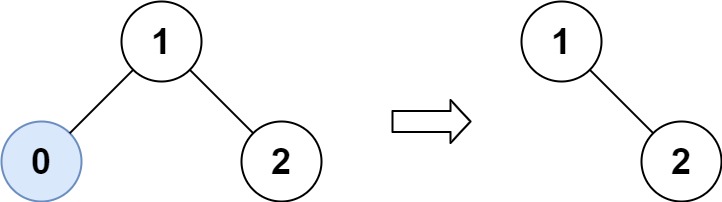
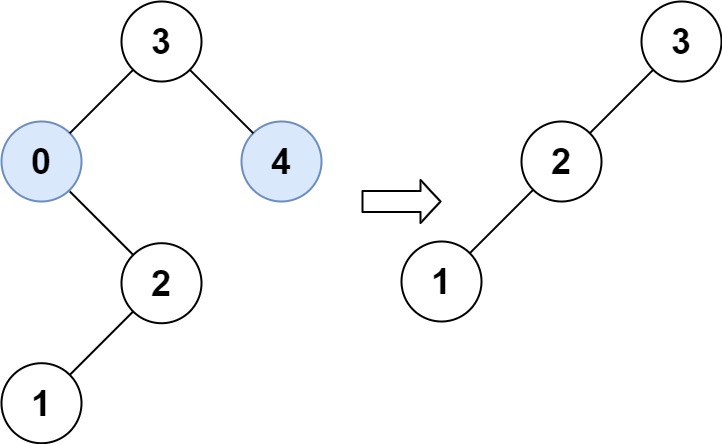
给你二叉搜索树的根节点 root ,同时给定最小边界low 和最大边界 high。通过修剪二叉搜索树,使得所有节点的值在[low, high]中。修剪树 不应该 改变保留在树中的元素的相对结构 (即,如果没有被移除,原有的父代子代关系都应当保留)。 可以证明,存在
唯一的答案 。
所以结果应当返回修剪好的二叉搜索树的新的根节点。注意,根节点可能会根据给定的边界发生改变。
示例 1:

**输入:** root = [1,0,2], low = 1, high = 2
**输出:** [1,null,2]
示例 2:

**输入:** root = [3,0,4,null,2,null,null,1], low = 1, high = 3
**输出:** [3,2,null,1]
提示:
- 树中节点数在范围
[1, 104] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 104- 树中每个节点的值都是 唯一 的
- 题目数据保证输入是一棵有效的二叉搜索树
0 <= low <= high <= 104
方法一:递归
对根结点 root 进行深度优先遍历。对于当前访问的结点,如果结点为空结点,直接返回空结点;如果结点的值小于 low,那么说明该结点及它的左子树都不符合要求,我们返回对它的右结点进行修剪后的结果;如果结点的值大于 high,那么说明该结点及它的右子树都不符合要求,我们返回对它的左子树进行修剪后的结果;如果结点的值位于区间 [\textit{low}, \textit{high}],我们将结点的左结点设为对它的左子树修剪后的结果,右结点设为对它的右子树进行修剪后的结果。
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| class Solution:
def trimBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], low: int, high: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
if root is None:
return None
if root.val < low:
return self.trimBST(root.right, low, high)
if root.val > high:
return self.trimBST(root.left, low, high)
root.left = self.trimBST(root.left, low, high)
root.right = self.trimBST(root.right, low, high)
return root
|
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
if (root->val < low) {
return trimBST(root->right, low, high);
} else if (root->val > high) {
return trimBST(root->left, low, high);
} else {
root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high);
root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high);
return root;
}
}
};
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| class Solution {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.val < low) {
return trimBST(root.right, low, high);
} else if (root.val > high) {
return trimBST(root.left, low, high);
} else {
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);
return root;
}
}
}
|
[sol1-C#]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public class Solution {
public TreeNode TrimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
if (root.val < low) {
return TrimBST(root.right, low, high);
} else if (root.val > high) {
return TrimBST(root.left, low, high);
} else {
root.left = TrimBST(root.left, low, high);
root.right = TrimBST(root.right, low, high);
return root;
}
}
}
|
[sol1-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| struct TreeNode* trimBST(struct TreeNode* root, int low, int high){
if (root == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (root->val < low) {
return trimBST(root->right, low, high);
} else if (root->val > high) {
return trimBST(root->left, low, high);
} else {
root->left = trimBST(root->left, low, high);
root->right = trimBST(root->right, low, high);
return root;
}
}
|
[sol1-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| var trimBST = function(root, low, high) {
if (!root) {
return null;
}
if (root.val < low) {
return trimBST(root.right, low, high);
} else if (root.val > high) {
return trimBST(root.left, low, high);
} else {
root.left = trimBST(root.left, low, high);
root.right = trimBST(root.right, low, high);
return root;
}
};
|
[sol1-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| func trimBST(root *TreeNode, low, high int) *TreeNode {
if root == nil {
return nil
}
if root.Val < low {
return trimBST(root.Right, low, high)
}
if root.Val > high {
return trimBST(root.Left, low, high)
}
root.Left = trimBST(root.Left, low, high)
root.Right = trimBST(root.Right, low, high)
return root
}
|
复杂度分析
方法二:迭代
如果一个结点 node 符合要求,即它的值位于区间 [\textit{low}, \textit{high}],那么它的左子树与右子树应该如何修剪?
我们先讨论左子树的修剪:
node 的左结点为空结点:不需要修剪
node 的左结点非空:
如果它的左结点 left 的值小于 low,那么 left 以及 left 的左子树都不符合要求,我们将 node 的左结点设为 left 的右结点,然后再重新对 node 的左子树进行修剪。
如果它的左结点 left 的值大于等于 low,又因为 node 的值已经符合要求,所以 left 的右子树一定符合要求。基于此,我们只需要对 left 的左子树进行修剪。我们令 node 等于 left ,然后再重新对 node 的左子树进行修剪。
以上过程可以迭代处理。对于右子树的修剪同理。
我们对根结点进行判断,如果根结点不符合要求,我们将根结点设为对应的左结点或右结点,直到根结点符合要求,然后将根结点作为符合要求的结点,依次修剪它的左子树与右子树。
[sol2-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class Solution:
def trimBST(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], low: int, high: int) -> Optional[TreeNode]:
while root and (root.val < low or root.val > high):
root = root.right if root.val < low else root.left
if root is None:
return None
node = root
while node.left:
if node.left.val < low:
node.left = node.left.right
else:
node = node.left
node = root
while node.right:
if node.right.val > high:
node.right = node.right.left
else:
node = node.right
return root
|
[sol2-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* trimBST(TreeNode* root, int low, int high) {
while (root && (root->val < low || root->val > high)) {
if (root->val < low) {
root = root->right;
} else {
root = root->left;
}
}
if (root == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
for (auto node = root; node->left; ) {
if (node->left->val < low) {
node->left = node->left->right;
} else {
node = node->left;
}
}
for (auto node = root; node->right; ) {
if (node->right->val > high) {
node->right = node->right->left;
} else {
node = node->right;
}
}
return root;
}
};
|
[sol2-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| class Solution {
public TreeNode trimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
while (root != null && (root.val < low || root.val > high)) {
if (root.val < low) {
root = root.right;
} else {
root = root.left;
}
}
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
for (TreeNode node = root; node.left != null; ) {
if (node.left.val < low) {
node.left = node.left.right;
} else {
node = node.left;
}
}
for (TreeNode node = root; node.right != null; ) {
if (node.right.val > high) {
node.right = node.right.left;
} else {
node = node.right;
}
}
return root;
}
}
|
[sol2-C#]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| public class Solution {
public TreeNode TrimBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
while (root != null && (root.val < low || root.val > high)) {
if (root.val < low) {
root = root.right;
} else {
root = root.left;
}
}
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
for (TreeNode node = root; node.left != null; ) {
if (node.left.val < low) {
node.left = node.left.right;
} else {
node = node.left;
}
}
for (TreeNode node = root; node.right != null; ) {
if (node.right.val > high) {
node.right = node.right.left;
} else {
node = node.right;
}
}
return root;
}
}
|
[sol2-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| struct TreeNode* trimBST(struct TreeNode* root, int low, int high){
while (root && (root->val < low || root->val > high)) {
if (root->val < low) {
root = root->right;
} else {
root = root->left;
}
}
if (root == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
for (struct TreeNode* node = root; node->left; ) {
if (node->left->val < low) {
node->left = node->left->right;
} else {
node = node->left;
}
}
for (struct TreeNode* node = root; node->right; ) {
if (node->right->val > high) {
node->right = node->right->left;
} else {
node = node->right;
}
}
return root;
}
|
[sol2-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| var trimBST = function(root, low, high) {
while (root && (root.val < low || root.val > high)) {
if (root.val < low) {
root = root.right;
} else {
root = root.left;
}
}
if (!root) {
return null;
}
for (let node = root; node.left; ) {
if (node.left.val < low) {
node.left = node.left.right;
} else {
node = node.left;
}
}
for (let node = root; node.right; ) {
if (node.right.val > high) {
node.right = node.right.left;
} else {
node = node.right;
}
}
return root;
};
|
[sol2-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| func trimBST(root *TreeNode, low, high int) *TreeNode {
for root != nil && (root.Val < low || root.Val > high) {
if root.Val < low {
root = root.Right
} else {
root = root.Left
}
}
if root == nil {
return nil
}
for node := root; node.Left != nil; {
if node.Left.Val < low {
node.Left = node.Left.Right
} else {
node = node.Left
}
}
for node := root; node.Right != nil; {
if node.Right.Val > high {
node.Right = node.Right.Left
} else {
node = node.Right
}
}
return root
}
|
复杂度分析