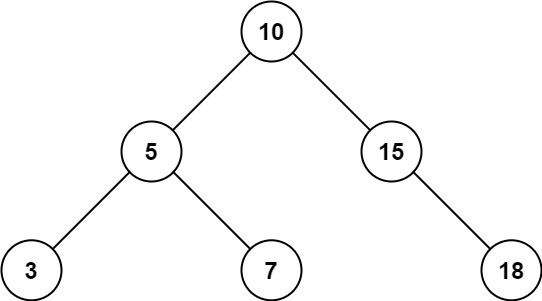
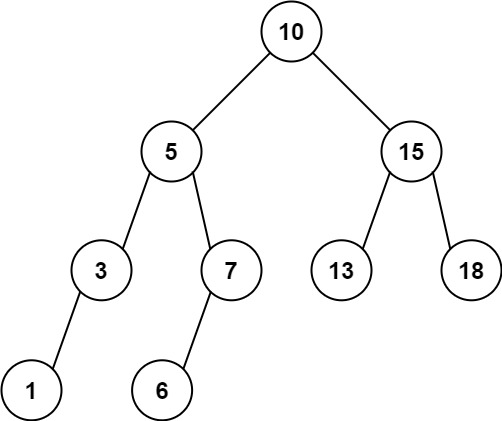
给定二叉搜索树的根结点 root,返回值位于范围 [low, high] 之间的所有结点的值的和。
示例 1:

**输入:** root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], low = 7, high = 15
**输出:** 32
示例 2:

**输入:** root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], low = 6, high = 10
**输出:** 23
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[1, 2 * 104] 内
1 <= Node.val <= 1051 <= low <= high <= 105- 所有
Node.val 互不相同
方法一:深度优先搜索
思路
按深度优先搜索的顺序计算范围和。记当前子树根节点为 root,分以下四种情况讨论:
root 节点为空
返回 0。
root 节点的值大于 high
由于二叉搜索树右子树上所有节点的值均大于根节点的值,即均大于 high,故无需考虑右子树,返回左子树的范围和。
root 节点的值小于 low
由于二叉搜索树左子树上所有节点的值均小于根节点的值,即均小于 low,故无需考虑左子树,返回右子树的范围和。
root 节点的值在 [\textit{low},\textit{high}] 范围内
此时应返回 root 节点的值、左子树的范围和、右子树的范围和这三者之和。
代码
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| class Solution {
public:
int rangeSumBST(TreeNode *root, int low, int high) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
if (root->val > high) {
return rangeSumBST(root->left, low, high);
}
if (root->val < low) {
return rangeSumBST(root->right, low, high);
}
return root->val + rangeSumBST(root->left, low, high) + rangeSumBST(root->right, low, high);
}
};
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| class Solution {
public int rangeSumBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
if (root.val > high) {
return rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high);
}
if (root.val < low) {
return rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high);
}
return root.val + rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high) + rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high);
}
}
|
[sol1-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| func rangeSumBST(root *TreeNode, low, high int) int {
if root == nil {
return 0
}
if root.Val > high {
return rangeSumBST(root.Left, low, high)
}
if root.Val < low {
return rangeSumBST(root.Right, low, high)
}
return root.Val + rangeSumBST(root.Left, low, high) + rangeSumBST(root.Right, low, high)
}
|
[sol1-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| var rangeSumBST = function(root, low, high) {
if (!root) {
return 0;
}
if (root.val > high) {
return rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high);
}
if (root.val < low) {
return rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high);
}
return root.val + rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high) + rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high);
};
|
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| class Solution:
def rangeSumBST(self, root: TreeNode, low: int, high: int) -> int:
if not root:
return 0
if root.val > high:
return self.rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high)
if root.val < low:
return self.rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high)
return root.val + self.rangeSumBST(root.left, low, high) + self.rangeSumBST(root.right, low, high)
|
[sol1-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| int rangeSumBST(struct TreeNode *root, int low, int high) {
if (root == NULL) {
return 0;
}
if (root->val > high) {
return rangeSumBST(root->left, low, high);
}
if (root->val < low) {
return rangeSumBST(root->right, low, high);
}
return root->val + rangeSumBST(root->left, low, high) + rangeSumBST(root->right, low, high);
}
|
复杂度分析
方法二:广度优先搜索
思路
使用广度优先搜索的方法,用一个队列 q 存储需要计算的节点。每次取出队首节点时,若节点为空则跳过该节点,否则按方法一中给出的大小关系来决定加入队列的子节点。
代码
[sol2-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| class Solution {
public:
int rangeSumBST(TreeNode *root, int low, int high) {
int sum = 0;
queue<TreeNode*> q({root});
while (!q.empty()) {
auto node = q.front();
q.pop();
if (node == nullptr) {
continue;
}
if (node->val > high) {
q.push(node->left);
} else if (node->val < low) {
q.push(node->right);
} else {
sum += node->val;
q.push(node->left);
q.push(node->right);
}
}
return sum;
}
};
|
[sol2-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Solution {
public int rangeSumBST(TreeNode root, int low, int high) {
int sum = 0;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
q.offer(root);
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = q.poll();
if (node == null) {
continue;
}
if (node.val > high) {
q.offer(node.left);
} else if (node.val < low) {
q.offer(node.right);
} else {
sum += node.val;
q.offer(node.left);
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
return sum;
}
}
|
[sol2-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| func rangeSumBST(root *TreeNode, low, high int) (sum int) {
q := []*TreeNode{root}
for len(q) > 0 {
node := q[0]
q = q[1:]
if node == nil {
continue
}
if node.Val > high {
q = append(q, node.Left)
} else if node.Val < low {
q = append(q, node.Right)
} else {
sum += node.Val
q = append(q, node.Left, node.Right)
}
}
return
}
|
[sol2-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| var rangeSumBST = function(root, low, high) {
let sum = 0;
const q = [root];
while (q.length) {
const node = q.shift();
if (!node) {
continue;
}
if (node.val > high) {
q.push(node.left);
} else if (node.val < low) {
q.push(node.right);
} else {
sum += node.val;
q.push(node.left);
q.push(node.right);
}
}
return sum;
};
|
[sol2-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| class Solution:
def rangeSumBST(self, root: TreeNode, low: int, high: int) -> int:
total = 0
q = collections.deque([root])
while q:
node = q.popleft()
if not node:
continue
if node.val > high:
q.append(node.left)
elif node.val < low:
q.append(node.right)
else:
total += node.val
q.append(node.left)
q.append(node.right)
return total
|
[sol2-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| int rangeSumBST(struct TreeNode *root, int low, int high) {
int sum = 0;
struct TreeNode *q[40000];
int left = 0, right = 0;
q[right++] = root;
while (left < right) {
struct TreeNode *node = q[left++];
if (node == NULL) {
continue;
}
if (node->val > high) {
q[right++] = node->left;
} else if (node->val < low) {
q[right++] = node->right;
} else {
sum += node->val;
q[right++] = node->left;
q[right++] = node->right;
}
}
return sum;
}
|
复杂度分析
4 月 22 日至 4 月 28 日,进入「学习 」,完成页面右上角的「让时间更有价值」限时阅读任务,可获得「2021 读书日纪念勋章」。更多活动详情戳上方标题了解更多👆
今日学习任务: