0885-螺旋矩阵 III
在 rows x cols 的网格上,你从单元格 (rStart, cStart)
面朝东面开始。网格的西北角位于第一行第一列,网格的东南角位于最后一行最后一列。
你需要以顺时针按螺旋状行走,访问此网格中的每个位置。每当移动到网格的边界之外时,需要继续在网格之外行走(但稍后可能会返回到网格边界)。
最终,我们到过网格的所有 rows x cols 个空间。
按照访问顺序返回表示网格位置的坐标列表。
示例 1:
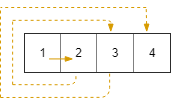
**输入:** rows = 1, cols = 4, rStart = 0, cStart = 0
**输出:** [[0,0],[0,1],[0,2],[0,3]]
示例 2:
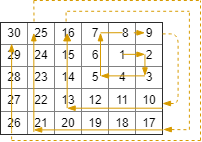
**输入:** rows = 5, cols = 6, rStart = 1, cStart = 4
**输出:** [[1,4],[1,5],[2,5],[2,4],[2,3],[1,3],[0,3],[0,4],[0,5],[3,5],[3,4],[3,3],[3,2],[2,2],[1,2],[0,2],[4,5],[4,4],[4,3],[4,2],[4,1],[3,1],[2,1],[1,1],[0,1],[4,0],[3,0],[2,0],[1,0],[0,0]]
提示:
1 <= rows, cols <= 1000 <= rStart < rows0 <= cStart < cols
方法:螺旋形行走
思路
我们可以从开始的正方形开始,以螺旋形的形状行走,而忽略我们是否呆在网格中。最终,我们一定已经到达了网格的每一个角落。
算法
检查我们在每个方向的行走长度,我们发现如下模式:1,1,2,2,3,3,4,4,... 即我们先向东走 1 单位,然后向南走 1 单位,再向西走 2 单位,再向北走 2 单位,再向东走 3 单位,等等。因为我们的行走方式是自相似的,所以这种模式会以我们期望的方式重复。
之后,算法很简单:按照我们访问的顺序执行遍历并记录网格的位置。有关更多细节,请阅读内联注释。
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution(object): |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O((\max(R, C))^2),潜在地,我们的行走需要螺旋式行进,直到我们向一个方向移动 R,向另一个方向移动 C,以便到达网格的每个单元格。
空间复杂度:O(R * C),答案用去的空间。
Comments