给定一个 m x n 整数矩阵 matrix ,找出其中 最长递增路径 的长度。
对于每个单元格,你可以往上,下,左,右四个方向移动。 不能 在 对角线 方向上移动或移动到 边界外 (即不允许环绕)。
示例 1:

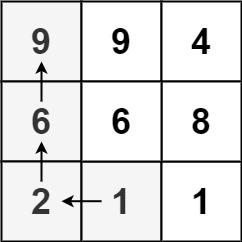
**输入:** matrix = [[9,9,4],[6,6,8],[2,1,1]]
**输出:** 4
**解释:** 最长递增路径为 [1, 2, 6, 9]。
示例 2:

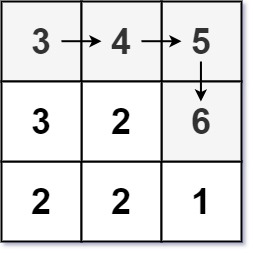
**输入:** matrix = [[3,4,5],[3,2,6],[2,2,1]]
**输出:** 4
**解释:** 最长递增路径是 [3, 4, 5, 6]。注意不允许在对角线方向上移动。
示例 3:
**输入:** matrix = [[1]]
**输出:** 1
提示:
m == matrix.lengthn == matrix[i].length1 <= m, n <= 2000 <= matrix[i][j] <= 231 - 1
注意:本题与主站 329 题相同: <https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-increasing-path-
in-a-matrix/>
方法一:记忆化深度优先搜索
将矩阵看成一个有向图,每个单元格对应图中的一个节点,如果相邻的两个单元格的值不相等,则在相邻的两个单元格之间存在一条从较小值指向较大值的有向边。问题转化成在有向图中寻找最长路径。
深度优先搜索是非常直观的方法。从一个单元格开始进行深度优先搜索,即可找到从该单元格开始的最长递增路径。对每个单元格分别进行深度优先搜索之后,即可得到矩阵中的最长递增路径的长度。
但是如果使用朴素深度优先搜索,时间复杂度是指数级,会超出时间限制,因此必须加以优化。
朴素深度优先搜索的时间复杂度过高的原因是进行了大量的重复计算,同一个单元格会被访问多次,每次访问都要重新计算。由于同一个单元格对应的最长递增路径的长度是固定不变的,因此可以使用记忆化的方法进行优化。用矩阵 memo 作为缓存矩阵,已经计算过的单元格的结果存储到缓存矩阵中。
使用记忆化深度优先搜索,当访问到一个单元格 (i,j) 时,如果 memo}[i][j] \neq 0,说明该单元格的结果已经计算过,则直接从缓存中读取结果,如果 memo}[i][j]=0,说明该单元格的结果尚未被计算过,则进行搜索,并将计算得到的结果存入缓存中。
遍历完矩阵中的所有单元格之后,即可得到矩阵中的最长递增路径的长度。
[sol1-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| class Solution {
public int[][] dirs = { {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1} };
public int rows, columns;
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
rows = matrix.length;
columns = matrix[0].length;
int[][] memo = new int[rows][columns];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; ++j) {
ans = Math.max(ans, dfs(matrix, i, j, memo));
}
}
return ans;
}
public int dfs(int[][] matrix, int row, int column, int[][] memo) {
if (memo[row][column] != 0) {
return memo[row][column];
}
++memo[row][column];
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int newRow = row + dir[0], newColumn = column + dir[1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[row][column]) {
memo[row][column] = Math.max(memo[row][column], dfs(matrix, newRow, newColumn, memo) + 1);
}
}
return memo[row][column];
}
}
|
[sol1-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| class Solution {
public:
static constexpr int dirs[4][2] = { {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1} };
int rows, columns;
int longestIncreasingPath(vector< vector<int> > &matrix) {
if (matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
rows = matrix.size();
columns = matrix[0].size();
auto memo = vector< vector<int> > (rows, vector <int> (columns));
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; ++j) {
ans = max(ans, dfs(matrix, i, j, memo));
}
}
return ans;
}
int dfs(vector< vector<int> > &matrix, int row, int column, vector< vector<int> > &memo) {
if (memo[row][column] != 0) {
return memo[row][column];
}
++memo[row][column];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int newRow = row + dirs[i][0], newColumn = column + dirs[i][1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[row][column]) {
memo[row][column] = max(memo[row][column], dfs(matrix, newRow, newColumn, memo) + 1);
}
}
return memo[row][column];
}
};
|
[sol1-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| class Solution:
DIRS = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]
def longestIncreasingPath(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if not matrix:
return 0
@lru_cache(None)
def dfs(row: int, column: int) -> int:
best = 1
for dx, dy in Solution.DIRS:
newRow, newColumn = row + dx, column + dy
if 0 <= newRow < rows and 0 <= newColumn < columns and matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[row][column]:
best = max(best, dfs(newRow, newColumn) + 1)
return best
ans = 0
rows, columns = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(columns):
ans = max(ans, dfs(i, j))
return ans
|
[sol1-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| const int dirs[4][2] = { {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1} };
int rows, columns;
int longestIncreasingPath(int** matrix, int matrixSize, int* matrixColSize) {
if (matrixSize == 0 || matrixColSize[0] == 0) {
return 0;
}
rows = matrixSize;
columns = matrixColSize[0];
int** memo = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * rows);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
memo[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * columns);
memset(memo[i], 0, sizeof(int) * columns);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; ++j) {
ans = fmax(ans, dfs(matrix, i, j, memo));
}
}
free(memo);
return ans;
}
int dfs(int** matrix, int row, int column, int** memo) {
if (memo[row][column] != 0) {
return memo[row][column];
}
++memo[row][column];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i) {
int newRow = row + dirs[i][0], newColumn = column + dirs[i][1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[row][column]) {
memo[row][column] = fmax(memo[row][column], dfs(matrix, newRow, newColumn, memo) + 1);
}
}
return memo[row][column];
}
|
[sol1-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| var (
dirs = [][]int{[]int{-1, 0}, []int{1, 0}, []int{0, -1}, []int{0, 1} }
rows, columns int
)
func longestIncreasingPath(matrix [][]int) int {
if len(matrix) == 0 || len(matrix[0]) == 0 {
return 0
}
rows, columns = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
memo := make([][]int, rows)
for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
memo[i] = make([]int, columns)
}
ans := 0
for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
for j := 0; j < columns; j++ {
ans = max(ans, dfs(matrix, i, j, memo))
}
}
return ans
}
func dfs(matrix [][]int, row, column int, memo [][]int) int {
if memo[row][column] != 0 {
return memo[row][column]
}
memo[row][column]++
for _, dir := range dirs {
newRow, newColumn := row + dir[0], column + dir[1]
if newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[row][column] {
memo[row][column] = max(memo[row][column], dfs(matrix, newRow, newColumn, memo) + 1)
}
}
return memo[row][column]
}
func max(x, y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}
|
复杂度分析
方法二:拓扑排序
从方法一可以看到,每个单元格对应的最长递增路径的结果只和相邻单元格的结果有关,那么是否可以使用动态规划求解?
根据方法一的分析,动态规划的状态定义和状态转移方程都很容易得到。方法一中使用的缓存矩阵 memo 即为状态值,状态转移方程如下:
\begin{aligned}
& \textit{memo}[i][j] = \max{\textit{memo}[x][y]} + 1 \
& 其中(x, y)与(i, j)在矩阵中相邻,并且~\textit{matrix}[x][y] > \textit{matrix}[i][j]
\end{aligned}
动态规划除了状态定义和状态转移方程,还需要考虑边界情况。这里的边界情况是什么呢?
如果一个单元格的值比它的所有相邻单元格的值都要大,那么这个单元格对应的最长递增路径是 1,这就是边界条件。这个边界条件并不直观,而是需要根据矩阵中的每个单元格的值找到作为边界条件的单元格。
仍然使用方法一的思想,将矩阵看成一个有向图,计算每个单元格对应的出度,即有多少条边从该单元格出发。对于作为边界条件的单元格,该单元格的值比所有的相邻单元格的值都要大,因此作为边界条件的单元格的出度都是 0。
基于出度的概念,可以使用拓扑排序求解。从所有出度为 0 的单元格开始广度优先搜索,每一轮搜索都会遍历当前层的所有单元格,更新其余单元格的出度,并将出度变为 0 的单元格加入下一层搜索。当搜索结束时,搜索的总层数即为矩阵中的最长递增路径的长度。
[sol2-Java]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
| class Solution {
public int[][] dirs = { {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1} };
public int rows, columns;
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
rows = matrix.length;
columns = matrix[0].length;
int[][] outdegrees = new int[rows][columns];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; ++j) {
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int newRow = i + dir[0], newColumn = j + dir[1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[i][j]) {
++outdegrees[i][j];
}
}
}
}
Queue<int[]> queue = new LinkedList<int[]>();
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; ++j) {
if (outdegrees[i][j] == 0) {
queue.offer(new int[]{i, j});
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
++ans;
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
int[] cell = queue.poll();
int row = cell[0], column = cell[1];
for (int[] dir : dirs) {
int newRow = row + dir[0], newColumn = column + dir[1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] < matrix[row][column]) {
--outdegrees[newRow][newColumn];
if (outdegrees[newRow][newColumn] == 0) {
queue.offer(new int[]{newRow, newColumn});
}
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
|
[sol2-C++]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
| class Solution {
public:
static constexpr int dirs[4][2] = { {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1} };
int rows, columns;
int longestIncreasingPath(vector< vector<int> > &matrix) {
if (matrix.size() == 0 || matrix[0].size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
rows = matrix.size();
columns = matrix[0].size();
auto outdegrees = vector< vector<int> > (rows, vector <int> (columns));
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int newRow = i + dirs[k][0], newColumn = j + dirs[k][1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[i][j]) {
++outdegrees[i][j];
}
}
}
}
queue < pair<int, int> > q;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; ++j) {
if (outdegrees[i][j] == 0) {
q.push({i, j});
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
while (!q.empty()) {
++ans;
int size = q.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
auto cell = q.front(); q.pop();
int row = cell.first, column = cell.second;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int newRow = row + dirs[k][0], newColumn = column + dirs[k][1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] < matrix[row][column]) {
--outdegrees[newRow][newColumn];
if (outdegrees[newRow][newColumn] == 0) {
q.push({newRow, newColumn});
}
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
|
[sol2-Python3]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
| class Solution:
DIRS = [(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, -1), (0, 1)]
def longestIncreasingPath(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if not matrix:
return 0
rows, columns = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
outdegrees = [[0] * columns for _ in range(rows)]
queue = collections.deque()
for i in range(rows):
for j in range(columns):
for dx, dy in Solution.DIRS:
newRow, newColumn = i + dx, j + dy
if 0 <= newRow < rows and 0 <= newColumn < columns and matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[i][j]:
outdegrees[i][j] += 1
if outdegrees[i][j] == 0:
queue.append((i, j))
ans = 0
while queue:
ans += 1
size = len(queue)
for _ in range(size):
row, column = queue.popleft()
for dx, dy in Solution.DIRS:
newRow, newColumn = row + dx, column + dy
if 0 <= newRow < rows and 0 <= newColumn < columns and matrix[newRow][newColumn] < matrix[row][column]:
outdegrees[newRow][newColumn] -= 1
if outdegrees[newRow][newColumn] == 0:
queue.append((newRow, newColumn))
return ans
|
[sol2-C]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
| const int dirs[4][2] = { {-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1} };
int rows, columns;
typedef struct point {
int x, y;
} point;
int longestIncreasingPath(int** matrix, int matrixSize, int* matrixColSize) {
if (matrixSize == 0 || matrixColSize[0] == 0) {
return 0;
}
rows = matrixSize;
columns = matrixColSize[0];
int** outdegrees = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*) * rows);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
outdegrees[i] = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * columns);
memset(outdegrees[i], 0, sizeof(int) * columns);
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; ++j) {
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int newRow = i + dirs[k][0], newColumn = j + dirs[k][1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[i][j]) {
++outdegrees[i][j];
}
}
}
}
point* q = (point*)malloc(sizeof(point) * rows * columns);
int l = 0, r = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; ++j) {
if (outdegrees[i][j] == 0) {
q[r++] = (point){i, j};
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
while (l < r) {
++ans;
int size = r - l;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
point cell = q[l++];
int row = cell.x, column = cell.y;
for (int k = 0; k < 4; ++k) {
int newRow = row + dirs[k][0], newColumn = column + dirs[k][1];
if (newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] < matrix[row][column]) {
--outdegrees[newRow][newColumn];
if (outdegrees[newRow][newColumn] == 0) {
q[r++] = (point){newRow, newColumn};
}
}
}
}
}
return ans;
}
|
[sol2-Golang]1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
| var (
dirs = [][]int{[]int{-1, 0}, []int{1, 0}, []int{0, -1}, []int{0, 1} }
rows, columns int
)
func longestIncreasingPath(matrix [][]int) int {
if len(matrix) == 0 || len(matrix[0]) == 0 {
return 0
}
rows, columns = len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
outdegrees := make([][]int, rows)
for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
outdegrees[i] = make([]int, columns)
}
for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
for j := 0; j < columns; j++ {
for _, dir := range dirs {
newRow, newColumn := i + dir[0], j + dir[1]
if newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] > matrix[i][j] {
outdegrees[i][j]++
}
}
}
}
queue := [][]int{}
for i := 0; i < rows; i++ {
for j := 0; j < columns; j++ {
if outdegrees[i][j] == 0 {
queue = append(queue, []int{i, j})
}
}
}
ans := 0
for len(queue) != 0 {
ans++
size := len(queue)
for i := 0; i < size; i++ {
cell := queue[0]
queue = queue[1:]
row, column := cell[0], cell[1]
for _, dir := range dirs {
newRow, newColumn := row + dir[0], column + dir[1]
if newRow >= 0 && newRow < rows && newColumn >= 0 && newColumn < columns && matrix[newRow][newColumn] < matrix[row][column] {
outdegrees[newRow][newColumn]--
if outdegrees[newRow][newColumn] == 0 {
queue = append(queue, []int{newRow, newColumn})
}
}
}
}
}
return ans
}
|
复杂度分析
思考题
为了让大家更好地理解这道题,小编出了四道思考题,欢迎感兴趣的同学在评论区互动哦。
「方法一」中使用了记忆化存储和深度优先搜索,这里的深度优先搜索可以替换成广度优先搜索吗?
「方法二」中基于拓扑排序对排序后的有向无环图做了层次遍历,如果没有拓扑排序直接进行广度优先搜索会发生什么?
「方法二」中如果不使用拓扑排序,而是直接按照矩阵中元素的值从大到小进行排序,并依此顺序进行状态转移,那么可以得到正确的答案吗?如果是从小到大进行排序呢?
「变式」给定一个整数矩阵,找出符合以下条件的路径的数量:这个路径是严格递增的,且它的长度至少是 3。矩阵的边长最大为 10^3,答案对 10^9 + 7 取模。其他条件和题目相同。思考:是否可以借鉴这道题的方法?