给你二叉树的根结点 root ,请你设计算法计算二叉树的 __垂序遍历 序列。
对位于 (row, col) 的每个结点而言,其左右子结点分别位于 (row + 1, col - 1) 和 (row + 1, col + 1) 。树的根结点位于 (0, 0) 。
二叉树的 垂序遍历
从最左边的列开始直到最右边的列结束,按列索引每一列上的所有结点,形成一个按出现位置从上到下排序的有序列表。如果同行同列上有多个结点,则按结点的值从小到大进行排序。
返回二叉树的 垂序遍历 序列。
示例 1:

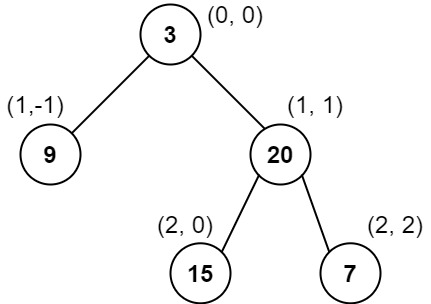
**输入:** root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
**输出:** [[9],[3,15],[20],[7]]
**解释:**
列 -1 :只有结点 9 在此列中。
列 0 :只有结点 3 和 15 在此列中,按从上到下顺序。
列 1 :只有结点 20 在此列中。
列 2 :只有结点 7 在此列中。
示例 2:

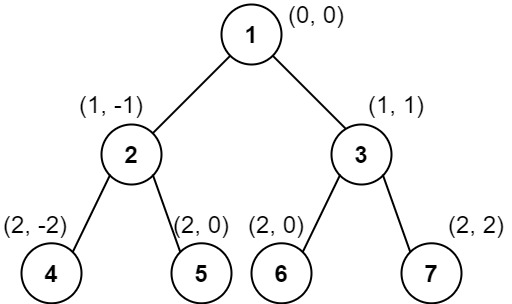
**输入:** root = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
**输出:** [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
**解释:**
列 -2 :只有结点 4 在此列中。
列 -1 :只有结点 2 在此列中。
列 0 :结点 1 、5 和 6 都在此列中。
1 在上面,所以它出现在前面。
5 和 6 位置都是 (2, 0) ,所以按值从小到大排序,5 在 6 的前面。
列 1 :只有结点 3 在此列中。
列 2 :只有结点 7 在此列中。
示例 3:

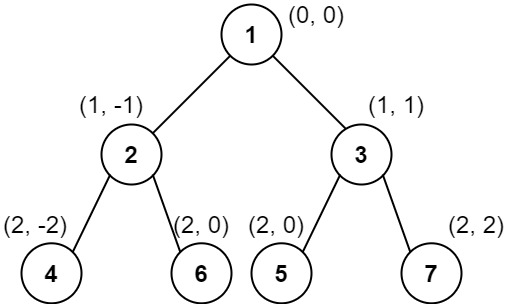
**输入:** root = [1,2,3,4,6,5,7]
**输出:** [[4],[2],[1,5,6],[3],[7]]
**解释:**
这个示例实际上与示例 2 完全相同,只是结点 5 和 6 在树中的位置发生了交换。
因为 5 和 6 的位置仍然相同,所以答案保持不变,仍然按值从小到大排序。
提示:
- 树中结点数目总数在范围
[1, 1000] 内
0 <= Node.val <= 1000
方法一:自定义排序
思路与算法
我们可以从根节点开始,对整棵树进行一次遍历,在遍历的过程中使用数组 nodes 记录下每个节点的行号 row,列号 col 以及值 value。在遍历完成后,我们按照 col 为第一关键字升序,row 为第二关键字升序,value 为第三关键字升序,对所有的节点进行排序即可。
在排序完成后,我们还需要按照题目要求,将同一列的所有节点放入同一个数组中。因此,我们可以对 nodes 进行一次遍历,并在遍历的过程中记录上一个节点的列号 lastcol。如果当前遍历到的节点的列号 col 与 lastcol 相等,则将该节点放入与上一个节点相同的数组中,否则放入不同的数组中。
代码
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<tuple<int, int, int>> nodes;
function<void(TreeNode*, int, int)> dfs = [&](TreeNode* node, int row, int col) {
if (!node) {
return;
}
nodes.emplace_back(col, row, node->val);
dfs(node->left, row + 1, col - 1);
dfs(node->right, row + 1, col + 1);
};
dfs(root, 0, 0);
sort(nodes.begin(), nodes.end());
vector<vector<int>> ans;
int lastcol = INT_MIN;
for (const auto& [col, row, value]: nodes) {
if (col != lastcol) {
lastcol = col;
ans.emplace_back();
}
ans.back().push_back(value);
}
return ans;
}
};
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
| class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<int[]> nodes = new ArrayList<int[]>();
dfs(root, 0, 0, nodes);
Collections.sort(nodes, new Comparator<int[]>() {
public int compare(int[] tuple1, int[] tuple2) {
if (tuple1[0] != tuple2[0]) {
return tuple1[0] - tuple2[0];
} else if (tuple1[1] != tuple2[1]) {
return tuple1[1] - tuple2[1];
} else {
return tuple1[2] - tuple2[2];
}
}
});
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
int size = 0;
int lastcol = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for (int[] tuple : nodes) {
int col = tuple[0], row = tuple[1], value = tuple[2];
if (col != lastcol) {
lastcol = col;
ans.add(new ArrayList<Integer>());
size++;
}
ans.get(size - 1).add(value);
}
return ans;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode node, int row, int col, List<int[]> nodes) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
nodes.add(new int[]{col, row, node.val});
dfs(node.left, row + 1, col - 1, nodes);
dfs(node.right, row + 1, col + 1, nodes);
}
}
|
[sol1-C#]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
| public class Solution {
public IList<IList<int>> VerticalTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Tuple<int, int, int>> nodes = new List<Tuple<int, int, int>>();
DFS(root, 0, 0, nodes);
nodes.Sort((a, b) => {
if (a.Item1 != b.Item1) {
return a.Item1 - b.Item1;
} else if (a.Item2 != b.Item2) {
return a.Item2 - b.Item2;
} else {
return a.Item3 - b.Item3;
}
});
IList<IList<int>> ans = new List<IList<int>>();
int size = 0;
int lastcol = int.MinValue;
foreach (Tuple<int, int, int> tuple in nodes) {
int col = tuple.Item1, row = tuple.Item2, value = tuple.Item3;
if (col != lastcol) {
lastcol = col;
ans.Add(new List<int>());
size++;
}
ans[size - 1].Add(value);
}
return ans;
}
public void DFS(TreeNode node, int row, int col, List<Tuple<int, int, int>> nodes) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
nodes.Add(new Tuple<int, int, int>(col, row, node.val));
DFS(node.left, row + 1, col - 1, nodes);
DFS(node.right, row + 1, col + 1, nodes);
}
}
|
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Solution:
def verticalTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[List[int]]:
nodes = list()
def dfs(node: TreeNode, row: int, col: int) -> None:
if not node:
return
nodes.append((col, row, node.val))
dfs(node.left, row + 1, col - 1)
dfs(node.right, row + 1, col + 1)
dfs(root, 0, 0)
nodes.sort()
ans, lastcol = list(), float("-inf")
for col, row, value in nodes:
if col != lastcol:
lastcol = col
ans.append(list())
ans[-1].append(value)
return ans
|
[sol1-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| var verticalTraversal = function(root) {
const nodes = [];
dfs(root, 0, 0, nodes);
nodes.sort((tuple1, tuple2) => {
if (tuple1[0] !== tuple2[0]) {
return tuple1[0] - tuple2[0];
} else if (tuple1[1] !== tuple2[1]) {
return tuple1[1] - tuple2[1];
} else {
return tuple1[2] - tuple2[2];
}
});
const ans = [];
let lastcol = -Number.MAX_VALUE;
for (const tuple of nodes) {
let col = tuple[0], row = tuple[1], value = tuple[2];
if (col !== lastcol) {
lastcol = col;
ans.push([]);
}
ans[ans.length - 1].push(value);
}
return ans;
}
const dfs = (node, row, col, nodes) => {
if (node === null) {
return;
}
nodes.push([col, row, node.val]);
dfs(node.left, row + 1, col - 1, nodes);
dfs(node.right, row + 1, col + 1, nodes);
}
|
[sol1-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
| type data struct{ col, row, val int }
func verticalTraversal(root *TreeNode) (ans [][]int) {
nodes := []data{}
var dfs func(*TreeNode, int, int)
dfs = func(node *TreeNode, row, col int) {
if node == nil {
return
}
nodes = append(nodes, data{col, row, node.Val})
dfs(node.Left, row+1, col-1)
dfs(node.Right, row+1, col+1)
}
dfs(root, 0, 0)
sort.Slice(nodes, func(i, j int) bool {
a, b := nodes[i], nodes[j]
return a.col < b.col || a.col == b.col && (a.row < b.row || a.row == b.row && a.val < b.val)
})
lastCol := math.MinInt32
for _, node := range nodes {
if node.col != lastCol {
lastCol = node.col
ans = append(ans, nil)
}
ans[len(ans)-1] = append(ans[len(ans)-1], node.val)
}
return
}
|
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n \log n),其中 n 是树中的节点个数。我们需要 O(n) 的时间对整棵树进行一次遍历(例如代码中的深度优先搜索),随后需要 O(n \log n) 的时间对数组 nodes 进行排序,以及 O(n) 的时间对数组 nodes 进行遍历得到最终的答案。由于 O(n \log n) 在渐近意义下大于 O(n),所以算法的总时间复杂度为 O(n \log n)。
空间复杂度:O(n)。深度优先搜索中需要 O(n) 的栈空间,同时数组 nodes 也需要 O(n) 的空间。