给你一个points 数组,表示 2D 平面上的一些点,其中 points[i] = [xi, yi] 。
连接点 [xi, yi] 和点 [xj, yj] 的费用为它们之间的 曼哈顿距离 :|xi - xj| + |yi - yj| ,其中|val| 表示 val 的绝对值。
请你返回将所有点连接的最小总费用。只有任意两点之间 有且仅有 一条简单路径时,才认为所有点都已连接。
示例 1:
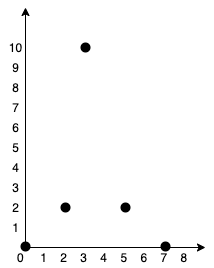
**输入:** points = [[0,0],[2,2],[3,10],[5,2],[7,0]]
**输出:** 20
**解释:**
我们可以按照上图所示连接所有点得到最小总费用,总费用为 20 。
注意到任意两个点之间只有唯一一条路径互相到达。
示例 2:
**输入:** points = [[3,12],[-2,5],[-4,1]]
**输出:** 18
示例 3:
**输入:** points = [[0,0],[1,1],[1,0],[-1,1]]
**输出:** 4
示例 4:
**输入:** points = [[-1000000,-1000000],[1000000,1000000]]
**输出:** 4000000
示例 5:
**输入:** points = [[0,0]]
**输出:** 0
提示:
1 <= points.length <= 1000-106 <= xi, yi <= 106所有点 (xi, yi) 两两不同。
写在前面 根据题意,我们得到了一张 n 个节点的完全图,任意两点之间的距离均为它们的曼哈顿距离。现在我们需要在这个图中取得一个子图,恰满足子图的任意两点之间有且仅有一条简单路径,且这个子图的所有边的总权值之和尽可能小。
能够满足任意两点之间有且仅有一条简单路径只有树,且这棵树包含 n 个节点。我们称这棵树为给定的图的生成树,其中总权值最小的生成树,我们称其为最小生成树。
最小生成树有一个非常经典的解法:Kruskal。
方法一:Kruskal 算法 思路及解法
Kruskal 算法是一种常见并且好写的最小生成树算法,由 Kruskal 发明。该算法的基本思想是从小到大加入边,是一个贪心算法。
其算法流程为:
将图 G={V,E\ 中的所有边按照长度由小到大进行排序,等长的边可以按任意顺序。
初始化图 G’ 为 {V,\varnothing\,从前向后扫描排序后的边,如果扫描到的边 e 在 G’ 中连接了两个相异的连通块,则将它插入 G’ 中。
最后得到的图 G’ 就是图 G 的最小生成树。
在实际代码中,我们首先将这张完全图中的边全部提取到边集数组中,然后对所有边进行排序,从小到大进行枚举,每次贪心选边加入答案。使用并查集维护连通性,若当前边两端不连通即可选择这条边。
代码
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 class DisjointSetUnion {private : vector<int > f, rank; int n; public : DisjointSetUnion (int _n) { n = _n; rank.resize (n, 1 ); f.resize (n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { f[i] = i; } } int find (int x) return f[x] == x ? x : f[x] = find (f[x]); } int unionSet (int x, int y) int fx = find (x), fy = find (y); if (fx == fy) { return false ; } if (rank[fx] < rank[fy]) { swap (fx, fy); } rank[fx] += rank[fy]; f[fy] = fx; return true ; } }; struct Edge { int len, x, y; Edge (int len, int x, int y) : len (len), x (x), y (y) { } }; class Solution {public : int minCostConnectPoints (vector<vector<int >>& points) auto dist = [&](int x, int y) -> int { return abs (points[x][0 ] - points[y][0 ]) + abs (points[x][1 ] - points[y][1 ]); }; int n = points.size (); DisjointSetUnion dsu (n) ; vector<Edge> edges; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n; j++) { edges.emplace_back (dist (i, j), i, j); } } sort (edges.begin (), edges.end (), [](Edge a, Edge b) -> int { return a.len < b.len; }); int ret = 0 , num = 1 ; for (auto & [len, x, y] : edges) { if (dsu.unionSet (x, y)) { ret += len; num++; if (num == n) { break ; } } } return ret; } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 class Solution { public int minCostConnectPoints (int [][] points) { int n = points.length; DisjointSetUnion dsu = new DisjointSetUnion (n); List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList <Edge>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n; j++) { edges.add(new Edge (dist(points, i, j), i, j)); } } Collections.sort(edges, new Comparator <Edge>() { public int compare (Edge edge1, Edge edge2) { return edge1.len - edge2.len; } }); int ret = 0 , num = 1 ; for (Edge edge : edges) { int len = edge.len, x = edge.x, y = edge.y; if (dsu.unionSet(x, y)) { ret += len; num++; if (num == n) { break ; } } } return ret; } public int dist (int [][] points, int x, int y) { return Math.abs(points[x][0 ] - points[y][0 ]) + Math.abs(points[x][1 ] - points[y][1 ]); } } class DisjointSetUnion { int [] f; int [] rank; int n; public DisjointSetUnion (int n) { this .n = n; this .rank = new int [n]; Arrays.fill(this .rank, 1 ); this .f = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { this .f[i] = i; } } public int find (int x) { return f[x] == x ? x : (f[x] = find(f[x])); } public boolean unionSet (int x, int y) { int fx = find(x), fy = find(y); if (fx == fy) { return false ; } if (rank[fx] < rank[fy]) { int temp = fx; fx = fy; fy = temp; } rank[fx] += rank[fy]; f[fy] = fx; return true ; } } class Edge { int len, x, y; public Edge (int len, int x, int y) { this .len = len; this .x = x; this .y = y; } }
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 type unionFind struct { parent, rank []int } func newUnionFind (n int ) parent := make ([]int , n) rank := make ([]int , n) for i := range parent { parent[i] = i rank[i] = 1 } return &unionFind{parent, rank} } func (uf *unionFind) int ) int { if uf.parent[x] != x { uf.parent[x] = uf.find(uf.parent[x]) } return uf.parent[x] } func (uf *unionFind) int ) bool { fx, fy := uf.find(x), uf.find(y) if fx == fy { return false } if uf.rank[fx] < uf.rank[fy] { fx, fy = fy, fx } uf.rank[fx] += uf.rank[fy] uf.parent[fy] = fx return true } func dist (p, q []int ) int { return abs(p[0 ]-q[0 ]) + abs(p[1 ]-q[1 ]) } func minCostConnectPoints (points [][]int ) int ) { n := len (points) type edge struct { v, w, dis int } edges := []edge{} for i, p := range points { for j := i + 1 ; j < n; j++ { edges = append (edges, edge{i, j, dist(p, points[j])}) } } sort.Slice(edges, func (i, j int ) bool { return edges[i].dis < edges[j].dis }) uf := newUnionFind(n) left := n - 1 for _, e := range edges { if uf.union(e.v, e.w) { ans += e.dis left-- if left == 0 { break } } } return } func abs (x int ) int { if x < 0 { return -x } return x }
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class DisjointSetUnion : def __init__ (self, n ): self.n = n self.rank = [1 ] * n self.f = list (range (n)) def find (self, x: int ) -> int : if self.f[x] == x: return x self.f[x] = self.find(self.f[x]) return self.f[x] def unionSet (self, x: int , y: int ) -> bool : fx, fy = self.find(x), self.find(y) if fx == fy: return False if self.rank[fx] < self.rank[fy]: fx, fy = fy, fx self.rank[fx] += self.rank[fy] self.f[fy] = fx return True class Solution : def minCostConnectPoints (self, points: List [List [int ]] ) -> int : dist = lambda x, y: abs (points[x][0 ] - points[y][0 ]) + abs (points[x][1 ] - points[y][1 ]) n = len (points) dsu = DisjointSetUnion(n) edges = list () for i in range (n): for j in range (i + 1 , n): edges.append((dist(i, j), i, j)) edges.sort() ret, num = 0 , 1 for length, x, y in edges: if dsu.unionSet(x, y): ret += length num += 1 if num == n: break return ret
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 var minCostConnectPoints = function (points ) { const dist = (x, y ) => { return Math .abs (points[x][0 ] - points[y][0 ]) + Math .abs (points[x][1 ] - points[y][1 ]); } const n = points.length ; const dsu = new DisjointSetUnion (n); const edges = []; for (let i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (let j = i + 1 ; j < n; j++) { edges.push ([dist (i, j), i, j]); } } edges.sort ((a, b ) => a[0 ] - b[0 ]); let ret = 0 , num = 1 ; for (const [length, x, y] of edges) { if (dsu.unionSet (x, y)) { ret += length; num += 1 ; if (num === n) { break ; } } } return ret; }; class DisjointSetUnion { constructor (n ) { this .n = n; this .rank = new Array (n).fill (1 ); this .f = new Array (n).fill (0 ).map ((element, index ) => index); } find (x ) { if (this .f [x] === x) { return x; } this .f [x] = this .find (this .f [x]); return this .f [x]; } unionSet (x, y ) { let fx = this .find (x), fy = this .find (y); if (fx === fy) { return false ; } if (this .rank [fx] < this .rank [fy]) { [fx, fy] = [fy, fx]; } this .rank [fx] += this .rank [fy]; this .f [fy] = fx; return true ; } }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 void swap (int * a, int * b) { int tmp = *a; *a = *b, *b = tmp; } struct Edge { int len, x, y; }; int cmp (struct Edge* a, struct Edge* b) { return a->len - b->len; } int find (int * f, int x) { return f[x] == x ? x : (f[x] = find(f, f[x])); } int unionSet (int * f, int * rank, int x, int y) { int fx = find(f, x), fy = find(f, y); if (fx == fy) { return false ; } if (rank[fx] < rank[fy]) { swap(&fx, &fy); } rank[fx] += rank[fy]; f[fy] = fx; return true ; } int minCostConnectPoints (int ** points, int pointsSize, int * pointsColSize) { int n = pointsSize; struct Edge edges [(n + 1) * n / 2]; int edgesSize = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n; j++) { edges[edgesSize].x = i; edges[edgesSize].y = j; edges[edgesSize++].len = fabs (points[i][0 ] - points[j][0 ]) + fabs (points[i][1 ] - points[j][1 ]); } } qsort(edges, edgesSize, sizeof (struct Edge), cmp); int f[n], rank[n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { f[i] = i; rank[i] = 1 ; } int ret = 0 , num = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < edgesSize; i++) { if (unionSet(f, rank, edges[i].x, edges[i].y)) { ret += edges[i].len; num++; if (num == n) { break ; } } } return ret; }
复杂度分析
方法二:建图优化的 Kruskal 思路及解法
方法一中,虽然使用了 Kruskal 算法,但时间复杂度仍然较高,因为本题中的边数是 O(n^2) 的,所以我们需要想办法将减少边数。为此,我们提出几个结论:
结论一 :对于图中的任意三点 A,B,C,假设边 AB,AC,BC 中 AB 为最长边,那么最终答案中必然不包含边 AB。
我们利用反证法证明:假设最后答案中包含 AB,那么此时 AC 与 BC 两边中至少有一条边是没有被选用的,我们总可以在保证连通性的情况下,将 AB 边替换为 AC 与 BC 两边中的某一个,使最小生成树的总权值变得更小。
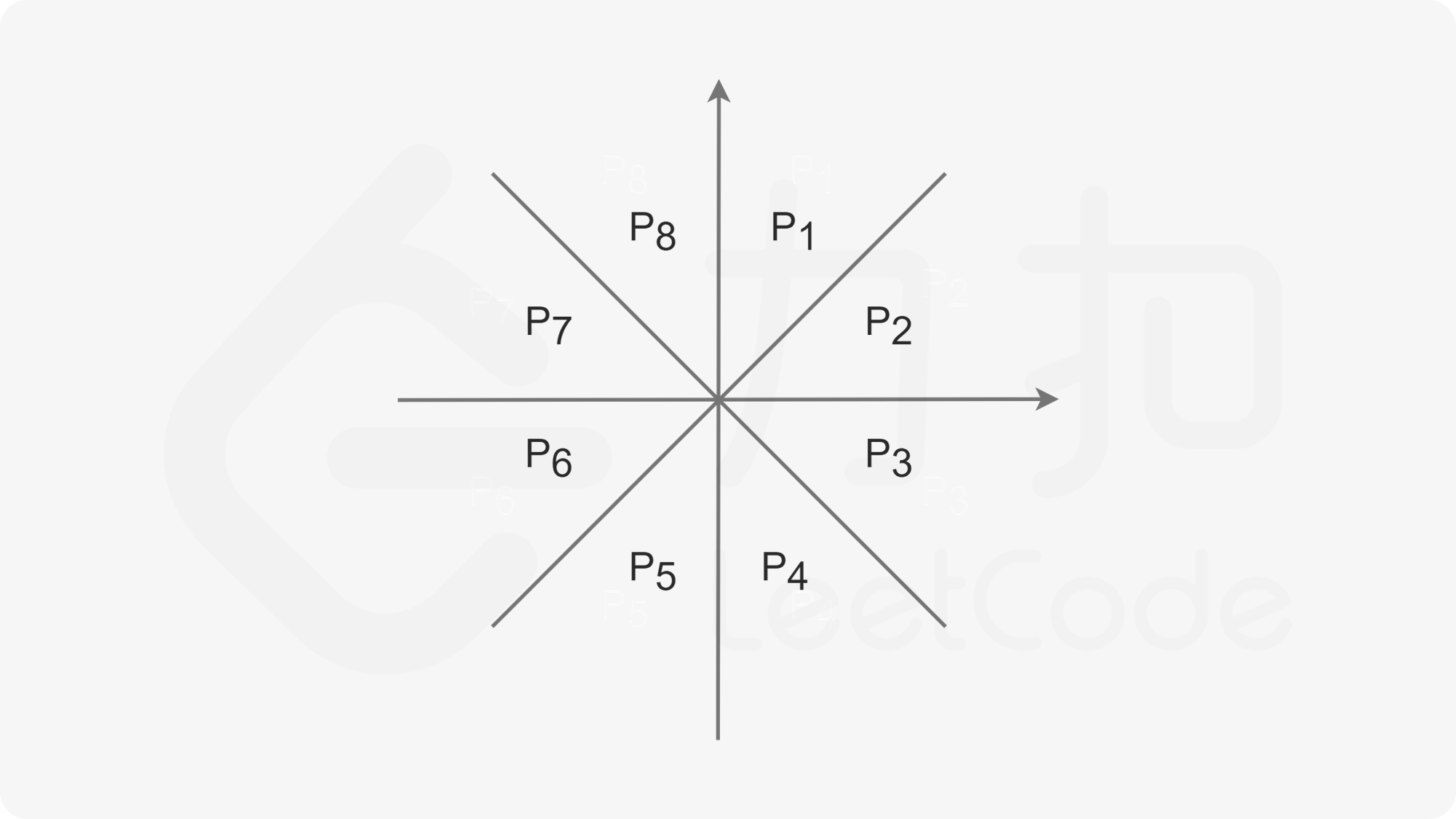
结论二 :对于下图中同属同一个区块的任意两点 B,C,A 为原点,那么 BC 不可能为三边中最长边。
图中任意一个区块的两分割线的夹角均为 45^\circ。
我们以 P1 区块为例,假设 B(x_B,y_B),C(x_C,y_C),不失一般性,假设 x_B + y_B \leq x_C + y_C。
因为处于 P1 区域,所以有 0 \leq x_B \leq y_B,0 \leq x_C \leq y_C。所以 BC = |x_B - x_C| + |y_B - y_C|。
下面我们尝试分类讨论:
当 x_B > x_C, y_B > y_C,这与 x_B + y_B \leq x_C + y_C 矛盾。
当 x_B \leq x_C, y_B > y_C,此时有 |BC| = x_C - x_B + y_B - y_C,|AC| - |BC| = x_C + y_C - x_C + x_B - y_B + y_C = x_B - y_B + 2 \times y_C。由前面各种关系可得 y_B > y_C > x_C > x_B。假设 |AC| < |BC|,即 y_B > 2 \times y_C + x_B,那么 |AB| = x_B + y_B > 2 \times x_B + 2 \times y_C,|AC| = x_C + y_C < 2 \times y_C < |AB| 与前提矛盾,故 |AC| \geq |BC|;
x_B > x_C 且 y_B \leq y_C。与 2 同理;
x_B \leq x_C 且 y_B \leq y_C。此时显然有 |AB| + |BC| = |AC|,即有 |AC| > |BC|。
综上有 |AC| \geq |BC|,这个性质可以从 P1 区域推导到其他七个区域。
结论三 :假设存在一点 A 在原点处,那么对于图中的任意一个 45^\circ 区域,我们都至多只选择其中的一个点与 A 相连,且该点必然为该区域中距离 A 最近的点。
我们首先利用反证法证明:假设最后答案中包含 AB 与 AC,且 B 与 C 均位于同一个 45^\circ 区域中。那么由结论二可知,BC 必不为三边中的最长边。即最长边必然为 AB 或 AC。由结论一可知,AB 与 AC 中必然有一个不包含在答案中,这与假设相悖,因此我们最多仅会选择一个点与 A 相连。
我们进一步思考,既然最多仅会选择一个点与 A 相连,且三边中的最长边不为 A 的对边,那么仅有距离 A 最近的点与 A 所连的边可能出现在答案中。证毕。
依据结论三我们可以知道,一个点至多连八条边,因此我们至多只需要连出 O(n) 条边。
细节
为防止重复连边,我们对每一个点只考虑对 P1,P2,P3,P4 连边的情况,假设 A 点坐标为 (x,y),对于这四个点,我们可以概括为:
对于 P1 区域的 (x_1,y_1),有 x_1 \geq x, y_1 - x_1 \geq y - x,其中最近点的 x_1 + y_1 最小。
对于 P2 区域的 (x_2,y_2),有 y_2 \geq y, y_2 - x_2 \leq y - x,其中最近点的 x_2 + y_2 最小。
对于 P3 区域的 (x_3,y_3),有 y_3 \leq y, y_3 + x_3 \geq y + x,其中最近点的 y_3 - x_3 最小。
对于 P4 区域的 (x_4,y_4),有 x_4 \geq x, y_4 + x_4 \leq y + x,其中最近点的 y_4 - x_4 最小。
这样,我们分别处理每一个区域即可,以 P1 区域为例,我们先通过排序使得所有点按照横坐标从大到小排列,然后将每一个点的 y_i - x_i 信息记录,将离散化后记录在数组的下标为 y_i - x_i 的位置中,并利用树状数组维护该数组的前缀最小值。这样我们就可以动态地、单次 O(\log n) 地计算每个点的 P1 区域所选择的点。
为了提升编码效率,实际代码中我们只实现了 P1 区域的算法,对于其它三个区域,我们通过巧妙的坐标变化使其条件变为 P1 区域,使得代码能够更加高效地复用。
代码
下面代码中的 Python 代码中需要 import 类型标注中的 Tuple,当然删去对应部分也可以成功运行。
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 class DisjointSetUnion {private : vector<int > f, rank; int n; public : DisjointSetUnion (int _n) { n = _n; rank.resize (n, 1 ); f.resize (n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { f[i] = i; } } int find (int x) return f[x] == x ? x : f[x] = find (f[x]); } int unionSet (int x, int y) int fx = find (x), fy = find (y); if (fx == fy) { return false ; } if (rank[fx] < rank[fy]) { swap (fx, fy); } rank[fx] += rank[fy]; f[fy] = fx; return true ; } }; class BIT {public : vector<int > tree, idRec; int n; BIT (int _n) { n = _n; tree.resize (n, INT_MAX); idRec.resize (n, -1 ); } int lowbit (int k) return k & (-k); } void update (int pos, int val, int id) while (pos > 0 ) { if (tree[pos] > val) { tree[pos] = val; idRec[pos] = id; } pos -= lowbit (pos); } } int query (int pos) int minval = INT_MAX; int j = -1 ; while (pos < n) { if (minval > tree[pos]) { minval = tree[pos]; j = idRec[pos]; } pos += lowbit (pos); } return j; } }; struct Edge { int len, x, y; Edge (int len, int x, int y) : len (len), x (x), y (y) { } bool operator <(const Edge& a) const { return len < a.len; } }; struct Pos { int id, x, y; bool operator <(const Pos& a) const { return x == a.x ? y < a.y : x < a.x; } }; class Solution {public : vector<Edge> edges; vector<Pos> pos; void build (int n) sort (pos.begin (), pos.end ()); vector<int > a (n) , b (n) ; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { a[i] = pos[i].y - pos[i].x; b[i] = pos[i].y - pos[i].x; } sort (b.begin (), b.end ()); b.erase (unique (b.begin (), b.end ()), b.end ()); int num = b.size (); BIT bit (num + 1 ) ; for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int poss = lower_bound (b.begin (), b.end (), a[i]) - b.begin () + 1 ; int j = bit.query (poss); if (j != -1 ) { int dis = abs (pos[i].x - pos[j].x) + abs (pos[i].y - pos[j].y); edges.emplace_back (dis, pos[i].id, pos[j].id); } bit.update (poss, pos[i].x + pos[i].y, i); } } void solve (vector<vector<int >>& points, int n) pos.resize (n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { pos[i].x = points[i][0 ]; pos[i].y = points[i][1 ]; pos[i].id = i; } build (n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { swap (pos[i].x, pos[i].y); } build (n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { pos[i].x = -pos[i].x; } build (n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { swap (pos[i].x, pos[i].y); } build (n); } int minCostConnectPoints (vector<vector<int >>& points) int n = points.size (); solve (points, n); DisjointSetUnion dsu (n) ; sort (edges.begin (), edges.end ()); int ret = 0 , num = 1 ; for (auto & [len, x, y] : edges) { if (dsu.unionSet (x, y)) { ret += len; num++; if (num == n) { break ; } } } return ret; } };
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 class Solution { List<Edge> edges = new ArrayList <Edge>(); Pos[] pos; public int minCostConnectPoints (int [][] points) { int n = points.length; solve(points, n); DisjointSetUnion dsu = new DisjointSetUnion (n); Collections.sort(edges, new Comparator <Edge>() { public int compare (Edge edge1, Edge edge2) { return edge1.len - edge2.len; } }); int ret = 0 , num = 1 ; for (Edge edge : edges) { int len = edge.len, x = edge.x, y = edge.y; if (dsu.unionSet(x, y)) { ret += len; num++; if (num == n) { break ; } } } return ret; } public void solve (int [][] points, int n) { pos = new Pos [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { pos[i] = new Pos (i, points[i][0 ], points[i][1 ]); } build(n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int temp = pos[i].x; pos[i].x = pos[i].y; pos[i].y = temp; } build(n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { pos[i].x = -pos[i].x; } build(n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { int temp = pos[i].x; pos[i].x = pos[i].y; pos[i].y = temp; } build(n); } public void build (int n) { Arrays.sort(pos, new Comparator <Pos>() { public int compare (Pos pos1, Pos pos2) { return pos1.x == pos2.x ? pos1.y - pos2.y : pos1.x - pos2.x; } }); int [] a = new int [n]; Set<Integer> set = new HashSet <Integer>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { a[i] = pos[i].y - pos[i].x; set.add(pos[i].y - pos[i].x); } int num = set.size(); int [] b = new int [num]; int index = 0 ; for (int element : set) { b[index++] = element; } Arrays.sort(b); BIT bit = new BIT (num + 1 ); for (int i = n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i--) { int poss = binarySearch(b, a[i]) + 1 ; int j = bit.query(poss); if (j != -1 ) { int dis = Math.abs(pos[i].x - pos[j].x) + Math.abs(pos[i].y - pos[j].y); edges.add(new Edge (dis, pos[i].id, pos[j].id)); } bit.update(poss, pos[i].x + pos[i].y, i); } } public int binarySearch (int [] array, int target) { int low = 0 , high = array.length - 1 ; while (low < high) { int mid = (high - low) / 2 + low; int num = array[mid]; if (num < target) { low = mid + 1 ; } else { high = mid; } } return low; } } class DisjointSetUnion { int [] f; int [] rank; int n; public DisjointSetUnion (int n) { this .n = n; this .rank = new int [n]; Arrays.fill(this .rank, 1 ); this .f = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { this .f[i] = i; } } public int find (int x) { return f[x] == x ? x : (f[x] = find(f[x])); } public boolean unionSet (int x, int y) { int fx = find(x), fy = find(y); if (fx == fy) { return false ; } if (rank[fx] < rank[fy]) { int temp = fx; fx = fy; fy = temp; } rank[fx] += rank[fy]; f[fy] = fx; return true ; } } class BIT { int [] tree; int [] idRec; int n; public BIT (int n) { this .n = n; this .tree = new int [n]; Arrays.fill(this .tree, Integer.MAX_VALUE); this .idRec = new int [n]; Arrays.fill(this .idRec, -1 ); } public int lowbit (int k) { return k & (-k); } public void update (int pos, int val, int id) { while (pos > 0 ) { if (tree[pos] > val) { tree[pos] = val; idRec[pos] = id; } pos -= lowbit(pos); } } public int query (int pos) { int minval = Integer.MAX_VALUE; int j = -1 ; while (pos < n) { if (minval > tree[pos]) { minval = tree[pos]; j = idRec[pos]; } pos += lowbit(pos); } return j; } } class Edge { int len, x, y; public Edge (int len, int x, int y) { this .len = len; this .x = x; this .y = y; } } class Pos { int id, x, y; public Pos (int id, int x, int y) { this .id = id; this .x = x; this .y = y; } }
[sol2-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 type unionFind struct { parent, rank []int } func newUnionFind (n int ) parent := make ([]int , n) rank := make ([]int , n) for i := range parent { parent[i] = i rank[i] = 1 } return &unionFind{parent, rank} } func (uf *unionFind) int ) int { if uf.parent[x] != x { uf.parent[x] = uf.find(uf.parent[x]) } return uf.parent[x] } func (uf *unionFind) int ) bool { fx, fy := uf.find(x), uf.find(y) if fx == fy { return false } if uf.rank[fx] < uf.rank[fy] { fx, fy = fy, fx } uf.rank[fx] += uf.rank[fy] uf.parent[fy] = fx return true } type fenwickTree struct { tree, idRec []int } func newFenwickTree (n int ) tree := make ([]int , n) idRec := make ([]int , n) for i := range tree { tree[i], idRec[i] = math.MaxInt64, -1 } return &fenwickTree{tree, idRec} } func (f *fenwickTree) int ) { for ; pos > 0 ; pos &= pos - 1 { if val < f.tree[pos] { f.tree[pos], f.idRec[pos] = val, id } } } func (f *fenwickTree) int ) int { minVal, minID := math.MaxInt64, -1 for ; pos < len (f.tree); pos += pos & -pos { if f.tree[pos] < minVal { minVal, minID = f.tree[pos], f.idRec[pos] } } return minID } func dist (p, q []int ) int { return abs(p[0 ]-q[0 ]) + abs(p[1 ]-q[1 ]) } func minCostConnectPoints (points [][]int ) int ) { n := len (points) for i, p := range points { points[i] = append (p, i) } type edge struct { v, w, dis int } edges := []edge{} build := func () sort.Slice(points, func (i, j int ) bool { a, b := points[i], points[j]; return a[0 ] < b[0 ] || a[0 ] == b[0 ] && a[1 ] < b[1 ] }) type pair struct { v, i int } ps := make ([]pair, n) for i, p := range points { ps[i] = pair{p[1 ] - p[0 ], i} } sort.Slice(ps, func (i, j int ) bool { return ps[i].v < ps[j].v }) kth := make ([]int , n) k := 1 kth[ps[0 ].i] = k for i := 1 ; i < n; i++ { if ps[i].v != ps[i-1 ].v { k++ } kth[ps[i].i] = k } t := newFenwickTree(k + 1 ) for i := n - 1 ; i >= 0 ; i-- { p := points[i] pos := kth[i] if j := t.query(pos); j != -1 { q := points[j] edges = append (edges, edge{p[2 ], q[2 ], dist(p, q)}) } t.update(pos, p[0 ]+p[1 ], i) } } build() for _, p := range points { p[0 ], p[1 ] = p[1 ], p[0 ] } build() for _, p := range points { p[0 ] = -p[0 ] } build() for _, p := range points { p[0 ], p[1 ] = p[1 ], p[0 ] } build() sort.Slice(edges, func (i, j int ) bool { return edges[i].dis < edges[j].dis }) uf := newUnionFind(n) left := n - 1 for _, e := range edges { if uf.union(e.v, e.w) { ans += e.dis left-- if left == 0 { break } } } return } func abs (x int ) int { if x < 0 { return -x } return x }
[sol2-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 class DisjointSetUnion : def __init__ (self, n ): self.n = n self.rank = [1 ] * n self.f = list (range (n)) def find (self, x: int ) -> int : if self.f[x] == x: return x self.f[x] = self.find(self.f[x]) return self.f[x] def unionSet (self, x: int , y: int ) -> bool : fx, fy = self.find(x), self.find(y) if fx == fy: return False if self.rank[fx] < self.rank[fy]: fx, fy = fy, fx self.rank[fx] += self.rank[fy] self.f[fy] = fx return True class BIT : def __init__ (self, n ): self.n = n self.tree = [float ("inf" )] * n self.idRec = [-1 ] * n self.lowbit = lambda x: x & (-x) def update (self, pos: int , val: int , identity: int ): while pos > 0 : if self.tree[pos] > val: self.tree[pos] = val self.idRec[pos] = identity pos -= self.lowbit(pos) def query (self, pos: int ) -> int : minval, j = float ("inf" ), -1 while pos < self.n: if minval > self.tree[pos]: minval = self.tree[pos] j = self.idRec[pos] pos += self.lowbit(pos) return j class Solution : def minCostConnectPoints (self, points: List [List [int ]] ) -> int : n = len (points) edges = list () def build (pos: List [Tuple [int , int , int ]] ): pos.sort() a = [y - x for (x, y, _) in pos] b = sorted (set (a)) num = len (b) bit = BIT(num + 1 ) for i in range (n - 1 , -1 , -1 ): poss = bisect.bisect(b, a[i]) j = bit.query(poss) if j != -1 : dis = abs (pos[i][0 ] - pos[j][0 ]) + abs (pos[i][1 ] - pos[j][1 ]) edges.append((dis, pos[i][2 ], pos[j][2 ])) bit.update(poss, pos[i][0 ] + pos[i][1 ], i) def solve (): pos = [(x, y, i) for i, (x, y) in enumerate (points)] build(pos) pos = [(y, x, i) for i, (x, y) in enumerate (points)] build(pos) pos = [(-y, x, i) for i, (x, y) in enumerate (points)] build(pos) pos = [(x, -y, i) for i, (x, y) in enumerate (points)] build(pos) solve() dsu = DisjointSetUnion(n) edges.sort() ret, num = 0 , 1 for length, x, y in edges: if dsu.unionSet(x, y): ret += length num += 1 if num == n: break return ret
复杂度分析
 {:width=”80%”}
{:width=”80%”}