对于某些非负整数 k ,如果交换 s1 中两个字母的位置恰好 k 次,能够使结果字符串等于 s2 ,则认为字符串 s1 和 s2 的相似度为 k ****。
给你两个字母异位词 s1 和 s2 ,返回 s1 和 s2 的相似度 k **** 的最小值。
示例 1:
**输入:** s1 = "ab", s2 = "ba"
**输出:** 1
示例 2:
**输入:** s1 = "abc", s2 = "bca"
**输出:** 2
提示:
1 <= s1.length <= 20s2.length == s1.lengths1 和 s2 只包含集合 {'a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f'} 中的小写字母s2 是 s1 的一个字母异位词
方法一:广度优先搜索 由于题目中给定的字符串的长度范围为 [1,20] 且只包含 6 种不同的字符,因此我们可以枚举所有可能的交换方案,在搜索时进行减枝从而提高搜索效率,最终找到最小的交换次数。
设字符串的长度为 n,如果当前第 i 个字符满足 s_1[i] \neq s_2[i],则从 s_1[i+1, \cdots] 选择一个合适的字符 s_1[j] 进行交换,其中满足 s_1[j] = s_2[i],j \in [i+1,n-1]。每次我们进行交换时,可将字符串 s_1 的前 x 个字符通过交换使得 s_1[0,\cdots,x - 1] = s_2[0,\cdots,x - 1],最终使得 s_1 的所有字符与 s_2 相等即可。我们通过以上变换,找到最小的交换次数使得 s_1 与 s_2 相等。
在搜索时,我们需要进行减枝,我们设当前的通过交换后的字符串 s_1’ 为一个中间状态,用哈希表记录这些中间状态,当通过交换时发现当前状态已经计算过,则此时我们可以直接跳过该状态。
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 class Solution : def kSimilarity (self, s1: str , s2: str ) -> int : step, n = 0 , len (s1) q, vis = [(s1, 0 )], {s1} while True : tmp = q q = [] for s, i in tmp: if s == s2: return step while i < n and s[i] == s2[i]: i += 1 for j in range (i + 1 , n): if s[j] == s2[i] != s2[j]: t = list (s) t[i], t[j] = t[j], t[i] t = '' .join(t) if t not in vis: vis.add(t) q.append((t, i + 1 )) step += 1
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 class Solution {public : int kSimilarity (string s1, string s2) int n = s1.size (); queue<pair<string, int >> qu; unordered_set<string> visit; qu.emplace (s1, 0 ); visit.emplace (s1); for (int step = 0 ;; step++) { int sz = qu.size (); for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; i++) { auto [cur, pos] = qu.front (); qu.pop (); if (cur == s2) { return step; } while (pos < n && cur[pos] == s2[pos]) { pos++; } for (int j = pos + 1 ; j < n; j++) { if (cur[j] != s2[j] && cur[j] == s2[pos]) { swap (cur[pos], cur[j]); if (!visit.count (cur)) { visit.emplace (cur); qu.emplace (cur, pos + 1 ); } swap (cur[pos], cur[j]); } } } } } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution { public int kSimilarity (String s1, String s2) { int n = s1.length(); Queue<Pair<String, Integer>> queue = new ArrayDeque <Pair<String, Integer>>(); Set<String> visit = new HashSet <String>(); queue.offer(new Pair <String, Integer>(s1, 0 )); visit.add(s1); int step = 0 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int sz = queue.size(); for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; i++) { Pair<String, Integer> pair = queue.poll(); String cur = pair.getKey(); int pos = pair.getValue(); if (cur.equals(s2)) { return step; } while (pos < n && cur.charAt(pos) == s2.charAt(pos)) { pos++; } for (int j = pos + 1 ; j < n; j++) { if (s2.charAt(j) == cur.charAt(j)) { continue ; } if (s2.charAt(pos) == cur.charAt(j)) { String next = swap(cur, pos, j); if (!visit.contains(next)) { visit.add(next); queue.offer(new Pair <String, Integer>(next, pos + 1 )); } } } } step++; } return step; } public String swap (String cur, int i, int j) { char [] arr = cur.toCharArray(); char c = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = c; return new String (arr); } }
[sol1-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 public class Solution { public int KSimilarity (string s1, string s2 int n = s1.Length; Queue<Tuple<string , int >> queue = new Queue<Tuple<string , int >>(); ISet<string > visit = new HashSet<string >(); queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<string , int >(s1, 0 )); visit.Add(s1); int step = 0 ; while (queue.Count > 0 ) { int sz = queue.Count; for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; i++) { Tuple<string , int > tuple = queue.Dequeue(); string cur = tuple.Item1; int pos = tuple.Item2; if (cur.Equals(s2)) { return step; } while (pos < n && cur[pos] == s2[pos]) { pos++; } for (int j = pos + 1 ; j < n; j++) { if (s2[j] == cur[j]) { continue ; } if (s2[pos] == cur[j]) { string next = Swap(cur, pos, j); if (!visit.Contains(next)) { visit.Add(next); queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<string , int >(next, pos + 1 )); } } } } step++; } return step; } public string Swap (string cur, int i, int j char [] arr = cur.ToCharArray(); char c = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = c; return new string (arr); } }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 #define MAX_STR_LEN 24 typedef struct Node { char str[MAX_STR_LEN]; int pos; struct Node * next ; } Node; typedef struct { char key[MAX_STR_LEN]; UT_hash_handle hh; } HashItem; HashItem *hashFindItem (HashItem **obj, const char * key) { HashItem *pEntry = NULL ; HASH_FIND_STR(*obj, key, pEntry); return pEntry; } bool hashAddItem (HashItem **obj, const char * key) { HashItem *pEntry = (HashItem *)malloc (sizeof (HashItem)); strcpy (pEntry->key, key); HASH_ADD_STR(*obj, key, pEntry); return true ; } void hashFree (HashItem **obj) { HashItem *curr = NULL , *tmp = NULL ; HASH_ITER(hh, *obj, curr, tmp) { HASH_DEL(*obj, curr); free (curr); } } static inline void swap (char *pa, char *pb) { char c = *pa; *pa = *pb; *pb = c; } int kSimilarity (char * s1, char * s2) { int n = strlen (s1); Node *head = NULL , *tail = NULL ; HashItem *visit = NULL ; hashAddItem(&visit, s1); head = tail = (Node *)malloc (sizeof (Node)); strcpy (tail->str, s1); tail->pos = 0 ; tail->next = NULL ; int step = 0 , queueSize = 1 ; while (queueSize > 0 ) { int sz = queueSize; char cur[MAX_STR_LEN]; for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; i++) { char *cur = head->str; int pos = head->pos; if (!strcmp (cur, s2)) { return step; } while (pos < n && cur[pos] == s2[pos]) { pos++; } for (int j = pos + 1 ; j < n; j++) { if (s2[j] == cur[j]) { continue ; } if (s2[pos] == cur[j]) { swap(&cur[pos], &cur[j]); if (!hashFindItem(&visit, cur)) { hashAddItem(&visit, cur); tail->next = (Node *)malloc (sizeof (Node)); tail = tail->next; strcpy (tail->str, cur); tail->pos = pos + 1 ; tail->next = NULL ; queueSize++; } swap(&cur[pos], &cur[j]); } } Node *p = head; head = head->next; queueSize--; free (p); } step++; } hashFree(&visit); return step; }
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 var kSimilarity = function (s1, s2 ) { const n = s1.length ; const queue = []; const visit = new Set (); queue.push ([s1, 0 ]); visit.add (s1); let step = 0 ; while (queue.length ) { const sz = queue.length ; for (let i = 0 ; i < sz; i++) { let [cur, pos] = queue.shift (); if (cur === s2) { return step; } while (pos < n && cur[pos] === s2[pos]) { pos++; } for (let j = pos + 1 ; j < n; j++) { if (s2[j] === cur[j]) { continue ; } if (s2[pos] === cur[j]) { const next = swap (cur, pos, j); if (!visit.has (next)) { visit.add (next); queue.push ([next, pos + 1 ]); } } } } step++; } return step; } const swap = (cur, i, j ) => { const arr = [...cur]; const c = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = c; return arr.join ('' ); };
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 func kSimilarity (s1, s2 string ) int ) { type pair struct { s string i int } q := []pair{{s1, 0 }} vis := map [string ]bool {s1: true } for n := len (s1); ; step++ { tmp := q q = nil for _, p := range tmp { s, i := p.s, p.i if s == s2 { return } for i < n && s[i] == s2[i] { i++ } t := []byte (s) for j := i + 1 ; j < n; j++ { if s[j] == s2[i] && s[j] != s2[j] { t[i], t[j] = t[j], t[i] if t := string (t); !vis[t] { vis[t] = true q = append (q, pair{t, i + 1 }) } t[i], t[j] = t[j], t[i] } } } } }
复杂度分析
该方法时空复杂度分析较为复杂,暂不讨论。
方法二:深度优先搜索 与方法一同样的交换思路,我们也可以采用深度优先搜索来实现,每次遇到不同的字符 s_1[i] \neq s_2[i] 时,则从 s_1[i+1, \cdots] 中选择处于不同位置的字符 s_1[j] = s_2[i],将其与 s_1[i] 进行交换,然后保持当前子状态,搜索下一个位置 i+1,直到所有字符串 s_1 全部与 s_2 匹配完成;当前子状态搜索完成后,然后恢复字符串,继续搜索下一个与 s_2[i] 相等的字符,并进行替换即可。在进行深度优先搜索时,由于每个搜索时每个子树的状态都是不同的,所以也可以不用哈希表去重,但是可以用一些特殊的减枝技巧。我们可以得到相似字符串交换次数的上限与下限:
对于长度为 n 的两个相似的字符串 s_1,s_2,s_1 最多需要 n-1 次交换变为 s_2,因为每进行一次有效交换时,我们可以将 s_1 的中的一个字符调整到与 s_2 相同,我们只需要将 s_1 的前 n-1 个字符调整到与 s_2 的前 n-1 个字符相同,则 s_1 的第 n 个字符此时也一定与 s_2 的第 n 个字符相同,因此我们最多需要 n-1 次交换,即可使得 s_1, s_2 相等。
对于长度为 n 的两个相似的字符串 s_1,s_2,且对于字符串中任意位置的字符均满足 s_1[i] \neq s_2[i]。我们可以观察到此时 s_1 最少需要 \lfloor \dfrac{n+1/2} \rfloor 次交换变为 s_2。每进行一次有效交换时,我们最多可以将 s_1 的中的两个字符调整到与 s_2 相同。比如当满足 s_1[i] = s_2[j],s_1[j] = s_2[i],此时我们交换位置 (i,j),可以将两个字符调整到正确的位置,我们分两种情况进行讨论:
当 n 为偶数时,由于每次交换时最多可以将两个字符同时移动到正确的位置,因此最少需要 \dfrac{n}{2 次交换可以使得 s_1 与 s_2 相等。
当 n 为奇数数时,每次交换时最多可以将两个字符同时移动到正确的位置,当最终剩下 3 个字符时,此时我们再交换一次时无法交换两个字符到正确的位置。根据前置条件所有位置的字符均满足 s_1[i] \neq s_2[i],假设此时还剩余 3 个字符满足 s_1[i] \neq s_2[i],s_1[j] \neq s_2[j],s_1[k] \neq s_2[k] 时,则此时任意交换一次两个字符使得 s_1[i] = s_2[i],s_1[j] = s_2[j],还剩余一个字符 s_1[k],s_2[k] 不相等,这与两个字符串相似矛盾,因此还需 2 次交换才能使得 s1,s_2 中剩余的 3 个字符相等。因此当 n 为奇数时,最少需要 \dfrac{n+1/2 次交换可以使得 s_1 与 s_2 相等。
根据以上结论,我们可以进行如下减枝:
我们只需要计算两个字符 s_1,s_2 中同一位置不同的字符的交换次数即可,同一位置相同的字符直接可以跳过。
根据之前的结论,假设当前已经通过计算得到的最少交换次数为 ans,假设当前字符字符串 s_1 已经过 cost 次交换变为了 s_1{‘,此时我们计算出字符串 s_1^{‘ 变为 s_2 还需要进行交换次数的下限为 minSwap}(s_1{‘}),则字符串 s_1 经过交换变为中间状态 s_1{‘,然后交换变为 s_2 所需的交换次数的下限为 cur} = \textit{cost} + \text{minSwap}(s_1^{‘}),如果当前最少交换次数下限满足 cur} \ge \textit{ans 时,则表明当前的字符串 s_1^{‘ 已经不是更优的搜索状态,可直接提前终止搜索。
[sol2-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 class Solution : def kSimilarity (self, s1: str , s2: str ) -> int : s, t = [], [] for x, y in zip (s1, s2): if x != y: s.append(x) t.append(y) n = len (s) if n == 0 : return 0 ans = n - 1 def dfs (i: int , cost: int ) -> None : nonlocal ans if cost > ans: return while i < n and s[i] == t[i]: i += 1 if i == n: ans = min (ans, cost) return diff = sum (s[j] != t[j] for j in range (i, len (s))) min_swap = (diff + 1 ) // 2 if cost + min_swap >= ans: return for j in range (i + 1 , n): if s[j] == t[i]: s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i] dfs(i + 1 , cost + 1 ) s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i] dfs(0 , 0 ) return ans
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 class Solution {public : int minSwap (const string &s1, const string &s2, const int &pos) int tot = 0 ; for (int i = pos; i < s1.size (); i++) { tot += s1[i] != s2[i]; } return (tot + 1 ) / 2 ; } int kSimilarity (string s1, string s2) string str1, str2; for (int i = 0 ; i < s1.size (); i++) { if (s1[i] != s2[i]) { str1.push_back (s1[i]); str2.push_back (s2[i]); } } int n = str1.size (); if (n == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int ans = n - 1 ; function<void (int , int )> dfs = [&](int pos, int cost) { if (cost > ans) { return ; } while (pos < n && str1[pos] == str2[pos]) { pos++; } if (pos == n) { ans = min (ans, cost); return ; } if (cost + minSwap (str1, str2, pos) >= ans) { return ; } for (int i = pos + 1 ; i < n; i++) { if (str1[i] == str2[pos]) { swap (str1[i], str1[pos]); dfs (pos + 1 , cost + 1 ); swap (str1[i], str1[pos]); } } }; dfs (0 , 0 ); return ans; } };
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 class Solution { int ans; public int kSimilarity (String s1, String s2) { StringBuilder str1 = new StringBuilder (); StringBuilder str2 = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i < s1.length(); i++) { if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(i)) { str1.append(s1.charAt(i)); str2.append(s2.charAt(i)); } } if (str1.length() == 0 ) { return 0 ; } ans = str1.length() - 1 ; dfs(0 , 0 , str1.length(), str1.toString(), str2.toString()); return ans; } public void dfs (int pos, int cost, int len, String str1, String str2) { if (cost > ans) { return ; } while (pos < str1.length() && str1.charAt(pos) == str2.charAt(pos)) { pos++; } if (pos == str1.length()) { ans = Math.min(ans, cost); return ; } if (cost + minSwap(str1, str2, pos) >= ans) { return ; } for (int i = pos + 1 ; i < str1.length(); i++) { if (str1.charAt(i) == str2.charAt(pos)) { String str1Next = swap(str1, i, pos); dfs(pos + 1 , cost + 1 , len, str1Next, str2); } } } public int minSwap (String s1, String s2, int pos) { int tot = 0 ; for (int i = pos; i < s1.length(); i++) { tot += s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(i) ? 1 : 0 ; } return (tot + 1 ) / 2 ; } public String swap (String cur, int i, int j) { char [] arr = cur.toCharArray(); char c = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = c; return new String (arr); } }
[sol2-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 public class Solution { int ans; public int KSimilarity (string s1, string s2 StringBuilder str1 = new StringBuilder(); StringBuilder str2 = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0 ; i < s1.Length; i++) { if (s1[i] != s2[i]) { str1.Append(s1[i]); str2.Append(s2[i]); } } if (str1.Length == 0 ) { return 0 ; } ans = str1.Length - 1 ; DFS(0 , 0 , str1.Length, str1.ToString(), str2.ToString()); return ans; } public void DFS (int pos, int cost, int len, string str1, string str2 if (cost > ans) { return ; } while (pos < str1.Length && str1[pos] == str2[pos]) { pos++; } if (pos == str1.Length) { ans = Math.Min(ans, cost); return ; } if (cost + MinSwap(str1, str2, pos) >= ans) { return ; } for (int i = pos + 1 ; i < str1.Length; i++) { if (str1[i] == str2[pos]) { string str1Next = Swap(str1, i, pos); DFS(pos + 1 , cost + 1 , len, str1Next, str2); } } } public int MinSwap (string s1, string s2, int pos int tot = 0 ; for (int i = pos; i < s1.Length; i++) { tot += s1[i] != s2[i] ? 1 : 0 ; } return (tot + 1 ) / 2 ; } public string Swap (string cur, int i, int j char [] arr = cur.ToCharArray(); char c = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = c; return new string (arr); } }
[sol2-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 #define MAX_STR_LEN 24 #define MIN(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) static inline void swap (char *pa, char *pb) { char c = *pa; *pa = *pb; *pb = c; } int minSwap (const char *s1, const char *s2, int pos) { int tot = 0 ; for (int i = pos; s1[i]; i++) { tot += s1[i] != s2[i]; } return (tot + 1 ) / 2 ; } void dfs (int pos, int cost, int len, char * str1, const char *str2, int *res) { if (cost > *res) { return ; } while (pos < len && str1[pos] == str2[pos]) { pos++; } if (pos == len) { *res = MIN(*res, cost); return ; } if (cost + minSwap(str1, str2, pos) >= *res) { return ; } for (int i = pos + 1 ; i < len; i++) { if (str1[i] == str2[pos]) { swap(&str1[i], &str1[pos]); dfs(pos + 1 , cost + 1 , len, str1, str2, res); swap(&str1[i], &str1[pos]); } } }; int kSimilarity (char * s1, char * s2) { char str1[MAX_STR_LEN], str2[MAX_STR_LEN]; int pos = 0 , len = strlen (s1); for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { if (s1[i] != s2[i]) { str1[pos] = s1[i]; str2[pos] = s2[i]; pos++; } } str1[pos] = '\0' ; str2[pos] = '\0' ; if (pos == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int res = pos - 1 ; dfs(0 , 0 , pos, str1, str2, &res); return res; }
[sol2-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 var kSimilarity = function (s1, s2 ) { let str1 = '' ; let str2 = '' ; for (let i = 0 ; i < s1.length ; i++) { if (s1[i] !== s2[i]) { str1 += s1[i]; str2 += s2[i]; } } if (str1.length === 0 ) { return 0 ; } let ans = str1.length - 1 ; const dfs = (pos, cost, len, str1, str2 ) => { if (cost > ans) { return ; } while (pos < str1.length && str1[pos] === str2[pos]) { pos++; } if (pos === str1.length ) { ans = Math .min (ans, cost); return ; } if (cost + minSwap (str1, str2, pos) >= ans) { return ; } for (let i = pos + 1 ; i < str1.length ; i++) { if (str1[i] === str2[pos]) { const str1Next = swap (str1, i, pos); dfs (pos + 1 , cost + 1 , len, str1Next, str2); } } } const minSwap = (s1, s2, pos ) => { let tot = 0 ; for (let i = pos; i < s1.length ; i++) { tot += s1[i] !== s2[i] ? 1 : 0 ; } return Math .floor ((tot + 1 ) / 2 ); } const swap = (cur, i, j ) => { const arr = [...cur]; const c = arr[i]; arr[i] = arr[j]; arr[j] = c; return arr.join ('' ); } dfs (0 , 0 , str1.length , str1, str2); return ans; }
[sol2-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 func kSimilarity (s1, s2 string ) int { var s, t []byte for i := range s1 { if s1[i] != s2[i] { s = append (s, s1[i]) t = append (t, s2[i]) } } n := len (s) if n == 0 { return 0 } minSwap := func (i int ) int { diff := 0 for j := i; j < n; j++ { if s[j] != t[j] { diff++ } } return (diff + 1 ) / 2 } ans := n - 1 var dfs func (int , int ) dfs = func (i, cost int ) if cost > ans { return } for i < n && s[i] == t[i] { i++ } if i == n { ans = min(ans, cost) return } if cost+minSwap(i) >= ans { return } for j := i + 1 ; j < n; j++ { if s[j] == t[i] { s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i] dfs(i+1 , cost+1 ) s[i], s[j] = s[j], s[i] } } } dfs(0 , 0 ) return ans } func min (a, b int ) int { if a > b { return b } return a }
复杂度分析
该方法时空复杂度分析较为复杂,暂不讨论。
方法三:A* 启发式搜索 本题我们还可以使用 A* 启发式搜索,可参考相关 A* 算法的基础知识,例如「Wikipedia - A* search algorithm 」或 「oi-wiki - A* 」,力扣上也可以参考类似题解「752. 打开转盘锁 」。
设估计函数为 f(x) = g(x) + h(x),其中 g(x) 表示起始状态到达状态 x 的实际交换次数,h(x) 为启发函数,在这里我们设 h(x) 表示状态 x 到达终态可能的最小交换次数,即方法二中提到的当前状态 x 还需要的交换次数的下限 minSwap}(x),h(x) 满足小于等于实际的最小步数。实际上我们观察到该启发函数本质为一种贪心策略,在同样的状态下尽可能的选择一次交换 (i,j) 使得 s_1 中两个位置 (i,j) 的字符与 s_2 相等,这样才能使得启发函数 h(x) 尽可能的小。
[sol3-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solution {public : int minSwap (const string &s1, const string &s2, const int &pos) int tot = 0 ; for (int i = pos; i < s1.size (); i++) { tot += s1[i] != s2[i]; } return (tot + 1 ) / 2 ; } int kSimilarity (string s1, string s2) typedef tuple<int , int , int , string> State; int n = s1.size (); priority_queue<State, vector<State>, greater<State>> pq; unordered_set<string> visit; pq.emplace (0 , 0 , 0 , s1); visit.emplace (s1); while (!pq.empty ()) { auto [_, cost, pos, cur] = pq.top (); pq.pop (); if (cur == s2) { return cost; } while (pos < n && cur[pos] == s2[pos]) { pos++; } for (int j = pos + 1 ; j < n; j++) { if (s2[j] == cur[j]) { continue ; } if (s2[pos] == cur[j]) { swap (cur[pos], cur[j]); if (!visit.count (cur)) { visit.emplace (cur); pq.emplace (cost + 1 + minSwap (s2, cur, pos + 1 ), cost + 1 , pos + 1 , cur); } swap (cur[pos], cur[j]); } } } return 0 ; } };
复杂度分析
启发式搜索不讨论时空复杂度。
方法四:动态规划 该解法思维难度较大且时间复杂度较高,可作为参考题解,同样的解题思路可以参考「zj-future04. 门店商品调配 」。
解法二中提到过长度为 n 两个相似的字符串的最大交换次数为 n-1,最小的交换次数为 \lfloor \dfrac{n+1/2} \rfloor。我们可以观察一下什么样的字符串交换次数为 n-1,比如长度以下字符串:
abcdef", bcdefa”} \ \text{ab", ba”} \ \text{abcd", bcda”} \
在上述字符中无法如何交换,每次均只能将一个字符调整到位,因此需要的交换次数为 n-1。对于部分字符串需要的交换次数少于 n-1,比如下列字符串:
abcdef", ecdbfa”} \ \text{acd", cad”} \ \text{abcd", dcba”} \
对于字符串 s = \text{abcdef" 可以拆分为两个分别与字符串 ecdbfa” 的子串 \_cdb\_\_", e___fa” 相似的字符串 p = a\_\_\_ef ", q = _bcd__“。设 ks}(s) 表示字符串 s 的转换为目标字符串的最小交换次数,则 ks}(s) = \textit{ks}(p) + \textit{ks}(q) = 2 + 2。我们可以看到字符串 ``abcdef” 的交换次数也即等于相同位置相似的子串的交换次之和,即 ks}(t) = \text{ks}(p) + \text{ks}(q)。设初始值 ks}(t) = \text{len}(t) - 1,其中 len}(t) 表示字符串 t 的长度,ks}(p) + \text{ks}(q) = \text{len}(p) + \text{len}(q) - 2 = len(t) - 2。我们可以观察到字符串 t 每进行一次相似子字符串拆分,则其交换次会减 1,字符串 s 可拆分为的相似的子串的个数越多,则其交换次数最小。我们设字符串 s 可以被拆分成 k 个相似的子字符串,长度分别为 C_1,C_2, \cdots, C_k,则 ks}(s) = \sum_{i=1}^{k} \limits (C_i - 1) = \text{len}(s) - k,由此只需求出字符串可拆分的最大次数即可求出最小交换步数。
字符串相似:即两个字符串中含有的字符和数量完全相等。我们应当将字符串尽可能的拆分成相似的子串,直到不能拆分为止。求字符串的最小交换次数则转换为求该字符串最多的相似子字符串的拆分次数。如果字符串不可拆分,则该字符串的最小交换次数即为字符串的长度减 1。
因此我们可以使用动态规划来解决这个问题,令 dp}(s) 表示字符串 s 最多拆分为相似子字符串 t 的数目,如果 s 不能继续拆分,则令 dp(s) = 1。枚举 s 的所有相似的子串 t,状态转移方程为 dp}(s) = \max(dp(t) + \textit{dp}(s - t))。由于题目中字符的长度串最多为 20,为了计算方便使用位图来表示字符串 s 的子串,如果字符串 t 为 s 的子串,则一定满足 (s \And t) = t,对于字符串 t 我们枚举其所有的子集即可。当然可以直接遍历所有子串的子集,则时间复杂度为 3^n,在题目给定的测试用例下会超时。此时需要进行减枝以降低时间复杂度,减枝技巧如下:
由于子串中只含有 6 种字符,因此长度大于 6 的字符串则其一定可以拆分为长度小于等于 6 的相似子串,此时字符串中一定含有相同的字符。我们可以将所有长度大于 6 的字符串删选出来,依次尝试将其拆分出一个长度小于等于 6 的子字符串。
通过筛选,只筛选出所有相似的子字符串,对于非相似的字符串直接忽略,因为只有相似的字符串才可以拆分成相似的子串。
对于所有筛选出来的相似的子字符串按照字符的个数进行排序,这样就能保证字符的子串一定排列在前面而保证最优的子状态现行进行计算。对于题目中给定的字符串 s_1 一定是与 s_2 相似的,我们求出 s_1 进行最多的拆分次数即可,最终返回结果即为 len(s_1) - dp(s1)。
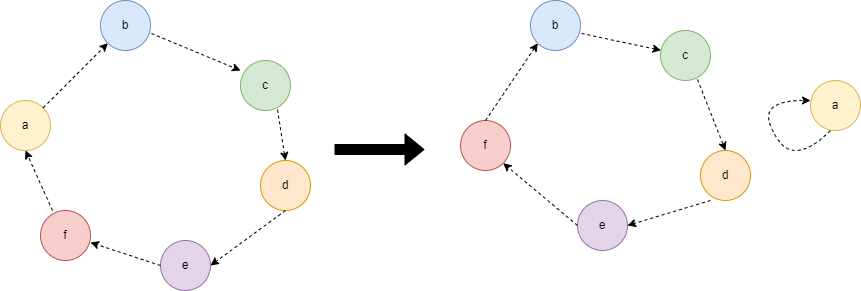
从图论的角度来分析相似字符串,设相似字符串 s_1,s_2,我们用有向图来表示相似字符串,每个字符为有向图中的一个节点,s_1 中的字符指向 s_2 中同一个位置的字符表示一条有向边 s_1[i] \rightarrow s_2[i],则该有向图一定由多个环组成,且每个节点都在环上。我们进行一次“有效”的字符交换(即将其中一个字符交换到最终位置),等价于把有向图中两条首尾相连的边变成一条新边和被一个节点的自环。我们最终的目标是把 s_1 中的所有字符都变成自环。一个长度为 k 的环则我们需要 k-1 次交换才能把所有的节点都变为自环。设长度为 n 的字符串 s_1 可以拆分为 m 个环,则此时需要的有效交换次数为 n - m。因此,求最少的交换次数即等价于 s_1 拆分成环的最大数目。
比如相似字符为:
s_1 = \text{abcdef"}, s_2 = \text{bcdefa”
将其交换一次后则变为:
s_1 = \text{fbcdea"}, s_2 = \text{bcdefa”
如下图所示可以看到交换后被拆分为一个新的环和一个字符的自环。
[sol4-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 class Solution {public : int kSimilarity (string s1, string s2) string str1, str2; for (int i = 0 ; i < s1.size (); i++) { if (s1[i] != s2[i]) { str1.push_back (s1[i]); str2.push_back (s2[i]); } } int n = str1.size (); if (n == 0 ) { return 0 ; } vector<int > smallCycles; vector<int > largeCycles; for (int i = 1 ; i < (1 << n); i++) { vector<int > cnt (6 ) ; for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (i & (1 << j)) { cnt[str1[j] - 'a' ]++; cnt[str2[j] - 'a' ]--; } } bool isCycle = true ; for (int j = 0 ; j < 6 ; j++) { if (cnt[j] != 0 ) { isCycle = false ; break ; } } if (isCycle) { int size = __builtin_popcount(i); if (size <= 6 ) { smallCycles.emplace_back (i); } else { largeCycles.emplace_back (i); } } } auto cmp = [](const int &a, const int &b)->bool { return __builtin_popcount(a) < __builtin_popcount(b); }; sort (smallCycles.begin (), smallCycles.end (), cmp); sort (largeCycles.begin (), largeCycles.end (), cmp); vector<int > dp (1 << n, 1 ) ; dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < smallCycles.size (); i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { int x = smallCycles[i], y = smallCycles[j]; if ((x & y) == y) { dp[x] = max (dp[x], dp[y] + dp[x ^ y]); } } } for (auto &x : largeCycles) { for (auto &y : smallCycles) { if ((x & y) == y) { dp[x] = max (dp[x], dp[y] + dp[x ^ y]); } } } return n - dp[(1 << n) - 1 ]; } };
[sol4-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 class Solution { public int kSimilarity (String s1, String s2) { StringBuilder str1 = new StringBuilder (); StringBuilder str2 = new StringBuilder (); for (int i = 0 ; i < s1.length(); i++) { if (s1.charAt(i) != s2.charAt(i)) { str1.append(s1.charAt(i)); str2.append(s2.charAt(i)); } } int n = str1.length(); if (n == 0 ) { return 0 ; } List<Integer> smallCycles = new ArrayList <Integer>(); List<Integer> largeCycles = new ArrayList <Integer>(); for (int i = 1 ; i < (1 << n); i++) { int [] cnt = new int [6 ]; for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if ((i & (1 << j)) != 0 ) { cnt[str1.charAt(j) - 'a' ]++; cnt[str2.charAt(j) - 'a' ]--; } } boolean isCycle = true ; for (int j = 0 ; j < 6 ; j++) { if (cnt[j] != 0 ) { isCycle = false ; break ; } } if (isCycle) { int size = Integer.bitCount(i); if (size <= 6 ) { smallCycles.add(i); } else { largeCycles.add(i); } } } Collections.sort(smallCycles, (a, b) -> Integer.bitCount(a) - Integer.bitCount(b)); Collections.sort(largeCycles, (a, b) -> Integer.bitCount(a) - Integer.bitCount(b)); int [] dp = new int [1 << n]; Arrays.fill(dp, 1 ); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < smallCycles.size(); i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { int x = smallCycles.get(i), y = smallCycles.get(j); if ((x & y) == y) { dp[x] = Math.max(dp[x], dp[y] + dp[x ^ y]); } } } for (int x : largeCycles) { for (int y : smallCycles) { if ((x & y) == y) { dp[x] = Math.max(dp[x], dp[y] + dp[x ^ y]); } } } return n - dp[(1 << n) - 1 ]; } }
[sol4-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 #define MAX_STR_LEN 24 #define MAX_CYCLE_SIZE 15000 #define MIN(a, b) ((a) < (b) ? (a) : (b)) #define MAX(a, b) ((a) > (b) ? (a) : (b)); static inline int cmp (const void *pa, const void *pb) { return __builtin_popcount(*(int *)pa) - __builtin_popcount(*(int *)pb); } int kSimilarity (char * s1, char * s2) { char str1[MAX_STR_LEN], str2[MAX_STR_LEN]; int len = strlen (s1), n = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < len; i++) { if (s1[i] != s2[i]) { str1[n] = s1[i]; str2[n] = s2[i]; n++; } } if (n == 0 ) { return 0 ; } int *smallCycles = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) * MAX_CYCLE_SIZE); int *largeCycles = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) * MAX_CYCLE_SIZE); int smallCyclesSize = 0 , largeCyclesSize = 0 ; int *dp = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) * (1 << n)); for (int i = 1 ; i < (1 << n); i++) { int cnt[6 ] = {0 }; for (int j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if (i & (1 << j)) { cnt[str1[j] - 'a' ]++; cnt[str2[j] - 'a' ]--; } } bool isCycle = true ; for (int j = 0 ; j < 6 ; j++) { if (cnt[j] != 0 ) { isCycle = false ; break ; } } if (isCycle) { int size = __builtin_popcount(i); dp[i] = 1 ; if (size <= 6 ) { smallCycles[smallCyclesSize++] = i; } else { largeCycles[largeCyclesSize++] = i; } } } qsort(smallCycles, smallCyclesSize, sizeof (int ), cmp); qsort(largeCycles, largeCyclesSize, sizeof (int ), cmp); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < smallCyclesSize; i++) { int maskx = smallCycles[i]; for (int j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { int masky = smallCycles[j]; if ((maskx & masky) == masky) { dp[maskx] = MAX(dp[maskx], dp[masky] + dp[maskx ^ masky]); } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < largeCyclesSize; i++) { for (int j = 0 ; j < smallCyclesSize; j++) { int maskx = largeCycles[i]; int masky = smallCycles[j]; if ((maskx & masky) == masky) { dp[maskx] = MAX(dp[maskx], dp[masky] + dp[maskx ^ masky]); } } } int ans = n - dp[(1 << n) - 1 ]; free (smallCycles); free (largeCycles); free (dp); return ans; }
[sol4-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 var kSimilarity = function (s1, s2 ) { let str1 = '' ; let str2 = '' ; for (let i = 0 ; i < s1.length ; i++) { if (s1[i] !== s2[i]) { str1 += s1[i]; str2 += s2[i]; } } const n = str1.length ; if (n === 0 ) { return 0 ; } const smallCycles = []; const largeCycles = []; for (let i = 1 ; i < (1 << n); i++) { const cnt = new Array (6 ).fill (0 ); for (let j = 0 ; j < n; j++) { if ((i & (1 << j)) !== 0 ) { cnt[str1[j].charCodeAt () - 'a' .charCodeAt ()]++; cnt[str2[j].charCodeAt () - 'a' .charCodeAt ()]--; } } let isCycle = true ; for (let j = 0 ; j < 6 ; j++) { if (cnt[j] !== 0 ) { isCycle = false ; break ; } } if (isCycle) { const size = bitCount (i); if (size <= 6 ) { smallCycles.push (i); } else { largeCycles.push (i); } } } smallCycles.sort ((a, b ) => bitCount (a) - bitCount (b)); largeCycles.sort ((a, b ) => bitCount (a) - bitCount (b)); const dp = new Array (1 << n).fill (1 ); dp[0 ] = 0 ; for (let i = 0 ; i < smallCycles.length ; i++) { for (let j = 0 ; j < i; j++) { const x = smallCycles[i], y = smallCycles[j]; if ((x & y) === y) { dp[x] = Math .max (dp[x], dp[y] + dp[x ^ y]); } } } for (const x of largeCycles) { for (const y of smallCycles) { if ((x & y) === y) { dp[x] = Math .max (dp[x], dp[y] + dp[x ^ y]); } } } return n - dp[(1 << n) - 1 ]; } const bitCount = (num ) => { return num.toString (2 ).split ('0' ).join ('' ).length ; }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(2^n \times |\Sigma| + 3^n),其中 n 为字符串的长度,|\Sigma| 表示字符集,在此题中字符集为 a',b’,c',d’,e',f’,本题中 |\Sigma| = 6。需要遍历并检测所有可能成环的子串,需要的时间为 O(2^n \times |\Sigma|),检测每个环的最小交换次数需要的时间上限为 O(3^n),因此时间复杂度为 O(2^n \times |\Sigma| + 3^n)。
空间复杂度:O(2^n),其中 n 为字符串的长度。需要记录字符串所有的子串的状态,因此需要的存储空间为 2^n。