给定一个二叉树,我们在树的节点上安装摄像头。
节点上的每个摄影头都可以监视 其父对象、自身及其直接子对象。
计算监控树的所有节点所需的最小摄像头数量。
示例 1:
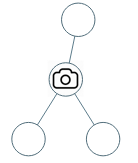
**输入:** [0,0,null,0,0]
**输出:** 1
**解释:** 如图所示,一台摄像头足以监控所有节点。
示例 2:
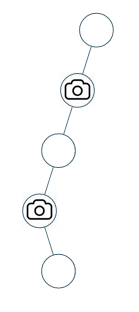
**输入:** [0,0,null,0,null,0,null,null,0]
**输出:** 2
**解释:** 需要至少两个摄像头来监视树的所有节点。 上图显示了摄像头放置的有效位置之一。
提示:
- 给定树的节点数的范围是
[1, 1000]。
- 每个节点的值都是 0。
方法一:动态规划
思路与算法
本题以二叉树为背景,不难想到用递归的方式求解。本题的难度在于如何从左、右子树的状态,推导出父节点的状态。
为了表述方便,我们约定:如果某棵树的所有节点都被监控,则称该树被「覆盖」。
假设当前节点为 root,其左右孩子为 left}, \textit{right。如果要覆盖以 root 为根的树,有两种情况:
- 若在 root 处安放摄像头,则孩子 left}, \textit{right 一定也会被监控到。此时,只需要保证 left 的两棵子树被覆盖,同时保证 right 的两棵子树也被覆盖即可。
- 否则, 如果 root 处不安放摄像头,则除了覆盖 root 的两棵子树之外,孩子 left}, \textit{right 之一必须要安装摄像头,从而保证 root 会被监控到。
根据上面的讨论,能够分析出,对于每个节点 root ,需要维护三种类型的状态:
- 状态 a:root 必须放置摄像头的情况下,覆盖整棵树需要的摄像头数目。
- 状态 b:覆盖整棵树需要的摄像头数目,无论 root 是否放置摄像头。
- 状态 c:覆盖两棵子树需要的摄像头数目,无论节点 root 本身是否被监控到。
根据它们的定义,一定有 a \geq b \geq c。
对于节点 root 而言,设其左右孩子 left}, \textit{right 对应的状态变量分别为 (l_a,l_b,l_c) 以及 (r_a,r_b,r_c)。根据一开始的讨论,我们已经得到了求解 a,b 的过程:
- a = l_c + r_c + 1
- b = \min(a, \min(l_a + r_b, r_a + l_b))
对于 c 而言,要保证两棵子树被完全覆盖,要么 root 处放置一个摄像头,需要的摄像头数目为 a;要么 root 处不放置摄像头,此时两棵子树分别保证自己被覆盖,需要的摄像头数目为 l_b + r_b。
需要额外注意的是,对于 root 而言,如果其某个孩子为空,则不能通过在该孩子处放置摄像头的方式,监控到当前节点。因此,该孩子对应的变量 a 应当返回一个大整数,用于标识不可能的情形。
最终,根节点的状态变量 b 即为要求出的答案。
代码
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| struct Status {
int a, b, c;
};
class Solution {
public:
Status dfs(TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return {INT_MAX / 2, 0, 0};
}
auto [la, lb, lc] = dfs(root->left);
auto [ra, rb, rc] = dfs(root->right);
int a = lc + rc + 1;
int b = min(a, min(la + rb, ra + lb));
int c = min(a, lb + rb);
return {a, b, c};
}
int minCameraCover(TreeNode* root) {
auto [a, b, c] = dfs(root);
return b;
}
};
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| class Solution {
public int minCameraCover(TreeNode root) {
int[] array = dfs(root);
return array[1];
}
public int[] dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new int[]{Integer.MAX_VALUE / 2, 0, 0};
}
int[] leftArray = dfs(root.left);
int[] rightArray = dfs(root.right);
int[] array = new int[3];
array[0] = leftArray[2] + rightArray[2] + 1;
array[1] = Math.min(array[0], Math.min(leftArray[0] + rightArray[1], rightArray[0] + leftArray[1]));
array[2] = Math.min(array[0], leftArray[1] + rightArray[1]);
return array;
}
}
|
[sol1-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| const inf = math.MaxInt32 / 2
func minCameraCover(root *TreeNode) int {
var dfs func(*TreeNode) (a, b, c int)
dfs = func(node *TreeNode) (a, b, c int) {
if node == nil {
return inf, 0, 0
}
la, lb, lc := dfs(node.Left)
ra, rb, rc := dfs(node.Right)
a = lc + rc + 1
b = min(a, min(la+rb, ra+lb))
c = min(a, lb+rb)
return
}
_, ans, _ := dfs(root)
return ans
}
func min(a, b int) int {
if a < b {
return a
}
return b
}
|
[sol1-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| var minCameraCover = function(root) {
const dfs = (root) => {
if (!root) {
return [Math.floor(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER / 2), 0, 0];
}
const [la, lb, lc] = dfs(root.left);
const [ra, rb, rc] = dfs(root.right);
const a = lc + rc + 1;
const b = Math.min(a, Math.min(la + rb, ra + lb));
const c = Math.min(a, lb + rb);
return [a, b, c];
}
return dfs(root)[1];
};
|
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| class Solution:
def minCameraCover(self, root: TreeNode) -> int:
def dfs(root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
if not root:
return [float("inf"), 0, 0]
la, lb, lc = dfs(root.left)
ra, rb, rc = dfs(root.right)
a = lc + rc + 1
b = min(a, la + rb, ra + lb)
c = min(a, lb + rb)
return [a, b, c]
a, b, c = dfs(root)
return b
|
[sol1-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| struct Status {
int a, b, c;
};
struct Status dfs(struct TreeNode* root) {
if (!root) {
return (struct Status){INT_MAX / 2, 0, 0};
}
struct Status l = dfs(root->left);
struct Status r = dfs(root->right);
int a = l.c + r.c + 1;
int b = fmin(a, fmin(l.a + r.b, r.a + l.b));
int c = fmin(a, l.b + r.b);
return (struct Status){a, b, c};
}
int minCameraCover(struct TreeNode* root) {
struct Status ret = dfs(root);
return ret.b;
}
|
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N),其中 N 为树中节点的数量。对于每个节点,我们在常数时间内计算出 a,b,c 三个状态变量。
空间复杂度:O(N)。每次递归调用时,我们需要开辟常数大小的空间存储状态变量的取值,而递归栈的深度等于树的深度,即 O(N)。