1311-获取你好友已观看的视频
有 n 个人,每个人都有一个 0 到 n-1 的唯一 id 。
给你数组 watchedVideos 和 friends ,其中 watchedVideos[i] 和 friends[i] 分别表示id = i 的人观看过的视频列表和他的好友列表。
Level 1 的视频包含所有你好友观看过的视频,level 2
的视频包含所有你好友的好友观看过的视频,以此类推。一般的,Level 为 k 的视频包含所有从你出发,最短距离为 k
的好友观看过的视频。
给定你的 id 和一个 level 值,请你找出所有指定 level
的视频,并将它们按观看频率升序返回。如果有频率相同的视频,请将它们按字母顺序从小到大排列。
示例 1:
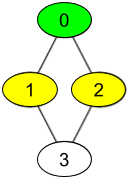
**输入:** watchedVideos = [["A","B"],["C"],["B","C"],["D"]], friends = [[1,2],[0,3],[0,3],[1,2]], id = 0, level = 1
**输出:** ["B","C"]
**解释:**
你的 id 为 0(绿色),你的朋友包括(黄色):
id 为 1 -> watchedVideos = ["C"]
id 为 2 -> watchedVideos = ["B","C"]
你朋友观看过视频的频率为:
B -> 1
C -> 2
示例 2:
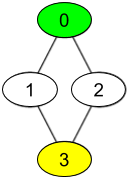
**输入:** watchedVideos = [["A","B"],["C"],["B","C"],["D"]], friends = [[1,2],[0,3],[0,3],[1,2]], id = 0, level = 2
**输出:** ["D"]
**解释:**
你的 id 为 0(绿色),你朋友的朋友只有一个人,他的 id 为 3(黄色)。
提示:
n == watchedVideos.length == friends.length2 <= n <= 1001 <= watchedVideos[i].length <= 1001 <= watchedVideos[i][j].length <= 80 <= friends[i].length < n0 <= friends[i][j] < n0 <= id < n1 <= level < n- 如果
friends[i]包含j,那么friends[j]包含i
说明
本题将几个面试中常考的知识点(广度优先搜索、Set/Map 的应用、排序)进行了结合。题目本身的难度不大,但需要仔细考虑清楚每一个模块之间的关系,并且能尽量做到一次性通过,否则调试起来会较为复杂。
方法一:广度优先搜索
步骤一:找出所有 Level k 的好友
我们可以使用广度优先搜索的方法,从编号为 id 的节点开始搜索,得到从 id 到其余所有节点的最短路径,则所有到 id 的最短路径为 k 的节点都是 Level k 的好友。
具体地,我们使用一个队列帮助我们进行搜索。队列中初始只有编号为 id 的节点。我们进行 k 轮搜索,在第 i 轮搜索开始前,队列中的节点是所有 Level i-1 的好友,而我们希望从这些节点得到所有 Level i 的好友。我们依次取出这些 Level i-1 的节点,设当前取出的节点为 x,我们遍历 x 的所有好友 friends[x],如果某个好友未被访问过,那么我们就能知道其为 Level i 的好友,可以将其加入队列。在 k 轮搜索结束之后,队列中就包含了所有 Level k 的好友。
步骤二:统计好友观看过的视频
我们使用一个哈希映射(HashMap)来统计 Level k 的好友观看过的视频。对于哈希映射中的每个键值对,键表示视频的名称,值表示视频被好友观看过的次数。对于队列中的每个节点 x,我们将 watchedVideos[x] 中的所有视频依次加入哈希映射,就可以完成这一步骤。
步骤三:将视频按照要求排序
在统计完成之后,我们将哈希映射中的所有键值对存储进数组中,并将它们按照观看次数为第一关键字、视频名称为第二关键字生序排序,即可得到最终的结果。
1 | using PSI = pair<string, int>; |
1 | class Solution: |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(N + M + V\log V),其中 N 是人数,M 是好友关系的总数,V 是电影的总数。
空间复杂度:O(N + V)。