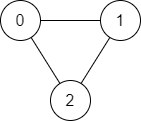
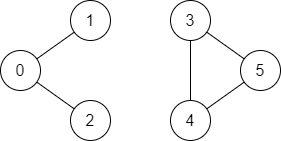
有一个具有 n 个顶点的 双向 图,其中每个顶点标记从 0 到 n - 1(包含 0 和 n - 1)。图中的边用一个二维整数数组 edges 表示,其中 edges[i] = [ui, vi] 表示顶点 ui 和顶点 vi最多一条 边连接,并且没有顶点存在与自身相连的边。
请你确定是否存在从顶点 source 开始,到顶点 destination 结束的 有效路径 。
给你数组 edges 和整数 n、source 和 destination,如果从 source 到 destination 存在有效路径 ,则返回 true,否则返回 false 。
示例 1:
**输入:** n = 3, edges = [[0,1],[1,2],[2,0]], source = 0, destination = 2
**输出:** true
**解释:** 存在由顶点 0 到顶点 2 的路径:
- 0 → 1 → 2
- 0 → 2
示例 2:
**输入:** n = 6, edges = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,5],[5,4],[4,3]], source = 0, destination = 5
**输出:** false
**解释:** 不存在由顶点 0 到顶点 5 的路径.
提示:
1 <= n <= 2 * 1050 <= edges.length <= 2 * 105edges[i].length == 20 <= ui, vi <= n - 1ui != vi0 <= source, destination <= n - 1不存在重复边
不存在指向顶点自身的边
前言 题目要求判断是否存在从起点 source 到终点 destination 的有效路径,等价于求图中两个顶点 source},\textit{destination 是否连通。两点连通性问题为经典问题,一般我们可以使用广度优先搜索或深度优先搜索,以及并查集来解决。
方法一:广度优先搜索 思路与算法
使用广度优先搜索判断顶点 source 到顶点 destination 的连通性,需要我们从顶点 source 开始按照层次依次遍历每一层的顶点,检测是否可以到达顶点 destination。遍历过程我们使用队列存储最近访问过的顶点,同时记录每个顶点的访问状态,每次从队列中取出顶点 vertex 时,将其未访问过的邻接顶点入队列。
初始时将顶点 source 设为已访问,并将其入队列。每次将队列中的节点 vertex 出队列,并将与 vertex 相邻且未访问的顶点 next 入队列,并将 next 设为已访问。当队列为空或访问到顶点 destination 时遍历结束,返回顶点 destination 的访问状态即可。
代码
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 class Solution {public : bool validPath (int n, vector<vector<int >>& edges, int source, int destination) vector<vector<int >> adj (n); for (auto &&edge : edges) { int x = edge[0 ], y = edge[1 ]; adj[x].emplace_back (y); adj[y].emplace_back (x); } vector<bool > visited (n, false ) ; queue<int > qu; qu.emplace (source); visited[source] = true ; while (!qu.empty ()) { int vertex = qu.front (); qu.pop (); if (vertex == destination) { break ; } for (int next: adj[vertex]) { if (!visited[next]) { qu.emplace (next); visited[next] = true ; } } } return visited[destination]; } };
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 class Solution { public boolean validPath (int n, int [][] edges, int source, int destination) { List<Integer>[] adj = new List [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { adj[i] = new ArrayList <Integer>(); } for (int [] edge : edges) { int x = edge[0 ], y = edge[1 ]; adj[x].add(y); adj[y].add(x); } boolean [] visited = new boolean [n]; Queue<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque <Integer>(); queue.offer(source); visited[source] = true ; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { int vertex = queue.poll(); if (vertex == destination) { break ; } for (int next : adj[vertex]) { if (!visited[next]) { queue.offer(next); visited[next] = true ; } } } return visited[destination]; } }
[sol1-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public class Solution { public bool ValidPath (int n, int [][] edges, int source, int destination IList<int >[] adj = new IList<int >[n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { adj[i] = new List<int >(); } foreach (int [] edge in edges) { int x = edge[0 ], y = edge[1 ]; adj[x].Add(y); adj[y].Add(x); } bool [] visited = new bool [n]; Queue<int > queue = new Queue<int >(); queue.Enqueue(source); visited[source] = true ; while (queue.Count > 0 ) { int vertex = queue.Dequeue(); if (vertex == destination) { break ; } foreach (int next in adj[vertex]) { if (!visited[next]) { queue.Enqueue(next); visited[next] = true ; } } } return visited[destination]; } }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 struct ListNode *creatListNode (int val) { struct ListNode *node =struct ListNode *)malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode)); node->val = val; node->next = NULL ; return node; } bool validPath (int n, int ** edges, int edgesSize, int * edgesColSize, int source, int destination) { struct ListNode * adj [n ]; bool visited[n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { adj[i] = NULL ; visited[i] = false ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < edgesSize; i++) { int x = edges[i][0 ], y = edges[i][1 ]; struct ListNode *nodex = nodex->next = adj[y]; adj[y] = nodex; struct ListNode *nodey = nodey->next = adj[x]; adj[x] = nodey; } int queue [n]; int head = 0 , tail = 0 ; queue [tail++] = source; visited[source] = true ; while (head != tail) { int vertex = queue [head++]; if (vertex == destination) { break ; } for (struct ListNode *p = adj[vertex]; p != NULL ; p = p->next) { int next = p->val; if (!visited[next]) { queue [tail++] = next; visited[next] = true ; } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (struct ListNode *p = adj[i]; p != NULL ;) { struct ListNode *cur = p = p->next; free (cur); } } return visited[destination]; }
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 var validPath = function (n, edges, source, destination ) { const adj = new Array (n).fill (0 ).map (() => new Array ()); for (const edge of edges) { const x = edge[0 ], y = edge[1 ]; adj[x].push (y); adj[y].push (x); } const visited = new Array (n).fill (false ); const queue = [source]; visited[source] = true ; while (queue.length ) { const vertex = queue.shift (); if (vertex === destination) { break ; } for (const next of adj[vertex]) { if (!visited[next]) { queue.push (next); visited[next] = true ; } } } return visited[destination]; };
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n + m),其中 n 表示图中顶点的数目,m 表示图中边的数目。对于图中的每个顶点或者每条边,我们最多只需访问一次,因此时间复杂度为 O(n + m)。
空间复杂度:O(n + m),其中 n 表示图中顶点的数目,m 表示图中边的数目。空间复杂度主要取决于邻接顶点列表、记录每个顶点访问状态的数组和队列,邻接顶点列表需要的空间为 O(n + m),记录访问状态需要 O(n) 的空间,进行广度优先搜索时队列中最多只有 n 个元素,因此总的空间复杂度为 (n + m)。
方法二:深度优先搜索 思路与算法
我们使用深度优先搜索检测顶点 source},\textit{destination 的连通性,需要从顶点 source 开始依次遍历每一条可能的路径,判断可以到达顶点 destination,同时还需要记录每个顶点的访问状态防止重复访问。
首先从顶点 source 开始遍历并进行递归搜索。搜索时每次访问一个顶点 vertex 时,如果 vertex 等于 destination 则直接返回,否则将该顶点设为已访问,并递归访问与 vertex 相邻且未访问的顶点 next。如果通过 next 的路径可以访问到 destination,此时直接返回 true,当访问完所有的邻接节点仍然没有访问到 destination,此时返回 false。
代码
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 class Solution {public : bool dfs (int source, int destination, vector<vector<int >> &adj, vector<bool > &visited) if (source == destination) { return true ; } visited[source] = true ; for (int next : adj[source]) { if (!visited[next] && dfs (next, destination, adj, visited)) { return true ; } } return false ; } bool validPath (int n, vector<vector<int >>& edges, int source, int destination) vector<vector<int >> adj (n); for (auto &edge : edges) { int x = edge[0 ], y = edge[1 ]; adj[x].emplace_back (y); adj[y].emplace_back (x); } vector<bool > visited (n, false ) ; return dfs (source, destination, adj, visited); } };
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 class Solution { public boolean validPath (int n, int [][] edges, int source, int destination) { List<Integer>[] adj = new List [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { adj[i] = new ArrayList <Integer>(); } for (int [] edge : edges) { int x = edge[0 ], y = edge[1 ]; adj[x].add(y); adj[y].add(x); } boolean [] visited = new boolean [n]; return dfs(source, destination, adj, visited); } public boolean dfs (int source, int destination, List<Integer>[] adj, boolean [] visited) { if (source == destination) { return true ; } visited[source] = true ; for (int next : adj[source]) { if (!visited[next] && dfs(next, destination, adj, visited)) { return true ; } } return false ; } }
[sol2-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 public class Solution { public bool ValidPath (int n, int [][] edges, int source, int destination IList<int >[] adj = new IList<int >[n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { adj[i] = new List<int >(); } foreach (int [] edge in edges) { int x = edge[0 ], y = edge[1 ]; adj[x].Add(y); adj[y].Add(x); } bool [] visited = new bool [n]; return DFS(source, destination, adj, visited); } public bool DFS (int source, int destination, IList<int >[] adj, bool [] visited if (source == destination) { return true ; } visited[source] = true ; foreach (int next in adj[source]) { if (!visited[next] && DFS(next, destination, adj, visited)) { return true ; } } return false ; } }
[sol2-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 struct ListNode *creatListNode (int val) { struct ListNode *node =struct ListNode *)malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode)); node->val = val; node->next = NULL ; return node; } bool dfs (int source, int destination, const struct ListNode **adj, bool *visited) { if (source == destination) { return true ; } visited[source] = true ; if (!visited[destination]) { for (struct ListNode *p = adj[source]; p != NULL ; p = p->next) { if (!visited[p->val] && dfs(p->val, destination, adj, visited)) { return true ; } } } return false ; } bool validPath (int n, int ** edges, int edgesSize, int * edgesColSize, int source, int destination) { struct ListNode * adj [n ]; bool visited[n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { adj[i] = NULL ; visited[i] = false ; } for (int i = 0 ; i < edgesSize; i++) { int x = edges[i][0 ], y = edges[i][1 ]; struct ListNode *nodex = nodex->next = adj[y]; adj[y] = nodex; struct ListNode *nodey = nodey->next = adj[x]; adj[x] = nodey; } bool ret = dfs(source, destination, adj, visited); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { for (struct ListNode *p = adj[i]; p != NULL ;) { struct ListNode *cur = p = p->next; free (cur); } } return ret; }
[sol2-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 var validPath = function (n, edges, source, destination ) { const adj = new Array (n).fill (0 ).map (() => new Array ()); for (const edge of edges) { const x = edge[0 ], y = edge[1 ]; adj[x].push (y); adj[y].push (x); } const visited = new Array (n).fill (0 ); return dfs (source, destination, adj, visited); } const dfs = (source, destination, adj, visited ) => { if (source === destination) { return true ; } visited[source] = true ; for (const next of adj[source]) { if (!visited[next] && dfs (next, destination, adj, visited)) { return true ; } } return false ; };
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n + m),其中 n 表示图中顶点的数目,m 表示图中边的数目。对于图中的每个顶点或者每条边,我们最多只需访问一次,对于每个顶因此时间复杂度为 O(n + m)。
空间复杂度:O(n + m),其中 n 表示图中顶点的数目,m 表示图中边的数目。空间复杂度主要取决于邻接顶点列表、记录每个顶点访问状态的数组和递归调用栈,邻接顶点列表需要 O(m + n) 的存储空间,记录每个顶点访问状态的数组和递归调用栈分别需要 O(n) 的空间,因此总的空间复杂度为 O(m + n)。
方法三:并查集 思路与算法
我们将图中的每个强连通分量视为一个集合,强连通分量中任意两点均可达,如果两个点 source 和 destination 处在同一个强连通分量中,则两点一定可连通,因此连通性问题可以使用并查集解决。
并查集初始化时,n 个顶点分别属于 n 个不同的集合,每个集合只包含一个顶点。初始化之后遍历每条边,由于图中的每条边均为双向边,因此将同一条边连接的两个顶点所在的集合做合并。
遍历所有的边之后,判断顶点 source 和顶点 destination 是否在同一个集合中,如果两个顶点在同一个集合则两个顶点连通,如果两个顶点所在的集合不同则两个顶点不连通。
代码
[sol3-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 class UnionFind {public : UnionFind (int n) { parent = vector <int >(n); rank = vector <int >(n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { parent[i] = i; } } void uni (int x, int y) int rootx = find (x); int rooty = find (y); if (rootx != rooty) { if (rank[rootx] > rank[rooty]) { parent[rooty] = rootx; } else if (rank[rootx] < rank[rooty]) { parent[rootx] = rooty; } else { parent[rooty] = rootx; rank[rootx]++; } } } int find (int x) if (parent[x] != x) { parent[x] = find (parent[x]); } return parent[x]; } bool connect (int x, int y) return find (x) == find (y); } private : vector<int > parent; vector<int > rank; }; class Solution {public : bool validPath (int n, vector<vector<int >>& edges, int source, int destination) if (source == destination) { return true ; } UnionFind uf (n) ; for (auto edge : edges) { uf.uni (edge[0 ], edge[1 ]); } return uf.connect (source, destination); } };
[sol3-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 class Solution { public boolean validPath (int n, int [][] edges, int source, int destination) { if (source == destination) { return true ; } UnionFind uf = new UnionFind (n); for (int [] edge : edges) { uf.uni(edge[0 ], edge[1 ]); } return uf.connect(source, destination); } } class UnionFind { private int [] parent; private int [] rank; public UnionFind (int n) { parent = new int [n]; rank = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { parent[i] = i; } } public void uni (int x, int y) { int rootx = find(x); int rooty = find(y); if (rootx != rooty) { if (rank[rootx] > rank[rooty]) { parent[rooty] = rootx; } else if (rank[rootx] < rank[rooty]) { parent[rootx] = rooty; } else { parent[rooty] = rootx; rank[rootx]++; } } } public int find (int x) { if (parent[x] != x) { parent[x] = find(parent[x]); } return parent[x]; } public boolean connect (int x, int y) { return find(x) == find(y); } }
[sol3-C#] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public class Solution { public bool ValidPath (int n, int [][] edges, int source, int destination if (source == destination) { return true ; } UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(n); foreach (int [] edge in edges) { uf.Uni(edge[0 ], edge[1 ]); } return uf.Connect(source, destination); } } class UnionFind { private int [] parent; private int [] rank; public UnionFind (int n parent = new int [n]; rank = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { parent[i] = i; } } public void Uni (int x, int y int rootx = Find(x); int rooty = Find(y); if (rootx != rooty) { if (rank[rootx] > rank[rooty]) { parent[rooty] = rootx; } else if (rank[rootx] < rank[rooty]) { parent[rootx] = rooty; } else { parent[rooty] = rootx; rank[rootx]++; } } } public int Find (int x if (parent[x] != x) { parent[x] = Find(parent[x]); } return parent[x]; } public bool Connect (int x, int y return Find(x) == Find(y); } }
[sol3-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 typedef struct { int *parent; int *rank; } UnionFind; UnionFind *creatUnionFind (int n) { UnionFind *obj = (UnionFind *)malloc (sizeof (UnionFind)); obj->parent = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) * n); obj->rank = (int *)malloc (sizeof (int ) * n); memset (obj->rank, 0 , sizeof (int ) * n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i++) { obj->parent[i] = i; } return obj; } void uni (UnionFind * obj, int x, int y) { int rootx = find(obj, x); int rooty = find(obj, y); if (rootx != rooty) { if (obj->rank[rootx] > obj->rank[rooty]) { obj->parent[rooty] = rootx; } else if (obj->rank[rootx] < obj->rank[rooty]) { obj->parent[rootx] = rooty; } else { obj->parent[rooty] = rootx; obj->rank[rootx]++; } } } int find (const UnionFind * obj, int x) { if (obj->parent[x] != x) { obj->parent[x] = find(obj, obj->parent[x]); } return obj->parent[x]; } bool connect (const UnionFind * obj, int x, int y) { return find(obj, x) == find(obj, y); } bool validPath (int n, int ** edges, int edgesSize, int * edgesColSize, int source, int destination) { if (source == destination) { return true ; } UnionFind *uf = creatUnionFind(n); for (int i = 0 ; i < edgesSize; i++) { uni(uf, edges[i][0 ], edges[i][1 ]); } return connect(uf, source, destination); }
[sol3-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 var validPath = function (n, edges, source, destination ) { if (source === destination) { return true ; } const uf = new UnionFind (n); for (const edge of edges) { uf.uni (edge[0 ], edge[1 ]); } return uf.connect (source, destination); } class UnionFind { constructor (n ) { this .parent = new Array (n).fill (0 ).map ((_, i ) => i) ; this .rank = new Array (n).fill (0 ); } uni (x, y ) { const rootx = this .find (x); const rooty = this .find (y); if (rootx !== rooty) { if (this .rank [rootx] > this .rank [rooty]) { this .parent [rooty] = rootx; } else if (this .rank [rootx] < this .rank [rooty]) { this .parent [rootx] = rooty; } else { this .parent [rooty] = rootx; this .rank [rootx]++; } } } find (x ) { if (this .parent [x] !== x) { this .parent [x] = this .find (this .parent [x]); } return this .parent [x]; } connect (x, y ) { return this .find (x) === this .find (y); } }
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n + m \times \alpha(m)),其中 n 是图中的顶点数,m 是图中边的数目,\alpha 是反阿克曼函数。并查集的初始化需要 O(n) 的时间,然后遍历 m 条边并执行 m 次合并操作,最后对 source 和 destination 执行一次查询操作,查询与合并的单次操作时间复杂度是 O(\alpha(m)),因此合并与查询的时间复杂度是 O(m \times \alpha(m)),总时间复杂度是 O(n + m \times \alpha(m))。
空间复杂度:O(n),其中 n 是图中的顶点数。并查集需要 O(n) 的空间。