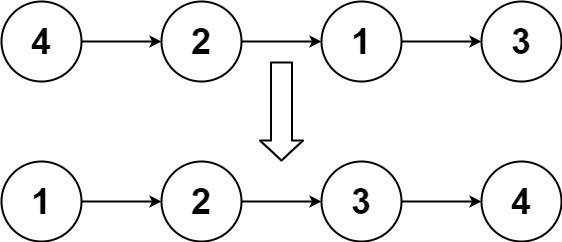
给定链表的头结点 head ,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表 。
示例 1:
**输入:** head = [4,2,1,3]
**输出:** [1,2,3,4]
示例 2:
**输入:** head = [-1,5,3,4,0]
**输出:** [-1,0,3,4,5]
示例 3:
**输入:** head = []
**输出:** []
提示:
链表中节点的数目在范围 [0, 5 * 104] 内
-105 <= Node.val <= 105
进阶: 你可以在 O(n log n) 时间复杂度和常数级空间复杂度下,对链表进行排序吗?
注意:本题与主站 148 题相同:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list/
前言 这道题考虑时间复杂度优于 O(n^2) 的排序算法。题目的进阶问题要求达到 O(n \log n) 的时间复杂度和 O(1) 的空间复杂度,时间复杂度是 O(n \log n) 的排序算法包括归并排序、堆排序和快速排序(快速排序的最差时间复杂度是 O(n^2)),其中最适合链表的排序算法是归并排序。
归并排序基于分治算法。最容易想到的实现方式是自顶向下的递归实现,考虑到递归调用的栈空间,自顶向下归并排序的空间复杂度是 O(\log n)。如果要达到 O(1) 的空间复杂度,则需要使用自底向上的实现方式。
方法一:自顶向下归并排序 对链表自顶向下归并排序的过程如下。
找到链表的中点,以中点为分界,将链表拆分成两个子链表。寻找链表的中点可以使用快慢指针的做法,快指针每次移动 2 步,慢指针每次移动 1 步,当快指针到达链表末尾时,慢指针指向的链表节点即为链表的中点。
对两个子链表分别排序。
将两个排序后的子链表合并,得到完整的排序后的链表。
上述过程可以通过递归实现。递归的终止条件是链表的节点个数小于或等于 1,即当链表为空或者链表只包含 1 个节点时,不需要对链表进行拆分和排序。
[sol1-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 class Solution { public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) { return sortList(head, null ); } public ListNode sortList (ListNode head, ListNode tail) { if (head == null ) { return head; } if (head.next == tail) { head.next = null ; return head; } ListNode slow = head, fast = head; while (fast != tail) { slow = slow.next; fast = fast.next; if (fast != tail) { fast = fast.next; } } ListNode mid = slow; ListNode list1 = sortList(head, mid); ListNode list2 = sortList(mid, tail); ListNode sorted = merge(list1, list2); return sorted; } public ListNode merge (ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2; while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null ) { if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) { temp.next = temp1; temp1 = temp1.next; } else { temp.next = temp2; temp2 = temp2.next; } temp = temp.next; } if (temp1 != null ) { temp.next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != null ) { temp.next = temp2; } return dummyHead.next; } }
[sol1-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 class Solution {public : ListNode* sortList (ListNode* head) { return sortList (head, nullptr ); } ListNode* sortList (ListNode* head, ListNode* tail) { if (head == nullptr ) { return head; } if (head->next == tail) { head->next = nullptr ; return head; } ListNode* slow = head, *fast = head; while (fast != tail) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next; if (fast != tail) { fast = fast->next; } } ListNode* mid = slow; return merge (sortList (head, mid), sortList (mid, tail)); } ListNode* merge (ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2) { ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode* temp = dummyHead, *temp1 = head1, *temp2 = head2; while (temp1 != nullptr && temp2 != nullptr ) { if (temp1->val <= temp2->val) { temp->next = temp1; temp1 = temp1->next; } else { temp->next = temp2; temp2 = temp2->next; } temp = temp->next; } if (temp1 != nullptr ) { temp->next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != nullptr ) { temp->next = temp2; } return dummyHead->next; } };
[sol1-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 const merge = (head1, head2 ) => { const dummyHead = new ListNode (0 ); let temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2; while (temp1 !== null && temp2 !== null ) { if (temp1.val <= temp2.val ) { temp.next = temp1; temp1 = temp1.next ; } else { temp.next = temp2; temp2 = temp2.next ; } temp = temp.next ; } if (temp1 !== null ) { temp.next = temp1; } else if (temp2 !== null ) { temp.next = temp2; } return dummyHead.next ; } const toSortList = (head, tail ) => { if (head === null ) { return head; } if (head.next === tail) { head.next = null ; return head; } let slow = head, fast = head; while (fast !== tail) { slow = slow.next ; fast = fast.next ; if (fast !== tail) { fast = fast.next ; } } const mid = slow; return merge (toSortList (head, mid), toSortList (mid, tail)); } var sortList = function (head ) { return toSortList (head, null ); };
[sol1-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 class Solution : def sortList (self, head: ListNode ) -> ListNode: def sortFunc (head: ListNode, tail: ListNode ) -> ListNode: if not head: return head if head.next == tail: head.next = None return head slow = fast = head while fast != tail: slow = slow.next fast = fast.next if fast != tail: fast = fast.next mid = slow return merge(sortFunc(head, mid), sortFunc(mid, tail)) def merge (head1: ListNode, head2: ListNode ) -> ListNode: dummyHead = ListNode(0 ) temp, temp1, temp2 = dummyHead, head1, head2 while temp1 and temp2: if temp1.val <= temp2.val: temp.next = temp1 temp1 = temp1.next else : temp.next = temp2 temp2 = temp2.next temp = temp.next if temp1: temp.next = temp1 elif temp2: temp.next = temp2 return dummyHead.next return sortFunc(head, None )
[sol1-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 func merge (head1, head2 *ListNode) dummyHead := &ListNode{} temp, temp1, temp2 := dummyHead, head1, head2 for temp1 != nil && temp2 != nil { if temp1.Val <= temp2.Val { temp.Next = temp1 temp1 = temp1.Next } else { temp.Next = temp2 temp2 = temp2.Next } temp = temp.Next } if temp1 != nil { temp.Next = temp1 } else if temp2 != nil { temp.Next = temp2 } return dummyHead.Next } func sort (head, tail *ListNode) if head == nil { return head } if head.Next == tail { head.Next = nil return head } slow, fast := head, head for fast != tail { slow = slow.Next fast = fast.Next if fast != tail { fast = fast.Next } } mid := slow return merge(sort(head, mid), sort(mid, tail)) } func sortList (head *ListNode) return sort(head, nil ) }
[sol1-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 struct ListNode* merge (struct ListNode* head1, struct ListNode* head2) { struct ListNode * dummyHead =malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode)); dummyHead->val = 0 ; struct ListNode *temp = while (temp1 != NULL && temp2 != NULL ) { if (temp1->val <= temp2->val) { temp->next = temp1; temp1 = temp1->next; } else { temp->next = temp2; temp2 = temp2->next; } temp = temp->next; } if (temp1 != NULL ) { temp->next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != NULL ) { temp->next = temp2; } return dummyHead->next; } struct ListNode* toSortList (struct ListNode* head, struct ListNode* tail) { if (head == NULL ) { return head; } if (head->next == tail) { head->next = NULL ; return head; } struct ListNode *slow = while (fast != tail) { slow = slow->next; fast = fast->next; if (fast != tail) { fast = fast->next; } } struct ListNode * mid = return merge(toSortList(head, mid), toSortList(mid, tail)); } struct ListNode* sortList (struct ListNode* head) { return toSortList(head, NULL ); }
复杂度分析
方法二:自底向上归并排序 使用自底向上的方法实现归并排序,则可以达到 O(1) 的空间复杂度。
首先求得链表的长度 length,然后将链表拆分成子链表进行合并。
具体做法如下。
用 subLength 表示每次需要排序的子链表的长度,初始时 subLength}=1。
每次将链表拆分成若干个长度为 subLength 的子链表(最后一个子链表的长度可以小于 subLength),按照每两个子链表一组进行合并,合并后即可得到若干个长度为 subLength} \times 2 的有序子链表(最后一个子链表的长度可以小于 subLength} \times 2)。
将 subLength 的值加倍,重复第 2 步,对更长的有序子链表进行合并操作,直到有序子链表的长度大于或等于 length,整个链表排序完毕。
如何保证每次合并之后得到的子链表都是有序的呢?可以通过数学归纳法证明。
初始时 subLength}=1,每个长度为 1 的子链表都是有序的。
如果每个长度为 subLength 的子链表已经有序,合并两个长度为 subLength 的有序子链表,得到长度为 subLength} \times 2 的子链表,一定也是有序的。
当最后一个子链表的长度小于 subLength 时,该子链表也是有序的,合并两个有序子链表之后得到的子链表一定也是有序的。
因此可以保证最后得到的链表是有序的。
[sol2-Java] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 class Solution { public ListNode sortList (ListNode head) { if (head == null ) { return head; } int length = 0 ; ListNode node = head; while (node != null ) { length++; node = node.next; } ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode (0 , head); for (int subLength = 1 ; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1 ) { ListNode prev = dummyHead, curr = dummyHead.next; while (curr != null ) { ListNode head1 = curr; for (int i = 1 ; i < subLength && curr.next != null ; i++) { curr = curr.next; } ListNode head2 = curr.next; curr.next = null ; curr = head2; for (int i = 1 ; i < subLength && curr != null && curr.next != null ; i++) { curr = curr.next; } ListNode next = null ; if (curr != null ) { next = curr.next; curr.next = null ; } ListNode merged = merge(head1, head2); prev.next = merged; while (prev.next != null ) { prev = prev.next; } curr = next; } } return dummyHead.next; } public ListNode merge (ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2; while (temp1 != null && temp2 != null ) { if (temp1.val <= temp2.val) { temp.next = temp1; temp1 = temp1.next; } else { temp.next = temp2; temp2 = temp2.next; } temp = temp.next; } if (temp1 != null ) { temp.next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != null ) { temp.next = temp2; } return dummyHead.next; } }
[sol2-C++] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 class Solution {public : ListNode* sortList (ListNode* head) { if (head == nullptr ) { return head; } int length = 0 ; ListNode* node = head; while (node != nullptr ) { length++; node = node->next; } ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode (0 , head); for (int subLength = 1 ; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1 ) { ListNode* prev = dummyHead, *curr = dummyHead->next; while (curr != nullptr ) { ListNode* head1 = curr; for (int i = 1 ; i < subLength && curr->next != nullptr ; i++) { curr = curr->next; } ListNode* head2 = curr->next; curr->next = nullptr ; curr = head2; for (int i = 1 ; i < subLength && curr != nullptr && curr->next != nullptr ; i++) { curr = curr->next; } ListNode* next = nullptr ; if (curr != nullptr ) { next = curr->next; curr->next = nullptr ; } ListNode* merged = merge (head1, head2); prev->next = merged; while (prev->next != nullptr ) { prev = prev->next; } curr = next; } } return dummyHead->next; } ListNode* merge (ListNode* head1, ListNode* head2) { ListNode* dummyHead = new ListNode (0 ); ListNode* temp = dummyHead, *temp1 = head1, *temp2 = head2; while (temp1 != nullptr && temp2 != nullptr ) { if (temp1->val <= temp2->val) { temp->next = temp1; temp1 = temp1->next; } else { temp->next = temp2; temp2 = temp2->next; } temp = temp->next; } if (temp1 != nullptr ) { temp->next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != nullptr ) { temp->next = temp2; } return dummyHead->next; } };
[sol2-JavaScript] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 const merge = (head1, head2 ) => { const dummyHead = new ListNode (0 ); let temp = dummyHead, temp1 = head1, temp2 = head2; while (temp1 !== null && temp2 !== null ) { if (temp1.val <= temp2.val ) { temp.next = temp1; temp1 = temp1.next ; } else { temp.next = temp2; temp2 = temp2.next ; } temp = temp.next ; } if (temp1 !== null ) { temp.next = temp1; } else if (temp2 !== null ) { temp.next = temp2; } return dummyHead.next ; } var sortList = function (head ) { if (head === null ) { return head; } let length = 0 ; let node = head; while (node !== null ) { length++; node = node.next ; } const dummyHead = new ListNode (0 , head); for (let subLength = 1 ; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1 ) { let prev = dummyHead, curr = dummyHead.next ; while (curr !== null ) { let head1 = curr; for (let i = 1 ; i < subLength && curr.next !== null ; i++) { curr = curr.next ; } let head2 = curr.next ; curr.next = null ; curr = head2; for (let i = 1 ; i < subLength && curr != null && curr.next !== null ; i++) { curr = curr.next ; } let next = null ; if (curr !== null ) { next = curr.next ; curr.next = null ; } const merged = merge (head1, head2); prev.next = merged; while (prev.next !== null ) { prev = prev.next ; } curr = next; } } return dummyHead.next ; };
[sol2-Python3] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 class Solution : def sortList (self, head: ListNode ) -> ListNode: def merge (head1: ListNode, head2: ListNode ) -> ListNode: dummyHead = ListNode(0 ) temp, temp1, temp2 = dummyHead, head1, head2 while temp1 and temp2: if temp1.val <= temp2.val: temp.next = temp1 temp1 = temp1.next else : temp.next = temp2 temp2 = temp2.next temp = temp.next if temp1: temp.next = temp1 elif temp2: temp.next = temp2 return dummyHead.next if not head: return head length = 0 node = head while node: length += 1 node = node.next dummyHead = ListNode(0 , head) subLength = 1 while subLength < length: prev, curr = dummyHead, dummyHead.next while curr: head1 = curr for i in range (1 , subLength): if curr.next : curr = curr.next else : break head2 = curr.next curr.next = None curr = head2 for i in range (1 , subLength): if curr and curr.next : curr = curr.next else : break succ = None if curr: succ = curr.next curr.next = None merged = merge(head1, head2) prev.next = merged while prev.next : prev = prev.next curr = succ subLength <<= 1 return dummyHead.next
[sol2-Golang] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 func merge (head1, head2 *ListNode) dummyHead := &ListNode{} temp, temp1, temp2 := dummyHead, head1, head2 for temp1 != nil && temp2 != nil { if temp1.Val <= temp2.Val { temp.Next = temp1 temp1 = temp1.Next } else { temp.Next = temp2 temp2 = temp2.Next } temp = temp.Next } if temp1 != nil { temp.Next = temp1 } else if temp2 != nil { temp.Next = temp2 } return dummyHead.Next } func sortList (head *ListNode) if head == nil { return head } length := 0 for node := head; node != nil ; node = node.Next { length++ } dummyHead := &ListNode{Next: head} for subLength := 1 ; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1 { prev, cur := dummyHead, dummyHead.Next for cur != nil { head1 := cur for i := 1 ; i < subLength && cur.Next != nil ; i++ { cur = cur.Next } head2 := cur.Next cur.Next = nil cur = head2 for i := 1 ; i < subLength && cur != nil && cur.Next != nil ; i++ { cur = cur.Next } var next *ListNode if cur != nil { next = cur.Next cur.Next = nil } prev.Next = merge(head1, head2) for prev.Next != nil { prev = prev.Next } cur = next } } return dummyHead.Next }
[sol2-C] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 struct ListNode* merge (struct ListNode* head1, struct ListNode* head2) { struct ListNode * dummyHead =malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode)); dummyHead->val = 0 ; struct ListNode *temp = while (temp1 != NULL && temp2 != NULL ) { if (temp1->val <= temp2->val) { temp->next = temp1; temp1 = temp1->next; } else { temp->next = temp2; temp2 = temp2->next; } temp = temp->next; } if (temp1 != NULL ) { temp->next = temp1; } else if (temp2 != NULL ) { temp->next = temp2; } return dummyHead->next; } struct ListNode* sortList (struct ListNode* head) { if (head == NULL ) { return head; } int length = 0 ; struct ListNode * node = while (node != NULL ) { length++; node = node->next; } struct ListNode * dummyHead =malloc (sizeof (struct ListNode)); dummyHead->next = head; for (int subLength = 1 ; subLength < length; subLength <<= 1 ) { struct ListNode *prev = while (curr != NULL ) { struct ListNode * head1 = for (int i = 1 ; i < subLength && curr->next != NULL ; i++) { curr = curr->next; } struct ListNode * head2 = curr->next = NULL ; curr = head2; for (int i = 1 ; i < subLength && curr != NULL && curr->next != NULL ; i++) { curr = curr->next; } struct ListNode * next =NULL ; if (curr != NULL ) { next = curr->next; curr->next = NULL ; } struct ListNode * merged = prev->next = merged; while (prev->next != NULL ) { prev = prev->next; } curr = next; } } return dummyHead->next; }
复杂度分析