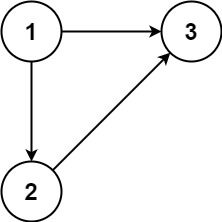
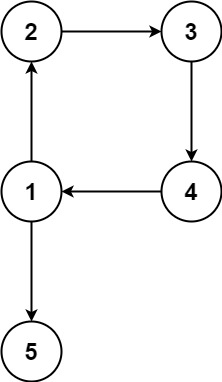
在本问题中,有根树指满足以下条件的 有向
输入一个有向图,该图由一个有着 n 个节点(节点值不重复,从 1 到 n)的树及一条附加的有向边构成。附加的边包含在 1 到 n
结果图是一个以边组成的二维数组 edges 。 每个元素是一对 [ui, vi],用以表示 有向 图中连接顶点 ui 和顶点 viui 是 vi 的一个父节点。
返回一条能删除的边,使得剩下的图是有 n 个节点的有根树。若有多个答案,返回最后出现在给定二维数组的答案。
示例 1:
**输入:** edges = [[1,2],[1,3],[2,3]]
**输出:** [2,3]
示例 2:
**输入:** edges = [[1,2],[2,3],[3,4],[4,1],[1,5]]
**输出:** [4,1]
提示:
n == edges.length3 <= n <= 1000edges[i].length == 21 <= ui, vi <= n
方法一:并查集 思路与算法
在一棵树中,边的数量比节点的数量少 1。如果一棵树有 n 个节点,则这棵树有 n-1 条边。这道题中的图在树的基础上多了一条附加的边,因此边的数量也是 n。
树中的每个节点都有一个父节点,除了根节点没有父节点。在多了一条附加的边之后,可能有以下两种情况:
要找到附加的边,需要遍历图中的所有的边构建出一棵树,在构建树的过程中寻找导致冲突(即导致一个节点有两个父节点)的边以及导致环路出现的边。
具体做法是,使用数组 parent 记录每个节点的父节点,初始时对于任何 1 \le i \le n 都有 parent}[i]=i,另外创建并查集,初始时并查集中的每个节点都是一个连通分支,该连通分支的根节点就是该节点本身。遍历每条边的过程中,维护导致冲突的边和导致环路出现的边,由于只有一条附加的边,因此最多有一条导致冲突的边和一条导致环路出现的边。
当访问到边 [u,v] 时,进行如下操作:
如果此时已经有 parent}[v] \ne v,说明 v 有两个父节点,将当前的边 [u,v] 记为导致冲突的边;
否则,令 parent}[v] = u,然后在并查集中分别找到 u 和 v 的祖先(即各自的连通分支中的根节点),如果祖先相同,说明这条边导致环路出现,将当前的边 [u,v] 记为导致环路出现的边,如果祖先不同,则在并查集中将 u 和 v 进行合并。
根据上述操作,同一条边不可能同时被记为导致冲突的边和导致环路出现的边。如果访问到的边确实同时导致冲突和环路出现,则这条边被记为导致冲突的边。
在遍历图中的所有边之后,根据是否存在导致冲突的边和导致环路出现的边,得到附加的边。
如果没有导致冲突的边,说明附加的边一定导致环路出现,而且是在环路中的最后一条被访问到的边,因此附加的边即为导致环路出现的边。
如果有导致冲突的边,记这条边为 [u,v],则有两条边指向 v,另一条边为 [\textit{parent}[v],v],需要通过判断是否有导致环路的边决定哪条边是附加的边。
如果有导致环路的边,则附加的边不可能是 [u,v](因为 [u,v] 已经被记为导致冲突的边,不可能被记为导致环路出现的边),因此附加的边是 [\textit{parent}[v],v]。
如果没有导致环路的边,则附加的边是后被访问到的指向 v 的边,因此附加的边是 [u,v]。
代码
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 class Solution { public int [] findRedundantDirectedConnection(int [][] edges) { int n = edges.length; UnionFind uf = new UnionFind (n + 1 ); int [] parent = new int [n + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) { parent[i] = i; } int conflict = -1 ; int cycle = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { int [] edge = edges[i]; int node1 = edge[0 ], node2 = edge[1 ]; if (parent[node2] != node2) { conflict = i; } else { parent[node2] = node1; if (uf.find(node1) == uf.find(node2)) { cycle = i; } else { uf.union(node1, node2); } } } if (conflict < 0 ) { int [] redundant = {edges[cycle][0 ], edges[cycle][1 ]}; return redundant; } else { int [] conflictEdge = edges[conflict]; if (cycle >= 0 ) { int [] redundant = {parent[conflictEdge[1 ]], conflictEdge[1 ]}; return redundant; } else { int [] redundant = {conflictEdge[0 ], conflictEdge[1 ]}; return redundant; } } } } class UnionFind { int [] ancestor; public UnionFind (int n) { ancestor = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { ancestor[i] = i; } } public void union (int index1, int index2) { ancestor[find(index1)] = find(index2); } public int find (int index) { if (ancestor[index] != index) { ancestor[index] = find(ancestor[index]); } return ancestor[index]; } }
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 func findRedundantDirectedConnection (edges [][]int ) int ) { n := len (edges) uf := newUnionFind(n + 1 ) parent := make ([]int , n+1 ) for i := range parent { parent[i] = i } var conflictEdge, cycleEdge []int for _, edge := range edges { from, to := edge[0 ], edge[1 ] if parent[to] != to { conflictEdge = edge } else { parent[to] = from if uf.find(from) == uf.find(to) { cycleEdge = edge } else { uf.union(from, to) } } } if conflictEdge == nil { return cycleEdge } if cycleEdge != nil { return []int {parent[conflictEdge[1 ]], conflictEdge[1 ]} } return conflictEdge } type unionFind struct { ancestor []int } func newUnionFind (n int ) ancestor := make ([]int , n) for i := 0 ; i < n; i++ { ancestor[i] = i } return unionFind{ancestor} } func (uf unionFind) int ) int { if uf.ancestor[x] != x { uf.ancestor[x] = uf.find(uf.ancestor[x]) } return uf.ancestor[x] } func (uf unionFind) int ) { uf.ancestor[uf.find(from)] = uf.find(to) }
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 struct UnionFind { vector <int > ancestor; UnionFind (int n) { ancestor.resize (n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { ancestor[i] = i; } } int find (int index) return index == ancestor[index] ? index : ancestor[index] = find (ancestor[index]); } void merge (int u, int v) ancestor[find (u)] = find (v); } }; class Solution {public : vector<int > findRedundantDirectedConnection (vector<vector<int >>& edges) { int n = edges.size (); UnionFind uf = UnionFind (n + 1 ); auto parent = vector <int >(n + 1 ); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) { parent[i] = i; } int conflict = -1 ; int cycle = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { auto edge = edges[i]; int node1 = edge[0 ], node2 = edge[1 ]; if (parent[node2] != node2) { conflict = i; } else { parent[node2] = node1; if (uf.find (node1) == uf.find (node2)) { cycle = i; } else { uf.merge (node1, node2); } } } if (conflict < 0 ) { auto redundant = vector<int > {edges[cycle][0 ], edges[cycle][1 ]}; return redundant; } else { auto conflictEdge = edges[conflict]; if (cycle >= 0 ) { auto redundant = vector<int > {parent[conflictEdge[1 ]], conflictEdge[1 ]}; return redundant; } else { auto redundant = vector<int > {conflictEdge[0 ], conflictEdge[1 ]}; return redundant; } } } };
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 class UnionFind : def __init__ (self, n ): self.ancestor = list (range (n)) def union (self, index1: int , index2: int ): self.ancestor[self.find(index1)] = self.find(index2) def find (self, index: int ) -> int : if self.ancestor[index] != index: self.ancestor[index] = self.find(self.ancestor[index]) return self.ancestor[index] class Solution : def findRedundantDirectedConnection (self, edges: List [List [int ]] ) -> List [int ]: n = len (edges) uf = UnionFind(n + 1 ) parent = list (range (n + 1 )) conflict = -1 cycle = -1 for i, (node1, node2) in enumerate (edges): if parent[node2] != node2: conflict = i else : parent[node2] = node1 if uf.find(node1) == uf.find(node2): cycle = i else : uf.union(node1, node2) if conflict < 0 : return [edges[cycle][0 ], edges[cycle][1 ]] else : conflictEdge = edges[conflict] if cycle >= 0 : return [parent[conflictEdge[1 ]], conflictEdge[1 ]] else : return [conflictEdge[0 ], conflictEdge[1 ]]
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 int * ancestor;int find (int index) { return index == ancestor[index] ? index : (ancestor[index] = find(ancestor[index])); } void merge (int u, int v) { ancestor[find(u)] = find(v); } int * findRedundantDirectedConnection (int ** edges, int edgesSize, int * edgesColSize, int * returnSize) { int n = edgesSize; ancestor = malloc (sizeof (int ) * (n + 1 )); for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) { ancestor[i] = i; } int parent[n + 1 ]; for (int i = 1 ; i <= n; ++i) { parent[i] = i; } int conflict = -1 ; int cycle = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { int node1 = edges[i][0 ], node2 = edges[i][1 ]; if (parent[node2] != node2) { conflict = i; } else { parent[node2] = node1; if (find(node1) == find(node2)) { cycle = i; } else { merge(node1, node2); } } } int * redundant = malloc (sizeof (int ) * 2 ); *returnSize = 2 ; if (conflict < 0 ) { redundant[0 ] = edges[cycle][0 ], redundant[1 ] = edges[cycle][1 ]; return redundant; } else { int * conflictEdge = edges[conflict]; if (cycle >= 0 ) { redundant[0 ] = parent[conflictEdge[1 ]], redundant[1 ] = conflictEdge[1 ]; return redundant; } else { redundant[0 ] = conflictEdge[0 ], redundant[1 ] = conflictEdge[1 ]; return redundant; } } return redundant; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n \log n),其中 n 是图中的节点个数。需要遍历图中的 n 条边,对于每条边,需要对两个节点查找祖先,如果两个节点的祖先不同则需要进行合并,需要进行 2 次查找和最多 1 次合并。一共需要进行 2n 次查找和最多 n 次合并,因此总时间复杂度是 O(2n \log n)=O(n \log n)。这里的并查集使用了路径压缩,但是没有使用按秩合并,最坏情况下的时间复杂度是 O(n \log n),平均情况下的时间复杂度依然是 O(n \alpha (n)),其中 \alpha 为阿克曼函数的反函数,\alpha (n) 可以认为是一个很小的常数。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是图中的节点个数。使用数组 parent 记录每个节点的父节点,并查集使用数组记录每个节点的祖先。