给你一个数组 pairs ,其中 pairs[i] = [xi, yi] ,并且满足:
令 ways 为满足下面条件的有根树的方案数:
树所包含的所有节点值都在 pairs 中。
一个数对 [xi, yi] 出现在 pairs 中 当且仅当 ****xi 是 yi 的祖先或者 yi 是 xi 的祖先。
注意: 构造出来的树不一定是二叉树。
两棵树被视为不同的方案当存在至少一个节点在两棵树中有不同的父节点。
请你返回:
如果 ways == 0 ,返回 0 。
如果 ways == 1 ,返回 1 。
如果 ways > 1 ,返回 2 。
一棵 有根树 指的是只有一个根节点的树,所有边都是从根往外的方向。
我们称从根到一个节点路径上的任意一个节点(除去节点本身)都是该节点的 祖先 。根节点没有祖先。
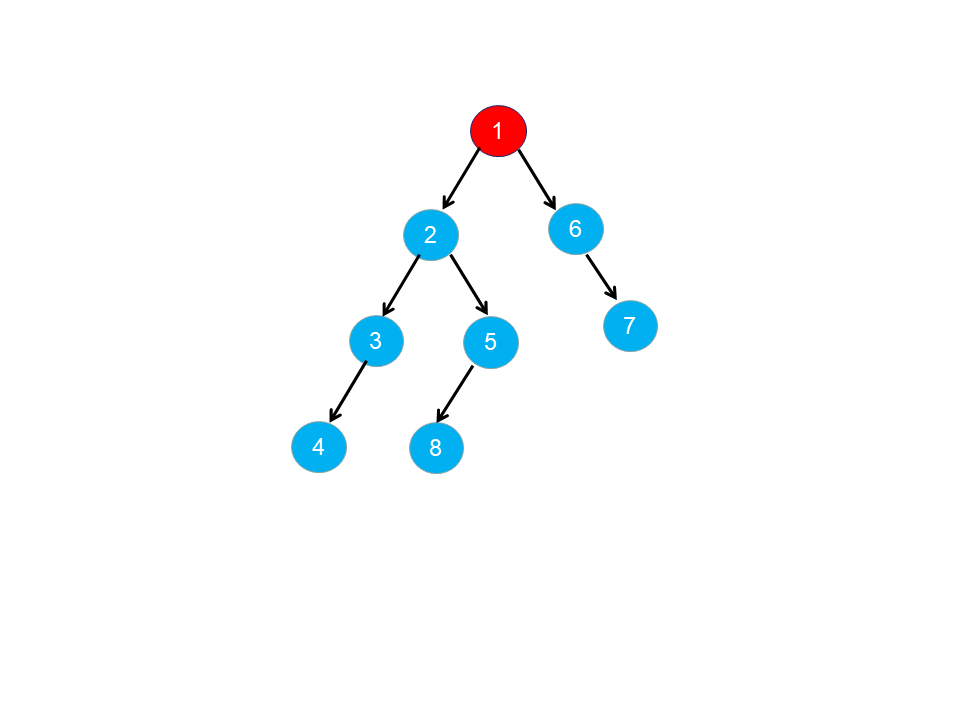
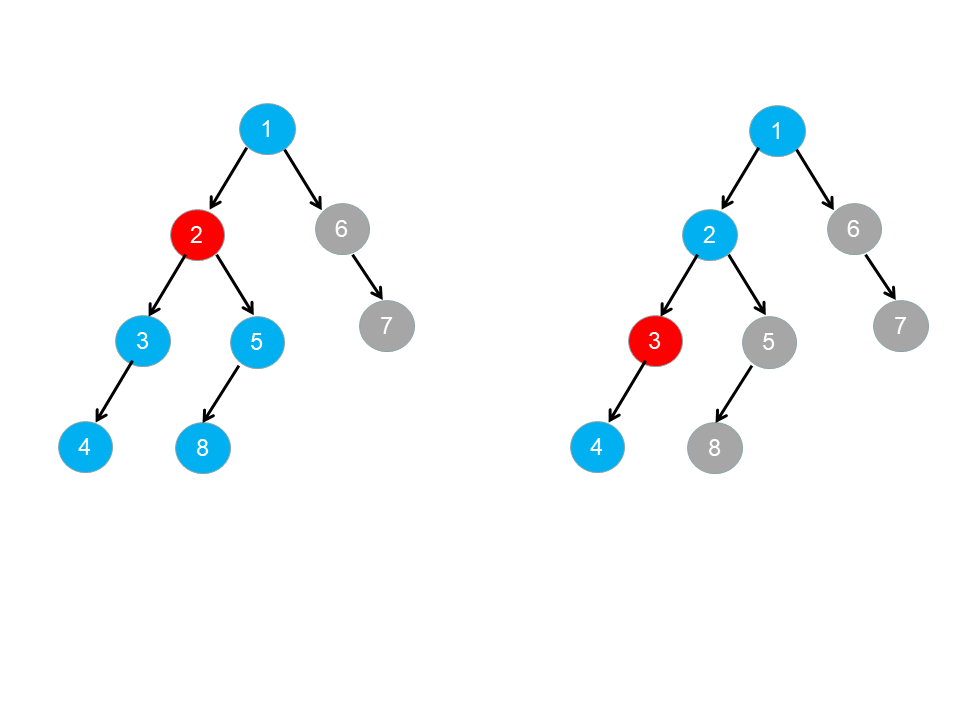
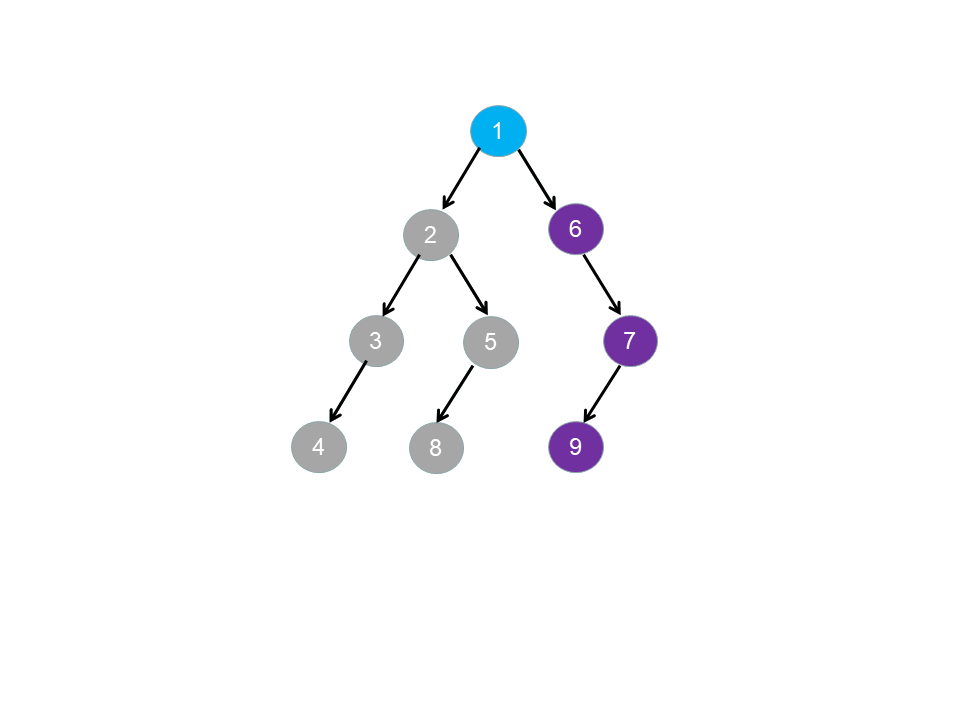
示例 1:
 -> int : adj = defaultdict(set ) for x, y in pairs: adj[x].add(y) adj[y].add(x) root = next ((node for node, neighbours in adj.items() if len (neighbours) == len (adj) - 1 ), -1 ) if root == -1 : return 0 ans = 1 for node, neighbours in adj.items(): if node == root: continue currDegree = len (neighbours) parent = -1 parentDegree = maxsize for neighbour in neighbours: if currDegree <= len (adj[neighbour]) < parentDegree: parent = neighbour parentDegree = len (adj[neighbour]) if parent == -1 or any (neighbour != parent and neighbour not in adj[parent] for neighbour in neighbours): return 0 if parentDegree == currDegree: ans = 2 return ans
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 class Solution {public : int checkWays (vector<vector<int >>& pairs) unordered_map<int , unordered_set<int >> adj; for (auto &p : pairs) { adj[p[0 ]].emplace (p[1 ]); adj[p[1 ]].emplace (p[0 ]); } int root = -1 ; for (auto &[node, neighbours] : adj) { if (neighbours.size () == adj.size () - 1 ) { root = node; break ; } } if (root == -1 ) { return 0 ; } int res = 1 ; for (auto &[node, neighbours] : adj) { if (node == root) { continue ; } int currDegree = neighbours.size (); int parent = -1 ; int parentDegree = INT_MAX; for (auto &neighbour : neighbours) { if (adj[neighbour].size () < parentDegree && adj[neighbour].size () >= currDegree) { parent = neighbour; parentDegree = adj[neighbour].size (); } } if (parent == -1 ) { return 0 ; } for (auto &neighbour : neighbours) { if (neighbour == parent) { continue ; } if (!adj[parent].count (neighbour)) { return 0 ; } } if (parentDegree == currDegree) { res = 2 ; } } return res; } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 class Solution { public int checkWays (int [][] pairs) { Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> adj = new HashMap <Integer, Set<Integer>>(); for (int [] p : pairs) { adj.putIfAbsent(p[0 ], new HashSet <Integer>()); adj.putIfAbsent(p[1 ], new HashSet <Integer>()); adj.get(p[0 ]).add(p[1 ]); adj.get(p[1 ]).add(p[0 ]); } int root = -1 ; Set<Map.Entry<Integer, Set<Integer>>> entries = adj.entrySet(); for (Map.Entry<Integer, Set<Integer>> entry : entries) { int node = entry.getKey(); Set<Integer> neighbours = entry.getValue(); if (neighbours.size() == adj.size() - 1 ) { root = node; } } if (root == -1 ) { return 0 ; } int res = 1 ; for (Map.Entry<Integer, Set<Integer>> entry : entries) { int node = entry.getKey(); Set<Integer> neighbours = entry.getValue(); if (node == root) { continue ; } int currDegree = neighbours.size(); int parent = -1 ; int parentDegree = Integer.MAX_VALUE; for (int neighbour : neighbours) { if (adj.get(neighbour).size() < parentDegree && adj.get(neighbour).size() >= currDegree) { parent = neighbour; parentDegree = adj.get(neighbour).size(); } } if (parent == -1 ) { return 0 ; } for (int neighbour : neighbours) { if (neighbour == parent) { continue ; } if (!adj.get(parent).contains(neighbour)) { return 0 ; } } if (parentDegree == currDegree) { res = 2 ; } } return res; } }
[sol1-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 public class Solution { public int CheckWays (int [][] pairs Dictionary<int , ISet<int >> adj = new Dictionary<int , ISet<int >>(); foreach (int [] p in pairs) { if (!adj.ContainsKey(p[0 ])) { adj.Add(p[0 ], new HashSet<int >()); } if (!adj.ContainsKey(p[1 ])) { adj.Add(p[1 ], new HashSet<int >()); } adj[p[0 ]].Add(p[1 ]); adj[p[1 ]].Add(p[0 ]); } int root = -1 ; foreach (KeyValuePair<int , ISet<int >> pair in adj) { int node = pair.Key; ISet<int > neighbours = pair.Value; if (neighbours.Count == adj.Count - 1 ) { root = node; } } if (root == -1 ) { return 0 ; } int res = 1 ; foreach (KeyValuePair<int , ISet<int >> pair in adj) { int node = pair.Key; ISet<int > neighbours = pair.Value; if (node == root) { continue ; } int currDegree = neighbours.Count; int parent = -1 ; int parentDegree = int .MaxValue; foreach (int neighbour in neighbours) { if (adj[neighbour].Count < parentDegree && adj[neighbour].Count >= currDegree) { parent = neighbour; parentDegree = adj[neighbour].Count; } } if (parent == -1 ) { return 0 ; } foreach (int neighbour in neighbours) { if (neighbour == parent) { continue ; } if (!adj[parent].Contains(neighbour)) { return 0 ; } } if (parentDegree == currDegree) { res = 2 ; } } return res; } }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 typedef struct { int key; UT_hash_handle hh; } HashEntry; void hashInsert (HashEntry ** obj, int key) { HashEntry * pEntry = NULL ; HASH_FIND(hh, *obj, &key, sizeof (int ), pEntry); if (NULL == pEntry) { pEntry = (HashEntry *)malloc (sizeof (HashEntry)); pEntry->key = key; HASH_ADD(hh, *obj, key, sizeof (int ), pEntry); } } bool hashFind (HashEntry ** obj, int key) { HashEntry * pEntry = NULL ; HASH_FIND(hh, *obj, &key, sizeof (int ), pEntry); if (NULL == pEntry) { return false ; } else { return true ; } } void hashFreeAll (HashEntry ** obj) { HashEntry *curr, *next; HASH_ITER(hh, *obj, curr, next) { HASH_DEL(*obj, curr); free (curr); } } #define MAX_NODE_SIZE 501 int checkWays (int ** pairs, int pairsSize, int * pairsColSize) { HashEntry * adj[MAX_NODE_SIZE]; memset (adj, 0 , sizeof (HashEntry *) * MAX_NODE_SIZE); for (int i = 0 ; i < pairsSize; i++) { hashInsert(&adj[pairs[i][0 ]], pairs[i][1 ]); hashInsert(&adj[pairs[i][1 ]], pairs[i][0 ]); } int nodeSize = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < MAX_NODE_SIZE; i++) { if (NULL != adj[i]) { nodeSize++; } } int root = -1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < MAX_NODE_SIZE; i++) { unsigned int degree = HASH_COUNT(adj[i]); if (degree == nodeSize - 1 ) { root = i; break ; } } if (root == -1 ) { return 0 ; } int res = 1 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < MAX_NODE_SIZE; i++) { if (root == i || NULL == adj[i]) { continue ; } int currDegree = HASH_COUNT(adj[i]); int parent = -1 ; int parentDegree = INT_MAX; HashEntry *curr = NULL , *next = NULL ; HASH_ITER(hh, adj[i], curr, next) { if (HASH_COUNT(adj[curr->key]) < parentDegree && HASH_COUNT(adj[curr->key]) >= currDegree) { parent = curr->key; parentDegree = HASH_COUNT(adj[curr->key]); } } if (parent == -1 ) { return 0 ; } HASH_ITER(hh, adj[i], curr, next) { if (curr->key == parent) { continue ; } if (!hashFind(&adj[parent], curr->key)) { return 0 ; } } if (parentDegree == currDegree) { res = 2 ; } } for (int i = 0 ; i < MAX_NODE_SIZE; i++) { hashFreeAll(&adj[i]); } return res; }
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 var checkWays = function (pairs ) { const adj = new Map (); for (const p of pairs) { if (!adj.has (p[0 ])) { adj.set (p[0 ], new Set ()); } if (!adj.has (p[1 ])) { adj.set (p[1 ], new Set ()); } adj.get (p[0 ]).add (p[1 ]); adj.get (p[1 ]).add (p[0 ]); } let root = -1 ; const entries = new Set (); for (const entry of adj.entries ()) { entries.add (entry); } for (const [node, neg] of entries) { if (neg.size === adj.size - 1 ) { root = node; } } if (root === -1 ) { return 0 ; } let res = 1 ; for (const [node, neg] of entries) { if (root === node) { continue ; } const currDegree = neg.size ; let parentNode = -1 ; let parentDegree = Number .MAX_SAFE_INTEGER ; for (const neighbour of neg) { if (adj.has (neighbour) && adj.get (neighbour).size < parentDegree && adj.get (neighbour).size >= currDegree) { parentNode = neighbour; parentDegree = adj.get (neighbour).size ; } } if (parentNode === -1 ) { return 0 ; } for (const neighbour of neg) { if (neighbour === parentNode) { continue ; } if (!adj.get (parentNode).has (neighbour)) { return 0 ; } } if (parentDegree === currDegree) { res = 2 ; } } return res; };
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 func checkWays (pairs [][]int ) int { adj := map [int ]map [int ]bool {} for _, p := range pairs { x, y := p[0 ], p[1 ] if adj[x] == nil { adj[x] = map [int ]bool {} } adj[x][y] = true if adj[y] == nil { adj[y] = map [int ]bool {} } adj[y][x] = true } root := -1 for node, neighbours := range adj { if len (neighbours) == len (adj)-1 { root = node break } } if root == -1 { return 0 } ans := 1 for node, neighbours := range adj { if node == root { continue } currDegree := len (neighbours) parent := -1 parentDegree := math.MaxInt32 for neighbour := range neighbours { if len (adj[neighbour]) < parentDegree && len (adj[neighbour]) >= currDegree { parent = neighbour parentDegree = len (adj[neighbour]) } } if parent == -1 { return 0 } for neighbour := range neighbours { if neighbour != parent && !adj[parent][neighbour] { return 0 } } if parentDegree == currDegree { ans = 2 } } return ans }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(m + n^2),其中 n 为树中节点的数目,m 表示数组 pairs 的长度。需要遍历 pairs ,时间复杂度为 O(m),然后遍历所有的节点,检测每个节点的父节点对应的集合是否包含当前节点的对应的集合,集合中最多有 n 个元素,时间复杂度为 O(n^2),因此总的时间复杂度为 O(m + n^2)。
空间复杂度:O(m),m 表示数组 pairs 的长度。需要 O(m) 的空间来存储节点对应的集合关系。