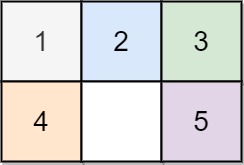
在一个 2 x 3 的板上(board)有 5 块砖瓦,用数字 1~5 来表示, 以及一块空缺用 0 来表示。一次 移动 定义为选择0 与一个相邻的数字(上下左右)进行交换.
最终当板 board 的结果是 [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]] 谜板被解开。
给出一个谜板的初始状态 board ,返回最少可以通过多少次移动解开谜板,如果不能解开谜板,则返回 -1 。
示例 1:
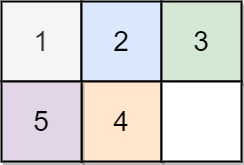
**输入:** board = [[1,2,3],[4,0,5]]
**输出:** 1
**解释:** 交换 0 和 5 ,1 步完成
示例 2:
**输入:** board = [[1,2,3],[5,4,0]]
**输出:** -1
**解释:** 没有办法完成谜板
示例 3:
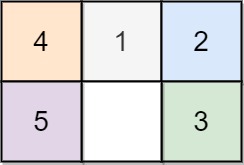
**输入:** board = [[4,1,2],[5,0,3]]
**输出:** 5
**解释:**
最少完成谜板的最少移动次数是 5 ,
一种移动路径:
尚未移动: [[4,1,2],[5,0,3]]
移动 1 次: [[4,1,2],[0,5,3]]
移动 2 次: [[0,1,2],[4,5,3]]
移动 3 次: [[1,0,2],[4,5,3]]
移动 4 次: [[1,2,0],[4,5,3]]
移动 5 次: [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]]
提示:
board.length == 2board[i].length == 30 <= board[i][j] <= 5board[i][j] 中每个值都 不同
方法一:广度优先搜索 思路与算法
我们可以使用广度优先搜索,找出从初始状态 board 到目标状态 [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]] 的最小交换次数。
具体地,我们在一开始将 (\textit{board}, 0) 加入队列,并使用该队列进行广度优先搜索。在搜索的过程中,设当前搜索到的状态为 status,操作的次数为 step,我们可以枚举 status 通过一次操作得到的状态。设其中的某个状态为 next_status,如果其没有被搜索过,我们就将 (\textit{next_status}, \textit{step} + 1) 加入队列。如果搜索到了 target,我们就返回其对应的操作次数。
在搜索的过程中,我们需要一个哈希表存储所有搜索到的状态,避免重复搜索。
如果搜索完成后,我们仍没有搜索到 [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]],说明我们无法解开谜板,返回 -1。
细节
本题中,搜索的状态 status 是一个 2\times 3 的二维数组,在很多语言中,我们无法将数组直接放入哈希表中,可行的解决方案有两种:
自行实现数组的哈希函数;
将数组转换成语言中可以直接进行哈希的类型。
在问题中,我们使用第二种解决方案,将 status 按照行优先 的顺序拼接成一个长度为 2\times 3=6 的字符串。例如目标状态 [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]] 可以表示为 123450。
在确定了解决方案后,我们还需要考虑如何有效地找出 status 通过一次操作得到的所有状态。根据题目中的规定,每一次操作可以将 status 中的 0 与相邻 位置的数字进行交换,因此我们同样可以按照行优先 的顺序给 2\times 3 的谜板进行编号:
这样一来,我们可以预处理出每一个位置的所有相邻位置,即:
0 的相邻位置是 1, 3;
1 的相邻位置是 0, 2, 4;
2 的相邻位置是 1, 5;
3 的相邻位置是 0, 4;
4 的相邻位置是 1, 3, 5;
5 的相邻位置是 2, 4。
因此,我们在 status 中找出 0 所在的位置 x,对于每一个与 x 相邻的位置 y,我们将 status}[x] 与 status}[y] 进行交换,即等同于进行了一次操作。注意:这里的 status 是已经拼接完成的字符串。
最后我们还需要注意一个细节:如果 board 就是目标状态 [[1,2,3],[4,5,0]],那么直接返回答案 0。
代码
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Solution {private : vector<vector<int >> neighbors = {{1 , 3 }, {0 , 2 , 4 }, {1 , 5 }, {0 , 4 }, {1 , 3 , 5 }, {2 , 4 }}; public : int slidingPuzzle (vector<vector<int >>& board) auto get = [&](string& status) -> vector<string> { vector<string> ret; int x = status.find ('0' ); for (int y: neighbors[x]) { swap (status[x], status[y]); ret.push_back (status); swap (status[x], status[y]); } return ret; }; string initial; for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; ++j) { initial += char (board[i][j] + '0' ); } } if (initial == "123450" ) { return 0 ; } queue<pair<string, int >> q; q.emplace (initial, 0 ); unordered_set<string> seen = {initial}; while (!q.empty ()) { auto [status, step] = q.front (); q.pop (); for (auto && next_status: get (status)) { if (!seen.count (next_status)) { if (next_status == "123450" ) { return step + 1 ; } q.emplace (next_status, step + 1 ); seen.insert (move (next_status)); } } } return -1 ; } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 class Solution { int [][] neighbors = {{1 , 3 }, {0 , 2 , 4 }, {1 , 5 }, {0 , 4 }, {1 , 3 , 5 }, {2 , 4 }}; public int slidingPuzzle (int [][] board) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; ++j) { sb.append(board[i][j]); } } String initial = sb.toString(); if ("123450" .equals(initial)) { return 0 ; } int step = 0 ; Queue<String> queue = new LinkedList <String>(); queue.offer(initial); Set<String> seen = new HashSet <String>(); seen.add(initial); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { ++step; int size = queue.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < size; ++i) { String status = queue.poll(); for (String nextStatus : get(status)) { if (!seen.contains(nextStatus)) { if ("123450" .equals(nextStatus)) { return step; } queue.offer(nextStatus); seen.add(nextStatus); } } } } return -1 ; } public List<String> get (String status) { List<String> ret = new ArrayList <String>(); char [] array = status.toCharArray(); int x = status.indexOf('0' ); for (int y : neighbors[x]) { swap(array, x, y); ret.add(new String (array)); swap(array, x, y); } return ret; } public void swap (char [] array, int x, int y) { char temp = array[x]; array[x] = array[y]; array[y] = temp; } }
[sol1-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 public class Solution { int [][] neighbors = new int [6 ][]{new []{1 , 3 }, new []{0 , 2 , 4 }, new []{1 , 5 }, new []{0 , 4 }, new []{1 , 3 , 5 }, new []{2 , 4 }}; public int SlidingPuzzle (int [][] board StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; ++j) { sb.Append(board[i][j]); } } string initial = sb.ToString(); if ("123450" .Equals(initial)) { return 0 ; } int step = 0 ; Queue<string > queue = new Queue<string >(); queue.Enqueue(initial); ISet<string > seen = new HashSet<string >(); seen.Add(initial); while (queue.Count > 0 ) { ++step; int size = queue.Count; for (int i = 0 ; i < size; ++i) { string status = queue.Dequeue(); foreach (string nextStatus in Get (status )) if (!seen.Contains(nextStatus)) { if ("123450" .Equals(nextStatus)) { return step; } queue.Enqueue(nextStatus); seen.Add(nextStatus); } } } } return -1 ; } public IList<string > Get (string status IList<string > ret = new List<string >(); char [] array = status.ToCharArray(); int x = status.IndexOf('0' ); foreach (int y in neighbors[x]) { Swap(array, x, y); ret.Add(new string (array)); Swap(array, x, y); } return ret; } public void Swap (char [] array, int x, int y char temp = array[x]; array[x] = array[y]; array[y] = temp; } }
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution : NEIGHBORS = [[1 , 3 ], [0 , 2 , 4 ], [1 , 5 ], [0 , 4 ], [1 , 3 , 5 ], [2 , 4 ]] def slidingPuzzle (self, board: List [List [int ]] ) -> int : def get (status: str ) -> Generator[str , None , None ]: s = list (status) x = s.index("0" ) for y in Solution.NEIGHBORS[x]: s[x], s[y] = s[y], s[x] yield "" .join(s) s[x], s[y] = s[y], s[x] initial = "" .join(str (num) for num in sum (board, [])) if initial == "123450" : return 0 q = deque([(initial, 0 )]) seen = {initial} while q: status, step = q.popleft() for next_status in get(status): if next_status not in seen: if next_status == "123450" : return step + 1 q.append((next_status, step + 1 )) seen.add(next_status) return -1
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 var slidingPuzzle = function (board ) { const neighbors = [[1 , 3 ], [0 , 2 , 4 ], [1 , 5 ], [0 , 4 ], [1 , 3 , 5 ], [2 , 4 ]]; const sb = []; for (let i = 0 ; i < 2 ; ++i) { for (let j = 0 ; j < 3 ; ++j) { sb.push (board[i][j]); } } const initial = sb.join ('' ); if ("123450" === initial) { return 0 ; } let step = 0 ; const queue = []; queue.push (initial); const seen = new Set (); seen.add (initial); const get = (status ) => { const ret = []; const array = Array .from (status); const x = status.indexOf ('0' ); for (const y of neighbors[x]) { [array[x], array[y]] = [array[y], array[x]]; ret.push (array.join ('' )); [array[x], array[y]] = [array[y], array[x]]; } return ret; } while (queue.length ) { ++step; const size = queue.length ; for (let i = 0 ; i < size; ++i) { const status = queue.shift (); for (const nextStatus of get (status)) { if (!seen.has (nextStatus)) { if ("123450" === nextStatus) { return step; } queue.push (nextStatus); seen.add (nextStatus); } } } } return -1 ; };
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 var neighbors = [6 ][]int {{1 , 3 }, {0 , 2 , 4 }, {1 , 5 }, {0 , 4 }, {1 , 3 , 5 }, {2 , 4 }}func slidingPuzzle (board [][]int ) int { const target = "123450" s := make ([]byte , 0 , 6 ) for _, r := range board { for _, v := range r { s = append (s, '0' +byte (v)) } } start := string (s) if start == target { return 0 } get := func (status string ) string ) { s := []byte (status) x := strings.Index(status, "0" ) for _, y := range neighbors[x] { s[x], s[y] = s[y], s[x] ret = append (ret, string (s)) s[x], s[y] = s[y], s[x] } return } type pair struct { status string step int } q := []pair{{start, 0 }} seen := map [string ]bool {start: true } for len (q) > 0 { p := q[0 ] q = q[1 :] for _, nxt := range get(p.status) { if !seen[nxt] { if nxt == target { return p.step + 1 } seen[nxt] = true q = append (q, pair{nxt, p.step + 1 }) } } } return -1 }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 struct HashTable { char str[7 ]; UT_hash_handle hh; }; struct Node { char str[7 ]; int val; }; const int neighbors[6 ][3 ] = {{1 , 3 , -1 }, {0 , 2 , 4 }, {1 , 5 , -1 }, {0 , 4 , -1 }, {1 , 3 , 5 }, {2 , 4 , -1 }};void swap (char * x, char * y) { char t = *x; *x = *y, *y = t; } char ** getNextStatus (char * status, int * retSize) { char ** ret = malloc (sizeof (char *) * 3 ); *retSize = 0 ; int x = 0 ; while (status[x] != '0' ) { x++; } for (int i = 0 ; i < 3 && neighbors[x][i] != -1 ; i++) { int y = neighbors[x][i]; swap(&status[x], &status[y]); ret[(*retSize)] = malloc (sizeof (char ) * 7 ); strcpy (ret[(*retSize)++], status); swap(&status[x], &status[y]); } return ret; } int slidingPuzzle (int ** board, int boardSize, int * boardColSize) { char str_0[] = "123450" ; char initial[7 ]; for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; ++j) { initial[i * 3 + j] = (char )(board[i][j] + '0' ); } } initial[6 ] = '\0' ; if (strcmp (initial, str_0) == 0 ) { return 0 ; } struct Node q [10001]; int left = 0 , right = 0 ; strcpy (q[right].str, initial); q[right++].val = 0 ; struct HashTable * seen =NULL ; struct HashTable * tmp =malloc (sizeof (struct HashTable)); strcpy (tmp->str, initial); HASH_ADD(hh, seen, str, sizeof (char ) * 7 , tmp); while (left < right) { char * status = q[left].str; int step = q[left++].val; int nextStatusSize; char ** nextStatus = getNextStatus(status, &nextStatusSize); for (int i = 0 ; i < nextStatusSize; i++) { HASH_FIND(hh, seen, nextStatus[i], sizeof (char ) * 5 , tmp); if (tmp == NULL ) { if (strcmp (nextStatus[i], str_0) == 0 ) { return step + 1 ; } strcpy (q[right].str, nextStatus[i]); q[right++].val = step + 1 ; tmp = malloc (sizeof (struct HashTable)); strcpy (tmp->str, nextStatus[i]); HASH_ADD(hh, seen, str, sizeof (char ) * 5 , tmp); } } } return -1 ; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O((mn)! \cdot mn),其中 m 和 n 分别是谜板的行数和列数,在本题中 m=2,n=3。谜板的状态的可能性一共有 (mn)! 种,这也是我们可以搜索到的状态数上限。对于每一个状态,我们需要 O(mn) 的时间找出 0 的位置,其最多可以和四个方向上相邻的数字进行交换,共需要 O(4mn) = O(mn) 的时间生成操作后的新状态,因此广度优先搜索的总时间复杂度为 O((mn)! \cdot mn)。
空间复杂度:O((mn)! \cdot mn)。我们最多需要在队列中存储 O((mn)!) 个长度为 mn 的字符串。
方法二:启发式搜索 概念
我们可以使用启发式搜索更快地找到最小旋转次数。这里我们可以使用 A* 算法。
读者可以自行查阅资料学习关于 A* 算法的基础知识,例如 Wikipedia - A* search algorithm 或 oi-wiki - A* 。它不是本题解的重点,因此这里不再赘述。读者可以阅读下面的段落检验自己的学习成果:
在 A* 算法中,我们需要使用四个距离函数 F(x), G(x), H(x), H^*(x),其中 F(x), G(x), H(x) 是可以求出的,而 H^*(x) 是无法求出的,我们需要用 H(x) 近似 H^*(x)。设起点为 s,终点为 t,这些距离函数的意义如下:
G(x) 表示从起点 s 到节点 x 的「实际」路径长度,注意 G(x) 并不一定是最短的;
H(x) 表示从节点 x 到终点 t 的「估计」最短路径长度,称为启发函数 ;
H^*(x) 表示从节点 x 到终点 t 的「实际」最短路径长度,这是我们在广度优先搜索的过程中无法求出的,我们需要用 H(x) 近似 H^*(x);
F(x) 满足 F(x) = G(x) + H(x),即为从起点 s 到终点 t 的「估计」路径长度。我们总是挑选出最小的 F(x) 对应的 x 进行搜索,因此 A* 算法需要借助优先队列 来实现。
如果读者熟悉求解最短路的 Dijkstra 算法,就可以发现 Dijkstra 算法是 A* 算法在 H(x) \equiv 0 时的特殊情况。
A* 算法具有两个性质:
如果对于任意的节点 x,H(x) \leq H^*(x) 恒成立,即我们「估计」出的从节点 x 到终点 t 的最短路径长度总是不超过「实际」的最短路径长度,那么称启发函数 H(x) 是可接纳的(admissible heuristic)。在这种情况下,A* 算法一定能找到最短路,但同一节点可能需要加入优先队列并搜索多次,即当我们从优先队列中取出节点 x 时,G(x) 并不一定等于从起点到节点 x 的「实际」最短 路径的长度;
如果对于任意的两个节点 x 和 y,并且 x 到 y 有一条长度为 D(x, y) 的有向边,H(x) - H(y) \leq D(x, y) 恒成立,并且 H(t)=0,那么称启发函数 H(x) 是一致的(consistent heuristic)。可以证明,一致的启发函数一定也是可接纳的。在这种情况下,同一节点只会被加入优先队列一次,并搜索不超过一次,即当我们从优先队列中取出节点 x 时,G(x) 一定等于从起点到节点 x 的「实际」最短 路径的长度。
思路与算法
我们可以设计如下的启发函数:
H(\textit{status}) = \sum_{i=1}^5i 的位置与目标状态中数字 i 的位置之间的曼哈顿距离\big)
在一次操作中,我们交换数字 0 和数字 i,非 0 的数字中只有 数字 i 的位置发生了变化。那么要想将数字 i 从初始状态中的位置移动到目标状态中的位置,我们至少需要进行「这两个位置之间的曼哈顿距离」次操作,因此我们解开谜板的需要的最少操作次数的下界为 H(\textit{status})。
根据定义,对于状态 status 和其通过一次操作得到的状态 next_status,H(\textit{status}) - H(\textit{next_status}) 要么为 1(数字 i 与其在目标状态中位置的曼哈顿距离减少了 1),要么为 -1(数字 i 与其在目标状态中位置的曼哈顿距离增加了 1),而 D(\textit{status}, \textit{next_status}) = 1,因此我们设计的启发函数是一致的。
我们在 A* 算法中使用该启发函数,即可得到最小的移动次数。
细节
我们可以预处理出任意两个位置的曼哈顿距离,位置的编号与方法一中的一致。距离矩阵如下:
\begin{bmatrix}
代码
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 struct AStar { static constexpr array<array<int , 6>, 6> dist = {{ {0 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 2 , 3 }, {1 , 0 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 2 }, {2 , 1 , 0 , 3 , 2 , 1 }, {1 , 2 , 3 , 0 , 1 , 2 }, {2 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 0 , 1 }, {3 , 2 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 0 } }}; static int getH (const string& status) int ret = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 6 ; ++i) { if (status[i] != '0' ) { ret += dist[i][status[i] - '1' ]; } } return ret; }; AStar (const string& status, int g): status_{status}, g_{g}, h_{getH (status)} { f_ = g_ + h_; } bool operator < (const AStar& that) const { return f_ > that.f_; } string status_; int f_, g_, h_; }; class Solution {private : vector<vector<int >> neighbors = {{1 , 3 }, {0 , 2 , 4 }, {1 , 5 }, {0 , 4 }, {1 , 3 , 5 }, {2 , 4 }};; public : int slidingPuzzle (vector<vector<int >>& board) auto get = [&](string& status) -> vector<string> { vector<string> ret; int x = status.find ('0' ); for (int y: neighbors[x]) { swap (status[x], status[y]); ret.push_back (status); swap (status[x], status[y]); } return ret; }; string initial; for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; ++j) { initial += char (board[i][j] + '0' ); } } if (initial == "123450" ) { return 0 ; } priority_queue<AStar> q; q.emplace (initial, 0 ); unordered_set<string> seen = {initial}; while (!q.empty ()) { AStar node = q.top (); q.pop (); for (auto && next_status: get (node.status_)) { if (!seen.count (next_status)) { if (next_status == "123450" ) { return node.g_ + 1 ; } q.emplace (next_status, node.g_ + 1 ); seen.insert (move (next_status)); } } } return -1 ; } };
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 class Solution { int [][] neighbors = {{1 , 3 }, {0 , 2 , 4 }, {1 , 5 }, {0 , 4 }, {1 , 3 , 5 }, {2 , 4 }}; public int slidingPuzzle (int [][] board) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 2 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 3 ; ++j) { sb.append(board[i][j]); } } String initial = sb.toString(); if ("123450" .equals(initial)) { return 0 ; } PriorityQueue<AStar> pq = new PriorityQueue <AStar>((a, b) -> a.f - b.f); pq.offer(new AStar (initial, 0 )); Set<String> seen = new HashSet <String>(); seen.add(initial); while (!pq.isEmpty()) { AStar node = pq.poll(); for (String nextStatus : get(node.status)) { if (!seen.contains(nextStatus)) { if ("123450" .equals(nextStatus)) { return node.g + 1 ; } pq.offer(new AStar (nextStatus, node.g + 1 )); seen.add(nextStatus); } } } return -1 ; } public List<String> get (String status) { List<String> ret = new ArrayList <String>(); char [] array = status.toCharArray(); int x = status.indexOf('0' ); for (int y : neighbors[x]) { swap(array, x, y); ret.add(new String (array)); swap(array, x, y); } return ret; } public void swap (char [] array, int x, int y) { char temp = array[x]; array[x] = array[y]; array[y] = temp; } } class AStar { public static int [][] dist = { {0 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 2 , 3 }, {1 , 0 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 2 }, {2 , 1 , 0 , 3 , 2 , 1 }, {1 , 2 , 3 , 0 , 1 , 2 }, {2 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 0 , 1 }, {3 , 2 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 0 } }; public String status; public int f, g, h; public AStar (String status, int g) { this .status = status; this .g = g; this .h = getH(status); this .f = this .g + this .h; } public static int getH (String status) { int ret = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 6 ; ++i) { if (status.charAt(i) != '0' ) { ret += dist[i][status.charAt(i) - '1' ]; } } return ret; } }
[sol2-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 class AStar : DIST = [ [0 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 2 , 3 ], [1 , 0 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 2 ], [2 , 1 , 0 , 3 , 2 , 1 ], [1 , 2 , 3 , 0 , 1 , 2 ], [2 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 0 , 1 ], [3 , 2 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 0 ], ] @staticmethod def getH (status: str ) -> int : ret = 0 for i in range (6 ): if status[i] != "0" : ret += AStar.DIST[i][int (status[i]) - 1 ] return ret def __init__ (self, status: str , g: str ) -> None : self.status = status self.g = g self.h = AStar.getH(status) self.f = self.g + self.h def __lt__ (self, other: "AStar" ) -> bool : return self.f < other.f class Solution : NEIGHBORS = [[1 , 3 ], [0 , 2 , 4 ], [1 , 5 ], [0 , 4 ], [1 , 3 , 5 ], [2 , 4 ]] def slidingPuzzle (self, board: List [List [int ]] ) -> int : def get (status: str ) -> Generator[str , None , None ]: s = list (status) x = s.index("0" ) for y in Solution.NEIGHBORS[x]: s[x], s[y] = s[y], s[x] yield "" .join(s) s[x], s[y] = s[y], s[x] initial = "" .join(str (num) for num in sum (board, [])) if initial == "123450" : return 0 q = [AStar(initial, 0 )] seen = {initial} while q: node = heapq.heappop(q) for next_status in get(node.status): if next_status not in seen: if next_status == "123450" : return node.g + 1 heapq.heappush(q, AStar(next_status, node.g + 1 )) seen.add(next_status) return -1
[sol2-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 type astar struct { g, h int status string } type hp []astarfunc (h hp) int { return len (h) }func (h hp) int ) bool { return h[i].g+h[i].h < h[j].g+h[j].h }func (h hp) int ) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }func (h *hp) interface {}) { *h = append (*h, v.(astar)) }func (h *hp) interface {} { a := *h; v := a[len (a)-1 ]; *h = a[:len (a)-1 ]; return v }var dist = [6 ][6 ]int { {0 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 2 , 3 }, {1 , 0 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 2 }, {2 , 1 , 0 , 3 , 2 , 1 }, {1 , 2 , 3 , 0 , 1 , 2 }, {2 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 0 , 1 }, {3 , 2 , 1 , 2 , 1 , 0 }, } func getH (status string ) int ) { for i, ch := range status { if ch != '0' { ret += dist[i][ch-'1' ] } } return } var neighbors = [6 ][]int {{1 , 3 }, {0 , 2 , 4 }, {1 , 5 }, {0 , 4 }, {1 , 3 , 5 }, {2 , 4 }}func slidingPuzzle (board [][]int ) int { const target = "123450" s := make ([]byte , 0 , 6 ) for _, r := range board { for _, v := range r { s = append (s, '0' +byte (v)) } } start := string (s) if start == target { return 0 } get := func (status string ) string ) { s := []byte (status) x := strings.Index(status, "0" ) for _, y := range neighbors[x] { s[x], s[y] = s[y], s[x] ret = append (ret, string (s)) s[x], s[y] = s[y], s[x] } return } type pair struct { status string step int } h := hp{{0 , getH(start), start}} seen := map [string ]bool {start: true } for len (h) > 0 { node := heap.Pop(&h).(astar) for _, nxt := range get(node.status) { if !seen[nxt] { if nxt == target { return node.g + 1 } seen[nxt] = true heap.Push(&h, astar{node.g + 1 , getH(nxt), nxt}) } } } return -1 }
复杂度分析
启发式搜索不讨论时空复杂度。
 {:width=”50%”}
{:width=”50%”}