在二叉树中,根节点位于深度 0 处,每个深度为 k 的节点的子节点位于深度 k+1 处。
如果二叉树的两个节点深度相同,但 父节点不同 ,则它们是一对 堂兄弟节点 。
我们给出了具有唯一值的二叉树的根节点 root ,以及树中两个不同节点的值 x 和 y 。
只有与值 x 和 y 对应的节点是堂兄弟节点时,才返回 true 。否则,返回 false。
示例 1:
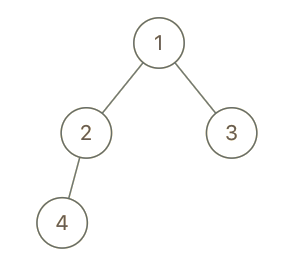
**输入:** root = [1,2,3,4], x = 4, y = 3
**输出:** false
示例 2:
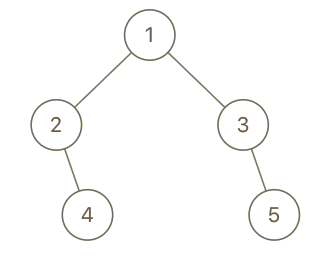
**输入:** root = [1,2,3,null,4,null,5], x = 5, y = 4
**输出:** true
示例 3:
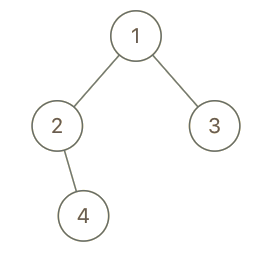
**输入:** root = [1,2,3,null,4], x = 2, y = 3
**输出:** false
提示:
- 二叉树的节点数介于
2 到 100 之间。
- 每个节点的值都是唯一的、范围为
1 到 100 的整数。
前言
要想判断两个节点 x 和 y 是否为堂兄弟节点,我们就需要求出这两个节点分别的「深度」以及「父节点」。
因此,我们可以从根节点开始,对树进行一次遍历,在遍历的过程中维护「深度」以及「父节点」这两个信息。当我们遍历到 x 或 y 节点时,就将信息记录下来;当这两个节点都遍历完成了以后,我们就可以退出遍历的过程,判断它们是否为堂兄弟节点了。
常见的遍历方法有两种:深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索。
方法一:深度优先搜索
思路与算法
我们只需要在深度优先搜索的递归函数中增加表示「深度」以及「父节点」的两个参数即可。
代码
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| class Solution {
private:
int x;
TreeNode* x_parent;
int x_depth;
bool x_found = false;
int y;
TreeNode* y_parent;
int y_depth;
bool y_found = false;
public:
void dfs(TreeNode* node, int depth, TreeNode* parent) {
if (!node) {
return;
}
if (node->val == x) {
tie(x_parent, x_depth, x_found) = tuple{parent, depth, true};
}
else if (node->val == y) {
tie(y_parent, y_depth, y_found) = tuple{parent, depth, true};
}
if (x_found && y_found) {
return;
}
dfs(node->left, depth + 1, node);
if (x_found && y_found) {
return;
}
dfs(node->right, depth + 1, node);
}
bool isCousins(TreeNode* root, int x, int y) {
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
dfs(root, 0, nullptr);
return x_depth == y_depth && x_parent != y_parent;
}
};
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| class Solution {
int x;
TreeNode xParent;
int xDepth;
boolean xFound = false;
int y;
TreeNode yParent;
int yDepth;
boolean yFound = false;
public boolean isCousins(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
dfs(root, 0, null);
return xDepth == yDepth && xParent != yParent;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode node, int depth, TreeNode parent) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
if (node.val == x) {
xParent = parent;
xDepth = depth;
xFound = true;
} else if (node.val == y) {
yParent = parent;
yDepth = depth;
yFound = true;
}
if (xFound && yFound) {
return;
}
dfs(node.left, depth + 1, node);
if (xFound && yFound) {
return;
}
dfs(node.right, depth + 1, node);
}
}
|
[sol1-C#]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| public class Solution {
int x;
TreeNode xParent;
int xDepth;
bool xFound = false;
int y;
TreeNode yParent;
int yDepth;
bool yFound = false;
public bool IsCousins(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
DFS(root, 0, null);
return xDepth == yDepth && xParent != yParent;
}
public void DFS(TreeNode node, int depth, TreeNode parent) {
if (node == null) {
return;
}
if (node.val == x) {
xParent = parent;
xDepth = depth;
xFound = true;
} else if (node.val == y) {
yParent = parent;
yDepth = depth;
yFound = true;
}
if (xFound && yFound) {
return;
}
DFS(node.left, depth + 1, node);
if (xFound && yFound) {
return;
}
DFS(node.right, depth + 1, node);
}
}
|
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| class Solution:
def isCousins(self, root: TreeNode, x: int, y: int) -> bool:
x_parent, x_depth, x_found = None, None, False
y_parent, y_depth, y_found = None, None, False
def dfs(node: TreeNode, depth: int, parent: TreeNode):
if not node:
return
nonlocal x_parent, y_parent, x_depth, y_depth, x_found, y_found
if node.val == x:
x_parent, x_depth, x_found = parent, depth, True
elif node.val == y:
y_parent, y_depth, y_found = parent, depth, True
if x_found and y_found:
return
dfs(node.left, depth + 1, node)
if x_found and y_found:
return
dfs(node.right, depth + 1, node)
dfs(root, 0, None)
return x_depth == y_depth and x_parent != y_parent
|
[sol1-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
| var isCousins = function(root, x, y) {
let x_parent = null, x_depth = null, x_found = false;
let y_parent = null, y_depth = null, y_found = false;
const dfs = (node, depth, parent) => {
if (!node) {
return;
}
if (node.val === x) {
[x_parent, x_depth, x_found] = [parent, depth, true];
} else if (node.val === y) {
[y_parent, y_depth, y_found] = [parent, depth, true];
}
if (x_found && y_found) {
return;
}
dfs(node.left, depth + 1, node);
if (x_found && y_found) {
return;
}
dfs(node.right, depth + 1, node);
}
dfs(root, 0, null);
return x_depth === y_depth && x_parent !== y_parent;
};
|
[sol1-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| func isCousins(root *TreeNode, x, y int) bool {
var xParent, yParent *TreeNode
var xDepth, yDepth int
var xFound, yFound bool
var dfs func(node, parent *TreeNode, depth int)
dfs = func(node, parent *TreeNode, depth int) {
if node == nil {
return
}
if node.Val == x {
xParent, xDepth, xFound = parent, depth, true
} else if node.Val == y {
yParent, yDepth, yFound = parent, depth, true
}
if xFound && yFound {
return
}
dfs(node.Left, node, depth+1)
if xFound && yFound {
return
}
dfs(node.Right, node, depth+1)
}
dfs(root, nil, 0)
return xDepth == yDepth && xParent != yParent
}
|
[sol1-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
int x_target;
struct TreeNode* x_parent;
int x_depth;
bool x_found;
int y_target;
struct TreeNode* y_parent;
int y_depth;
bool y_found;
void dfs(struct TreeNode* node, int depth, struct TreeNode* parent) {
if (!node) {
return;
}
if (node->val == x_target) {
x_parent = parent;
x_depth = depth;
x_found = true;
} else if (node->val == y_target) {
y_parent = parent;
y_depth = depth;
y_found = true;
}
if (x_found && y_found) {
return;
}
dfs(node->left, depth + 1, node);
if (x_found && y_found) {
return;
}
dfs(node->right, depth + 1, node);
}
bool isCousins(struct TreeNode* root, int x, int y) {
x_target = x;
y_target = y;
x_found = false;
y_found = false;
dfs(root, 0, NULL);
return x_depth == y_depth && x_parent != y_parent;
}
|
复杂度分析
方法二:广度优先搜索
思路与算法
在广度优先搜索的过程中,每当我们从队首取出一个节点,它就会作为「父节点」,将最多两个子节点放入队尾。因此,除了节点以外,我们只需要在队列中额外存储「深度」的信息即可。
代码
[sol2-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| class Solution {
private:
int x;
TreeNode* x_parent;
int x_depth;
bool x_found = false;
int y;
TreeNode* y_parent;
int y_depth;
bool y_found = false;
public:
void update(TreeNode* node, TreeNode* parent, int depth) {
if (node->val == x) {
tie(x_parent, x_depth, x_found) = tuple{parent, depth, true};
}
else if (node->val == y) {
tie(y_parent, y_depth, y_found) = tuple{parent, depth, true};
}
}
bool isCousins(TreeNode* root, int x, int y) {
this->x = x;
this->y = y;
queue<pair<TreeNode*, int>> q;
q.emplace(root, 0);
update(root, nullptr, 0);
while (!q.empty()) {
auto&& [node, depth] = q.front();
if (node->left) {
q.emplace(node->left, depth + 1);
update(node->left, node, depth + 1);
}
if (node->right) {
q.emplace(node->right, depth + 1);
update(node->right, node, depth + 1);
}
if (x_found && y_found) {
break;
}
q.pop();
}
return x_depth == y_depth && x_parent != y_parent;
}
};
|
[sol2-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
| class Solution {
int x;
TreeNode xParent;
int xDepth;
boolean xFound = false;
int y;
TreeNode yParent;
int yDepth;
boolean yFound = false;
public boolean isCousins(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
Queue<Integer> depthQueue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
nodeQueue.offer(root);
depthQueue.offer(0);
update(root, null, 0);
while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeQueue.poll();
int depth = depthQueue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(node.left);
depthQueue.offer(depth + 1);
update(node.left, node, depth + 1);
}
if (node.right != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(node.right);
depthQueue.offer(depth + 1);
update(node.right, node, depth + 1);
}
if (xFound && yFound) {
break;
}
}
return xDepth == yDepth && xParent != yParent;
}
public void update(TreeNode node, TreeNode parent, int depth) {
if (node.val == x) {
xParent = parent;
xDepth = depth;
xFound = true;
} else if (node.val == y) {
yParent = parent;
yDepth = depth;
yFound = true;
}
}
}
|
[sol2-C#]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| public class Solution {
int x;
TreeNode xParent;
int xDepth;
bool xFound = false;
int y;
TreeNode yParent;
int yDepth;
bool yFound = false;
public bool IsCousins(TreeNode root, int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
Queue<Tuple<TreeNode, int>> queue = new Queue<Tuple<TreeNode, int>>();
queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<TreeNode, int>(root, 0));
Update(root, null, 0);
while (queue.Count > 0) {
Tuple<TreeNode, int> tuple = queue.Dequeue();
TreeNode node = tuple.Item1;
int depth = tuple.Item2;
if (node.left != null) {
queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<TreeNode, int>(node.left, depth + 1));
Update(node.left, node, depth + 1);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<TreeNode, int>(node.right, depth + 1));
Update(node.right, node, depth + 1);
}
if (xFound && yFound) {
break;
}
}
return xDepth == yDepth && xParent != yParent;
}
public void Update(TreeNode node, TreeNode parent, int depth) {
if (node.val == x) {
xParent = parent;
xDepth = depth;
xFound = true;
} else if (node.val == y) {
yParent = parent;
yDepth = depth;
yFound = true;
}
}
}
|
[sol2-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| class Solution:
def isCousins(self, root: TreeNode, x: int, y: int) -> bool:
x_parent, x_depth, x_found = None, None, False
y_parent, y_depth, y_found = None, None, False
def update(node: TreeNode, parent: TreeNode, depth: int):
if node.val == x:
nonlocal x_parent, x_depth, x_found
x_parent, x_depth, x_found = parent, depth, True
elif node.val == y:
nonlocal y_parent, y_depth, y_found
y_parent, y_depth, y_found = parent, depth, True
q = collections.deque([(root, 0)])
update(root, None, 0)
while q:
node, depth = q.popleft()
if node.left:
q.append((node.left, depth + 1))
update(node.left, node, depth + 1)
if node.right:
q.append((node.right, depth + 1))
update(node.right, node, depth + 1)
if x_found and y_found:
break
return x_depth == y_depth and x_parent != y_parent
|
[sol2-JavaScript]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
| var isCousins = function(root, x, y) {
let x_parent = null, x_depth = null, x_found = false;
let y_parent = null, y_depth = null, y_found = false;
const update = (node, parent, depth) => {
if (node.val === x) {
[x_parent, x_depth, x_found] = [parent, depth, true];
} else if (node.val === y) {
[y_parent, y_depth, y_found] = [parent, depth, true];
}
}
q = [[root, 0]];
update(root, null, 0);
while (q.length) {
const [node, depth] = q.shift()
if (node.left){
q.push([node.left, depth + 1]);
update(node.left, node, depth + 1);
}
if (node.right) {
q.push([node.right, depth + 1]);
update(node.right, node, depth + 1);
}
if (x_found && y_found) {
break;
}
}
return x_depth === y_depth && x_parent !== y_parent;
};
|
[sol2-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| func isCousins(root *TreeNode, x, y int) bool {
var xParent, yParent *TreeNode
var xDepth, yDepth int
var xFound, yFound bool
update := func(node, parent *TreeNode, depth int) {
if node.Val == x {
xParent, xDepth, xFound = parent, depth, true
} else if node.Val == y {
yParent, yDepth, yFound = parent, depth, true
}
}
type pair struct {
node *TreeNode
depth int
}
q := []pair{{root, 0}}
update(root, nil, 0)
for len(q) > 0 && (!xFound || !yFound) {
node, depth := q[0].node, q[0].depth
q = q[1:]
if node.Left != nil {
q = append(q, pair{node.Left, depth + 1})
update(node.Left, node, depth+1)
}
if node.Right != nil {
q = append(q, pair{node.Right, depth + 1})
update(node.Right, node, depth+1)
}
}
return xDepth == yDepth && xParent != yParent
}
|
[sol2-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
|
int x_target;
struct TreeNode* x_parent;
int x_depth;
bool x_found;
int y_target;
struct TreeNode* y_parent;
int y_depth;
bool y_found;
void update(struct TreeNode* node, struct TreeNode* parent, int depth) {
if (node->val == x_target) {
x_parent = parent;
x_depth = depth;
x_found = true;
} else if (node->val == y_target) {
y_parent = parent;
y_depth = depth;
y_found = true;
}
}
struct Node {
struct TreeNode* node;
int depth;
};
bool isCousins(struct TreeNode* root, int x, int y) {
x_target = x;
y_target = y;
x_found = false;
y_found = false;
struct Node q[100];
int left = 0, right = 0;
q[right++] = (struct Node){root, 0};
update(root, NULL, 0);
while (left < right) {
if (q[left].node->left) {
q[right++] = (struct Node){q[left].node->left, q[left].depth + 1};
update(q[left].node->left, q[left].node, q[left].depth + 1);
}
if (q[left].node->right) {
q[right++] = (struct Node){q[left].node->right, q[left].depth + 1};
update(q[left].node->right, q[left].node, q[left].depth + 1);
}
if (x_found && y_found) {
break;
}
left++;
}
return x_depth == y_depth && x_parent != y_parent;
}
|
复杂度分析
✨扣友帮帮团 - 互动答疑
 {:width=260px}
{:width=260px}
即日起 - 5 月 30 日,点击 这里 前往「扣友帮帮团 」活动页,把你遇到的问题大胆地提出来,让扣友为你解答~
🎁 奖励规则
被采纳数量排名 1~3 名:「力扣极客套装」 *1 并将获得「力扣神秘应援团」内测资格
被采纳数量排名 4~10 名:「力扣鼠标垫」 *1 并将获得「力扣神秘应援团」内测资格
「诲人不倦」:活动期间「解惑者」只要有 1 个回答被采纳,即可获得 20 LeetCoins 奖励!
「求知若渴」:活动期间「求知者」在活动页发起一次符合要求的疑问帖并至少采纳一次「解惑者」的回答,即可获得 20 LeetCoins 奖励!
活动详情猛戳链接了解更多:活动|你有 BUG 我来帮 - 力扣互动答疑季
 {:width=260px}
{:width=260px}