给你一个二维整数数组 orders ,其中每个 orders[i] = [pricei, amounti, orderTypei] 表示有
amounti 笔类型为 orderTypei 、价格为 pricei 的订单。
订单类型 orderTypei 可以分为两种:
0 表示这是一批采购订单 buy1 表示这是一批销售订单 sell
注意,orders[i] 表示一批共计 amounti 笔的独立订单,这些订单的价格和类型相同。对于所有有效的 i ,由 orders[i]
表示的所有订单提交时间均早于 orders[i+1] 表示的所有订单。
存在由未执行订单组成的 积压订单 。积压订单最初是空的。提交订单时,会发生以下情况:
- 如果该订单是一笔采购订单
buy ,则可以查看积压订单中价格 最低 的销售订单 sell 。如果该销售订单 sell 的价格 低于或等于 当前采购订单 buy 的价格,则匹配并执行这两笔订单,并将销售订单 sell 从积压订单中删除。否则,采购订单 buy 将会添加到积压订单中。
- 反之亦然,如果该订单是一笔销售订单
sell ,则可以查看积压订单中价格 最高 的采购订单 buy 。如果该采购订单 buy 的价格 高于或等于 当前销售订单 sell 的价格,则匹配并执行这两笔订单,并将采购订单 buy 从积压订单中删除。否则,销售订单 sell 将会添加到积压订单中。
输入所有订单后,返回积压订单中的 订单总数 。由于数字可能很大,所以需要返回对 109 + 7 取余的结果。
示例 1:
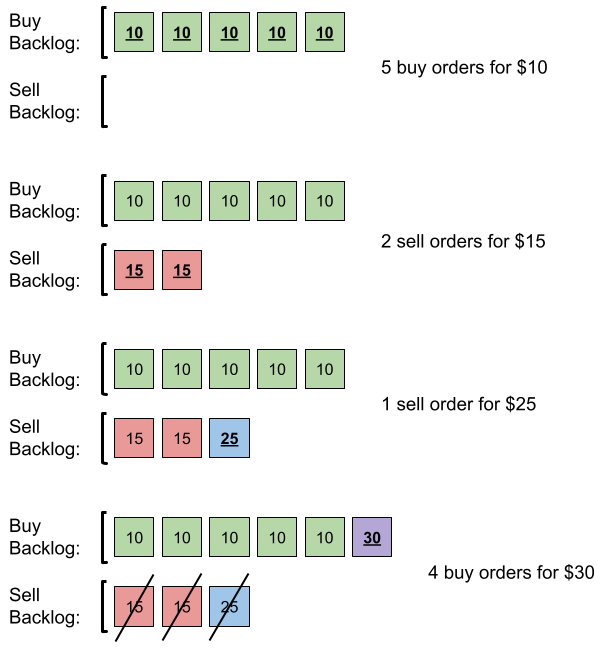
**输入:** orders = [[10,5,0],[15,2,1],[25,1,1],[30,4,0]]
**输出:** 6
**解释:** 输入订单后会发生下述情况:
- 提交 5 笔采购订单,价格为 10 。没有销售订单,所以这 5 笔订单添加到积压订单中。
- 提交 2 笔销售订单,价格为 15 。没有采购订单的价格大于或等于 15 ,所以这 2 笔订单添加到积压订单中。
- 提交 1 笔销售订单,价格为 25 。没有采购订单的价格大于或等于 25 ,所以这 1 笔订单添加到积压订单中。
- 提交 4 笔采购订单,价格为 30 。前 2 笔采购订单与价格最低(价格为 15)的 2 笔销售订单匹配,从积压订单中删除这 2 笔销售订单。第 3 笔采购订单与价格最低的 1 笔销售订单匹配,销售订单价格为 25 ,从积压订单中删除这 1 笔销售订单。积压订单中不存在更多销售订单,所以第 4 笔采购订单需要添加到积压订单中。
最终,积压订单中有 5 笔价格为 10 的采购订单,和 1 笔价格为 30 的采购订单。所以积压订单中的订单总数为 6 。
示例 2:
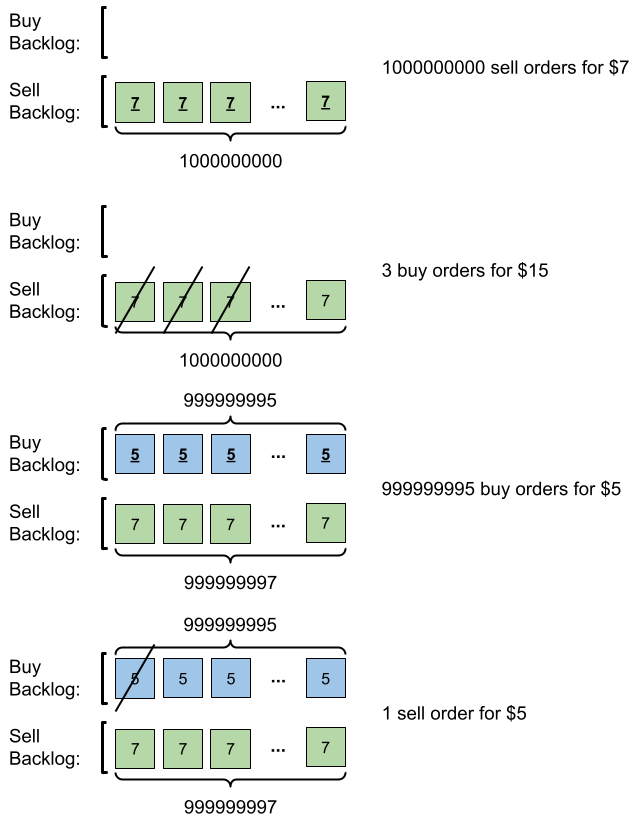
**输入:** orders = [[7,1000000000,1],[15,3,0],[5,999999995,0],[5,1,1]]
**输出:** 999999984
**解释:** 输入订单后会发生下述情况:
- 提交 109 笔销售订单,价格为 7 。没有采购订单,所以这 109 笔订单添加到积压订单中。
- 提交 3 笔采购订单,价格为 15 。这些采购订单与价格最低(价格为 7 )的 3 笔销售订单匹配,从积压订单中删除这 3 笔销售订单。
- 提交 999999995 笔采购订单,价格为 5 。销售订单的最低价为 7 ,所以这 999999995 笔订单添加到积压订单中。
- 提交 1 笔销售订单,价格为 5 。这笔销售订单与价格最高(价格为 5 )的 1 笔采购订单匹配,从积压订单中删除这 1 笔采购订单。
最终,积压订单中有 (1000000000-3) 笔价格为 7 的销售订单,和 (999999995-1) 笔价格为 5 的采购订单。所以积压订单中的订单总数为 1999999991 ,等于 999999984 % (109 + 7) 。
提示:
1 <= orders.length <= 105orders[i].length == 31 <= pricei, amounti <= 109orderTypei 为 0 或 1
方法一:优先队列模拟
根据题意,需要遍历数组 orders 中的订单并依次处理。对于遍历到的每个订单,需要找到类型相反的积压订单,如果可以匹配则执行这两笔订单并将积压订单删除,否则将当前订单添加到积压订单中。
由于寻找已有的积压订单时,需要寻找价格最高的采购订单或者价格最低的销售订单,因此可以使用两个优先队列分别存储积压的采购订单和积压的销售订单,两个优先队列称为采购订单优先队列和销售订单优先队列,分别满足队首元素是价格最高的采购订单和价格最低的销售订单。
遍历数组 orders,对于 order} = [\textit{price}, \textit{amount}, \textit{orderType}],执行如下操作。
如果 orderType} = 0,则表示 amount 个价格为 price 的采购订单,需要将这些采购订单和积压的销售订单匹配并执行。当销售订单优先队列中存在价格小于等于 price 的销售订单时,将当前采购订单和积压的销售订单匹配并执行,直到当前采购订单全部匹配执行、积压的销售订单全部匹配执行或者剩余积压的销售订单的价格都大于 price。如果还有剩余的当前采购订单尚未匹配执行,则将剩余的采购订单添加到采购订单优先队列中。
如果 orderType} = 1,则表示 amount 个价格为 price 的销售订单,需要将这些销售订单和积压的采购订单匹配并执行。当采购订单优先队列中存在价格大于等于 price 的采购订单时,将当前销售订单和积压的采购订单匹配并执行,直到当前销售订单全部匹配执行、积压的采购订单全部匹配执行或者剩余积压的采购订单的价格都小于 price。如果还有剩余的当前销售订单尚未匹配执行,则将剩余的销售订单添加到销售订单优先队列中。
遍历数组 orders 之后,两个优先队列中剩余的元素表示输入所有订单之后的积压订单,计算两个优先队列中剩余的订单总数并返回。
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
| class Solution:
def getNumberOfBacklogOrders(self, orders: List[List[int]]) -> int:
MOD = 10 ** 9 + 7
buyOrders, sellOrders = [], []
for price, amount, type in orders:
if type == 0:
while amount and sellOrders and sellOrders[0][0] <= price:
if sellOrders[0][1] > amount:
sellOrders[0][1] -= amount
amount = 0
break
amount -= heappop(sellOrders)[1]
if amount:
heappush(buyOrders, [-price, amount])
else:
while amount and buyOrders and -buyOrders[0][0] >= price:
if buyOrders[0][1] > amount:
buyOrders[0][1] -= amount
amount = 0
break
amount -= heappop(buyOrders)[1]
if amount:
heappush(sellOrders, [price, amount])
return (sum(x for _, x in buyOrders) + sum(x for _, x in sellOrders)) % MOD
|
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| class Solution {
public int getNumberOfBacklogOrders(int[][] orders) {
final int MOD = 1000000007;
PriorityQueue<int[]> buyOrders = new PriorityQueue<int[]>((a, b) -> b[0] - a[0]);
PriorityQueue<int[]> sellOrders = new PriorityQueue<int[]>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
for (int[] order : orders) {
int price = order[0], amount = order[1], orderType = order[2];
if (orderType == 0) {
while (amount > 0 && !sellOrders.isEmpty() && sellOrders.peek()[0] <= price) {
int[] sellOrder = sellOrders.poll();
int sellAmount = Math.min(amount, sellOrder[1]);
amount -= sellAmount;
sellOrder[1] -= sellAmount;
if (sellOrder[1] > 0) {
sellOrders.offer(sellOrder);
}
}
if (amount > 0) {
buyOrders.offer(new int[]{price, amount});
}
} else {
while (amount > 0 && !buyOrders.isEmpty() && buyOrders.peek()[0] >= price) {
int[] buyOrder = buyOrders.poll();
int buyAmount = Math.min(amount, buyOrder[1]);
amount -= buyAmount;
buyOrder[1] -= buyAmount;
if (buyOrder[1] > 0) {
buyOrders.offer(buyOrder);
}
}
if (amount > 0) {
sellOrders.offer(new int[]{price, amount});
}
}
}
int total = 0;
for (PriorityQueue<int[]> pq : Arrays.asList(buyOrders, sellOrders)) {
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
int[] order = pq.poll();
total = (total + order[1]) % MOD;
}
}
return total;
}
}
|
[sol1-C#]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| public class Solution {
public int GetNumberOfBacklogOrders(int[][] orders) {
const int MOD = 1000000007;
PriorityQueue<int[], int> buyOrders = new PriorityQueue<int[], int>();
PriorityQueue<int[], int> sellOrders = new PriorityQueue<int[], int>();
foreach (int[] order in orders) {
int price = order[0], amount = order[1], orderType = order[2];
if (orderType == 0) {
while (amount > 0 && sellOrders.Count > 0 && sellOrders.Peek()[0] <= price) {
int[] sellOrder = sellOrders.Dequeue();
int sellAmount = Math.Min(amount, sellOrder[1]);
amount -= sellAmount;
sellOrder[1] -= sellAmount;
if (sellOrder[1] > 0) {
sellOrders.Enqueue(sellOrder, sellOrder[0]);
}
}
if (amount > 0) {
buyOrders.Enqueue(new int[]{price, amount}, -price);
}
} else {
while (amount > 0 && buyOrders.Count > 0 && buyOrders.Peek()[0] >= price) {
int[] buyOrder = buyOrders.Dequeue();
int buyAmount = Math.Min(amount, buyOrder[1]);
amount -= buyAmount;
buyOrder[1] -= buyAmount;
if (buyOrder[1] > 0) {
buyOrders.Enqueue(buyOrder, -buyOrder[0]);
}
}
if (amount > 0) {
sellOrders.Enqueue(new int[]{price, amount}, price);
}
}
}
int total = 0;
foreach (PriorityQueue<int[], int> pq in new PriorityQueue<int[], int>[]{buyOrders, sellOrders}) {
while (pq.Count > 0) {
int[] order = pq.Dequeue();
total = (total + order[1]) % MOD;
}
}
return total;
}
}
|
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| class Solution {
public:
int getNumberOfBacklogOrders(vector<vector<int>>& orders) {
const int MOD = 1000000007;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, less<pair<int, int>>> buyOrders;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> sellOrders;
for (auto &&order : orders) {
int price = order[0], amount = order[1], orderType = order[2];
if (orderType == 0) {
while (amount > 0 && !sellOrders.empty() && sellOrders.top().first <= price) {
auto sellOrder = sellOrders.top();
sellOrders.pop();
int sellAmount = min(amount, sellOrder.second);
amount -= sellAmount;
sellOrder.second -= sellAmount;
if (sellOrder.second > 0) {
sellOrders.push(sellOrder);
}
}
if (amount > 0) {
buyOrders.emplace(price, amount);
}
} else {
while (amount > 0 && !buyOrders.empty() && buyOrders.top().first >= price) {
auto buyOrder = buyOrders.top();
buyOrders.pop();
int buyAmount = min(amount, buyOrder.second);
amount -= buyAmount;
buyOrder.second -= buyAmount;
if (buyOrder.second > 0) {
buyOrders.push(buyOrder);
}
}
if (amount > 0) {
sellOrders.emplace(price, amount);
}
}
}
int total = 0;
while (!buyOrders.empty()) {
total = (total + buyOrders.top().second) % MOD;
buyOrders.pop();
}
while (!sellOrders.empty()) {
total = (total + sellOrders.top().second) % MOD;
sellOrders.pop();
}
return total;
}
};
|
[sol1-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| func getNumberOfBacklogOrders(orders [][]int) (ans int) {
buyOrders, sellOrders := hp{}, hp2{}
for _, o := range orders {
price, amount := o[0], o[1]
if o[2] == 0 {
for amount > 0 && len(sellOrders) > 0 && sellOrders[0].price <= price {
if sellOrders[0].left > amount {
sellOrders[0].left -= amount
amount = 0
break
}
amount -= heap.Pop(&sellOrders).(pair).left
}
if amount > 0 {
heap.Push(&buyOrders, pair{price, amount})
}
} else {
for amount > 0 && len(buyOrders) > 0 && buyOrders[0].price >= price {
if buyOrders[0].left > amount {
buyOrders[0].left -= amount
amount = 0
break
}
amount -= heap.Pop(&buyOrders).(pair).left
}
if amount > 0 {
heap.Push(&sellOrders, pair{price, amount})
}
}
}
for _, p := range buyOrders {
ans += p.left
}
for _, p := range sellOrders {
ans += p.left
}
return ans % (1e9 + 7)
}
type pair struct{ price, left int }
type hp []pair
func (h hp) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h hp) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].price > h[j].price }
func (h hp) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *hp) Push(v interface{}) { *h = append(*h, v.(pair)) }
func (h *hp) Pop() interface{} { a := *h; v := a[len(a)-1]; *h = a[:len(a)-1]; return v }
type hp2 []pair
func (h hp2) Len() int { return len(h) }
func (h hp2) Less(i, j int) bool { return h[i].price < h[j].price }
func (h hp2) Swap(i, j int) { h[i], h[j] = h[j], h[i] }
func (h *hp2) Push(v interface{}) { *h = append(*h, v.(pair)) }
func (h *hp2) Pop() interface{} { a := *h; v := a[len(a)-1]; *h = a[:len(a)-1]; return v }
|
复杂度分析