在一个 106 x 106 的网格中,每个网格上方格的坐标为 (x, y) 。
现在从源方格 source = [sx, sy] 开始出发,意图赶往目标方格 target = [tx, ty] 。数组 blockedblocked[i] = [xi, yi] 表示坐标为 (xi, yi) 的方格是禁止通行的。
每次移动,都可以走到网格中在四个方向上相邻的方格,只要该方格 不 在给出的封锁列表 blocked 上。同时,不允许走出网格。
只有在可以通过一系列的移动从源方格 source 到达目标方格 target 时才返回 true。否则,返回 false。
示例 1:
**输入:** blocked = [[0,1],[1,0]], source = [0,0], target = [0,2]
**输出:** false
**解释:**
从源方格无法到达目标方格,因为我们无法在网格中移动。
无法向北或者向东移动是因为方格禁止通行。
无法向南或者向西移动是因为不能走出网格。
示例 2:
**输入:** blocked = [], source = [0,0], target = [999999,999999]
**输出:** true
**解释:**
因为没有方格被封锁,所以一定可以到达目标方格。
提示:
0 <= blocked.length <= 200blocked[i].length == 20 <= xi, yi < 106source.length == target.length == 20 <= sx, sy, tx, ty < 106source != target题目数据保证 source 和 target 不在封锁列表内
方法一:有限步数的广度优先搜索 思路
判断能否从 source 走到 target,最简单且直观的方法就是从 source 开始进行广度优先搜索,如果搜索的过程中经过了 target,则说明可以到达。
然而本题中给定的网格规模是 10^6 \times 10^6 的,常规的广度优先搜索会达到 O(10^6 \times 10^6) = O(10^{12}) 的时间复杂度,远远超出了时间限制。因此我们必须进行优化。
注意到障碍的个数不超过 200 个,这说明网格中大部分的位置都不是障碍,只有极少一部分的位置是障碍。分析从 source 无法走到 target 的情况,无非就是以下两种:
在「障碍的个数不超过 200 个前提下」,我们可以猜测「包围圈」的大小也不会很大。也就是说,如果障碍的个数为 n 个,那么我们希望得到「包围圈」中包含的非障碍位置的数量的上界,假设其为 limit,那么:
如果我们从 source 开始进行广度优先搜索,搜索到的非障碍位置的数量严格大于 limit,那么说明 source 一定不在任何包围圈中。同时,如果从 target 开始进行广度优先搜索也是如此,那么同样说明 target 一定也不在任何包围圈中。此时我们就可以断定,一定能从 source 走到 target。
因此我们的目标就是正确估计「包围圈」的上界。当障碍的个数固定为 n 个时(我们只考虑 n \geq 2 的情况,如果 n=0,1,那么无法形成「包围圈」,任意两个位置都互相可达),要想使得非障碍位置的数量最大,这些障碍一定是靠着网格的一个角进行包围的,因为这样可以利用到网格的两条边。
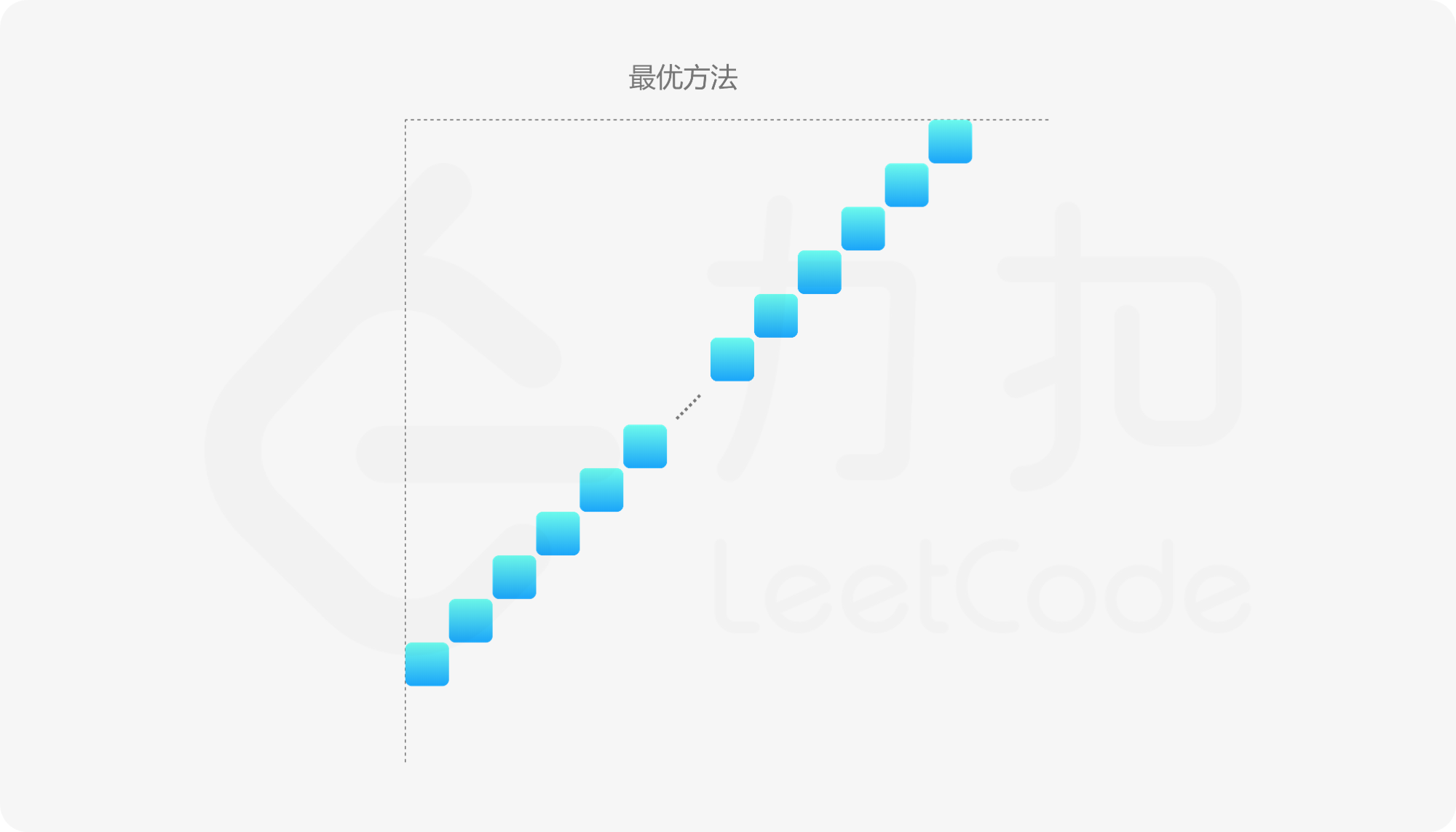
不失一般性,我们假设靠着的是网格的左上角,那么可以证明,最优的包围方法一定是选择:
(0, n-1), (1, n-2), (2, n-3), \cdots, (n-3, 2), (n-2, 1), (n-1, 0)
这 n 个位置,此时「包围圈」组成一个等腰直角三角形,如下图所示。
其中包含的非障碍位置的数量为:
n(n-1)}{2}
最优性可以通过构造法证明。可以发现,上面给出的包围方法保证了每一行和每一列不会有超过 1 个障碍。对于其它的包围方法,不失一般性,设某一行有 2 个或以上的障碍,此时有两种情况:
因此,最优的包围方法一定保证每一行和每一列不会有超过 1 个障碍。由于我们需要包围住左上角,因此列坐标的必须取 0, 1, 2, \cdots, n-1 这 n 个位置(如果取 \geq n,那么该障碍就无法与「包围圈」连通,因为它至少还需要借助 n 个障碍来连接到左边界)。同时,每一行只有一个障碍,因此每个障碍右侧的所有位置是不可能被包围的,只有左侧的位置才可能被包围。而左侧位置的总数为:
0 + 1 + 2 + \cdots + (n-1) = n(n-1)}{2}
因此最多包含非障碍位置的数量为 \dfrac{n(n-1)}{2。
算法
通过上述的证明,我们就可以设计出如下的算法:
我们从 source 开始进行广度优先搜索。如果经过了不超过 \dfrac{n(n-1)}{2 个非障碍位置就已经结束搜索,说明 source 在「包围圈」中。但如果我们在过程中经过了 target,那么说明它们是可达的,否则一定不可达。
我们再从 target 开始进行广度优先搜索。如果经过了不超过 \dfrac{n(n-1)}{2 个非障碍位置就已经结束搜索,说明 target 在「包围圈」中。否则说明 source 和 target 均不在「包围圈」中,此时一定可达。
搜索的过程中需要借助哈希表来标记每个位置是否已经搜索过。
代码
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 class Solution {private : static constexpr int BLOCKED = -1 ; static constexpr int VALID = 0 ; static constexpr int FOUND = 1 ; static constexpr int dirs[4 ][2 ] = { {0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 } }; static constexpr int BOUNDARY = 1000000 ; public : bool isEscapePossible (vector<vector<int >>& blocked, vector<int >& source, vector<int >& target) if (blocked.size () < 2 ) { return true ; } auto hash_fn = [fn = hash <long long >()](const pair<int , int >& o) -> size_t { auto & [x, y] = o; return fn ((long long )x << 20 | y); }; unordered_set<pair<int , int >, decltype (hash_fn)> hash_blocked (0 , hash_fn); for (const auto & pos: blocked) { hash_blocked.emplace (pos[0 ], pos[1 ]); } auto check = [&](vector<int >& start, vector<int >& finish) -> int { int sx = start[0 ], sy = start[1 ]; int fx = finish[0 ], fy = finish[1 ]; int countdown = blocked.size () * (blocked.size () - 1 ) / 2 ; queue<pair<int , int >> q; q.emplace (sx, sy); unordered_set<pair<int , int >, decltype (hash_fn)> visited (0 , hash_fn); visited.emplace (sx, sy); while (!q.empty () && countdown > 0 ) { auto [x, y] = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int d = 0 ; d < 4 ; ++d) { int nx = x + dirs[d][0 ], ny = y + dirs[d][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < BOUNDARY && ny >= 0 && ny < BOUNDARY && !hash_blocked.count ({nx, ny}) && !visited.count ({nx, ny})) { if (nx == fx && ny == fy) { return FOUND; } --countdown; q.emplace (nx, ny); visited.emplace (nx, ny); } } } if (countdown > 0 ) { return BLOCKED; } return VALID; }; if (int result = check (source, target); result == FOUND) { return true ; } else if (result == BLOCKED) { return false ; } else { result = check (target, source); if (result == BLOCKED) { return false ; } return true ; } } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 class Solution { static final int BLOCKED = -1 ; static final int VALID = 0 ; static final int FOUND = 1 ; static final int [][] dirs = { {0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 } }; static final int BOUNDARY = 1000000 ; public boolean isEscapePossible (int [][] blocked, int [] source, int [] target) { if (blocked.length < 2 ) { return true ; } Set<Pair> hashBlocked = new HashSet <Pair>(); for (int [] pos : blocked) { hashBlocked.add(new Pair (pos[0 ], pos[1 ])); } int result = check(blocked, source, target, hashBlocked); if (result == FOUND) { return true ; } else if (result == BLOCKED) { return false ; } else { result = check(blocked, target, source, hashBlocked); return result != BLOCKED; } } public int check (int [][] blocked, int [] start, int [] finish, Set<Pair> hashBlocked) { int sx = start[0 ], sy = start[1 ]; int fx = finish[0 ], fy = finish[1 ]; int countdown = blocked.length * (blocked.length - 1 ) / 2 ; Pair startPair = new Pair (sx, sy); Queue<Pair> queue = new ArrayDeque <Pair>(); queue.offer(startPair); Set<Pair> visited = new HashSet <Pair>(); visited.add(startPair); while (!queue.isEmpty() && countdown > 0 ) { Pair pair = queue.poll(); int x = pair.x, y = pair.y; for (int d = 0 ; d < 4 ; ++d) { int nx = x + dirs[d][0 ], ny = y + dirs[d][1 ]; Pair newPair = new Pair (nx, ny); if (nx >= 0 && nx < BOUNDARY && ny >= 0 && ny < BOUNDARY && !hashBlocked.contains(newPair) && !visited.contains(newPair)) { if (nx == fx && ny == fy) { return FOUND; } --countdown; queue.offer(newPair); visited.add(newPair); } } } if (countdown > 0 ) { return BLOCKED; } return VALID; } } class Pair { int x; int y; public Pair (int x, int y) { this .x = x; this .y = y; } @Override public int hashCode () { return (int ) ((long ) x << 20 | y); } @Override public boolean equals (Object obj) { if (obj instanceof Pair) { Pair pair2 = (Pair) obj; return x == pair2.x && y == pair2.y; } return false ; } }
[sol1-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 public class Solution { const int BLOCKED = -1 ; const int VALID = 0 ; const int FOUND = 1 ; int [][] dirs = {new int []{0 , 1 }, new int []{0 , -1 }, new int []{1 , 0 }, new int []{-1 , 0 } }; const int BOUNDARY = 1000000 ; public bool IsEscapePossible (int [][] blocked, int [] source, int [] target if (blocked.Length < 2 ) { return true ; } ISet<Pair> hashBlocked = new HashSet<Pair>(); foreach (int [] pos in blocked) { hashBlocked.Add(new Pair(pos[0 ], pos[1 ])); } int result = Check(blocked, source, target, hashBlocked); if (result == FOUND) { return true ; } else if (result == BLOCKED) { return false ; } else { result = Check(blocked, target, source, hashBlocked); return result != BLOCKED; } } public int Check (int [][] blocked, int [] start, int [] finish, ISet<Pair> hashBlocked int sx = start[0 ], sy = start[1 ]; int fx = finish[0 ], fy = finish[1 ]; int countdown = blocked.Length * (blocked.Length - 1 ) / 2 ; Pair startPair = new Pair(sx, sy); Queue<Pair> queue = new Queue<Pair>(); queue.Enqueue(startPair); ISet<Pair> visited = new HashSet<Pair>(); visited.Add(startPair); while (queue.Count > 0 && countdown > 0 ) { Pair pair = queue.Dequeue(); int x = pair.X, y = pair.Y; for (int d = 0 ; d < 4 ; ++d) { int nx = x + dirs[d][0 ], ny = y + dirs[d][1 ]; Pair newPair = new Pair(nx, ny); if (nx >= 0 && nx < BOUNDARY && ny >= 0 && ny < BOUNDARY && !hashBlocked.Contains(newPair) && !visited.Contains(newPair)) { if (nx == fx && ny == fy) { return FOUND; } --countdown; queue.Enqueue(newPair); visited.Add(newPair); } } } if (countdown > 0 ) { return BLOCKED; } return VALID; } } public class Pair { public int X { get ; set ; } public int Y { get ; set ; } public Pair (int x, int y this .X = x; this .Y = y; } public override int GetHashCode () return (int ) (((long ) X) << 20 | Y); } public override bool Equals (object obj Pair pair2 = obj as Pair; if (pair2 == null ) { return false ; } return X == pair2.X && Y == pair2.Y; } }
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 class Solution : def isEscapePossible (self, blocked: List [List [int ]], source: List [int ], target: List [int ] ) -> bool : """ BLOCKED: 在包围圈中 VALID: 不在包围圈中 FOUND: 无论在不在包围圈中,但在 n(n-1)/2 步搜索的过程中经过了 target """ BLOCKED, VALID, FOUND = -1 , 0 , 1 BOUNDARY = 10 **6 if len (blocked) < 2 : return True hash_blocked = set (tuple (pos) for pos in blocked) def check (start: List [int ], finish: List [int ] ) -> int : sx, sy = start fx, fy = finish countdown = len (blocked) * (len (blocked) - 1 ) // 2 q = deque([(sx, sy)]) visited = set ([(sx, sy)]) while q and countdown > 0 : x, y = q.popleft() for nx, ny in [(x + 1 , y), (x - 1 , y), (x, y + 1 ), (x, y - 1 )]: if 0 <= nx < BOUNDARY and 0 <= ny < BOUNDARY and (nx, ny) not in hash_blocked and (nx, ny) not in visited: if (nx, ny) == (fx, fy): return FOUND countdown -= 1 q.append((nx, ny)) visited.add((nx, ny)) if countdown > 0 : return BLOCKED return VALID if (result := check(source, target)) == FOUND: return True elif result == BLOCKED: return False else : result = check(target, source) if result == BLOCKED: return False return True
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 type pair struct { x, y int }var dirs = []pair{ {-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {0 , 1 } }func isEscapePossible (block [][]int , source, target []int ) bool { const ( blocked = -1 valid = 0 found = 1 boundary int = 1e6 ) n := len (block) if n < 2 { return true } blockSet := map [pair]bool {} for _, b := range block { blockSet[pair{b[0 ], b[1 ]}] = true } check := func (start, finish []int ) int { sx, sy := start[0 ], start[1 ] fx, fy := finish[0 ], finish[1 ] countdown := n * (n - 1 ) / 2 q := []pair{ {sx, sy} } vis := map [pair]bool { {sx, sy}: true } for len (q) > 0 && countdown > 0 { p := q[0 ] q = q[1 :] for _, d := range dirs { x, y := p.x+d.x, p.y+d.y np := pair{x, y} if 0 <= x && x < boundary && 0 <= y && y < boundary && !blockSet[np] && !vis[np] { if x == fx && y == fy { return found } countdown-- vis[np] = true q = append (q, np) } } } if countdown > 0 { return blocked } return valid } res := check(source, target) return res == found || res == valid && check(target, source) != blocked }
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 const BLOCKED = -1 ;const VALID = 0 ;const FOUND = 1 ;const dirs = [[0 , 1 ], [0 , -1 ], [1 , 0 ], [-1 , 0 ]];const BOUNDARY = 1000000 ;var isEscapePossible = function (blocked, source, target ) { if (blocked.length < 2 ) { return true ; } const hashBlocked = new Set (); for (const pos of blocked) { hashBlocked.add ([pos[0 ], pos[1 ]].toString ()); } let result = check (blocked, source, target, hashBlocked); if (result === FOUND ) { return true ; } else if (result === BLOCKED ) { return false ; } else { result = check (blocked, target, source, hashBlocked); return result !== BLOCKED ; } }; const check = (blocked, start, finish, hashBlocked ) => { const sx = start[0 ], sy = start[1 ]; const fx = finish[0 ], fy = finish[1 ]; let countdown = Math .floor (blocked.length * (blocked.length - 1 ) / 2 ); const startPair = [sx, sy]; const queue = []; queue.push (startPair); const visited = new Set (); visited.add (startPair.toString ()); while (queue.length && countdown > 0 ) { const [x, y] = queue.shift (); for (let d = 0 ; d < 4 ; ++d) { const nx = x + dirs[d][0 ], ny = y + dirs[d][1 ]; const newPair = [nx, ny]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < BOUNDARY && ny >= 0 && ny < BOUNDARY && !hashBlocked.has (newPair.toString ()) && !visited.has (newPair.toString ())) { if (nx === fx && ny === fy) { return FOUND ; } --countdown; queue.push (newPair); visited.add (newPair.toString ()); } } } if (countdown > 0 ) { return BLOCKED ; } return VALID ; }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 #define BLOCKED -1 #define VALID 0 #define FOUND 1 #define BOUNDARY 1000000 int dirs[4 ][2 ] = { {0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 } };#define HashCode(x, y) ((long long)(x) << 20 | (y)) struct Pair { int x; int y; }; struct HashEntry { long long key; long long val; UT_hash_handle hh; }; void hashAddItem (struct HashEntry **obj, long long key) { struct HashEntry *pEntry ; pEntry = malloc (sizeof (struct HashEntry)); pEntry->key = key; pEntry->val = 1 ; HASH_ADD(hh, *obj, key, sizeof (long long ), pEntry); } struct HashEntry *hashFindItem (struct HashEntry **obj, long long key) { struct HashEntry *pEntry =NULL ; HASH_FIND(hh, *obj, &key, sizeof (long long ), pEntry); return pEntry; } void hashEraseItem (struct HashEntry **obj, long long key) { struct HashEntry *pEntry =NULL ; HASH_FIND(hh, *obj, &key, sizeof (long long ), pEntry); if (NULL != pEntry) { HASH_DEL(*obj, pEntry); free (pEntry); } } void hashFreeAll (struct HashEntry **obj) { struct HashEntry *curr , *next ; HASH_ITER(hh, *obj, curr, next) { HASH_DEL(*obj, curr); free (curr); } } int check (int ** blocked, int blockedSize, const int * start, const int * finish, struct HashEntry ** hashBlocked) { int sx = start[0 ], sy = start[1 ]; int fx = finish[0 ], fy = finish[1 ]; int countdown = blockedSize * (blockedSize - 1 ) / 2 ; int head = 0 ; int tail = 0 ; struct Pair * queue =struct Pair *)malloc (sizeof (struct Pair) * countdown * 4 ); queue [tail].x = sx; queue [tail].y = sy; tail++; struct HashEntry * visited =NULL ; hashAddItem(&visited, HashCode(sx, sy)); while (head != tail && countdown > 0 ) { int x = queue [head].x; int y = queue [head].y; head++; for (int d = 0 ; d < 4 ; d++) { int nx = x + dirs[d][0 ], ny = y + dirs[d][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx < BOUNDARY && ny >= 0 && ny < BOUNDARY && !hashFindItem(hashBlocked, HashCode(nx, ny)) && !hashFindItem(&visited, HashCode(nx, ny))) { if (nx == fx && ny == fy) { hashFreeAll(&visited); free (queue ); return FOUND; } countdown--; queue [tail].x = nx; queue [tail].y = ny; tail++; hashAddItem(&visited, HashCode(nx, ny)); } } } if (countdown > 0 ) { hashFreeAll(&visited); free (queue ); return BLOCKED; } hashFreeAll(&visited); free (queue ); return VALID; } bool isEscapePossible (int ** blocked, int blockedSize, int * blockedColSize, int * source, int sourceSize, int * target, int targetSize) { if (blockedSize < 2 ) { return true ; } struct HashEntry * hashBlocked =NULL ; for (int i = 0 ; i < blockedSize; i++) { hashAddItem(&hashBlocked, HashCode(blocked[i][0 ], blocked[i][1 ])); } int result = check(blocked, blockedSize, source, target, &hashBlocked); if (result == FOUND) { hashFreeAll(&hashBlocked); return true ; } else if (result == BLOCKED) { hashFreeAll(&hashBlocked); return false ; } else { result = check(blocked, blockedSize, target, source, &hashBlocked); hashFreeAll(&hashBlocked); return result != BLOCKED; } }
复杂度分析
方法二:离散化 + 广度优先搜索 思路与算法
我们也可以借助离散化技巧将网格「压缩」成一个规模较小的但等价的新网格,并在新网格上进行常规的广度优先搜索。
以网格的每一行为例,可以发现,不同的行坐标只有:
因此不同的行坐标最多只有 n+4 个,我们可以对行坐标进行离散化,具体的规则如下:
我们将行坐标进行升序排序;
将上边界离散化为 -1。上边界是排序后的第 0 个行坐标;
如果排序后的第 i 个行坐标与第 i-1 个行坐标相同,那么它们离散化之后的值也相同;
如果排序后的第 i 个行坐标与第 i-1 个行坐标相差 1,那么它们离散化之后的值也相差 1;
如果排序后的第 i 个行坐标与第 i-1 个行坐标相差超过 1,那么它们离散化之后的值相差 2。
这样的正确性在于:在离散化前,如果两个行坐标本身相邻,那么在离散化之后它们也必须相邻。如果它们不相邻,可以把它们之间间隔的若干行直接「压缩」成一行,即行坐标相差 2。
对于列坐标的离散化方法也是如此。在离散化完成之后,新的网格的规模不会超过 2(n+4) \times 2(n+4),进行广度优先搜索需要的时间是可接受的。
代码
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 class Solution {private : static constexpr int BOUNDARY = 1000000 ; static constexpr int dirs[4 ][2 ] = { {0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 } }; public : bool isEscapePossible (vector<vector<int >>& blocked, vector<int >& source, vector<int >& target) if (blocked.size () < 2 ) { return true ; } vector<int > rows, columns; for (const auto & pos: blocked) { rows.push_back (pos[0 ]); columns.push_back (pos[1 ]); } rows.push_back (source[0 ]); rows.push_back (target[0 ]); columns.push_back (source[1 ]); columns.push_back (target[1 ]); sort (rows.begin (), rows.end ()); sort (columns.begin (), columns.end ()); rows.erase (unique (rows.begin (), rows.end ()), rows.end ()); columns.erase (unique (columns.begin (), columns.end ()), columns.end ()); unordered_map<int , int > r_mapping, c_mapping; int r_id = (rows[0 ] == 0 ? 0 : 1 ); r_mapping[rows[0 ]] = r_id; for (int i = 1 ; i < rows.size (); ++i) { r_id += (rows[i] == rows[i - 1 ] + 1 ? 1 : 2 ); r_mapping[rows[i]] = r_id; } if (rows.back () != BOUNDARY - 1 ) { ++r_id; } int c_id = (columns[0 ] == 0 ? 0 : 1 ); c_mapping[columns[0 ]] = c_id; for (int i = 1 ; i < columns.size (); ++i) { c_id += (columns[i] == columns[i - 1 ] + 1 ? 1 : 2 ); c_mapping[columns[i]] = c_id; } if (columns.back () != BOUNDARY - 1 ) { ++c_id; } vector<vector<int >> grid (r_id + 1 , vector <int >(c_id + 1 )); for (const auto & pos: blocked) { int x = pos[0 ], y = pos[1 ]; grid[r_mapping[x]][c_mapping[y]] = 1 ; } int sx = r_mapping[source[0 ]], sy = c_mapping[source[1 ]]; int tx = r_mapping[target[0 ]], ty = c_mapping[target[1 ]]; queue<pair<int , int >> q; q.emplace (sx, sy); grid[sx][sy] = 1 ; while (!q.empty ()) { auto [x, y] = q.front (); q.pop (); for (int d = 0 ; d < 4 ; ++d) { int nx = x + dirs[d][0 ], ny = y + dirs[d][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx <= r_id && ny >= 0 && ny <= c_id && grid[nx][ny] != 1 ) { if (nx == tx && ny == ty) { return true ; } q.emplace (nx, ny); grid[nx][ny] = 1 ; } } } return false ; } };
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 class Solution { static final int BOUNDARY = 1000000 ; static final int [][] dirs = { {0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 } }; public boolean isEscapePossible (int [][] blocked, int [] source, int [] target) { if (blocked.length < 2 ) { return true ; } TreeSet<Integer> rows = new TreeSet <Integer>(); TreeSet<Integer> columns = new TreeSet <Integer>(); for (int [] pos : blocked) { rows.add(pos[0 ]); columns.add(pos[1 ]); } rows.add(source[0 ]); rows.add(target[0 ]); columns.add(source[1 ]); columns.add(target[1 ]); Map<Integer, Integer> rMapping = new HashMap <Integer, Integer>(); Map<Integer, Integer> cMapping = new HashMap <Integer, Integer>(); int firstRow = rows.first(); int rId = (firstRow == 0 ? 0 : 1 ); rMapping.put(firstRow, rId); int prevRow = firstRow; for (int row : rows) { if (row == firstRow) { continue ; } rId += (row == prevRow + 1 ? 1 : 2 ); rMapping.put(row, rId); prevRow = row; } if (prevRow != BOUNDARY - 1 ) { ++rId; } int firstColumn = columns.first(); int cId = (firstColumn == 0 ? 0 : 1 ); cMapping.put(firstColumn, cId); int prevColumn = firstColumn; for (int column : columns) { if (column == firstColumn) { continue ; } cId += (column == prevColumn + 1 ? 1 : 2 ); cMapping.put(column, cId); prevColumn = column; } if (prevColumn != BOUNDARY - 1 ) { ++cId; } int [][] grid = new int [rId + 1 ][cId + 1 ]; for (int [] pos : blocked) { int x = pos[0 ], y = pos[1 ]; grid[rMapping.get(x)][cMapping.get(y)] = 1 ; } int sx = rMapping.get(source[0 ]), sy = cMapping.get(source[1 ]); int tx = rMapping.get(target[0 ]), ty = cMapping.get(target[1 ]); Queue<int []> queue = new ArrayDeque <int []>(); queue.offer(new int []{sx, sy}); grid[sx][sy] = 1 ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int [] arr = queue.poll(); int x = arr[0 ], y = arr[1 ]; for (int d = 0 ; d < 4 ; ++d) { int nx = x + dirs[d][0 ], ny = y + dirs[d][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx <= rId && ny >= 0 && ny <= cId && grid[nx][ny] != 1 ) { if (nx == tx && ny == ty) { return true ; } queue.offer(new int []{nx, ny}); grid[nx][ny] = 1 ; } } } return false ; } }
[sol2-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 public class Solution { const int BOUNDARY = 1000000 ; int [][] dirs = {new int []{0 , 1 }, new int []{0 , -1 }, new int []{1 , 0 }, new int []{-1 , 0 } }; public bool IsEscapePossible (int [][] blocked, int [] source, int [] target if (blocked.Length < 2 ) { return true ; } ISet<int > rowsSet = new HashSet<int >(); ISet<int > columnsSet = new HashSet<int >(); List<int > rows = new List<int >(); List<int > columns = new List<int >(); foreach (int [] pos in blocked) { if (rowsSet.Add(pos[0 ])) { rows.Add(pos[0 ]); } if (columnsSet.Add(pos[1 ])) { columns.Add(pos[1 ]); } } if (rowsSet.Add(source[0 ])) { rows.Add(source[0 ]); } if (rowsSet.Add(target[0 ])) { rows.Add(target[0 ]); } if (columnsSet.Add(source[1 ])) { columns.Add(source[1 ]); } if (columnsSet.Add(target[1 ])) { columns.Add(target[1 ]); } rows.Sort(); columns.Sort(); Dictionary<int , int > rDictionary = new Dictionary<int , int >(); Dictionary<int , int > cDictionary = new Dictionary<int , int >(); int rId = (rows[0 ] == 0 ? 0 : 1 ); rDictionary.Add(rows[0 ], rId); for (int i = 1 ; i < rows.Count; ++i) { rId += (rows[i] == rows[i - 1 ] + 1 ? 1 : 2 ); rDictionary.Add(rows[i], rId); } if (rows[rows.Count - 1 ] != BOUNDARY - 1 ) { ++rId; } int cId = (columns[0 ] == 0 ? 0 : 1 ); cDictionary.Add(columns[0 ], cId); for (int i = 1 ; i < columns.Count; ++i) { cId += (columns[i] == columns[i - 1 ] + 1 ? 1 : 2 ); cDictionary.Add(columns[i], cId); } if (columns[columns.Count - 1 ] != BOUNDARY - 1 ) { ++cId; } int [][] grid = new int [rId + 1 ][]; for (int i = 0 ; i <= rId; ++i) { grid[i] = new int [cId + 1 ]; } foreach (int [] pos in blocked) { int x = pos[0 ], y = pos[1 ]; grid[rDictionary[x]][cDictionary[y]] = 1 ; } int sx = rDictionary[source[0 ]], sy = cDictionary[source[1 ]]; int tx = rDictionary[target[0 ]], ty = cDictionary[target[1 ]]; Queue<Tuple<int , int >> queue = new Queue<Tuple<int , int >>(); queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<int , int >(sx, sy)); grid[sx][sy] = 1 ; while (queue.Count > 0 ) { Tuple<int , int > tuple = queue.Dequeue(); int x = tuple.Item1, y = tuple.Item2; for (int d = 0 ; d < 4 ; ++d) { int nx = x + dirs[d][0 ], ny = y + dirs[d][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx <= rId && ny >= 0 && ny <= cId && grid[nx][ny] != 1 ) { if (nx == tx && ny == ty) { return true ; } queue.Enqueue(new Tuple<int , int >(nx, ny)); grid[nx][ny] = 1 ; } } } return false ; } }
[sol2-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution : def isEscapePossible (self, blocked: List [List [int ]], source: List [int ], target: List [int ] ) -> bool : if len (blocked) < 2 : return True BOUNDARY = 10 **6 rows = sorted (set (pos[0 ] for pos in blocked) | {source[0 ], target[0 ]}) columns = sorted (set (pos[1 ] for pos in blocked) | {source[1 ], target[1 ]}) r_mapping, c_mapping = dict (), dict () r_id = (0 if rows[0 ] == 0 else 1 ) r_mapping[rows[0 ]] = r_id for i in range (1 , len (rows)): r_id += (1 if rows[i] == rows[i - 1 ] + 1 else 2 ) r_mapping[rows[i]] = r_id if rows[-1 ] != BOUNDARY - 1 : r_id += 1 c_id = (0 if columns[0 ] == 0 else 1 ) c_mapping[columns[0 ]] = c_id for i in range (1 , len (columns)): c_id += (1 if columns[i] == columns[i - 1 ] + 1 else 2 ) c_mapping[columns[i]] = c_id if columns[-1 ] != BOUNDARY - 1 : c_id += 1 grid = [[0 ] * (c_id + 1 ) for _ in range (r_id + 1 )] for x, y in blocked: grid[r_mapping[x]][c_mapping[y]] = 1 sx, sy = r_mapping[source[0 ]], c_mapping[source[1 ]] tx, ty = r_mapping[target[0 ]], c_mapping[target[1 ]] q = deque([(sx, sy)]) grid[sx][sy] = 1 while q: x, y = q.popleft() for nx, ny in [(x + 1 , y), (x - 1 , y), (x, y + 1 ), (x, y - 1 )]: if 0 <= nx <= r_id and 0 <= ny <= c_id and grid[nx][ny] != 1 : if (nx, ny) == (tx, ty): return True q.append((nx, ny)) grid[nx][ny] = 1 return False
[sol2-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 type pair struct { x, y int }var dirs = []pair{ {-1 , 0 }, {1 , 0 }, {0 , -1 }, {0 , 1 } }func discrete (a []int ) map [int ]int , int ) { sort.Ints(a) id := 0 if a[0 ] > 0 { id = 1 } mapping := map [int ]int {a[0 ]: id} pre := a[0 ] for _, v := range a[1 :] { if v != pre { if v == pre+1 { id++ } else { id += 2 } mapping[v] = id pre = v } } const boundary int = 1e6 if a[len (a)-1 ] != boundary-1 { id++ } return mapping, id } func isEscapePossible (block [][]int , source, target []int ) bool { n := len (block) if n < 2 { return true } rows := []int {source[0 ], target[0 ]} cols := []int {source[1 ], target[1 ]} for _, b := range block { rows = append (rows, b[0 ]) cols = append (cols, b[1 ]) } rMapping, rBound := discrete(rows) cMapping, cBound := discrete(cols) grid := make ([][]bool , rBound+1 ) for i := range grid { grid[i] = make ([]bool , cBound+1 ) } for _, b := range block { grid[rMapping[b[0 ]]][cMapping[b[1 ]]] = true } sx, sy := rMapping[source[0 ]], cMapping[source[1 ]] tx, ty := rMapping[target[0 ]], cMapping[target[1 ]] grid[sx][sy] = true q := []pair{ {sx, sy} } for len (q) > 0 { p := q[0 ] q = q[1 :] for _, d := range dirs { x, y := p.x+d.x, p.y+d.y if 0 <= x && x <= rBound && 0 <= y && y <= cBound && !grid[x][y] { if x == tx && y == ty { return true } grid[x][y] = true q = append (q, pair{x, y}) } } } return false }
[sol2-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 #define BOUNDARY 1000000 int dirs[4 ][2 ] = { {0 , 1 }, {0 , -1 }, {1 , 0 }, {-1 , 0 } };struct Pair { int x; int y; }; struct HashEntry { int key; int val; UT_hash_handle hh; }; void hashAddItem (struct HashEntry **obj, int key, int val) { struct HashEntry *pEntry ; pEntry = malloc (sizeof (struct HashEntry)); pEntry->key = key; pEntry->val = val; HASH_ADD(hh, *obj, key, sizeof (int ), pEntry); } struct HashEntry *hashFindItem (struct HashEntry **obj, int key) { struct HashEntry *pEntry =NULL ; HASH_FIND(hh, *obj, &key, sizeof (int ), pEntry); return pEntry; } int hashGetValue (struct HashEntry **obj, int key) { struct HashEntry *pEntry =NULL ; HASH_FIND(hh, *obj, &key, sizeof (int ), pEntry); return pEntry->val; } void hashEraseItem (struct HashEntry **obj, int key) { struct HashEntry *pEntry =NULL ; HASH_FIND(hh, *obj, &key, sizeof (int ), pEntry); if (NULL != pEntry) { HASH_DEL(*obj, pEntry); free (pEntry); } } void hashFreeAll (struct HashEntry **obj) { struct HashEntry *curr , *next ; HASH_ITER(hh, *obj, curr, next) { HASH_DEL(*obj, curr); free (curr); } } int cmp (const void * pa, const void * pb) { int a = *((int *)pa); int b = *((int *)pb); return a - b; } int unique (int ** arr, int arrSize) { int pos = 0 ; int * p = *arr; qsort(*arr, arrSize, sizeof (int ), cmp); for (int i = 1 ; i < arrSize; i++) { if (p[i] > p[pos]) { pos++; p[pos] = p[i]; } } return pos + 1 ; } bool isEscapePossible (int ** blocked, int blockedSize, int * blockedColSize, int * source, int sourceSize, int * target, int targetSize) { if (blockedSize < 2 ) { return true ; } int * rows = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) * (blockedSize + 2 )); int * columns = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) * (blockedSize + 2 )); for (int i = 0 ; i < blockedSize; i++) { rows[i] = blocked[i][0 ]; columns[i] = blocked[i][1 ]; } rows[blockedSize] = source[0 ]; rows[blockedSize + 1 ] = target[0 ]; columns[blockedSize] = source[1 ]; columns[blockedSize + 1 ] = target[1 ]; int rowsSize = unique(&rows, blockedSize + 2 ); int columnsSize = unique(&columns, blockedSize + 2 ); struct HashEntry * r_mapping =NULL ; struct HashEntry * c_mapping =NULL ; int r_id = (rows[0 ] == 0 ? 0 : 1 ); hashAddItem(&r_mapping, rows[0 ], r_id); for (int i = 1 ; i < rowsSize; i++) { r_id += (rows[i] == rows[i - 1 ] + 1 ? 1 : 2 ); hashAddItem(&r_mapping, rows[i], r_id); } if (rows[rowsSize - 1 ] != BOUNDARY - 1 ) { r_id++; } int c_id = (columns[0 ] == 0 ? 0 : 1 ); hashAddItem(&c_mapping, columns[0 ], c_id); for (int i = 1 ; i < columnsSize; ++i) { c_id += (columns[i] == columns[i - 1 ] + 1 ? 1 : 2 ); hashAddItem(&c_mapping, columns[i], c_id); } if (columns[columnsSize - 1 ] != BOUNDARY - 1 ) { c_id++; } int ** grid = (int **)malloc (sizeof (int *) * (r_id + 1 )); for (int i = 0 ; i <= r_id; i++) { grid[i] = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) * (c_id + 1 )); } for (int i = 0 ; i < blockedSize; i++) { int x = hashGetValue(&r_mapping, blocked[i][0 ]); int y = hashGetValue(&c_mapping, blocked[i][1 ]); grid[x][y] = 1 ; } int sx = hashGetValue(&r_mapping, source[0 ]); int sy = hashGetValue(&c_mapping, source[1 ]); int tx = hashGetValue(&r_mapping, target[0 ]); int ty = hashGetValue(&c_mapping, target[1 ]); struct Pair * queue =struct Pair *)malloc (sizeof (struct Pair) * c_id * r_id * 4 ); int head = 0 , tail = 0 ; queue [tail].x = sx; queue [tail].y = sy; tail++; grid[sx][sy] = 1 ; while (head != tail) { int x = queue [head].x; int y = queue [head].y; head++; for (int d = 0 ; d < 4 ; ++d) { int nx = x + dirs[d][0 ], ny = y + dirs[d][1 ]; if (nx >= 0 && nx <= r_id && ny >= 0 && ny <= c_id && grid[nx][ny] != 1 ) { if (nx == tx && ny == ty) { hashFreeAll(&r_mapping); hashFreeAll(&c_mapping); free (rows); free (columns); free (queue ); return true ; } queue [tail].x = nx; queue [tail].y = ny; tail++; grid[nx][ny] = 1 ; } } } hashFreeAll(&r_mapping); hashFreeAll(&c_mapping); free (rows); free (columns); free (queue ); return false ; }
复杂度分析
结语 除了基于广度优先搜索的方法外,本题还有时间复杂度更优(例如可以达到 O(n) 线性时间复杂度)的,基于「交点数判定」的方法。这种方法的精髓在于:如果 source 和 target 相互可达,那么任意一条从 source 到 target 的路径(可以直接越过障碍),以及任意一个「包围圈」,「进入」该「包围圈」和「离开」该「包围圈」的次数必须相等。我们可以这样理解:如果路径从外界进入了某一个「包围圈」,那么它必须在未来的某一时刻再离开该「包围圈」并返回外界,否则它就被困在该「包围圈」内部了。同理,如果路径离开了某一个「包围圈」,那么它必须在未来的某一时刻再从外界进入该「包围圈」。
因此,我们可以随意挑选一条从 source 到 target 的路径(最简单的路径就是先水平走到与 target 同一列的位置,再竖直走到 target),并统计这条路径上进入「包围圈」和离开「包围圈」的次数,不同的「包围圈」需要分别进行统计。无论是进入「包围圈」还是离开「包围圈」,它在路径上的表现形式均为,上一个非障碍的位置在包围圈外(内)侧,而当前非障碍的位置在包围圈内(外)侧,也就是说:上一个非障碍的位置与当前非障碍的位置不连通 。我们可以使用并查集维护「包围圈」本身的连通性,而由于我们需要考虑的非障碍位置一定是与障碍相邻的,因此同样使用并查集维护所有障碍的上下左右四连通的非障碍位置的连通性。这样一来,我们就可以知道上一个非障碍的位置与当前非障碍的位置是否连通了。
由于进入「包围圈」和离开「包围圈」(对于同一个「包围圈」而言)一定是交替出现的,因此我们只需要统计进入「包围圈」和离开「包围圈」的次数之和即可,而不需要区分究竟是进入还是离开。我们需要保证每一个「包围圈」的次数之和均为偶数。
这种方法过于复杂且思维难度和编码难度都较大,因此这里不给出具体的代码实现。感兴趣的读者可以参考其它题解。