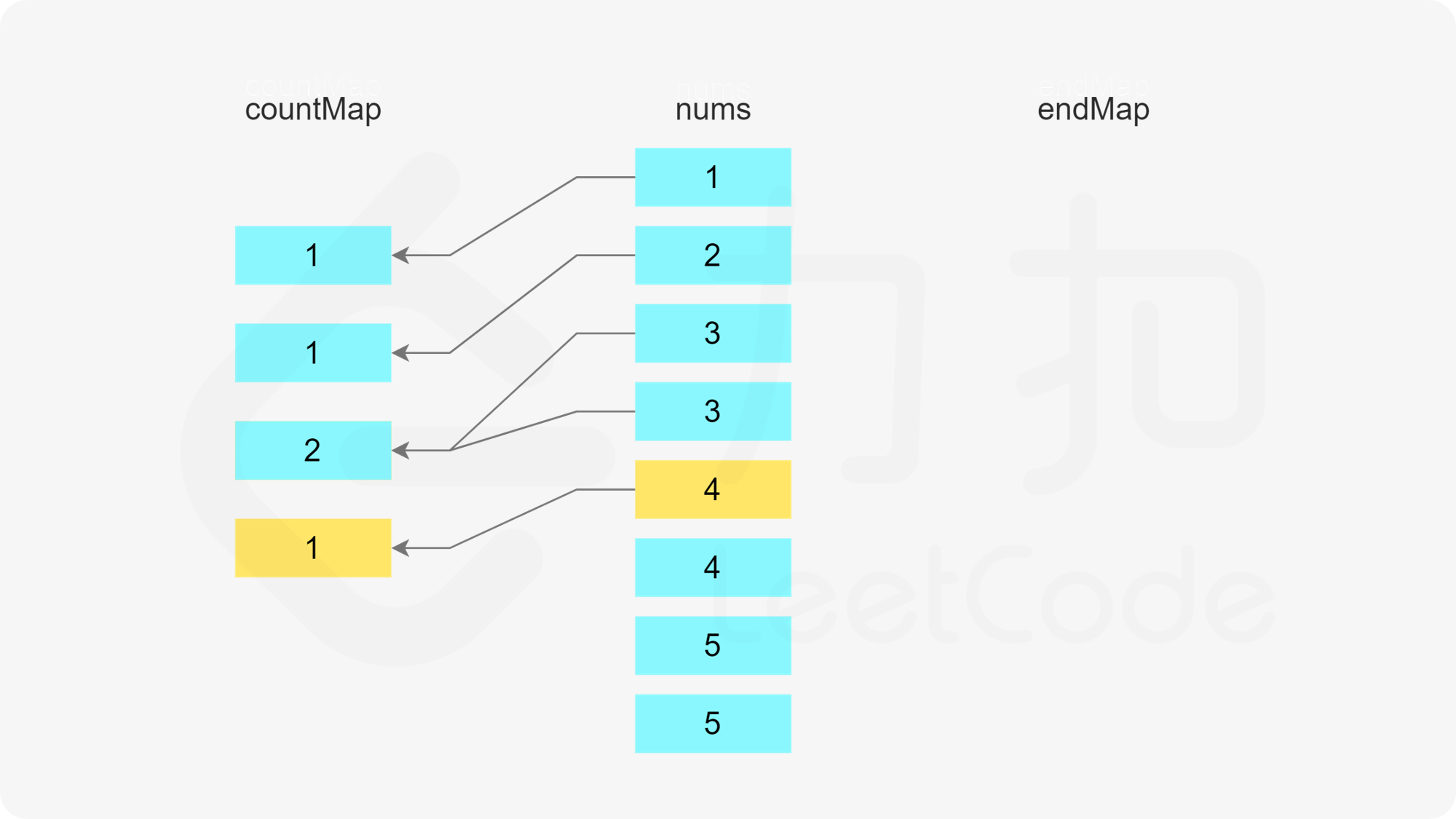
否则,x 为一个子序列的第一个数,为了得到长度至少为 3 的子序列,x+1 和 x+2 必须在子序列中,因此需要判断在第一个哈希表中 x+1 和 x+2 的剩余次数是否都大于 0。
当 x+1 和 x+2 的剩余次数都大于 0 时,可以新建一个长度为 3 的子序列 [x,x+1,x+2]。由于这三个数都被使用了一次,因此需要在第一个哈希表中将这三个数的剩余次数分别减 1。又由于该子序列的最后一个数字是 x+2,因此需要在第二个哈希表中将 x+2 作为结尾的子序列的数量加 1。
否则,无法得到长度为 3 的子序列 [x,x+1,x+2],因此无法完成分割,返回 false。
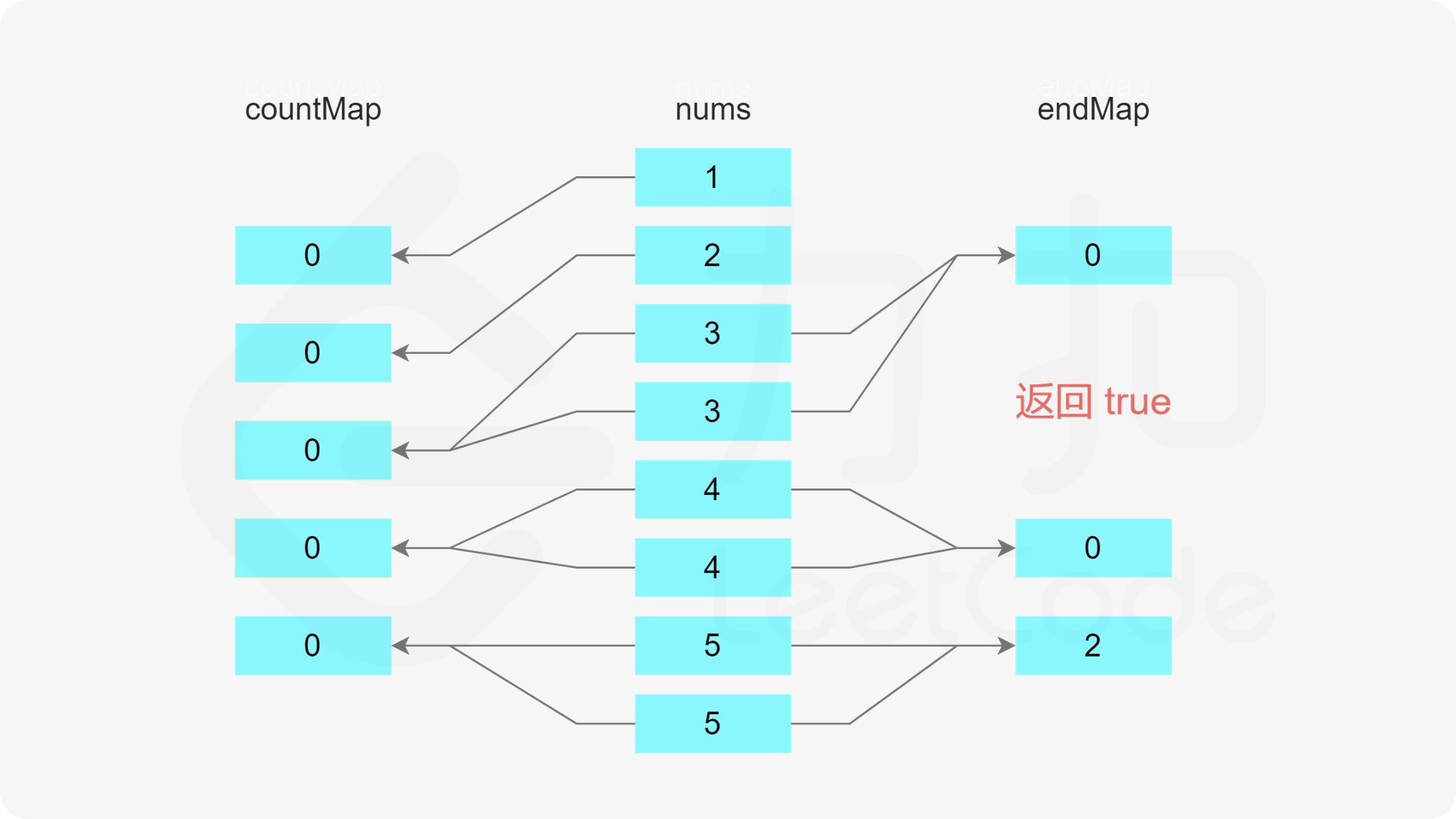
如果整个数组遍历结束时,没有遇到无法完成分割的情况,则可以完成分割,返回 true。
<
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution { public boolean isPossible (int [] nums) { Map<Integer, Integer> countMap = new HashMap <Integer, Integer>(); Map<Integer, Integer> endMap = new HashMap <Integer, Integer>(); for (int x : nums) { int count = countMap.getOrDefault(x, 0 ) + 1 ; countMap.put(x, count); } for (int x : nums) { int count = countMap.getOrDefault(x, 0 ); if (count > 0 ) { int prevEndCount = endMap.getOrDefault(x - 1 , 0 ); if (prevEndCount > 0 ) { countMap.put(x, count - 1 ); endMap.put(x - 1 , prevEndCount - 1 ); endMap.put(x, endMap.getOrDefault(x, 0 ) + 1 ); } else { int count1 = countMap.getOrDefault(x + 1 , 0 ); int count2 = countMap.getOrDefault(x + 2 , 0 ); if (count1 > 0 && count2 > 0 ) { countMap.put(x, count - 1 ); countMap.put(x + 1 , count1 - 1 ); countMap.put(x + 2 , count2 - 1 ); endMap.put(x + 2 , endMap.getOrDefault(x + 2 , 0 ) + 1 ); } else { return false ; } } } } return true ; } }
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 class Solution {public : bool isPossible (vector<int >& nums) unordered_map<int , int > countMap; unordered_map<int , int > endMap; for (auto & x : nums) { int count = countMap[x] + 1 ; countMap[x] = count; } for (auto & x : nums) { int count = countMap[x]; if (count > 0 ) { int prevEndCount = endMap[x - 1 ]; if (prevEndCount > 0 ) { countMap[x] = count - 1 ; endMap[x - 1 ] = prevEndCount - 1 ; endMap[x] = endMap[x] + 1 ; } else { int count1 = countMap[x + 1 ]; int count2 = countMap[x + 2 ]; if (count1 > 0 && count2 > 0 ) { countMap[x] = count - 1 ; countMap[x + 1 ] = count1 - 1 ; countMap[x + 2 ] = count2 - 1 ; endMap[x + 2 ] = endMap[x + 2 ] + 1 ; } else { return false ; } } } } return true ; } };
[sol2-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 var isPossible = function (nums ) { const countMap = new Map (); const endMap = new Map (); for (const x of nums) { const count = (countMap.get (x) || 0 ) + 1 ; countMap.set (x, count); } for (const x of nums) { const count = countMap.get (x) || 0 ; if (count > 0 ) { const prevEndCount = endMap.get (x - 1 ) || 0 ; if (prevEndCount > 0 ) { countMap.set (x, count - 1 ); endMap.set (x - 1 , prevEndCount - 1 ); endMap.set (x, (endMap.get (x, 0 ) || 0 ) + 1 ); } else { const count1 = countMap.get (x + 1 , 0 ); const count2 = countMap.get (x + 2 , 0 ); if (count1 > 0 && count2 > 0 ) { countMap.set (x, count - 1 ); countMap.set (x + 1 , count1 - 1 ); countMap.set (x + 2 , count2 - 1 ); endMap.set (x + 2 , (endMap.get (x + 2 ) || 0 ) + 1 ); } else { return false ; } } } } return true ; };
[sol2-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution : def isPossible (self, nums: List [int ] ) -> bool : countMap = collections.Counter(nums) endMap = collections.Counter() for x in nums: if (count := countMap[x]) > 0 : if (prevEndCount := endMap.get(x - 1 , 0 )) > 0 : countMap[x] -= 1 endMap[x - 1 ] = prevEndCount - 1 endMap[x] += 1 else : if (count1 := countMap.get(x + 1 , 0 )) > 0 and (count2 := countMap.get(x + 2 , 0 )) > 0 : countMap[x] -= 1 countMap[x + 1 ] -= 1 countMap[x + 2 ] -= 1 endMap[x + 2 ] += 1 else : return False return True
[sol2-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 func isPossible (nums []int ) bool { left := map [int ]int {} for _, v := range nums { left[v]++ } endCnt := map [int ]int {} for _, v := range nums { if left[v] == 0 { continue } if endCnt[v-1 ] > 0 { left[v]-- endCnt[v-1 ]-- endCnt[v]++ } else if left[v+1 ] > 0 && left[v+2 ] > 0 { left[v]-- left[v+1 ]-- left[v+2 ]-- endCnt[v+2 ]++ } else { return false } } return true }
[sol2-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 struct hashTable { int key; int val; UT_hash_handle hh; }; struct hashTable* find (struct hashTable** hashtable, int ikey) { struct hashTable * tmp ; HASH_FIND_INT(*hashtable, &ikey, tmp); return tmp; } void insert (struct hashTable** hashtable, int ikey, int ival) { struct hashTable * tmp =malloc (sizeof (struct hashTable)); tmp->key = ikey, tmp->val = ival; HASH_ADD_INT(*hashtable, key, tmp); } int query (struct hashTable** hashtable, int ikey) { struct hashTable * tmp ; HASH_FIND_INT(*hashtable, &ikey, tmp); if (tmp == NULL ) { return 0 ; } return tmp->val; } void modify (struct hashTable** hashtable, int ikey, int ival) { struct hashTable * tmp = if (tmp == NULL ) { insert(hashtable, ikey, ival); } else { tmp->val = ival; } } void inc (struct hashTable** hashtable, int ikey) { struct hashTable * tmp = if (tmp == NULL ) { insert(hashtable, ikey, 1 ); } else { tmp->val++; } } bool isPossible (int * nums, int numsSize) { struct hashTable * countMap =NULL ; struct hashTable * endMap =NULL ; for (int i = 0 ; i < numsSize; i++) { inc(&countMap, nums[i]); } for (int i = 0 ; i < numsSize; i++) { int count = query(&countMap, nums[i]); if (count > 0 ) { int prevEndCount = query(&endMap, nums[i] - 1 ); if (prevEndCount > 0 ) { modify(&countMap, nums[i], count - 1 ); modify(&endMap, nums[i] - 1 , prevEndCount - 1 ); inc(&endMap, nums[i]); } else { int count1 = query(&countMap, nums[i] + 1 ); int count2 = query(&countMap, nums[i] + 2 ); if (count1 > 0 && count2 > 0 ) { modify(&countMap, nums[i], count - 1 ); modify(&countMap, nums[i] + 1 , count1 - 1 ); modify(&countMap, nums[i] + 2 , count2 - 1 ); inc(&endMap, nums[i] + 2 ); } else { return false ; } } } } return true ; }
复杂度分析
 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
> ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
,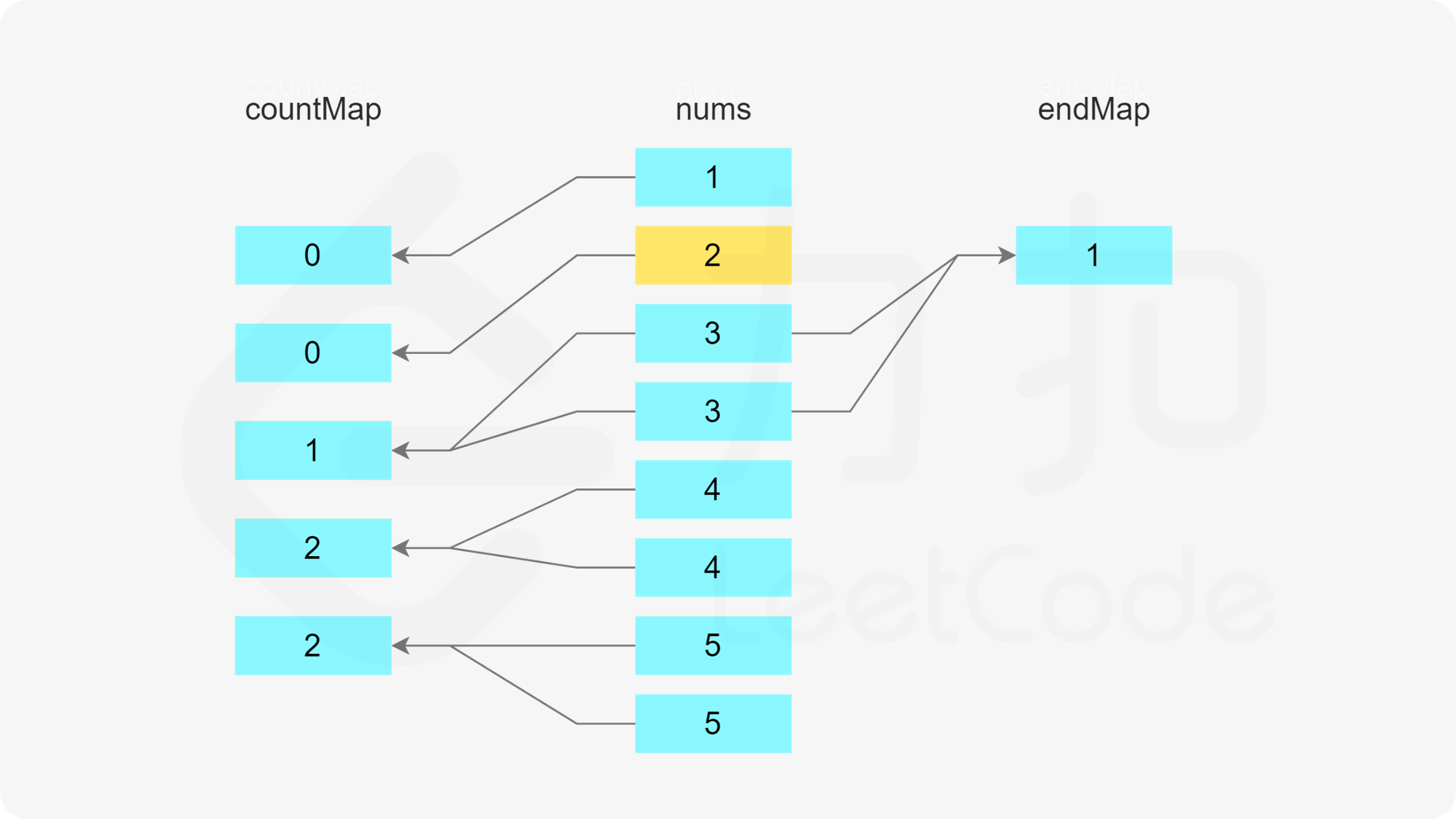 ,
,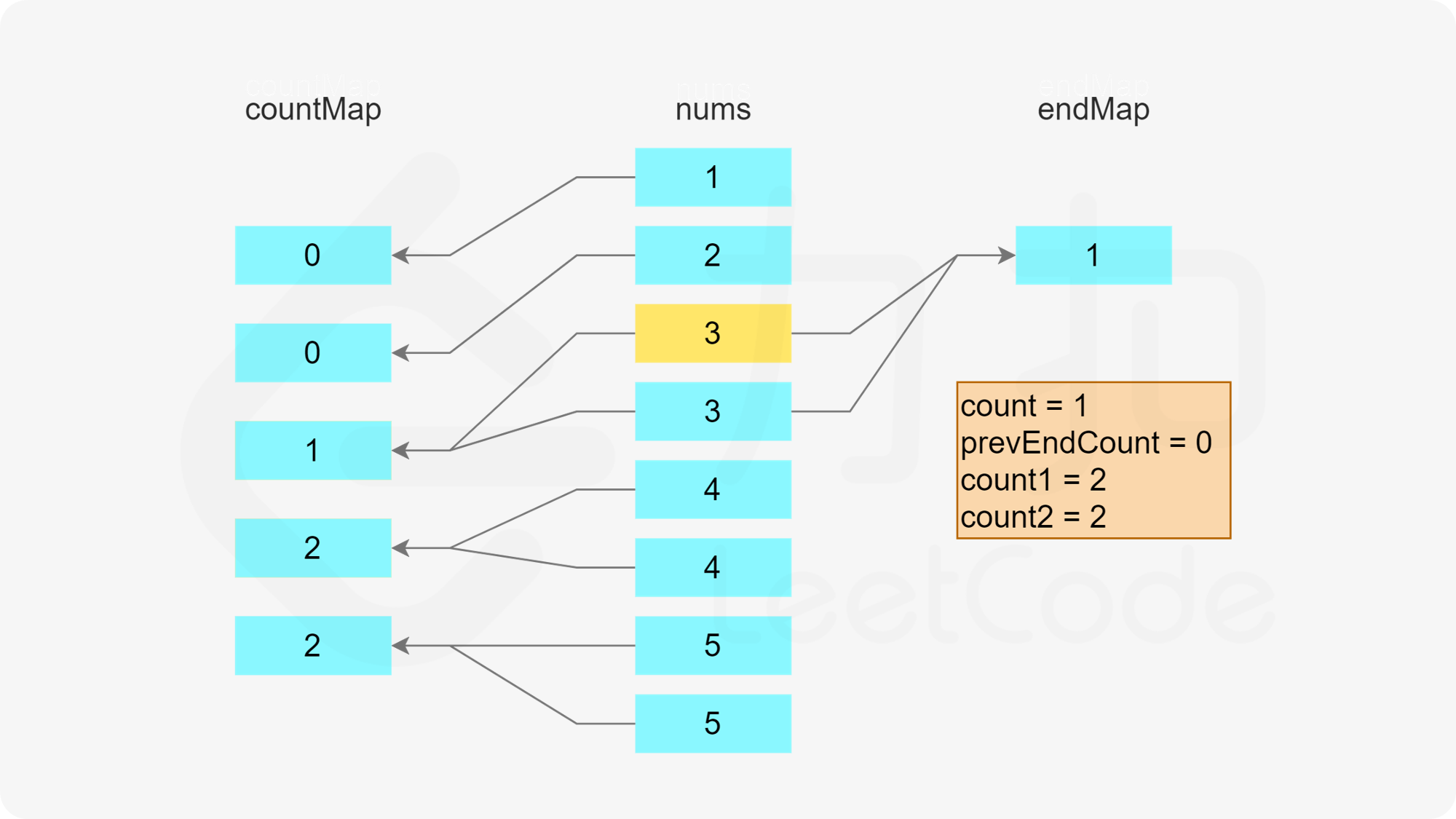 ,
,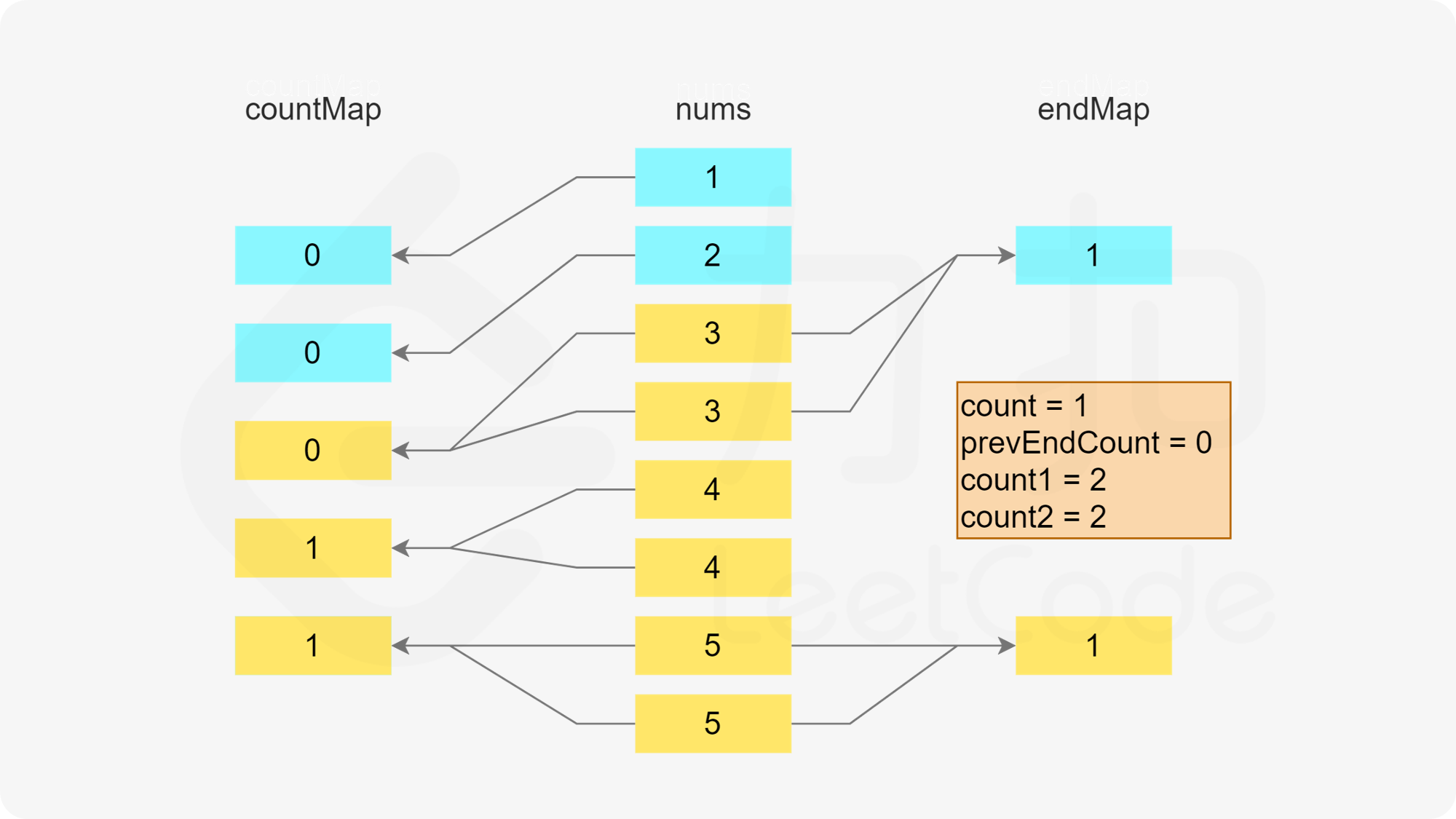 ,
,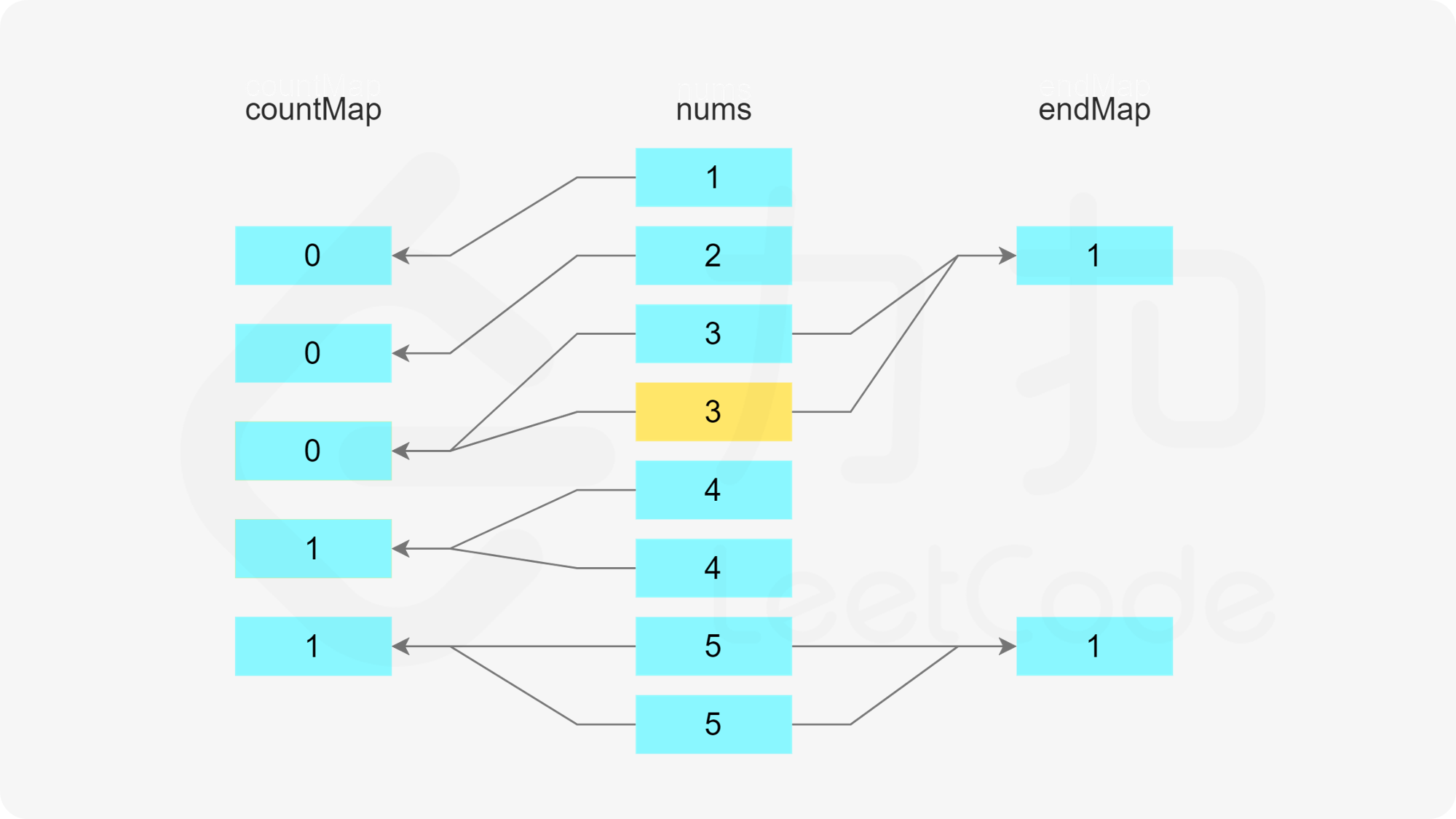 ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, ,
, >
>